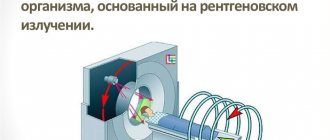
Previous Next MRI of the pituitary gland is a separate, separate scan protocol and should not be confused with MRI of the brain. These are two different examinations. The focus of tomography of the pituitary gland is the pituitary gland itself and the area of the sella turcica. The technique for studying the pituitary gland using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner is based on the relaxing properties of hydrogen atoms. Most people are made up of water, the molecules of which include hydrogen protons. Depending on the saturation of water, soft and bone tissues have different relaxing properties, and therefore appear differently on tomograms.
- MRI
- Ultrasound
MRI tomograph:
Siemens Magnetom C
Type:
Open (expert class)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written report from a radiologist, recording of tomograms on CD + free consultation with a neurologist or orthopedist after an MRI of the spine or joint
Ultrasound machine
HITACHI HI VISION Avius
Class:
Expert (installation year 2019)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written diagnostic report
MRI of the pituitary gland with and without contrast - what is the difference?
When a patient comes to the MRI center for examination of the pituitary gland, depending on the diagnostic purposes, he is offered an MRI with or without contrast enhancement. It should be said right away that tomography of the pituitary gland in the vast majority of cases must be carried out with the introduction of a contrast agent. It is contrast that makes it possible to detect all, even very small pituitary tumors. For example, using non-contrast, native MRI, it is impossible to find a pituitary microadenoma due to its small size. It is the introduction of contrast that allows doctors to:
- assess the distribution, boundaries and relationship of pathological processes;
- identify all neoplasms, their size, location and degree of fusion with surrounding tissues;
- identify and evaluate inflammatory processes and the level of tissue necrosis;
- assess the degree of vascularization, that is, the rate of accumulation and release of the contrast agent, for differential diagnosis. This characteristic allows specialists to judge the benignity or malignancy of the neoplasm.
Small but important. When is an MRI of the pituitary gland needed?
Although this organ is small, its importance for the body is extremely important. The pituitary gland is called a regulator of vital functions and a guarantor of good health. Evgeniy Nikolaevich Klikich, a radiologist at MRI Expert Novosibirsk, told us about in what cases and how an MRI examination of the pituitary gland is performed.
- Evgeniy Nikolaevich, what kind of organ is this - the pituitary gland? What role does it perform in the body?
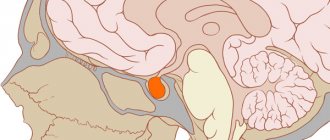
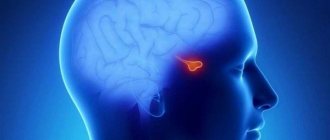
— The pituitary gland (otherwise known as the pituitary gland) is a small structure located at the base of the skull, which is rightly called the “patron of hormones.” Being the size of a small bean, this organ produces more than ten hormones that affect human growth, the functioning of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and glands of the reproductive system. That is, the pituitary gland controls and directs the activities of these endocrine organs, maintaining hormonal balance in the body.
— When is magnetic resonance imaging of the pituitary gland required?
“In the vast majority of cases, endocrinologists refer patients to us for this study. Why do they order an MRI of the pituitary gland? Most often, in order to exclude micro- and macroadenomas of the pituitary gland - one of the common pathologies of the organ. This type of study is also recommended for hypophysitis – inflammatory changes in the pituitary tissue.
A targeted MRI of the pituitary gland may be needed after detection of pathological changes in its structure, or in the area of its location, after an MRI of the brain. This information will be useful to neurologists and neurosurgeons. Sometimes ophthalmologists recommend this type of examination to patients for visual impairment. This is due to the peculiar location of the pituitary gland and the possibility of compression of the optic nerves due to pathological changes, with subsequent visual impairment.
— What does an MRI of the pituitary gland show? What organ changes can be seen on an MRI image?
- Tumor formations are well visualized - macro- and microadenomas, cysts, inflammatory changes in the organ, abnormalities of its development, craniopharyngiomas, tumor metastases.
— What is the purpose of conducting an MRI study of the pituitary gland with contrast?
— Practice shows that MRI of this organ without the use of contrast is not very informative. We usually perform MRI diagnostics of the pituitary gland with dynamic contrast. The peculiarity of this study is that the specialist injects a contrast agent into a vein and simultaneously takes a series of images in different contrast phases. This allows you to determine the location and size of microadenomas and other pituitary tumors, identify their relationship with surrounding tissues, and also assess the intensity of blood flow in the area under study.
MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast is also recommended for patients before neurosurgical intervention to remove tumors in this part of the brain.
Read more about MRI studies with contrast agent in our article
— What is the preparation for an MRI of the pituitary gland?
— There is no specific training. However, as before any magnetic resonance examination, you should remove all metal accessories. Patients should inform the doctor about their allergies in order to exclude the possibility of developing an allergic reaction to the administered drug.
— Are there any contraindications to MRI of the pituitary gland?
- Yes. These include the presence in the patient’s body of ferromagnetic implants, electronic devices (for example, a pacemaker), and artificial heart valves. For pregnant women, MRI of the pituitary gland is prescribed in exceptional cases, and in the first trimester such a procedure is not performed at all. Contrast studies are also not performed in patients with grade 3-4 chronic renal failure.
Read the material on the topic: Dos and don’ts in MRI
— How is MRI of the pituitary gland performed?
— The person lies down on the tomograph table, on his back. To ensure maximum immobility, the head is fixed with a special mount. Then a scan is carried out. The duration of the study is 30 – 40 minutes.
— What is the advantage of magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosing pathological processes of the pituitary gland compared to other research methods?
— Magnetic resonance diagnostics is considered the “gold standard” in the study of the pituitary gland.
Regarding the question of which is better - X-ray diagnostics, CT or MRI of the pituitary gland, I can say that magnetic resonance imaging is safer (no ionizing radiation) and highly informative. On CT images, small microadenomas can easily be confused with the tissue of the gland itself, while on MRI the smallest neoplasms are very clearly visualized. Changes in the pituitary fossa on an x-ray are visible only in large tumors of the pituitary gland, therefore this research method is of little use for the early detection of pathological changes.
Read more about computed tomography here
I would like to note that patients are often referred to us for an MRI of the brain, meaning that in the images it will be possible to see and evaluate in detail the pathologies of the pituitary gland, as a part of the brain. This is a misconception because the two studies are significantly different. When performing a brain scan, images are taken of sections 5 mm thick, and when conducting a targeted study of the pituitary gland, we obtain sections every 2-3 mm. Such detail allows you to see the smallest changes in the organ.
Interviewed by Sevilya Ibraimova
For reference:
Klikich Evgeniy Nikolaevich
In 2015 he graduated from the medical and biological faculty of the Siberian State Medical University.
From 2015 to 2021, he completed an internship at the same university in the specialty “Radiology”.
Radiologist at MRI Expert Novosibirsk. Receives at the address: st. Yakusheva 41, k2
The editors recommend:
Sugar? Not only! What is diabetes insipidus?
Myths and truth about thyroid diseases
When is an ultrasound of the thyroid gland necessary?
Indications
There are a lot of hormones produced by the pituitary gland, and with the help of MRI of the pituitary gland, doctors have a chance to understand where the cause of many pathological processes in the body lies. The symptoms of diseases of this organ depend on the production of which hormone is disrupted by the tumor. So:
- Many pathological processes in the brain in the pituitary gland zone change the synthesis of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4).
- Tumors in the sella turcica area can cause overproduction of cortisol, the excess production of which leads to Cushing's disease.
- Growth hormone (somatotropic hormone) is responsible for the growth of the entire body. Overproduction of this substance due to adenoma causes the process of acromegaly.
- A lack of luteinizing hormone and oxytocin, which are responsible for ovulation, causes infertility in women and a lack of testosterone in the stronger sex.
- A pituitary adenoma can affect the production of prolactin, which directly regulates the functioning of the mammary glands.
- Failures in the synthesis of follicle-stimulating hormone lead to a lack of follicle growth in the ovaries in the fair sex and the formation of low-active sperm in men.
- A disruption in the production of antidiuretic hormonal substances leads to problems with urination and can cause the development of diabetes insipidus.
- There is also a hormone of the intermediate lobe of the pituitary gland, the so-called lipotropin and proopimelanocortin, which control the pigmentation of our skin and enhance the metabolism of fats.
Pituitary gland: what it is, description and functions
The pituitary gland is a small (up to 1 gram) gland located at the base of the brain. The hormones secreted by the pituitary gland are involved in regulating the functioning of the entire human endocrine system. Disturbances in the functioning of the pituitary gland affect the functioning of the entire body, cause changes in development, and can cause obesity, infertility, and other pathological conditions.
Pituitary tumors, among which adenoma is the most common, are well identified using MRI, which allows timely treatment to begin.
What will a tomography of the pituitary gland with contrast show?
Most often, as a result of magnetic resonance diagnostics, the following diseases of the pituitary gland are detected:
- Rathke's pouch cyst. It is also called a pseudocyst because it is often a residual structure of Rathke's pouch.
- Pituitary ectopia is an abnormal development of the pituitary gland or its abnormal position.
- Empty sella turcica.
- Macro- and microadenomas of the pituitary gland.
- Congenital adrenogenital syndrome.
- Lymphocytic hypophysitis is an autoimmune pathology characterized by inflammatory changes.
- Tumor of benign and malignant nature.
- Hamartoma is a tumor of the hypothalamus.
- Craniopharyngioma is a benign tumor in the area of the sella turcica.
- Cancer metastases in the pituitary gland area.
Referral for MRI and preparation
Most medical centers in St. Petersburg accept patients for tomography of the pituitary gland, both with and without a referral from a doctor. If a person has concerns or doubts about his health, he can independently come to the diagnostic center and voice the problem. Radiologists will help you decide on the area of study, and based on the results of the tomography, advise on further steps. If the patient has any medical history or results of previous examinations, it is better to bring them with you for diagnosis. The tomographic procedure of the head does not require any special preparation from the patient. You can do it any day without having to diet.
Procedure for tomography of the pituitary gland with contrast
To do an MRI with contrast, before the scan begins, a special drug is injected into the patient through a vein, which almost never causes an allergic reaction. The magnetic resonance examination procedure is painless for a person and takes 40 minutes. To obtain high-quality MRI images, the patient must lie still without moving his head. Native MRI of the pituitary gland can be performed in situations where a person has contraindications to the administration of a contrast agent - renal failure, bronchial asthma, pregnancy. The price for an MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast is not the cheapest, since the cost of the contrast agent will need to be added to the price of the basic scan, which is calculated based on the patient's weight. But the information content, accuracy and diagnostic value of contrast magnetic resonance imaging are worth the expense.
Indications and contraindications for CT scan of the pituitary gland
There are the following indications for CT scanning of the pituitary gland: frequent headaches, metabolic disorders (and, as a result, obesity), menstrual cycle disorders, vision disorders, suspicion of a pituitary adenoma, the presence of hormonally inactive neoplasms or vascular pathologies.
There are also contraindications for CT, they can be divided into:
- Absolute: pregnancy, excessive body weight (depending on the maximum permissible load on the work table of the CT machine).
- Relative: breastfeeding, renal failure (severe), children up to 14 years of age, multiple myeloma (blood cancer).
Decoding
During the examination, the doctor evaluates the following anatomical features:
- The shape of the sella turcica, the edges of its bottom and walls;
- Pituitary gland, dimensions, its contours;
- Gland structure;
- Chiasm and the distance from the upper surface of the pituitary gland to the chiasm and between the mediobasal parts of the temporal;
- Cavernous sinuses;
- Optic chiasm, carotid siphons;
- Adjacent parts of the brain;
- Sinus of the sphenoid bone.
Example of an MRI report
A series of MR tomograms obtained images of the pituitary gland in coronal, axial and sagittal projections.
The pituitary gland in the sella turcica is not enlarged, somewhat asymmetrical in the craniocaudal direction: on the right - 0.8 cm, on the left - 0.7 cm, coronal size - 1.8 cm, sagittal - 1.0 cm. The structure of the pituitary gland is somewhat heterogeneous due to the presence in the central sections of a poorly defined hypointense focus, measuring 0.2x0.2 cm.
The funnel is located in the middle.
The chiasma and suprasellar cistern are without deformations.
After administration of the contrast agent Magnevist 20.0 ml during dynamic observation, the contrast enhancement is expressed unevenly, and there is a lag in the accumulation of paramagnetic by the identified focus.
Conclusion:
— MRI signs of pituitary microadenoma. Recommended: Dynamic MR monitoring in the context of the clinical picture and clinical and laboratory data.
“Second independent opinion” service Medicine is an area where we want to be 100% sure . Therefore, at your request, we will be happy to offer you the service of a second independent opinion from the leading consultant of our clinic, Candidate of Medical Sciences , a doctor of the highest category with 18 years of experience in the field of tomography and radiology N.V. Marchenko.
Author: Telegina Natalya Dmitrievna
Therapist with 25 years of experience
How is the examination carried out?
The CT machine consists of a sliding table and the tomograph itself. Before the procedure, the patient lies down on the table. Special belts and pillows are used to secure the body and provide comfort. Next, the work table is pushed into the tomograph ring. The radiologist leaves the room, turns on the machine and monitors the patient through a special window. The patient can report his feelings and well-being to the medical staff using voice communication. The CT procedure lasts approximately 15-20 minutes. After this, the radiologist evaluates the received images and begins to interpret them.
CT pituitary gland with contrast
If bone tissue is visualized quite well on CT images, then the structure of the soft tissue surrounding the pituitary gland can only be correctly assessed using contrast enhancement. To do this, before the CT scan, the patient is given intravenous auxiliary iodine-containing drugs. It is also possible that contrast is supplied to the patient’s blood throughout the entire scanning procedure (bolus injection). For this purpose, special devices called injectors are used.
There are a number of contraindications to the use of contrast enhancement:
- allergy to iodine-containing drugs;
- renal or liver failure;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- diabetes.
What determines the price of an MRI?
The power of the tomograph The higher the induction level of the device, the more expensive tomography will cost you. Therefore, before doing an MRI, be sure to consult about the best power of the device to choose.
Promotions and discounts Pay attention to promotions at night. Night discounts usually start from 23.00 to 7.00. The cost reduction reaches 30% of the daily price.
Doctor's qualifications
It is the medical examination of the radiologist that guarantees the success and quality of interpretation of MRI images.
Use of contrast Native MRI costs almost half as much as contrast MRI, since contrasting adds the cost of a contrast composition, calculated based on the patient’s body weight.
The price of MRI of the pituitary gland in medical centers in St. Petersburg includes: direct diagnosis, preparation and interpretation of the results, free consultation with a doctor and recording of the results on an electronic medium.
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| MRI of the brain | 3300 rub. | 2490 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of cerebral vessels (arteries) / MR angiography of cerebral vessels | 3300 rub. | 2490 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the brain and cerebral vessels | 6600 rub. | 4980 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland (without contrast) | 3500 rub. | 2490 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast | from 6500 rub. | not implemented | from 5900 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland and brain | 6800 rub. | 4980 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MRI of the central nervous system (MRI of the brain, MRI of the cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral region) | 13200 rub. | 9290 rub. | 10790 rub. |
| Comprehensive head diagnostics (MRI of the brain, MRI of cerebral vessels, ultrasound of neck vessels, consultation with a neurologist) | 10900 rub. | 7500 rub. | |
| Contrast administration (based on patient weight) | from 3000 to 5000 rub. | from 3000 to 5000 rub. |
How is MRI of the pituitary gland performed, how long does it take?
Special preparation is required only for MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast.
Before a routine examination, you will need to remove metal jewelry, hairpins, and watches. Wallets with credit cards, pens and glasses will also have to be left outside the room where the device is installed.
The patient is positioned on a movable table, which moves inside the tomograph for the examination. The entire study takes from 30 to 60 minutes, during which time you must lie still so that the results are not distorted (fixing belts may be used).
To make MRI of the pituitary gland more comfortable, it is recommended to use earplugs or special headphones, since the noise of the machine can cause discomfort.