But it is the skull that most often causes brain damage during trauma. As you know, between the bones of the skull and the brain there are meninges and a special liquid - cerebrospinal fluid, which additionally protects the brain. During a head impact, the brain continues to move by inertia, that is, it moves inside the skull, sharply colliding with the bones of the skull. Liquor dampens this movement, but not always. And in case of severe trauma, if there is a fracture of the skull bones, the brain can be damaged by bone fragments.
A child's skull is an even more fragile and vulnerable structure. The likelihood of brain injury from a head impact is much higher in children than in adults. Especially in the first year of life, when the fontanelle has not yet closed, and the bones of the skull are easily displaced upon impact.
Adults must know where the baby is in danger. Falling onto the floor from a changing table or falling out of a stroller is a “hobby” for infants. Older children master the world by testing its strength with their own foreheads. The young traveler doesn’t even need sharp corners - he will hit a bump literally out of the blue. And it’s good if there’s a bump. And when the baby grows up and starts running, it is not known who grabs his head more often - the frightened mother or himself.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely protect a child from injury. If your child rarely falls, are you trembling too much over him? According to Benjamin Spock, “It will keep his bones, but it will ruin his character.” How can you and I, if not protect the baby, then at least reduce the risk of head injury?
Classification
The injury can be open, that is, damage to the skin is observed, and blood vessels are also affected.
If the injury is penetrating, then the dura mater of the brain is affected, sometimes a fracture of the base of the skull is diagnosed - one of the most dangerous injuries. With closed injuries, the skin is not injured. The following groups of brain damage have been identified:
- A concussion is a mild degree of traumatic brain injury, the manifestations of which disappear after a few days, there are no symptoms of vascular damage, and functional disorders are reversible. A bruise is a more severe injury and may cause brain damage. Manifested by such symptoms as nausea, vomiting, pale skin, tissue swelling, pain.
- compression of the affected area of the brain (foreign object, hematoma, air, bone fragment);
- hemorrhage in the subarachnoid space (the cavity between the arachnoid and pia mater);
- diffuse damage.
A severe brain contusion can result from a combined injury.
With a head injury, there are 2 types of bruises:
- Brain contusion.
- Contusion of the soft tissues of the head.
Sometimes the injury is accompanied by hemorrhage. This is often accompanied by fractures of the bone tissue of the skull.
Types of damage are identified depending on location:
- contusion of the back of the head;
- damage to the temporal region;
- bruise of the frontal part of the head;
- damage to the parietal lobe.
Changes that occur in the brain as a result of a bruise are divided into primary and secondary. Primary ones are caused by the injury itself, and secondary ones are caused by deterioration of tissue nutrition and increased intracranial pressure, the appearance of edema, and hematomas.
In case of serious injuries, contusion of several areas of the brain is sometimes diagnosed.
When a child bruises the soft tissues of the head, a lump appears. However, as a result of the blow, brain injuries are also possible, the consequences of which can appear in adulthood, after 40 years or later. Therefore, even if a lump simply appears after a blow, it is recommended to seek medical help.
Causes
A brain contusion is a contusion that is life-threatening. It is important to know what causes this injury, this will help in the future to provide the correct treatment. Some of them cause damage with complications, while others cause minor harm to health.
Brain contusion with contusion can occur due to the following reasons:
- a traffic accident resulting in a severe blow to the head;
- sports injuries;
- receiving injuries and damage in a production environment when performing hazardous work;
- traumatic injuries in children;
- criminal incidents, fights;
- domestic injuries;
- Often, patients who suffer from epilepsy experience severe falls to the ground or floor during a seizure. During this, they may receive a strong blow to their head on a surface made of hard material.
Symptoms
What can happen to the brain after a stroke? The brain, by inertia, sharply shifts in the opposite direction, so it is damaged not only at the site of the impact, but also on the opposite side, this causes vascular spasms and swelling. Due to edema, intracranial pressure increases.
A severe head injury is often accompanied by fractures of the skull bones, which worsen the person’s condition; the risk of developing an infection in the affected area also increases. In any case, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Symptoms of a head injury are determined by the location and force of the blow:
- A mild bruise is characterized by pain that subsides after a few hours. When the subcutaneous vessels are damaged, a hematoma forms. The victim complains of constant drowsiness, double vision and darkening of the eyes, and sometimes fainting occurs. Symptoms disappear after a few weeks;
- moderate injuries are accompanied by prolonged fainting (several hours), severe headaches, inhibited reactions and impaired awareness of what is happening. Speech is unclear and slow;
- for fractures of the skull bones, the main clinical symptoms are dizziness, vomiting, and nosebleeds;
- contusion of the back of the head is manifested by blurred vision, dizziness, loss of consciousness and general weakness.
In case of serious injury, patients are unconscious for a long time (up to several days), and coma may occur. There is a disturbance in speech, breathing and swallowing, and the pupils may vary in size. Partial or complete memory loss cannot be ruled out.
Features of diagnosis
A concussion or contusion of the brain is a serious injury, so it must be fully examined using the latest technology.
Closed traumatic brain injury and brain contusion are diagnosed by assessing several important conditions:
- general condition of the patient;
- condition of vital internal organs;
- identification of neuralgic disorders.
How is the general state of consciousness assessed?
During a brain injury, serious changes occur in the consciousness of the victim. If the injury is mild, then they are not particularly noticeable, but if severe damage is observed, then more dangerous and irreversible changes in consciousness may be observed.
The state of consciousness during a bruise is divided into the following types:
- clear. During it, a person perceives everything that happens around him quite normally, he understands what those around him and all actions are telling him. He is oriented normally, he has no mental disorders;
- Moderate stun. The victim experiences light sleep, which may occur at times. Orientation in space and time may be a little lost. The patient's responses and verbal commands may cause some slowdown in reactions. In case of pain and other unpleasant irritating factors, a full-fledged reaction occurs;
- deep stunning. The patient usually experiences disorientation in space and time. He experiences prolonged sleep. When questioned, he answers reluctantly, with nods. The patient exhibits completely normal reactions to pain and other irritating factors;
- soporous state. During it, the patient may be constantly depressed and depressed. But it fully retains protection against the influence of various irritating factors. Sleep also occurs in a pathological form. He can lie for a long time with his eyes closed without changing position;
- comatose state with a moderate course. It is unconscious, during which the patient does not perceive surrounding actions. He cannot be brought out of this state on his own. The eyes do not respond to irritating factors or pain, but trembling or withdrawal of the arms and legs may be observed. Difficulties in the swallowing reflex are noted. There are no serious changes in the activity of vital organs that could become a dangerous threat to the patient’s life;
- deep coma. It usually develops as a result of a bruise with cerebral edema. During it, the patient remains unconscious for a long time and does not respond to various stimuli. He does not show any reaction or defense to various painful influences. In a deep comatose state, severe disturbances occur with the frequency of the heart and respiratory rhythm;
- terminal coma. Severe swelling of the brain from a bruise, as well as other complications, cause a terminal coma. Victims experience serious and sometimes fatal conditions in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels. Blood pressure levels drop to 60 mm Hg. Art. There is an increase or decrease in heart rate. There may be disruptions in the functioning of the respiratory system, sometimes breathing stops for a long time. There may also be pathological processes of Cheyne-Stokes, Biot and Kussmaul respiration.
Checking the condition of organs important for the functioning of the body
Closed brain injuries can cause problems in internal organs. For this reason, when making a diagnosis, the doctor must conduct a thorough examination of all the internal systems of the victim.
The first step is to monitor the work of the heart and blood vessels, namely, the specialist must determine the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle. Blood pressure is measured. The respiratory system measures the rhythm and frequency of breathing. Body temperature indicators are also determined.
With open and closed contusion of the brain, the following features of organ activity that are important for the life of the body can be identified:
- normal work without disturbances . When the body is normal, all its important organs function fully. For example, breathing proceeds as it should - 12-18 movements in 60 seconds. No pathological manifestations in respiratory activity are detected. Cardiac muscle contractions are in the range of 60-90 beats per minute. Blood pressure also returns to normal - the upper level is 110-140 mm Hg. Art., and the lower 60-80 mm Hg. Art. The temperature does not exceed 37 degrees;
- moderate disorders. In this condition, the heart rate can be moderately low - within 50-58 beats per 60 seconds, or, on the contrary, moderately increased - 87-101 beats per 60 seconds. When checking blood pressure, slight hypertension may be detected - from 140 over 80 to 180 over 110 mm Hg. Art. Respiratory rate indicators may be increased - 20-30. When measuring temperature, the readings on the thermometer can be from 37 to 37.9 degrees;
- pronounced violations. The heart rate may be low or high (less than 50 beats per minute or greater than 120 beats per minute). Breathing may be weak or too frequent - less than 11 or more than 29-30 movements per minute. There is a strong fever, body temperature remains at 38-38.9 degrees;
- severe disorders. The victim has a strong and low frequency - less than 40-38 beats per minute or more than 120 beats in 60 seconds. Blood pressure reaches a high level, it can be above 220/120 mm Hg. Art. The temperature can reach 39.9 degrees;
- critical violations. In this condition, if the necessary treatment measures are not taken in a timely manner, organ disorders can lead to death. It often occurs with a brain contusion, during which severe swelling of the brain develops. The victim has periodic shallow respiratory movements with prolonged apnea. Blood pressure drops to critical levels, reaching 60 mmHg. High tachycardia, in which the number of heart beats per minute cannot be counted. Severe increase in body temperature, its readings can be more than 40 degrees.
Features of neurological disorders
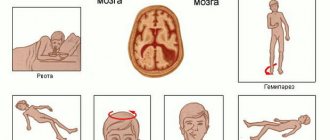
During traumatic brain injuries, damage to brain structures often occurs. They can cause neurological disorders, the nature of which depends on the degree of damage. If a mild bruise is observed, then the neurological symptoms are usually mild.
If serious damage is detected, dangerous changes develop in the brain and multiple hemorrhages in the gray and white matter, this usually leads to disability. In addition, it causes serious disturbances in the motor and mental systems.
With brain injuries, the following neurological disorders may be detected:
- no problems. The doctor must examine the pupils; they are usually the same size. When exposed to light, the pupils react normally and constrict. Full tendon reactions are detected. When a hammer hits the tendon area, a response occurs in the form of contraction of muscle tissue. Legs and arms move normally and exhibit full sensory responses;
- moderate disorders. There is a slight change in pupil size and clonic nystagmus. Sometimes mild speech impairments are observed. There may be minor dysfunction in one arm or leg;
- pronounced disorders. During them, a clear dilation of the pupil is detected in one eye. A weak reaction to the influence of a light stimulus is noted. Severe disorders are often accompanied by the appearance of meningeal symptoms. In the affected area, weakening of the tendons is noted. Cramps in the limbs often occur;
- gross violations. A floating gaze is revealed. A number of signs may also be detected that occur when the frontal and occipital region is affected. Sometimes multiple convulsive manifestations, paralysis in the arms or legs may occur;
critical disorders. Typically, these disorders occur with severe brain contusion. Bilateral dilation of the pupils is detected, and there is a complete absence of reactions to light stimuli. If critical disturbances are noted, a lack of muscle tone and any other reflexes may occur. During critical illness, constant limb spasms occur.
Other diagnostic methods
A brain contusion or contusion requires special diagnostics, which should determine its extent and the presence of associated injuries. Of course, important criteria for assessing consciousness, the state of internal organs, and the degree of complexity of neurological disorders are of particular importance when making a diagnosis. But also do not forget about carrying out additional examination methods.
During the examination, dynamic observation must be carried out, which will help to identify all changes in the condition. When making a diagnosis, the fact of the presence of injury, the period of loss of consciousness, clinical manifestations, and all data that were obtained during a neurological examination and additional examination should be taken into account.
To obtain the most accurate information about the state of the brain during examination, the following diagnostic methods are performed:
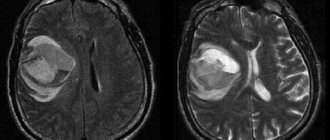
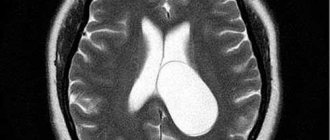
- conducting magnetic resonance imaging and CT for brain contusions. These examination methods make it possible to identify lesions with damage, the presence of hemorrhages, their size and nature, the condition of the ventricles of the brain and other pathological changes;
- X-ray examination of the skull. Using this study, you can identify cracks and fractures in bone tissue;
- performing echoencephalography. This method allows you to identify displacements in brain structures;
- performing a lumbar puncture and examining the cerebrospinal fluid. These methods can detect subarachnoid hemorrhage and intracranial hypertension. It is not recommended to perform this if there is a threat of wedging of the brain stem into the foramen magnum.
First aid for head injury
For a head injury, first aid consists of the following:
- put cold on the site of the impact, this will make it possible to reduce pain and swelling, keep it for several hours, but avoid hypothermia.
- the victim must be laid on a horizontal surface, which will make it possible to avoid another fall due to weakness and dizziness;
- regardless of the severity of the condition, take the victim to the hospital or call an ambulance; exclude intake of water, food and medications;
- in case of hematoma, apply a compressive bandage;
- Warming compresses with alcohol can only be used after a few days.
First aid for a head injury can be provided by anyone, but qualified medical assistance will still be required.
If a child suffers a head injury, first aid must be provided; it must also be taken into account that the symptoms in children may not appear as pronounced as in adults.
Signs
First aid for traumatic brain injury mainly involves determining the patient's neurological clinical picture and externally noticeable damage.
TBI has symptoms that require special attention and mandatory medical assistance:
- intense bleeding;
- blood flow from the ears and nose;
- acute pain in the head;
- irregularities in rhythm or weakness of breathing;
- disturbance of consciousness;
- long-term loss of consciousness;
- malfunctions of the vestibular apparatus, loss of balance, unbalanced movements;
- complete loss of mobility of some skeletal limbs or weakness in muscle tissue;
- convulsions;
- vomit;
- lack of clarity of words;
- lack of a reflex reaction of the pupil to a beam of light, etc.
In case of a traumatic brain injury, the patient must be taken to a medical facility. Even with externally absent damage, it requires additional examination and an accurate diagnosis.
The human head contains many nerve endings responsible for smell, swallowing, maintaining balance, hearing, vision, etc. Failures in the functioning of one of the internal organs should be the reason for a doctor to prescribe treatment and provide emergency care for a traumatic brain injury.
Treatment
Some people self-medicate for a head injury, which is not recommended, especially if there is even the slightest suspicion of a concussion or hemorrhage. How to treat a head injury is determined by the doctor; the methods depend on the nature of the injury and its location.
Drug treatment
Medicines are prescribed to reduce symptoms:
- analgesics – to reduce pain;
- medications to regulate the functioning of the autonomic nervous system;
- sleeping pills to normalize sleep;
- nootropic drugs are prescribed to prevent complications, as well as to restore brain function;
- diuretics;
- anticonvulsants - prescribed in more severe cases in the presence of seizures.
For topical use, ointments are used that have a strengthening effect on blood vessels, relieve swelling and help eliminate hematomas. During the rehabilitation period after injury, doctors prescribe physiotherapeutic measures.
A specialist will tell you how to treat a bruise at home. For this, compresses made from tincture of ginseng, lemongrass, and eleutherococcus are recommended.
Surgical intervention
In severe cases, surgical treatment is indicated, for example, for a head injury from a fall, if it is accompanied by damage to the integrity of the brain structures.
Most often, operations are prescribed for damage to the temporal and frontal lobes of the brain. Craniotomy is performed by drilling a hole through which dead tissue is removed. During the postoperative period, the patient should be under the supervision of doctors.
In case of a head injury due to a fall, treatment is prescribed based on the diagnosis. If the injury is not dangerous, then the following recommendations must be followed:
- bed rest for several days;
- adhere to the instructions of the treating specialist and ensure that you take prescribed medications;
- during the rehabilitation period, exclude physical activity;
- if the left side of the brain is injured, then it is better to lie on the right side, and vice versa;
- during the recovery period, it is better to avoid using gadgets and TV or limit such leisure activities to a minimum;
- Long walks in the fresh air are necessary.
If the back of the head is bruised, bruises and bumps also cannot be ignored, especially if unpleasant symptoms appear. In such cases, you should immediately consult a doctor to avoid unpleasant complications.
Severity
- Mild degree.
A mild brain contusion has many similar symptoms to a concussion. Only with the help of computed tomography (CT) can minor damage to the brain substance be detected. After an injury, the victim loses consciousness for a short time, and when he comes to, he has amnesia: he does not remember the short period of time before the injury and the very moment of its receipt.
He also has the following symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- headache;
- minor heartbeat disturbance, etc.
- Average degree.
A moderate brain contusion is characterized by an intensification of previous symptoms, and the victim also has severe neurological symptoms, and minor mental disorders may be observed.
- Severe degree.
A severe brain contusion is, as a rule, an open head injury, when not only the meninges are injured, but also the brain tissue itself. This is often a complex diagnosis that combines several injuries.
If the injury is severe, the victim may remain unconscious for up to several weeks and subsequently fall into a coma.
He also exhibits the following symptoms.
- high blood pressure;
- involuntary urination or bowel movements;
- partial or complete paralysis of the body;
- high body temperature;
- mental disorders;
- epileptic seizures, etc.