Hemiparesis is usually understood as a disease that is a consequence of damage to higher subcortical functions. As a result, a person experiences incomplete loss of sensation on a certain side of the body.
This may manifest as right-sided or left-sided hemiparesis. Also, a person often has an upper or lower localization of the disorder.
In any case, it is very important to take adequate measures in a timely manner to help avoid dangerous consequences.
Many people are interested in what is the difference between hemiparesis and hemiplegia. Thus, hemiparesis is usually understood as a decrease in strength in half of the body. In this case, hemiplegia is a complete lack of strength in half the body. In essence, this disorder is paralysis.
Pathogenesis of the disorder
Hemiparesis is a disease characterized by partial paralysis, which provokes weakening of muscle tissue on a certain side of the body. At the same time, the other side remains healthy.
This condition is a consequence of damage to the upper motor neurons, as well as their axons. In addition, there may be a disruption in the functioning of motor neurons. In most cases, this disease is of cerebral rather than spinal origin.
To determine the severity of the manifestations of the disease, you need to pay attention to the symptoms of focal damage to the cortex. To them
Wernicke-Mann gait in hemiparesis
include speech disorders, problems with making purposeful movements, and difficulties in perception. A person may also experience epileptic seizures, sensory disturbances, and cognitive disorders.
Individual brainstem lesions are characterized by a combination of ipsilateral lesions of the nerves located in the head with contralateral hemiparesis.
If a person has abnormalities in the structure of the body, the disease develops more rapidly.
In this case, the patient may experience postictal hemiparesis, which develops after a focal motor attack.
This disease is characterized by the presence of epileptic seizures, which affect the formation of a brain abscess or tumor.
Prognosis of paralysis
Is recovery possible if the left side of the body is paralyzed after a stroke?
The general life prognosis for such patients is favorable.
However, it is important to understand that the process of restoring lost abilities and returning to normal life is determined by several factors.
To begin with, what is important is the fact which part of the brain was affected by the pathological process.
Equally important is the volume of hemorrhage. The smaller it is, the less will be the degree of negative impact on the body. One of the key factors is the speed of first aid. And finally, the prognosis for improvement of the patient’s condition will depend on the chosen recovery methods.
Useful video on the topic:
Causes
The cause of hemiparesis can be a huge number of congenital or acquired diseases. These usually include the following:
- stem tumor formations;
- intracerebral or epidural injuries;
- the appearance of subdural hydroma , which is of traumatic origin;
- cerebral stroke or infarction, acute ischemia;
- a hematoma in the brain , which is the result of carotid artery thrombosis that occurs in Todd's palsy;
- parenchymal hemorrhage;
- Farah's disease - characterized by the appearance of brain stones;
- hysteria;
- multiple sclerosis;
- hemiplegic migraine , which can be spontaneous or genetically determined;
- Brown-Sicard syndrome - is a spinal tumor that is localized in the cervical region;
- syphilitic gumma - is a soft tumor formation in tissues.
Hemiparesis in children in most cases is congenital. This is due to intrauterine abnormalities in brain development. Also, this disease can be caused by deviations during childbirth, which are accompanied by compression of nerve fibers. In children, in most cases, left-sided hemiparesis is observed.
Congenital and acquired disorder
In adults, an acquired form of the disease usually occurs.
Acquired hemiparesis can cause:
In children, most often, hemiparesis is congenital and develops as a result of a malformation of the brain or trauma received during childbirth.
In this case, there is a left-sided form of the disease, which becomes visible several months after the birth of the baby. At an early stage of pathology, minor disturbances in the motor activity of the limbs may occur:
- asymmetrical movements;
- weak movements of the affected limbs;
- clenching the hand into a fist;
- poor support function on the affected side;
- spread hips in a lying position.
The doctor makes the final diagnosis at approximately 12-18 months. When the baby begins to move, the disturbances become more noticeable. In complex cases, the pathology is accompanied by impaired speech and mental abilities.
How long do they live?
About 75% of victims survive an ischemic stroke. About 15-25% of patients die in the first month. Only 35% of patients live more than a year. In order to get into this percentage, you must constantly be registered with a cardiologist and strictly follow his instructions.
The most common cause of death after a stroke is the development of complications. Cerebral edema, pneumonia, kidney failure, etc.
Monitor your body, and at the first symptoms similar to pathological abnormalities due to ischemia, immediately call an ambulance. The most important thing when treating a stroke is time, which is important not to waste by procrastinating in the hope that it will go away on its own.
source
Left-sided and right-sided hemiparesis
Neurologists were able to establish a certain relationship between symptoms in a certain part of the body and the brain hemisphere in which the abnormal focus is present. This connection is inverse.
If a feeling of weakness is present in the right limbs, right-sided hemiparesis is diagnosed, but if the symptoms are localized on the left, left-sided hemiparesis is diagnosed.
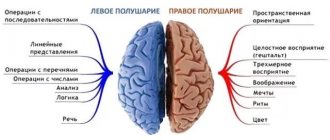
Moreover, each hemisphere of the brain is responsible for performing certain functions of the body. So, if left-sided hemiparesis develops as a result of a traumatic injury or stroke, the person often experiences serious speech impairments.
It is the right-sided hemiparesis that is one of the most common complications of stroke, since circulatory disorders often occur in the left artery of the brain. These processes provoke loss of sensitivity and motor activity.
If a person has a left-sided form of the disorder, then the patient may experience mental disorders. This is due to the fact that in the right hemisphere of the brain there is a maximum number of nerve centers that are responsible for mental functions. It is important to note that the left-sided form of the disease is much less common.
Symptoms
The following symptoms can help identify a right-sided stroke:
- the occurrence of headaches and a feeling of numbness in the left side of the body;
- paralysis of the left upper or lower limb. In this regard, when the patient tries to stretch both arms forward, a situation is observed where the left hand lags behind the right;
- patient complaints of dizziness, nausea and weakness;
- left-sided facial paralysis ;
- increased heart rate and pulse;
- decreased visual and hearing ability on the left side;
- the patient’s ability to independently rely exclusively on the right leg;
- impaired logical thinking;
- spasms ;
- at some point, a patient with right hemisphere damage may be found unconscious ;
- with this condition, patients report disturbed sleep, a state of exhaustion and a poor emotional state.
In a situation where a stroke has developed in an elderly patient, a coma is likely to occur, which will last no more than a day. If a person does not regain consciousness within the specified time, then the likelihood of acquiring disability increases at a tremendous rate every day.
Treatment methods depending on the situation
The child has left-sided hemiparesis
For treatment to be effective, it is very important to eliminate the causes of the syndrome.
The main goal of therapy is to eliminate or reduce the symptoms of hemiparesis and restore normal motor activity.
The treatment method is chosen by the doctor taking into account the causes of the disease.
To completely cope with the pathology, you need to select complex therapy:
- If the cause lies in damage to the brain or spinal cord , surgery may be necessary. To eliminate the symptoms of the disease, the doctor can remove the tumor formation, hemorrhage, or abscess.
- In case of circulatory problems in the brain, medications are prescribed to improve this process. Usually there is a need to use nootropics and angioprotectors.
- In case of infectious lesions of the brain, there is a need to use antibacterial drugs.
- For botulism, the doctor administers a special anti-botulinum serum.
- For myasthenia gravis , medications are used that help improve neuromuscular conduction.
In mild cases, the doctor prescribes a special course of therapeutic exercises. In addition, the following means are used:
- swimming;
- massage;
- reflexology;
- hardening;
- Charcot's shower;
- fitball exercises;
- hippotherapy;
- dousing
In difficult cases, specialists select medications. After discharge from the hospital, therapy continues at home.
Once the diagnosis is determined, the specialist selects drug treatment methods. In this case, the use of medications should be accompanied by special physical exercises.
Since the development of hemiparesis is accompanied by damage to certain areas of the brain, an increase in muscle tone is often observed. To reduce it, the doctor may prescribe muscle relaxants - these are the drugs that reduce the severity of the symptoms of the pathology.
These medications are important not only for muscle relaxation. They also help prepare the patient for massage and therapeutic exercises. At the same time, it is necessary to treat associated disorders.
For this purpose, speech or vision correction can be carried out, and anticonvulsant treatment is carried out, the need for which appears in case of epilepsy. Many patients with this diagnosis need consultation with a psychologist.
Muscle relaxants are usually prescribed in long courses, which can last up to six months. This is due to the duration of the recovery period of the affected areas. Such drugs do not allow cells to recover, but they create favorable conditions for the rehabilitation of patients.
Quite often, therapy for this disease is carried out using the following medications:
- Mydocalm;
- Baclofen;
- Pantogam;
- Piracetam;
- Neuromidin.
In addition, effective therapy is impossible without the use of vitamin complexes. Vitamins B and E are especially useful.
If the affected area has not recovered within a year, treatment may be delayed. Courses of drug therapy are repeated from time to time. Along with this, the use of massage, therapeutic exercises and acupuncture is indicated.
Exercise therapy can be done in special rehabilitation centers. If this is not possible, you can do the exercises at home. However, this must be done systematically in order to achieve tangible results.
With this diagnosis, various types of massage are very useful. In addition, experts advise working out your abs, jumping on one leg, developing hand motor skills, and stretching the muscle tissue on the affected side.
Various sports play an important role in recovery - swimming, water gymnastics, and horse riding are especially useful.
Diagnostics
Accurate diagnosis is carried out in a clinical setting and includes:
- Taking anamnesis and visual examination of the patient;
- CBC and biochemical blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- ECG;
- CT or MRI of the brain, cervical spine, spinal cord;
- EEG;
- Dopplerography of cerebral vessels;
- Electroencephalography;
- CSF analysis;
- Cerebrospinal fluid analysis;
- The muscle strength of both sides of the body is compared;
- Muscle resistance test;
- Barre test - holding hands in weight;
- For children, in addition to early examination by a neurologist, ultrasound of the brain is used.
Since left-sided hemiparesis is a consequence of the underlying disease, then, first of all, it is necessary to treat it. But at the same time, it is equally important to devote time to symptomatic therapy against hemiparesis.
Mainly, in the treatment of children, emphasis is placed on:
- Classes with a speech therapist for the treatment of speech dysfunction;
- Classes with a defectologist for developmental delays;
- Treatment of episyndrome;
- Drug therapy.
In addition to this, it can help a lot:
- Gymnastics;
- Therapeutic baths and mud;
- Use of orthopedic beds, orthopedic shoes;
- Surgical intervention, if necessary;
- Holidays at resorts.
Prognosis and complications
The prognosis is largely influenced by the stage and severity of the syndrome and the causes of its occurrence. In addition, good results can only be achieved if a person receives timely and adequate therapy.
Otherwise, there is a risk of developing dangerous complications. If not treated correctly, the patient may develop complete loss of muscle strength on the affected side.
Hemiparesis is a very serious disorder that can be congenital or acquired. To cope with this disease, you need to establish the causes of its occurrence and, based on this, select adequate therapy.
Consequences
Paralysis and disturbance of spatial perception
Due to the fact that the left side of the brain controls the sequence of perception of the world and allows one to analyze what is happening, it is more difficult for the patient to rehabilitate after the onset of paralysis.
This happens because a person cannot be aware of his body, as a result of which he does not notice motor dysfunctions.
Without realizing the problem, it is impossible to solve it, therefore, to recover from a left-sided stroke, sometimes it is necessary to work with a psychotherapist.
Treatment includes physiotherapy, exercises, massages and medications.
Behavior disorder
From time to time there are such manifestations of atypical behavior as:
- apathy;
- unmotivated anger;
- hysterical laughter or crying;
- insomnia and sleep phase disorder;
- attacks of excessive psychomotor agitation, etc.
For adjustments, a visit to a psychiatrist is necessary. Depending on the situation, the patient is prescribed psychotherapy and a course of antidepressants.
Memory impairment and weakening of mental abilities
After a stroke you may experience:
- Hypomnesia - weakening of memory functions;
- Hypermnesia is the inability to filter out unimportant information, which subsequently completely ends up in the long-term memory department;
- Paramnesia is a distortion of memories or their complete replacement with false ones;
- Amnesia is the complete loss of some memories.
Rehabilitation requires constant training both with specialists in centers and at home.
Visual impairment
The peculiarity of getting rid of ophthalmological problems after an attack is the uselessness of drug treatment without an integrated approach to recovery. In addition to taking medications, you must:
- follow a diet rich in vitamin A;
- systematic moisturizing of mucous membranes with gels and drops;
- performing a special program to strengthen the eye muscles;
- taking a course of vitamins for vision.
We invite you to watch an interesting video on the topic:
Ischemic stroke of the left hemisphere
In modern society, the incidence of strokes is increasing. Only 15-20% of patients can return to normal social activities after an attack. In 75% of cases, stroke of the ischemic type develops. Therefore, prevention of the disease and urgent treatment at a medical facility at the first symptoms of an attack are so important. This article will discuss left-sided ischemic stroke, its symptoms, diagnostic methods and treatment.
Classification
What classification allows you to distinguish between strokes? The most significant category is the extent or extent of the lesion. The following types are distinguished:
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA). Symptoms are isolated and disappear within 1 hour. The maximum duration of their existence is 12-24 hours. Typically, a TIA does not leave any focal changes in the brain that are noticeable on an MRI or CT scan.
- “Minor stroke” is a transient attack, the symptoms of which last for 2-21 days. In this case, complete regression of the neurological clinic is observed a month after the attack;
- Progressive stroke. There are general cerebral and focal syndromes. The acute phase develops over 2-3 days, followed by incomplete restoration of function;
- Completed stroke. With it, a focus of necrosis has formed, there is a loss of functions and only partial regression of the clinic in the recovery period.
Recovery
The effect of the recovery process depends on the extent of the stroke, the age of the patient, and the start of rehabilitation.
Nutrition
You should give preference to healthy foods. The Mediterranean diet is a priority: limiting meat, increasing fish consumption, vegetables and a small amount of carbohydrates. Alcoholic products should be avoided in the first year after the attack.
Important! For diabetes mellitus, a low-carbohydrate diet is recommended to carefully control this pathology. It is patients with decompensated diabetes who are most often at risk of recurrent stroke.
Depending on the degree of damage
| Stroke severity | Duration and completeness of recovery |
| Stroke with minimal neurological deficit (mild paralysis of the limbs and face, dizziness, problems with coordination and vision) | After 1-2 months, full rehabilitation gives partial recovery; Completeness occurs closer to the 3rd month. |
| Stroke with persistent paralysis of the limbs and loss of coordination | Partial functions are restored after 6 months, full recovery lasts for years. There is still the possibility of lifelong loss of some skills. |
| Severe form of stroke (paralysis of one side and other neurological defects) | The ability to move independently in bed and sit appears after 1-2 years. Complete recovery is extremely rarely achieved. |
Physiotherapy
This rehabilitation method allows you to restore muscle activity, restore blood circulation, relieve spasm and painful tension in the affected limbs. Physiotherapy procedures are prescribed together with the attending physician and physiotherapist. They are selected taking into account possible contraindications. This can be magnetic therapy, laser, EMS, acupuncture.
Exercise therapy for stroke is developed by a specialist. The muscle tone on the affected limb is taken into account. It is necessary to dose the force with which the exercise is performed. Charging should be done daily. The work should affect all muscle groups (face, neck, shoulders, torso, lower limbs). An example complex can be found by following the link.
Work with the paralyzed side is carried out first in passive mode. A physical therapy specialist develops a paretic limb, repeating all normal movements. After independent tone and strength appear, it is necessary to load the arm and leg, allowing them to work.
Breathing exercises
This type of exercise is important for the prevention of congestive pneumonia. It must be performed while the patient is in bed. After this, breathing exercises are effective in restoring the reserves of the cardiovascular system.
A left-sided stroke is difficult for the patient and his family. Quick delivery of the patient to a medical facility and timely initiation of therapy can save a person’s life and improve the prognosis of rehabilitation.
Treatment
A stroke is an emergency. If the patient shows signs of stroke, you should immediately call an ambulance and take him to the hospital. Any delay can cost a person his life.
First aid
What needs to be done before the doctors arrive?
- Lay the patient on his side. Free him from tight clothing (tie, collar). Provide access to fresh air (open windows). The head should be higher than the body;
- Measure blood pressure and pulse at the radial artery;
- When vomiting, turn your head to the side to prevent aspiration of vomit;
- If the patient is conscious, it is allowed to give 10 glycine tablets under the tongue.
Conservative treatment
- An important point in the treatment of ischemic stroke is assessing the possibility of thrombolysis. It is performed in the first 4 hours upon admission of the patient to the hospital and diagnosis. Thrombolysis is performed only in the absence of contraindications (there are about 30 of them). Complications of the procedure include bleeding, hemorrhagic shock, and death;
- Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents (clopidogrel, cardiomagnyl, rivaroxaban, dabigatran, warfarin);
- Nootropics (citicoline, cerebrolysin, choline alfoscerate);
- Prevention of cerebral edema (mannitol);
- Behavior-correcting drugs (neuroleptics, antidepressants).
Surgical treatment
In some cases, mechanical thrombectomy is performed. This is an angiographic study that is performed under x-ray guidance. A stent retriever is inserted into the brain vessels. It “removes” the blood clot. In addition, local administration of plasminogen activator (alteplase) is carried out.
The operation is indicated for certain types of thrombosis anatomy, a large volume of occlusion, and contraindications to systemic thrombolysis. The effectiveness of reperfusion (restoration of blood flow) after this treatment method is high. Level of evidence: 1A.
What it is?
Most often, atherothrombotic stroke is recorded. It accounts for 35% of the ischemic subtype. The pathogenesis of this disease is as follows: an atherosclerotic plaque forms on the inner wall of the vessel over the years. It builds up, slowly closing the blood flow in a certain pool. But at the same time, chronic ischemia of brain tissue is formed.
A dangerous situation arises when the surface of the plaque is destroyed. The inflammatory process starts on it and a blood clot begins to form. It grows instantly, acutely blocking the lumen of the vessel. In this case, an ischemic atherothrombotic stroke develops. And the only help for the patient is to get rid of the blood clot as quickly as possible.
Most often, the lesion occurs in the middle cerebral artery (MCA). The following symptoms are characteristic of ischemia in this area:
- Contralateral hemiparesis or hemiplegia. These symptoms occur on the side opposite to the lesion. For example, when the left MCA is damaged, right-sided paralysis of the face and upper limb occurs. Symptoms on the leg are less common;
- Dysarthria (Sylvian fissure - the speech center of the brain is located in the blood supply area of the MCA);
- Hemianesthesia (numbness of half the body on the opposite side). This means that with a left-sided stroke, sensitivity on the right side disappears;
- Half of the visual field on the side opposite to the lesion disappears. In the case of a left-sided stroke, half the visual field of the right eye is lost;
- Aphasia or apraxia (loss of speech and purposeful movement);
- Denial of half of space (right half of the body).
What is ischemia?
Ischemia is a local cessation of blood supply to an organ or tissue. Against the background of oxygen starvation, cells lose their function and even die. Cerebral ischemia occurs when there is no blood circulation through the arteries. Or when oxygen supply to the body stops. There are acute and chronic cerebral ischemia.
Acute ischemia develops when the blood supply to a vessel suddenly stops. When the lesion lasts more than several hours, a focus of necrosis forms in the brain tissue. This is where the cells die. Around it there is a center of “penumbra”. The viability of these cells is lost, but they can regain their functionality with adequate treatment. It is acute ischemia that occurs during a stroke.
Chronic ischemia develops with prolonged stenosis of an arterial vessel. Cells receive less oxygen every year. Due to this, their metabolism decreases. Degenerative changes form in the white and gray matter. They are called What is leukoaraiosis?
This is a lesion of white matter tissue. It appears as a result of disruption of the cerebral vessels. To treat the process, drugs are used that improve blood supply to the brain and dilate its blood vessels.
Pathology in adults develops in old age. It is a sign of cerebral ischemia. Leukoaraiosis in children is a consequence of intrauterine hypoxia or infection.
CT does not provide an accurate diagnosis. Leukoaraiosis is determined by the results of MRI performed in T2-weighted mode. Currently, doctors distinguish three degrees of severity of the pathological process.
Pathogenesis
The type of stroke plays a key role in the pathogenesis of stroke. In atherothrombotic, vessel stenosis is formed due to the formation of a blood clot on the inflamed plaque. In cardioembolic embolism , the embol “flies” into the arteries of the brain from the brachiocephalic vessels or from the chambers of the heart.
In hemodynamic stroke, insufficiency of blood supply against the background of atherosclerosis develops against the background of decreased cardiac output. The reasons for this may be changes in the myocardium of the heart or its conduction system (atrial fibrillation, sick sinus syndrome, acute myocardial infarction).
In lacunar infarction, the cause of the formation of a large focus of necrosis is arterial hypertension. As a result of high pressure, the capillary wall swells and blocks the lumen of the vessel. It is also worth considering changes in blood viscosity. A sharp increase in fluid density in capillaries promotes thrombus formation and is the cause of hemorheological stroke.
Reasons for young people
The main risk factors are obesity, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking and physical inactivity. In young people, stroke most often develops against the background of arterial hypertension and uncontrolled diabetes (the first type is especially dangerous).
Cases of stroke before 45 years of age due to alcohol and drug abuse are not uncommon. You should also consider the impact of stress. Severe vascular accident often occurs in men under the age of 50 who hold responsible leadership positions.
In addition, a stroke can develop against the background of autoimmune or infectious vasculitis, coagulopathies (antiphospholipid syndrome in pregnant women).
Causes in older people
After the age of 65, stroke develops against the background of systemic atherosclerosis, high blood cholesterol, high blood pressure, and diabetes. In old age, the problem of hypercoagulation becomes acute, which can lead to the formation of blood clots.
Signs of a stroke on the left side
- Hemiparesis (lack of independent movements in the arm and leg) on the right;
- Monoparesis (no independent movements in only one limb, usually the upper) on the right;
- Sensory disorders;
- Loss of balance, unsteadiness when walking, unsteady gait;
- Vision problems, loss of visual fields, passing blindness in one or both eyes;
- Strong headache.
Characteristic symptoms:
- Aphasia (loss of ability to speak clearly);
- Partial memory loss (inability to remember the names of objects);
- Inability to control one’s actions and perform precise movements;
- Problems pronouncing words.
If the anterior cerebral artery is damaged:
- Contralateral hemiparesis affecting the right leg;
- Inability to make purposeful movements when walking;
- Urinary incontinence;
- Problems with logical thinking and spontaneity.
If the middle cerebral artery is damaged:
- Contralateral hemiparesis of the face and arm on the right;
- Dysarthria;
- Visual impairment on the opposite side;
- Damage to the sensitivity of half the body;
- Aphasia with damage to the dominant hemisphere;
- Ignoring and denying half of the body (the paralyzed part).
With damage to the posterior cerebral artery:
- Loss of half of the visual field on the opposite side;
- Paresis of 3 pairs of cranial nerves;
- Amnesia;
- Hemiballismus (when one limb imitates throwing).
Severity
Mild ischemic stroke . With it, the symptoms are mild. Regression of the disease is observed within 3 weeks after the attack.
Moderate severity of stroke . This attack occurs with a predominance of focal cerebral symptoms. General symptoms: coma, stupor – absent.
In severe strokes, consciousness is depressed. Focal symptoms are common and severely disabling. The development of dislocation symptoms is possible.
Which stroke is more dangerous - left-sided or right-sided?
The consequences of a stroke are difficult to predict. The course of the disease is significantly influenced by the patient’s age, concomitant diseases, and the extent of the lesion during an attack. The characteristic differences between right-sided and left-sided lesions are clinical symptoms. Of course, they depend on which hemisphere is dominant in a person.
So, with a left-sided lesion, signs of hemiparesis or plegia appear on the right side. With right-sided, motor activity is disrupted on the left. This difference does not have a significant impact on the duration of rehabilitation. With left-sided lesions, speech and word understanding disorders appear. All this is characterized by the term aphasia. It includes:
- Inability to speak;
- Read;
- Write;
- Listen;
- Understand spoken and written language;
- Choose the right words.
Speech problems are an unfavorable factor for recovery. Therefore, people with right-sided stroke have a better prognosis here. With a left-sided stroke, the challenge in recovery is denial of the presence of the affected side of the body. This neurological deviation makes it difficult for a physical therapy specialist to work and to carry out independent development exercises.