01.12.2018
28. Oka Y. Thirst driving and suppressing signals encoded by distinct neural populations in the brain.
29. Saker P. Regional brain responses associated with drinking water during thirst and after its satiation.
30. Dohi K. Molecular hydrogen in drinking water protects against neurodegenerative changes induced by traumatic brain injury.
31. Meinders A. How much water do we really need to drink?
32. Jéquier E. Water as an essential nutrient: the physiological basis of hydration.
33. Aguado E. Hypodynamia Alters Bone Quality and Trabecular Microarchitecture.
34. Mukhamedieva L. Human's breath during modeled prolonged hypodynamia.
35. Ye F. A systematic review of mobility/immobility in thromboembolism risk assessment models for hospitalized patients.
36. Boraxbekk C. Physical activity over a decade modifies age-related decline in perfusion, gray matter volume, and functional connectivity of the posterior default-mode network-A multimodal approach.
37. Kemi O. High-intensity aerobic exercise training improves the heart in health and disease.
38. Hautala A. Heart rate dynamics after controlled training followed by a home-based exercise program.
39. Treatment exercises for the spine with osteochondrosis.
40. Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, special exercises from Dr. Butrimov
‘>
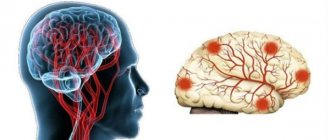
Causes of cerebral circulatory disorders
The brain is the main organ of the central nervous system; it consists of neurons united by synaptic connections. By interacting with each other, neurons form chains of electrical impulses that regulate the activity of the body1.
The functioning of the brain requires large amounts of energy, which it receives through the bloodstream. Blood enters the brain through four arteries - two carotid and two vertebral, and outflow - through two jugular veins. With an average weight of 2% of the total body weight, the brain at rest consumes 15% of all blood circulating in the body, 20-25% of the oxygen received during respiration, and up to 50% of all glucose reserves entering the blood from the liver2.
Blood supply to the brain and blood circulation within the organ play a crucial role in its functioning, since without the provision and distribution of energy, oxygen, vitamins and amino acids entering the bloodstream, neurons cannot grow and divide. 85% of all pathologies associated with brain function are due to circulatory disorders3. Improving blood circulation in the brain is necessary for any pathologies and conditions that can lead to vasoconstriction or impaired blood circulation within the organ.
Pathological causes of vasoconstriction and their consequences:
- Arterial hypertension. In response to increased blood pressure, the walls of blood vessels spasm, and additional layers grow on the inside of the vessels. Thickening impairs blood flow4,5,6.
– Hypercholesterolemia. Violation of lipid metabolism in the direction of increasing low-density lipoproteins (“bad cholesterol”) leads to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels. Plaques completely or partially block a vessel, disrupting blood circulation, including in the brain7.
– Thrombosis. The formation of a thrombus (a clot of coagulated blood) can have various origins, as a rule, these are damage and cracks in the walls of blood vessels. Blood clots lead to blockage of blood vessels and increase blood viscosity, impairing blood circulation to the brain8,9.
- Diabetes. With increased levels of glucose in the blood, thickening of the vascular walls is stimulated, which leads to disruption of the natural flow of blood, and blood supply to the brain is disrupted10,11.
– Osteochondrosis of intervertebral discs. The vertebral artery is one of the main vessels through which blood flows to the brain. With pathology of cartilage tissue, intervertebral discs compress this artery, disrupting the blood supply to the brain12,13.
- Cardiopsychoneurosis. This is a complex of disorders of the cardiovascular system that can lead to disturbances in blood supply and circulation in various organs, including the brain14,15.
Impaired blood circulation in the brain can result from traumatic brain injuries, including concussions and bruises, as well as traumatic injuries to the spine, accompanied by impaired blood flow.
Neurocirculatory dystonia in the context of cerebral circulatory disorders is considered separately. The difficulty is that this disease often does not have an acute phase, and its main symptoms without targeted diagnosis can be explained by a number of typical pathologies such as chronic fatigue syndrome16. In other words, many simply do not know that they have this disease (sometimes called a syndrome in the medical literature).
Symptoms of neurocirculatory dystonia are nervousness, increased fatigue, sleep disturbances, weakness, impaired cognitive function, and subsequently palpitations, cardialgia, shortness of breath, and blood pressure disorders. In the future, it leads to arrhythmia, tachycardia, and chronic vascular insufficiency. All these symptoms are explained, among other things, by impaired blood circulation in the brain17.
Reasons for the development of neurocirculatory dystonia18:
– genetic predisposition;
– psycho-emotional stress;
– lack of sleep (inconsistency with circadian rhythms);
– lack of physical activity;
– unbalanced diet, obesity;
– alcohol abuse, smoking.
That is, lifestyle directly affects the development of neurocirculatory dystonia, which leads to chronic cerebral circulatory disorders. Under conditions of lack of oxygen and nutrients, the rate of formation of neurons decreases, connections between control departments, as well as the transmission and inhibition of nerve impulses within the central nervous system are disrupted.
As a result, memory, concentration, reaction and coordination of movements deteriorate, constant fatigue and drowsiness are observed, and performance drops to 50%19. This condition can lead to massive death of brain cells and the appearance of local foci of necrosis. That’s why improving blood circulation in the brain is vitally important; let’s look at how to do it point by point.
Medical examination
A neurologist diagnoses and treats cerebrovascular accidents. The doctor must act quickly in such conditions. He may ask the family some questions: How and when did the symptoms appear? Has a similar condition occurred before? What chronic diseases does the patient suffer from and what treatment does he receive?
A neurological examination is then performed. The doctor assesses the patient’s state of consciousness, speech, movement, sensitivity, and reflexes. Blood pressure is measured. An ophthalmologist is invited to examine the fundus.
We improve blood circulation in the brain - sufficient and complete sleep
According to research, the duration of proper sleep is 7-8 hours per day20. Sleep should be regular - that is, it is recommended to fall asleep and wake up at approximately the same time. It is necessary to sleep in absolute darkness and silence, so the brain can fully analyze and systematize the information received during the day, as well as update the neurochemical mechanisms responsible for long-term memory21.
Research shows that adequate sleep normalizes blood circulation in the brain, ensuring adequate daily intake of oxygen and nutrients by brain cells. Lack of sleep, on the contrary, impairs blood supply to the brain and blood circulation, leads to the death of neurons and extensive damage to the central nervous system (including disruption of the function of the blood-brain barrier, which protects the brain from infections and toxins that can enter it through the blood)22,23. Therefore, in order to improve blood circulation in the brain, you must first normalize sleep; without this measure, other methods will be less effective.
Improving blood circulation in the brain - diet and drinking regimen
A diet to improve blood circulation in the brain is selected based on the metabolic characteristics and condition of a particular person. Before adjusting the diet, it is recommended to conduct the following studies: daily blood pressure monitoring, blood tests for glucose and cholesterol, and a coagulogram. Based on research results, it is necessary to adjust the amount of salt, sugar, animal fat and other products in the diet24,25,26.
Diet recommendations to improve blood circulation in the brain:
– The consumption of salted, smoked and canned foods is usually limited in the presence of arterial hypertension, based on the recommendation - no more than 4.5 grams of salt per day.
– Restrictions on the amount of animal fat (fatty meat, lard, milk, butter) are determined by the presence of hypercholesterolemia, which sets the upper limit - 1 gram of fat per 1 kg of weight.
– The amount of monosaccharides and disaccharides (glucose, sucrose and foods high in them) is limited when blood glucose is high. In this case, preference is given to polysaccharides, which are found, for example, in durum cereals and pasta.
– Since vitamin K actively stimulates blood clotting, if this indicator increases, it is recommended to limit all foods high in vitamin K (white cabbage, broccoli, spinach, lettuce, soy, eggs, dairy products, green tea).
Research shows27 that foods high in sodium reduce central perfusion pressure, which measures the level of blood flow to the brain. In this regard, outside of pathologies, it is recommended to avoid excessive consumption of foods high in sodium - salt, herring, caviar, almost all cheeses, beef kidneys, feta cheese, dry cream, powdered eggs.
Treatment
Treatment of stroke will include first emergency care and subsequent therapy. Further therapy consists of a number of measures to normalize and support brain function. The doctor informs the patient about how to take nootropics for stroke and other medications, nutritional habits of patients with stroke, clinical recommendations for stroke. Treatment of acute cerebrovascular accidents includes basic and specific therapy. Basic therapy contains the following measures:
- Restoring and maintaining respiratory function.
- Maintaining optimal blood pressure and cardiovascular activity. The patient is given intravenous medications (labetalol, nicardipine, sodium nitroprusside) according to indications; anaprilin, enaprilin, captopril, esmolol are used to correct blood pressure. Antihypertensive therapy depends on the type of stroke - hemorrhagic or ischemic.
- Treatment of cerebral edema.
- Fighting seizures, intracranial hypertension, various neurological complications.
Specific therapy includes:
- Carrying out intravenous or intra-arterial thrombolysis depending on the time of onset of the first symptoms of the disease. Aspirin is prescribed, and anticoagulants are prescribed according to indications.
- Maintaining optimal blood pressure.
- In certain cases, surgery is performed to remove the brain hematoma, and the hemicraniectomy method is used to decompress the brain.
Treatment of stroke is carried out in a hospital setting. The faster the patient receives medical assistance, the higher the chance of recovery.
Procedure for providing medical care
The scope of medical care for stroke or stroke will depend on the severity of the patient’s condition. It is important to get to the hospital as soon as possible. If the cause of the stroke is a blood clot, then it is necessary to take an antithrombotic drug within 3 hours after the onset of cerebrovascular accident to reduce the consequences.
Treatment of stroke occurs in a hospital, its duration is from two weeks (for mild damage). The patient is prescribed infusion therapy, medications to stabilize blood pressure, and medications to normalize the functioning of nerve cells. In the future, the patient will need a rehabilitation course to restore lost skills or adapt to new living conditions. Rehabilitation is a very important part of treatment. It is rehabilitation measures, when performed regularly, that contribute to the restoration of working capacity.
At the Yusupov Hospital you can undergo a full course of treatment for acute stroke and stroke, including emergency care and rehabilitation. The hospital employs the best neurologists, cardiologists, surgeons in Moscow, doctors of science, and doctors of the highest category who have extensive experience in successfully treating these conditions. The hospital is equipped with everything necessary for a speedy and high-quality recovery of patients.
Artificial ventilation for acute stroke
When a patient is admitted with stroke or stroke, the doctor assesses the adequacy of spontaneous breathing and the level of oxygen in the blood. If the patient has a low level of consciousness, there is a risk of aspiration, high rates of intracranial hypertension, he requires artificial ventilation (ALV).
Ventilation is also performed for:
- Violation of central regulation of breathing;
- Obstruction of the tracheobronchial tree;
- Pulmonary embolism.
Treatment with a dropper (infusion therapy)
Infusion therapy begins from the moment a patient is admitted with stroke or stroke. A 0.9% sodium chloride solution is prescribed. With stroke, hypovolemia (decreased blood volume) quite often occurs, which can be eliminated by infusion therapy. Infusion is also necessary to control the water balance in the body. Infusion therapy is canceled gradually, after confirmation of normalization of the level of electrolytes and other elements in a blood test.
Normalization of blood pressure
The first three days are critical after stroke. During this period, repeated violations or the development of a major stroke are possible. Now it is necessary to stabilize the patient's condition and respond to any changes. Some important indicators are intracranial pressure and blood pressure. Pressure level indicators should not exceed the permissible norm or be below the norm. Therefore, pressure monitoring is carried out constantly. To normalize the indicators, special drugs are first administered intravenously, and then switched to tablet form of drugs.
Elimination of convulsive syndrome
With stroke, there is a high risk of seizures. However, there is no prevention for this condition. Anticonvulsants are prescribed immediately when a seizure occurs. The drugs are administered orally or intravenously.
Use of neuroprotectors and nootropics
An important direction in the treatment of stroke and stroke is the restoration of damaged nerve tissue and the protection of healthy tissue from the spread of “vascular catastrophe”. Treatment is performed with the help of neuroreparants and neuroprotectors.
Nutritional Features
If swallowing is impaired, the patient is prescribed feeding through a tube. At the beginning of treatment, food contains the necessary elements to maintain the functioning of the body, combined with infusion therapy. The calorie content of food increases gradually. In the future, the method of eating will depend on the severity of the brain damage. The course of rehabilitation of patients after acute stroke and strokes includes the restoration of self-care skills, so with the proper effort and capabilities of the patient, he can feed himself again. Food should be varied, contain all the necessary microelements and vitamins, that is, comply with the principles of rational nutrition.
Products to improve blood circulation in the brain:
– amino acids of animal and plant origin (meat, legumes);
– seafood (mussels, shrimp) and sea fish (mackerel);
– vegetables and fruits high in vitamin C and group B;
– cereals, nuts, berries and citrus fruits (rich in bioflavonoids).
Drinking regime
– a separate item in the program for improving blood circulation in the brain. Research shows that sufficient water consumption (2.5 liters per day in the absence of additional instructions due to pathologies) is the prevention of blood clots. However, in case of pathologies, it is still necessary to use antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants prescribed by a doctor.
Thirst quenching is also necessary for the development of neural populations28,29. The latest research shows that molecular hydrogen in drinking water protects the brain from neurodegenerative changes of various origins, including those caused by traumatic brain injury30. Therefore, to improve blood supply to the brain, it is necessary to drink enough water, and the drinking regime should be regular - the recommended 2.5 liters must be evenly distributed throughout the entire waking period.
Please note that 2.5 liters is an average. According to research, women on average need to drink less water than men (2.2 liters and 3 liters per day, respectively)31. Also, the recommended daily amount of water is determined by weight, age and lifestyle32. Below is a table of recommended daily water intake.
Improving blood circulation in the brain - physical activity and exercise
Physical inactivity (lack of physical activity) can be caused by many factors - from sedentary work to basic laziness. It has a number of negative consequences, including problems with the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, bones33,34.
In the context of cerebral circulation, lack of physical activity is associated with an increased risk of blood clots35 and deterioration of the conductive capacity of gray matter (a major component of the central nervous system)36. Therefore, anyone who leads a sedentary lifestyle is recommended to take regular walks, run every night, practice Nordic walking, or workout in the gym.
Research shows that regular physical exercise has a beneficial effect on blood flow throughout the body, including the brain37,38. There are special sets of exercises to improve blood circulation in the brain, and there are also specialized programs implemented in the presence of certain pathologies.
A set of exercises to improve blood circulation in the brain:
– Take a sitting position, looking straight ahead, turn your head 45 degrees to one side, then to the other.
– Slowly rotate your head in a circle, first to the right, then to the left.
– Tilt your head up so that your chin points to the ceiling. Then lower your head to your chest and touch your chin to your chest.
– Bend to the right and left towards your shoulders so that your ear touches your shoulder. The shoulders are motionless.
– Looking straight ahead, stretch your head forward as much as possible, return it to its original position and pull it back as far as possible.
The entire complex is performed as slowly and carefully as possible. The purpose of exercises to improve blood circulation in the brain is to relax the muscles that compress the blood vessels and normalize blood flow. Each movement is performed 10-15 times; for sedentary work, it is recommended to perform the complex 2-3 times during the day at approximately equal intervals.
Exercises to improve blood circulation in the brain with cervical osteochondrosis include neck rotations, lateral flexions, rotation, retractions, and stretching of the trapezius muscle. The figure below shows an example of such a complex.
There are many specialized complexes of medical gymnastics to improve blood circulation in the brain in case of osteochondrosis of various joints39,40. It is unacceptable to perform these exercises on your own; they are performed only under the supervision of a specialist, or as directed and after consulting a doctor.
Providing emergency assistance
Acute cerebrovascular accident requires emergency care, since it will not be possible to normalize the patient’s condition on his own. The standard for emergency medical care for acute stroke and stroke states that the patient should be taken to the hospital within 3-5 hours after the onset of the attack. In this case, it is possible to stop the spread of the pathological condition and minimize the severity of the consequences. Help for a person with a stroke can only be provided in a hospital. At home you can do the following:
- Call an ambulance;
- Lay the person on a flat surface (floor, bed), placing a pillow, blanket or folded sweater under the head;
- Turn the person on their side if they feel sick;
- Open the windows to let in fresh air;
- Unfasten clothing that impedes blood flow and air flow (belt, collar, scarf, tight buttons);
- While waiting for doctors, collect documents and personal belongings.
In case of an emergency, it is necessary to provide assistance to the patient before the medical team arrives. If you lose consciousness, you should check your breathing and pulse, and place the person in a position that will not interfere with breathing. If there is no breathing or pulse, it is necessary to begin mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration and chest compressions. If convulsions occur, the patient should be protected from injury: remove nearby sharp and blunt hard objects. You should not try to restrain the patient or unclench his teeth. It is better to wait until the attack ends and check the airway.
If stroke develops, you can go to the Yusupov Hospital, whose emergency department is open 24 hours a day, seven days a week. The hospital has an ambulance, so the patient will receive all necessary medical care in a timely manner. In the intensive care unit of the Yusupov Hospital, the patient will be able to provide the required assistance to stabilize his condition.
The procedure for providing medical care to patients with stroke after admission to the hospital emergency department is as follows:
- Medical examination, ECG, blood tests;
- Examination by specialized specialists: neurologist, cardiologist, neurosurgeon, resuscitator;
- Performing a computed tomography scan of the brain;
- Evaluation of survey results;
- Start of therapy.
After the patient is admitted to the hospital and before the start of therapy, no more than an hour should pass. If necessary, the patient is sent to the intensive care unit immediately, after which the necessary examinations are performed.
Improving blood circulation in the brain - bioactive supplements
Most dietary supplements for improving brain circulation are nootropics, the mechanism of action of which is related to stimulating blood flow. One of the popular nootropics with this mechanism of action is glycine. This is an aliphatic amino acid that functions as a neurotransmitter and has an “inhibitory” effect on neurons, which gives a mild sedative effect.
Glycine reduces the release of GABA and glutamic acid and stimulates blood circulation in the brain. Target effects – relieves irritability and aggressiveness, eliminates chronic fatigue syndrome, improves brain function, stimulating cognitive functions (memory, reaction, attention).
Among nootropics there are not only amino acids, but also extracts, for example, ginkgo biloba extract. It contains 24% flavonoids, vitamins, minerals and other bioactive substances. It has a vasodilating effect, improves blood flow to the brain and blood flow inside the organ. It also stabilizes blood pressure and cholesterol levels, improves microcirculation. Helps eliminate neurocirculatory dystonia and chronic fatigue syndrome caused by psycho-emotional stress.
Complex supplements, such as “Healthy Sleep,” will help improve blood circulation in the brain, eliminate anxiety and normalize sleep. This supplement includes glycine, gamma-aminobutyric acid, tryptophan, melatonin and 4 extracts - lemon balm, passionflower, valerian and chamomile. The benefit of the supplement is that it not only stimulates blood circulation in the brain and improves cognitive function, but also stabilizes the sleep/wake cycle, helping to get enough sleep.
Vasodilators
The list of effective medications that help improve cerebral circulation is diverse and broad. In general, this is a large group of medications that have different mechanisms of pharmacological action on the vascular structures of the brain. Therefore, a doctor must prescribe this or that drug that can improve cerebral blood flow after diagnostic procedures. Subgroups of vasodilator drugs:
Antispasmodics – promote relaxation of smooth muscles in the vascular wall, thereby increasing the diameter of the lumen. However, it is worth considering that the process occurs not only inside the skull, but throughout the entire body. They are usually prescribed for a short course. Popular remedies are Drotaverine, No-shpa.
Calcium channel blockers - dilate cerebral vascular structures without harming peripheral circulation, but may lower blood pressure. They are contraindicated for people prone to hypotension - with low blood pressure numbers. The doctors' arsenal includes the following drugs: Norvasc, Cordafen, Amodipine, Nimotop, Verapamil, Cardipin, Normodipine, Sakur.
Nootropics are widely prescribed drugs because they not only correct the blood supply to the head, but also improve the tone of the veins: Nootropil, Piracetam, Cerebrolysin, Lucetam.
The dosage and duration of the course of medication are determined by the doctor, taking into account the severity of negative symptoms and the state of blood circulation inside the skull as a whole.
Improving blood circulation in the brain - vitamins
Among the vitamins for improving blood circulation in the brain, one can highlight Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid), which is necessary for the functioning of nerve fibers, the division of epithelial cells and the formation of the inner wall of blood vessels. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is involved in the functioning of the nervous system, is necessary for the formation of a number of neurotransmitters, and reduces the level of lipids in the blood. Vitamin B8 (inositol) is part of the protective membrane of brain cells, stabilizes lipid metabolism, and normalizes mood.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) normalizes blood clotting, stabilizing blood flow, stabilizes capillary permeability, and is an antioxidant. Also, complexes with minerals - phosphorus, magnesium, selenium and zinc - are useful to improve blood circulation in the brain. All these minerals are necessary to maintain the functioning of brain cells. Examples of such complexes are Magnesium + Vitamin B6, Zinc + Vitamin B6, Multivitamin complex 360.