Effect of anticonvulsants
During an attack, a person experiences not only muscle spasms, but also pain due to them. The action of anticonvulsants is aimed at eliminating these manifestations, stopping the attack so that it does not progress from pain to epileptic, convulsive phenomena. A nerve impulse is activated along with a specific group of neurons, just as it does when transmitted from motor neurons in the cerebral cortex.
Anticonvulsant pills should relieve pain and muscle spasms without suppressing the central nervous system. Such medications are selected individually, taking into account the degree of complexity of the pathology. Depending on this, medications can be used for a certain period or throughout life if a genetic or chronic form of the disease is diagnosed.
How does the disease appear?
Many patients wonder what caused the onset of the disease, because this is a dangerous condition and requires mandatory medical supervision. Medicine identifies three main groups of factors that can lead to the development of the disease:
- Idiopathic (genetic predisposition). Even after tens of generations, the disease can be transmitted. In this case, there are no organic defects or damage in the brain, but there is a certain reaction of neurons. With this form of pathology, an epileptic attack can begin without a reason.
- Symptomatic. The disease can appear after injury, intoxication or tumor processes in the brain. This form of epilepsy occurs spontaneously, and a seizure can occur unpredictably.
- Cryptogenic. A little-studied factor, the exact cause of which has not yet been established. A seizure can occur due to any psycho-emotional stimulus.
The disease can manifest itself at any age, however, according to statistics, epilepsy is more likely to affect young children, adolescents and adults over 60 years of age. To date, medicine has identified about 40 different types of epilepsy. Therefore, the treating doctor must carry out an accurate diagnosis to establish the form of the disease and determine the nature of the seizures.
The effectiveness of the results in certain cases depends entirely on the adequacy of the choice of antiepileptic drug and the prescription of the treatment regimen. If treatment is untimely or inadequate, the patient may die. Therefore, a full examination of the patient and an accurate diagnosis of the disease is necessary.
Groups of anticonvulsants
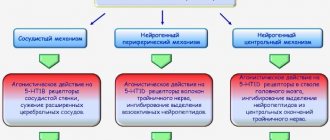
To prevent epileptic seizures and convulsions, doctors have developed various means that differ in their principle of action. The doctor should prescribe specific anticonvulsants based on the nature of the seizures. The following groups of anticonvulsants are distinguished:
| Group | Name | Action |
| Barbiturates and derivatives | Phenobarbital, Benzamil, Benzoylbarbamyl, Benzonal, Benzobamyl. | Aimed at inhibiting neurons of the epileptic focus. As a rule, it has an indiscriminate depressant effect on the central nervous system. |
| Benzodiazepine-based drugs | Rivotril, Clonazepam, Ictorivil, Antelepsin, Ravatril, Klonopin, Ictoril. | These medications affect the activity of inhibitory neurons by acting on GABA receptors. |
| Iminostilbenes | Carbamazepine, Zeptol, Finlepsin, Amizepine, Tegretol. | They have a restrictive effect on the propagation of electrical potential along neurons. |
| Sodium valproate and derivatives | Acediprol, Epilim, Sodium Valproate, Apilepsin, Valparin, Diplexil, Konvulex. | They have a sedative, tranquilizing effect, and improve the emotional state of the patient. |
| Succinimides | Ethosuximide, Pufemid, Ronton, Sucimal, Etimal, Suxilep, Pycnolepsin, Valparin, Diphenin, Xanax, Keppra, Actinerval; | Prescribed for the treatment of absence seizures, the tablets are a calcium channel blocker. Eliminate muscle spasms due to neuralgia. |
Anticonvulsants for epilepsy
Some products are available without a prescription, some only with one. Any pills for epilepsy should only be prescribed by a doctor to avoid side effects and not provoke complications. It is important to go to the hospital in a timely manner; quick diagnosis will increase the chances of remission and the duration of taking the medication. Popular anticonvulsant drugs for epilepsy are listed below:
- Feniton . The tablets belong to the hydantoin group and are used to slightly slow down the reaction of nerve endings. This helps stabilize neural membranes. It is usually prescribed to patients who suffer from frequent seizures.
- Phenobarbital . Included in the list of barbiturates, it is actively used for therapy in the first stages, to maintain remission. The medicine has a calming, mild effect, which is not always enough during epilepsy, so it is often prescribed along with other drugs.
- Lamotrigine . It is considered one of the most powerful antiepileptic drugs. A properly prescribed course of treatment can completely stabilize the functioning of the nervous system without disrupting the release of amino acids.
- Benzobamyl . This drug has low toxicity and a mild effect, so it can be prescribed to a child who suffers from seizures. The drug is contraindicated for people with pathologies of the heart, kidneys, and liver.
- Sodium valproate. This is an antiepileptic drug, also prescribed for behavioral disorders. It has a number of serious side effects: the appearance of a rash, deterioration in clarity of consciousness, decreased blood clotting, obesity, and deterioration of blood circulation.
- Primidon . This antiepileptic drug is used for severe attacks of epilepsy. The medicine has a powerful inhibitory effect on damaged neurons, which helps stop attacks. You can take this anticonvulsant only after consulting your doctor.
Painkillers
Sometimes attacks are accompanied by pain. In these cases, doctors solve several problems at once:
- relief of severe pain;
- preventing its manifestation in the future;
- return of the patient to physical activity.
In this case, remedies are chosen without pronounced side effects; there are already enough of them for such an illness.
Cinnarizine for epilepsy:
- Bulgarian prescription drug in tablet form;
- has not only an analgesic, but also a vasodilator effect without affecting blood pressure;
- taken after meals in doses up to 25 mg;
- Use with caution during pregnancy and Parkinson's disease.
Mexidol:
- It is believed that with similar effects, the drug also improves memory;
- causes a minimum of allergic reactions;
- Recently the drug has been declared a prescription drug.
Anticonvulsants for neuralgia
It is recommended to start treatment as early as possible; to do this, you need to consult a specialist after the first symptoms of the disease. Therapy is based on a whole range of medications to eliminate the causes and signs of nerve damage. Anticonvulsants play a leading role in treatment. They are needed to prevent epilepsy attacks and seizures. The following anticonvulsants are used for neuralgia:
- Clonazepam . It is a benzodiazepine derivative and differs in that it has anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, and sedative effects. The mechanism of action of the active substance helps to improve sleep and relax muscles. It is not recommended to use it without a doctor’s prescription, even according to the instructions.
- Carbamazepine . According to the classification, the medicine belongs to iminostilbenes. It has a pronounced anticonvulsant, moderate antidepressant effect, and normalizes the emotional background. Helps significantly reduce pain due to neuralgia. The antiepileptic drug acts quickly, but the course will always be long, because if you stop taking the medication prematurely, the pain may return.
- Phenobarbital . Belongs to the group of barbiturates, which act as a sedative and hypnotic drug in the treatment of neuralgia. This anticonvulsant is not prescribed in large doses; it should be taken strictly as prescribed by the doctor, because the side effects of anticonvulsants are contraindicated in a number of other diseases.
Polytherapy: combined treatment regimen
When treating this pathology, the doctor strives to achieve monotherapy. This allows you to select the appropriate drug, optimal dosage and appropriate treatment regimen, as well as achieve high clinical effectiveness. In addition, monotherapy minimizes the side effects of treatment.
However, in some situations it is more advisable to choose a combined drug regimen. This is what they do:
- In the form of the pathological process, which combines several types of attacks and there is no possibility of complete monotherapy;
- For conditions accompanied by the same type of epileptic seizures, but not treatable with any medication.
In these cases, medications with different mechanisms of action are used in treatment regimens. However, the chosen treatment tactics must be rational and combine drugs that do not interfere with each other. For example, a prohibited combination is the simultaneous use of phenobarbital with primidone and benzobarbital or phenytoin with lamotrigine.
When using a combined treatment technique, a slight decrease in the therapeutic effect is possible. Often, patients experience signs of intoxication when using one of the drugs that was previously well tolerated. Therefore, at the initial stages of polytherapy, monitoring the level of drugs used in the blood plasma is necessary.
Anticonvulsants for children
The choice in this case falls on medications that should significantly reduce the excitability of the central nervous system. Many medications of this type can be dangerous for the baby because they depress breathing. Anticonvulsants for children are divided into two groups according to the degree of danger to the child:
- Drugs that have little effect on breathing: lidocaine, benzodiazepines, hydroxybutyrates, fentanyl, droperidol.
- More dangerous substances that have an inhibitory effect: barbiturates, chloral hydrate, magnesium sulfate.
- Rice porridge with pumpkin: recipes with photos
- How to lighten hair with hydrogen peroxide at home. Masks for lightening hair at home, video
- The simplest and most effective diets for weight loss
When choosing a medicine for children, the pharmacology of the drug is very important; adults are less susceptible to side effects than a child. The list of main drugs used in the treatment of children includes the following medications:
- Droperidol, Fentanyl - have an effective effect on the hippocampus, from which the signal for seizures comes, but does not contain morphine, which can cause breathing problems in infants under 1 year of age. This problem can be eliminated with nalorphine.
- Benzodiazepines - as a rule, sibazone is used, which may be called diazepam or seduxen. Intravenous administration of the drug stops seizures within 5 minutes; respiratory depression can be observed with large doses of the drug. The situation can be corrected by administering physostigmine intramuscularly.
- Lidocaine . The drug can almost immediately suppress any type of seizure in children if given intravenously. In therapy, as a rule, a saturating dose is first administered, then droppers are used.
- Phenobarbital . Used for prevention and treatment. It is prescribed, as a rule, for mild attacks, because the result from use develops within 4-6 hours. The main advantage of the medication is that the effect in children can last up to 2 days. Good results are observed when taken simultaneously with Sibazon.
- Hexenal . A strong drug, but it has a depressant effect on breathing, which greatly limits its use in children.
Duration of treatment
The cessation or reduction of epileptic seizures, reducing their duration, alleviating and improving the psycho-emotional state of the patient is already considered a positive trend in treatment. The use of the latest pharmacotherapy techniques makes it possible to achieve complete relief or significant minimization of seizures.
The duration of drug therapy is determined by the type of attacks and form of the disease, age and individual characteristics of the patient. Practical recovery can occur with idiopathic forms of epilepsy. A small percentage of relapses occur in idiopathic forms with absence seizures that occur in childhood or adolescence.
Termination of therapeutic treatment is carried out gradually, with a reduction in dosage to 1/8 daily over 6-12 months. Antiepileptic therapy should not be discontinued in patients with severe symptoms.
New generation anticonvulsants
When choosing a medication, the doctor must take into account the origin of the pathology. New generation anticonvulsants are aimed at solving a wider range of causes and causing a minimum number of side effects. Developments are ongoing, so over time, more and more modern products appear that cannot be bought in an online store or ordered home. Among the modern options, the following effective new generation antiepileptic drugs are distinguished:
- Difenin - indicated for severe seizures, trigeminal neuralgia.
- Zarontin (aka Suxilep) . A remedy that has proven to be highly effective must be treated continuously.
- Keppra contains the substance Levetiracetam; the mechanism of its effect on the body is not fully understood. Experts suggest that the drug acts on glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors. A positive effect has been confirmed in the treatment of generalized seizures of epilepsy and partial seizures with Keppra.
- Ospolot is a new generation anticonvulsant; the effect of the active substance has not been fully studied. The use of the drug for partial epileptic seizures is justified. The doctor prescribes a daily dose, which should be divided into 2-3 doses.
- Petnidan - the active ingredient called ethosuximide, is highly effective in the treatment of absence seizures. It is imperative to coordinate your appointment with your doctor.
Names of dietary supplements
Many doctors are quite skeptical about dietary supplements in the treatment of serious diseases.
But some of them, specifically as an additional stimulant, have proven themselves to be quite good in the fight against epilepsy.
- Tianshi dietary supplements. The drugs from this corporation stabilize the presence of biocalcium in the body, which has a beneficial effect on the nervous system and can alleviate attacks of epilepsy. The line began to be developed in 1993 and contains teas, nutritional supplements and ointment additives.
- Leviron duo for epilepsy. This is an oily liquid prepared from larch extract. Contains many natural components that can support metabolic processes in the body. For epilepsy, it significantly reduces the side effects of all drugs, especially hormonal and anticonvulsant drugs.
- Carnitine for epilepsy. It also improves metabolic processes and is available in the form of tablets and injection solution. It is considered a biologically active agent.
Side effects of anticonvulsants
Most anticonvulsants are available by prescription and are not available over the counter. This is due to the large number and high risk of side effects from drug overdose. A doctor can choose the right drug based on test results; it is not recommended to buy medications on your own. The most common side effects of anticonvulsants when taken in violation of the rules are:
- lack of confidence when walking;
- dizziness;
- vomiting, drowsiness, nausea;
- double vision;
- respiratory depression;
- allergic reactions (rash, deterioration of hematopoiesis, liver failure).
Sleeping pills and sedatives
Since epilepsy is a disease of increased excitability, the components of this group are prescribed without fail.
Valerian for epilepsy:
- Available over-the-counter in the form of tablets and tinctures;
- has a depressing effect on the nervous system;
- relaxes muscle tension;
- slows down the heart rate;
- take 3-4 tablets or 30-40 ml 3 times a day;
- Contraindicated in case of fructose intolerance.
Phenazepam for epilepsy:
- prescription;
- Available in tablet form;
- single dosage – from 0.5 mg to 7-9 mg in difficult cases;
- quickly becomes addictive;
- side effects: urinary incontinence, dizziness;
- Contraindicated for glaucoma and alcohol poisoning.
Afobazole for epilepsy:
- available without a prescription in tablet form;
- has a mild effect;
- the daily dose should not exceed 30 mg, taken 3 times a day;
- Side effects include dry mouth and dizziness;
- compatible with alcohol, but for epilepsy this combination, like alcohol in general, is not recommended;
What injection is given for epilepsy? Relanium for epilepsy:
- prescription; Available in the form of ampoules for intramuscular or intravenous administration;
- the main side effects are drowsiness, dizziness;
- perfectly relieves feelings of anxiety, as the beginning of increased arousal;
- Contraindications – acute respiratory failure, pregnancy, allergic reactions.
Tenoten for epilepsy:
- available in tablet form without a prescription;
- daily dose: 1 tablet 2 times a day, regardless of meals;
- Contraindications include intolerance and hypersensitivity to lactose.
Price of anticonvulsants
Most medications can be found in a catalog on pharmacy websites, but for some groups of medications you will need a doctor's prescription. The cost of medicines may vary depending on the manufacturer and place of sale. The estimated price for anticonvulsants in the Moscow region is as follows:
| Name | Price, rubles |
| Keppra 30 pcs., 250 Mg | 760-950 |
| Droperidol 0.25%, 1 ampoule | 58-70 |
| Sedkusen, 20 pcs. pills. | From 25 |
| Feniton, 200 pcs. 100 mg each. | From 4000 |