In terms of the degree of danger to human life and health, cerebral circulatory disorders can be placed on a par with cancer. In most cases, a stroke results in disability. As is known, damage to brain cells negatively affects the patient’s quality of life, depriving him of control over his own body, including the ability to walk, speak, and perceive communication.
Cause of speech impediment
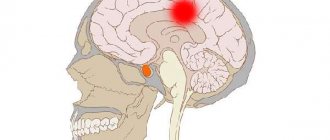
Sensorimotor aphasia after stroke is one of the most serious complications. Complete or partial loss of speech occurs when certain brain functions are suppressed and the activity of specific areas of the cortex decreases. Sensorimotor aphasia can also be a consequence of trauma, indicate the presence of benign or malignant tumors, encephalitis, and meningitis. Unlike other speech disorders that occur with brain damage, this form is considered the most severe. The combination of symptoms of sensory and motor aphasia is a difficult to treat consequence of a stroke, since it is associated with the development of a pathological process in the hemisphere responsible for speech and motor activity.
How do the forms of the disease manifest?
The above classification corresponds to the provisions of neuropsychology, at the origins of which stood Academician A. R. Luria.
Aphasia – differentiation by characteristics:
- Afferent motor – the patient distorts the articulatory postures necessary for pronunciation, intensely searches for the right one, there are no speech utterances.
- Efferent-motor - utterances are broken, the patient gets stuck on individual words, syllables, cannot read, write, or understand the words addressed to him. Unlike the previous form, with efferent-motor aphasia, the pronunciation not of individual sounds, but of entire words and phrases, is lost.
- Dynamic - the patient speaks in clichés or approximately the way the text of a telegram is written, the statements are meager, the answers are monosyllabic. Words are inconsistent, grammar and articulation suffer.
- Sensory – sounds are perceived by the patient distorted and mixed. He tries to catch up with the elusive sounds, words and syllables, replaces them. Trying to disguise the defective pronunciation, he reproduces a large number of unnecessary statements.
- Acoustic-mnestic – there is a deficit of words, a visual image of an object does not arise.
- Semantic – the patient is unable to identify prepositions, adverbs, or coordinate words according to grammatical categories.
Childhood aphasia is diagnosed when the disorder occurs after the formation of speech skills. This age is 2.5 - 3 years. The older children with this pathology become, the more seriously oral and written speech skills, reading, writing, and phoneme discrimination suffer.
Signs in children:
- Motor - children speak in fragments of words and sentences, and cannot reproduce what they are told. They completely inappropriately use words and phrases like “here, this, myself.” The perception of written speech and the ability to read are impaired, the personality suffers, as the child is not confident in himself and becomes depressed.
- Sensory - children cannot reproduce words previously known to them. At the onset of aphasia, they may not understand speech addressed to them at all; over time, they may not perceive only individual phrases. Children distort and replace speech units.
With sensory speech disorders, the student does not recognize what is written, does not distinguish between letters, and is unable to form a word from them.
What are the symptoms of the disease?
Why does sensorimotor aphasia occur, what is it? After a stroke, in some cases, the functionality of the inferior frontal gyrus, which provides a person with the ability to pronounce words, is impaired. In parallel with the development of this pathology, a malfunction occurs in the cortical region of the brain, in particular the upper lobe of the temporal regions of both hemispheres, which leads to a loss of the ability to understand the meaning of speech. The patient continues to hear himself and those around him, but can no longer perceive words.
The second name of the disease is acoustic-gnostic aphasia. The progression of the disease leads to spontaneously appearing speech, which, if left untreated, becomes more like an inarticulate mooing. The degree of loss of the ability to speak correctly and recognize what others say is determined by the severity of the brain damage and the individual characteristics of the person. With total or severe sensorimotor aphasia, which implies impairment of all speech functions, other symptoms may occur. The most common manifestations are:
- absent-mindedness;
- drowsiness;
- apathy to what is happening;
- inability to concentrate;
- partial paralysis of the muscles of the body.
Neurology Center in Moscow
Aphasia refers to the partial or complete loss of speech function. This disorder is associated with organic brain damage. May result from acute cerebrovascular accident, brain tumor or traumatic brain injury. The development and degree of aphasia depends on the location of the brain lesion.
Aphasia ranges from mild to severe forms. Total aphasia implies a complete absence of speech and its understanding. Then the transition of total aphasia to a motor or sensory form is possible.
Motor aphasia
With motor aphasia, a person understands speech addressed to him. However, he can only communicate with others using one word or sound combination. So, motor aphasia is a condition in which a person cannot speak, but can understand speech addressed to him. Motor aphasia is associated with damage to the frontal lobes of the cerebral cortex.
Sometimes the patient can still pronounce words with great difficulty (he sometimes speaks words in syllables). A person tries to avoid complex words in words, limiting himself to simple ones. The patient's speech is quite difficult to distinguish. However, in most cases the speech is understandable. With motor aphasia, speech is always meaningful - this is different from sensory aphasia. Speech is accompanied by eloquent gestures, this is how the patient helps himself to express himself.
Every year, acute cerebrovascular accident affects a large number of people. Afferent motor aphasia develops if the pathological focus is located in the parietal lobe of the brain. A characteristic feature of this disorder is confusion of sounds that are similar in pronunciation. This type of motor aphasia is also characterized by reading impairment. Motor aphasia has a better prognosis than sensory aphasia. Treatment of these types of diseases in stroke patients is carried out by highly qualified speech therapists at the Yusupov Hospital.
Sensory aphasia
Aphasia is a language disorder that affects expressive and expressive language and the ability to read and write.
Aphasia can be so severe that communication with the patient is almost impossible, or the disorder can be very mild. This can affect the ability to select words, the ability to combine words in sentences, and the ability to read. Typically, several aspects of communication are disrupted while some channels remain available for limited information exchange.
With sensory aphasia, speech understanding is impaired. A person does not understand either his own speech or someone else’s, but the ability to speak is often preserved. The condition is associated with damage to the left temporal lobe of the brain. As is correct, the patient is talkative and talks a lot. However, he does not understand himself or those around him. The patient's speech is incomprehensible. There is no meaning in the patient’s words - due to the lack of understanding of one’s own and others’ speech, there is a loss of control over speech. The patient can invent new words, change words, rearrange letters and syllables, pronounce unrelated strings of sentences and words. Since the perception of sounds is impaired, the speech of others becomes incomprehensible to the patient.
Sensory aphasia is otherwise called acoustic-gnostic. The auditory zone of the cerebral cortex is affected. This is the so-called Wernicke's area lesion. Damage occurs to the auditory analyzer - the primary auditory field.
Aphasia refers to the destruction of already established speech. This usually occurs as a result of brain damage. A person can no longer speak normally, ceases to understand other people’s speech, read and write. Neurolinguistics deals with the problem of speech impairment after brain damage. Aphasiologists and neuropsychologists are involved in the study of this problem.
Causes of aphasia
Aphasia often develops due to brain injury or stroke, especially in older people. Aphasia can also be caused by brain tumors or infections.
The most common cause of aphasia is stroke. Sometimes seriously ill patients after a stroke experience aphasia, but this is a temporary phenomenon, and then speech is restored. Less common causes of aphasia are traumatic brain injury, neuroinfection, and neurosurgical intervention.
Aphasia is characterized by difficulty remembering words. Sometimes the fluency of speech is impaired. Such patients have a limited vocabulary and speak little. There are constant hesitations in speech. Speech is distorted and incorrect. Severe situations of aphasia are manifested by the use of just one word or syllable in any communication situations. Aphasia affects adults with already formed speech skills - this is its difference from alalia.
The consequence of aphasia is problems with the perception of the surrounding world. A sick person is unable to recognize sounds, voices, or objects. The sentences are distorted and short. The patient finds it difficult to perform simple language gestures: he cannot fold his tongue into a tube, click his tongue, or put his tongue between his teeth and upper lip.
Dynamic motor aphasia is characteristic of damage to the anterior and middle parts of the inferior frontal gyrus. This is an area located next to Broca's area. There is a decrease in speech initiative. The amount of spontaneous speech decreases. With aphasia, only “remnants” of speech may remain - truncated words and syllables. This disorder is effectively treated at the Yusupov Hospital. Corrective work is carried out by highly qualified speech therapists.
Aphasia after stroke
Aphasia after a stroke is a disease that requires the help of a highly qualified speech therapist. Aphasia is a condition where a person can no longer speak coherently. Speech disorders significantly affect self-confidence and social status.
Speech restoration specialists work at the Yusupov Hospital. The clinic uses special rehabilitation methods such as therapeutic massage, physiotherapy and electrical stimulation. Restoring speech after a stroke is not a passive process. The patient must be ready to study, he must believe in himself, and be patient. In aphasia, cells in one or more of the brain's language centers die. This is a consequence of a stroke. As a result, the patient's speech becomes slurred and severely truncated. Sometimes the patient speaks in syllables or uses one word. Daily therapy should be carried out to the extent feasible for the patient.
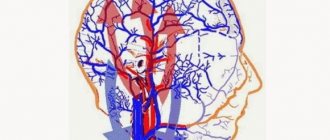
One of the treatments for aphasia is physical therapy. After a stroke, to treat aphasia, physiotherapeutic procedures are performed that improve cerebral circulation. What are the responsibilities of a doctor who treats speech disorders after a stroke? First of all, you need daily activity that affects the areas of the brain that are located next to the dead zone.
With medication, you should try to ensure sufficient blood supply to the brain, especially in the affected area. The brain must be provided with the necessary supply of oxygen. These are the principles of treating aphasia after stroke. Therapy should be started as early as possible, immediately after cerebral edema is relieved - it manifests itself as convulsions, hallucinations, depression of consciousness (up to coma). It is necessary to start therapy as early as possible. Treatment of aphasia after stroke is one of the very important tasks of early rehabilitation of stroke patients.
Sign up for the Neurology Center:
- by phone: +7 925 191 50 55
- fill out the form: APPLICATION FOR TREATMENT
- Get advice by email [email protected]
- Clinic address: Moscow, Nagornaya st., 17 to 6
+7 (495) 506 61 01 –
REQUEST TO THE CLINIC
What can interfere with recovery?
A patient’s chances of recovery from sensorimotor aphasia depend on a number of factors, which include the general condition of the patient, the presence of concomitant diseases and the effectiveness of the rehabilitation therapy used. Indeed, it is much more difficult to regain the lost ability to speak and understand speech if the patient:
- repeated hemorrhage occurred;
- atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension or other cardiovascular diseases are diagnosed;
- ischemic attacks often occur;
- progressive diabetes mellitus.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of sensory aphasia is primarily aimed at identifying the cause of the disease. The diagnostic study must be comprehensive and consist of the following stages:
- Consultation and questioning of the patient to determine the history of life and illness. Also, during the initial appointment, the doctor examines the patient and studies specific symptom complexes. The neurologist looks for concomitant diseases that manifest themselves not only by external signs, but also by conducting additional tests and studies. During the examination, a specialist neurologist determines the lesions, the nature and course of the pathological process, assesses the general condition of the patient, as well as the blood supply to the brain. Makes a prognosis and subsequent treatment plan in accordance with the patient’s age. Its individual characteristics and concomitant somatic diseases. As well as the level of damage to the central nervous system.
- Consultation with a speech therapist, psychologist and other specialists. They determine the severity of the speech function defect and coordinate further tactics for restoring lost functions with the attending physician.
- Conducting additional instrumental and laboratory studies to verify and clarify the clinical diagnosis. Studies such as computer and magnetic resonance imaging, electroencephalography, angiography of cerebral vessels are carried out. These studies are carried out to identify the level and area of brain damage, the presence of space-occupying formations in the nervous tissue, aneurysms and hemorrhages in the brain tissue, foci of abscess, and the consequences of a stroke.
How to regain speech after a stroke: treatment methods
Motor and sensory aphasia after stroke is treated in at least two areas. Speech therapy and conservative medicine are the main ways to restore speech function.
Together with medications and speech therapy exercises to activate the functions of the cerebral cortex in sensorimotor aphasia, the following may be prescribed:
- neurosurgical treatment (including in the presence of an abscess, intracranial hematoma),
- exercise therapy course;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- massage;
- sessions of psychological influence.
What is this
Aphasia is speech problems of varying degrees of complexity (up to complete absence of speaking) associated with incorrect brain activity.
Similar prerequisites have:
- Apraxia, in which the ability to fully control one’s movements is lost (often this is dressing and undressing)
- Agnosia, which prevents one from perceiving the world through sight, hearing, and touch.
- Ataxia is uncoordinated action.
In general, the etiology of aphasia is associated with impaired functioning of individual areas of the brain. Depending on this, scientists classify the disease.
Neuropsychological classification
In Russia and the post-Soviet space, the classification of aphasia by A.R. Luria , Russian neuropsychologist.
Luria identifies the following types:
- Acoustic-mnestic;
- Acoustic-gnostic, or sensory aphasia;
- Semantic aphasia;
- Motor: Afferent motor aphasia Efferent motor aphasia Dynamic aphasia
The acoustic-mnestic variety occurs when the temporal region of the head is affected. Characteristic symptoms:
It is difficult to comprehend fast, multi-threaded speech (in a large group of people, noisy environment), speech containing long sentences, atypical phrases.
- To reading, with a slight decrease in speed and quality.
- Independent expression of thoughts, including in writing.
acoustic-gnostic aphasia are damage to the sensory speech area.
The etiology of acoustic-gnostic aphasia leads to incorrect phonemic analysis and synthesis, which leads to the following consequences:
- Manifestations of agraphia and alexia
- Speaking is confused, parts of phonemes are in the wrong order
- Auditory perception is limited or absent.
- The remaining consequences are similar to those given above for the acoustic-mnestic variety.
semantic aphasia manifests itself . The main symptom for the diagnosis of “semantic aphasia” is a lack of understanding of grammar, in particular:
- Passive voice (the distinction between “the author sculpts a sculpture” and “the author sculpts a sculpture” is erased)
- Locations expressed by prepositions (“on the table” and “under the table” can become synonymous concepts).
Semantic aphasia, like others, from the outside looks like communication with a person from a foreign language environment.
Efferent motor aphasia is characterized by the phrase “I understand everything, but I can’t say anything”:
- What is said is abrupt and inconsistent in declensions and cases
- Duplicating individual pieces, replacing them in places
- Reading or writing anything is extremely problematic.
It is diagnosed in the lower frontal lobes.
If motor aphasia is afferent, then we are talking about problems of the lower parietal region. It follows from here:
- Difficulty moving the muscles of the face, tongue, jaw
- Articulation disorders
- Diction is unclear, blurry
- The simplest manipulations of the lips are impossible (pout, stretch into a wide smile, roll into a tube).
Dynamic aphasia is associated with incorrect functioning of the frontal lobe on the left side. Even the slightest injury due to TBI can be to blame.
The disease reveals itself as problems:
- With retelling
- With phrase construction
- Poor vocabulary
- With long monologues
Neurological classification of Wernicke-Lichtheim
Three subgroups include the Lichtheim-Wernicke classification of , used abroad:
- Sensory, or Wernicke's aphasia (resembles acoustic-gnostic).
- Motor, or Broca's aphasia (develops when Broca's center is damaged and has the same clinical manifestations as efferent motor aphasia).
- Transcortical (motor and sensory aphasia, the same as dynamic aphasia. A patient with sensory aphasia differs from a person with damaged Wernicke’s area only in the ability to repeat phrases after others).
- Conduction aphasia (characterized by the complete absence of this skill).
- Amnestic (observed when the temporo-parietal part of the head is affected).
- Amnestic-semantic (prevents memorizing what is heard).
- Optic-mnestic (recognition of things suffers - if a person is shown a card with an object, he will not remember the name).
- Acoustic-mnestic (expressed in the difficulty of choosing words and giving definitions).
- Sensorimotor aphasia (in the worst case, it becomes synonymous with the diagnosis “total aphasia” - complete loss of communicative abilities).
Medicines to stimulate cerebral circulation
So, perhaps, we should start with the drugs that are prescribed to patients with speech disorders. A course of medications usually consists of neurotrophic drugs, the action of which is aimed at normalizing metabolic processes in the brain and increasing blood circulation. For total aphasia, doctors prescribe:
- Piracetam is a nootropic drug used for speech and cognitive disorders. The duration of the course is determined by a neurologist and most often ranges from 2 to 6 months. The medicine is used by injection, administered intravenously or intramuscularly.
- "Pyritinol" - activates cholinergic processes in the brain. After a stroke, aphasia is prescribed for 3-4 months.
- "Vasobral" is a combination drug whose active components stimulate the functioning of the central nervous system. The duration of the course is on average 2-3 months.
- "Cerebrolysin" is a nootropic generation drug that provides metabolism, neuroprotection, neuromodulation functionality and neurotrophic activity. The course of therapy can be up to 12 months.
Carrying out appropriate treatment if pathology develops
Treatment for total aphasia sometimes brings its own surprises. Therefore, recovery can begin unexpectedly, which speaks to the phenomenal capabilities of the human brain. But in most cases, the patient will need serious rehabilitation, lasting at least three months after receiving an injury or stroke.
To achieve noticeable results, you need to do special sets of exercises at least three hours a week for several months. Experts say that it is necessary to stimulate the restoration of speech activity by ear. The help of a speech therapist can be different, and it depends on the type of lesion. A speech therapist identifies the type of aphasia and prescribes appropriate treatment. To diagnose the species, specially prepared tests are performed. If total aphasia is suspected, the speech therapist conducts more extensive examinations of the patient's speech to confirm the diagnosis.
Nowadays, other methods that are restorative therapy are also being implemented. This includes using a computer to improve speech abilities. Such therapy helps a person more actively restore some elements of speech, and special programs speed up recovery, but to achieve the best results, the help and participation of the patient’s family members in the treatment process will be required.
Help from a speech therapist: exercises to correct speech function
Speech therapy correction for sensorimotor aphasia is as fundamental a treatment method as the use of medications. To restore the patient’s speech, various exercises are used to activate the activity of the right cerebral hemisphere. The set of training sessions described below for a patient who has suffered a stroke is aimed at restoring in his memory the skills of mobility of the jaws, tongue, and lips. It must be performed together with the patient - he must repeat after the instructor.
To restore speech with sensorimotor aphasia, it is necessary to train the speech apparatus every day as follows:
- Fold your lips into a tube, stretch them out as much as possible and hold them in this position for a few seconds, then relax. The exercises are repeated 10 times.
- You need to lightly grab your lower lip with your teeth, as if trying to bite it, then let go and relax. Do the same with the upper lip.
- Stick your tongue out as far as possible, tense your neck and hold your breath for 3 seconds, then exhale. Repeat several times.
- Lick your lips with your tongue, confidently moving it in a circle clockwise and in the opposite direction.
- With maximum tongue tension, try to roll it into a tube, and then touch the tip of it to the upper palate.
Treatment
The treatment process aimed at restoring the consequences resulting from aphasia requires a long time and enormous dedication, both from the patient and his relatives, and from medical personnel and specialists who have undergone special training. The restoration work of such a pathological condition consists of the following points:
- Pharmacological (drug) therapy. It mainly includes the use of drugs from the group of nootropics, drugs that increase the metabolism and trophic potential of the brain, vitamin therapy with neuroprotective B vitamins. Additional therapy is selected individually and prescribed in accordance with the cause of sensory aphasia. For example, in the case of a stroke, thrombolytic or hemostatic drugs are added, in the case of an infectious inflammatory lesion, antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or antifungal agents are added.
- Session with a speech therapist. The main difficulty that arises when attempting to contact the victim is the lack of understanding of the specialist’s approach to the patient. Violation of communicative activity requires long-term correction and perseverance. There are also difficulties in interpreting what the patient says. Because his speech is uninformative. It is very difficult to identify the main idea. Consultations with a speech therapist help restore the patient’s vocabulary, correct pronunciation of sounds and meaningful speech. With the help of special exercises and equipment, you can actively interact with the patient even at home.
- Surgical interventions. In some cases, with deep or severe brain damage, the patient requires emergency surgery to eliminate the threat to life. In case of an aneurysm, clipping or sclerosis of the aneurysm can be performed using X-ray control. If aphasia is caused by tumor growth, then stereotactic surgery can be performed to destroy the tumor focus.
- Additional treatment methods can speed up the recovery processes in the victim’s nervous tissue, and also increase the effectiveness of the main therapy. In the treatment of sensory aphasia, methods such as physical therapy, massage, physiotherapeutic methods, and the use of computer programs that stimulate the speech center and improve speech abilities are used. A positive effect has also been noted in contact with animals, so the following can be used in therapy: hippotherapy, feline therapy and dolphin therapy.
At the Clinical Institute of the Brain there is a specialized rehabilitation and recovery center that deals with the correction of disorders in patients with aphasia. Together with treatment, we manage to achieve a quick, step-by-step recovery process. There is a close connection between treatment and rehabilitation, which helps to quickly adapt the patient to new living conditions, thereby significantly increasing the effectiveness of therapy and recovery.
Melodic chants to restore speech
When performing exercises for sensorimotor aphasia, experts also focus on the therapy of melodic intonation. This technique is based on activating the functions of the legal cerebral hemisphere. Singing or simply your favorite musical compositions will help you achieve the desired result. If you often hum melodic tunes previously familiar to the patient, he will one day want to sing along with his instructor, trying to pronounce the endings of phrases or individual words. Tongue twisters that are spoken to a patient who is already recovering also help. This method works effectively, contributing to the speedy restoration of speech.
WHAT IS APHASIA AFTER STROKE?
When I was brought from the hospital on September 29, 2017. to the Neurorehabilitation Center, I didn’t speak at all, I just made inarticulate sounds.
03.10.2017. During examination by an aphasiologist, a diagnosis was made: complex sensory aphasia (acoustic-gnostic, acoustic-mnestic). Non-dynamic disorders of the type of complex motor aphasia (efferent-afferent). Defect of severe severity.
I don’t know, apparently the body regulates what information a sick person can receive.
At that time, I understood that I was sick, but I was sure that in a month or two I would recover and go to work.
I didn’t know that it would take so long and painfully to restore the body and functions we need for a normal life without the help of other people. If I knew about this, I would go crazy.
I had two tasks: walk and talk, walk and talk.
Surgery for incurable aphasia
The surgical method of treating the consequences of a stroke involves direct intervention in the patient’s skull to perform revascularization of the impaired speech area. Today, such intervention is carried out through extra-intracranial craniotomy. Microanastomosis helps improve blood circulation in the brain and optimize the condition of nerve cells, returning them to normal functionality.
It is worth noting that this procedure is not prescribed immediately after the first manifestations of sensorimotor aphasia, since the operation is associated with considerable risk and does not always give a positive result. Extra-intracranial microanastomosis is recommended if the use of conservative methods of speech restoration has been ineffective.
Forms
During the first time after injury, the patient most often suffers from complete loss of speech. This is the most severe form of aphasia - total. Symptoms include a lack of understanding of human speech. Sometimes the disease gives way to milder forms - sensory or motor. In such cases, the patient recognizes the words, is aware of everything, but expresses himself only through the “embolus” - it is the same sound, sometimes the intonations change.
The semantic form manifests itself in disturbances in the activity of the occipital region. As a result, a person does not understand complex sentences and the relationship between them in the text.
The amnestic form is typical for those who have damage to the temporal area. Patients understand speech in general, but lose the ability to recognize a number of objects.
Afferent aphasia is characterized by the fact that the patient confuses similar letters and can rearrange sounds in syllables. The dynamic form manifests itself in the understanding of speech, attempts to answer, but the words are placed incorrectly, and as a result the phrase becomes meaningless. A person is aware of this, but phenomena of this kind are beyond his control.
Broca's aphasia occurs in those who have lost normal activity in a specific area of the brain - Broca's area. It ensures articulation consistency. As a result, a person is able to reproduce individual words, pauses, and finds it difficult to switch from one syllable to another. Similar phenomena also occur in written speech. In this case, the patient often pronounces nearby words whose meaning is opposite. He often becomes fixated on the same sound.
Physiotherapy for speech restoration
Physiotherapeutic procedures are useful for stimulating the speech muscles. For aphasia, acupuncture and electrophoresis are prescribed. However, to date, physical therapy after stroke is not widespread. With local and shallow damage to an area of the cerebral cortex, the techniques actually help to correct articulation, but they are ineffective in restoring the perception of speech heard by the patient. Biofeedback tactics also lack precise confirmation of effectiveness. Meanwhile, today this treatment tactic is used for visual control over the restoration of the patient’s speech.
How to recognize
After a stroke, the following types of dysphasia may occur:
- Wernicke's aphasia. It is accompanied by a loss of the ability to understand spoken and written language. The patient’s speech usually maintains speed and intonation, but does not carry any meaning: the patient pronounces chaotic letters, words and phrases, because he does not understand what he is saying. Neologisms are characteristic - invented new words. With a large ischemic focus, a symptom of “word salad” is observed, when speech is filled with neologisms, incomprehensible sounds and fragments of words.
- Broca's aphasia. It is characterized by a violation of the formation, construction and pronunciation of speech. The patient is usually silent, speaks little (reduced speech production) and does not understand much (articulation is impaired). The clinical picture includes perseveration - repeating the same word several times. The patient has difficulty writing and does not fully understand dialogical speech, but after a few days these symptoms disappear.
- Transcortical sensory aphasia. The clinical picture resembles Wernicke's dysphasia, but the symptoms are less pronounced. Characteristic differences: fluent speech, uninformative, there are paraphasias (agrammatisms and violation of the logical sequence of the story).
- Transcortical motor (dynamic) dysphasia. Also resembles Broca's aphasia. The patient has difficulty starting to speak (initiation disorder); he repeats the same words several times. There is a symptom of “word salad”.
- Total sensorimotor dysphasia.
This is a mixed disorder consisting of impairments in speech comprehension and production. It occurs when the ischemic zone covers the basin of the left middle cerebral artery. Often combined with unilateral muscle paresis and visual impairment due to brain damage.
What is the likelihood of recovery?
The prognosis of sensorimotor aphasia after a stroke is relative, since it is impossible to say exactly how much time it will take to rehabilitate the patient. As a rule, long-term hard work with specialists gives noticeable results after 6 months. You should not hope for spontaneous recovery. On average, with comprehensive speech therapy correction, patients’ speech is restored only after 2-3 years.
The prognosis for recovery also depends on the individual characteristics of the patient and his age. More often, older people have a more difficult time coping with speech impairment; it is extremely rare that they are able to fully restore their previous ability to communicate with others. However, with significant damage to the cerebral cortex, there is little chance of complete rehabilitation even in relatively young people. It is important to start treatment as early as possible and unquestioningly follow all medical instructions. The success of a patient with sensorimotor aphasia in recovery is unlikely without the help of loved ones.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis of aphasia is made in tandem by a speech therapist and a neurologist.
Aphasia in children is identified and corrected with the following set of exercises:
- “Look, there are pictures in front of us. Here the hedgehog is dragging an empty basket, and here it is filled to the brim with mushrooms - arrange the pictures one by one and try to tell what story happened here.”
- “There are fruits in front of us: banana, apple, orange and kiwi. And there are four baskets, each of which has a picture of the same fruit pasted on it. Put everything in its place!”
- “Look at this! We have a message from the wizard! Only while it was going on, some of the letters were wiped off and washed away by the rain - let’s try together to guess which words were lost.”
- “Have you read it? Now you need to write the answer. I’ll dictate, and you write it down carefully.”
- “Let's play echo. I will say something, and you will need to repeat everything exactly the same.”
- “I can’t remember some phraseological units at all. Can you explain what “being led by the nose” means? "Fool around"?
- We blow out the candles on the cake, blow the fluff off the dandelion, lick ourselves like a kitten and click our tongue, imitating the sound of horse hooves - this will reveal articulation failures.
- “Reach the nose with your tongue - can you? What about your upper lip? Great, now stroke his chin with your tongue so that he doesn’t feel offended.”
The main rule: remedial training will not bear fruit if you do not practice it constantly.
Speech restoration in sensory aphasia and other forms that make it difficult to understand what is said can be carried out with the help of auxiliary materials - illustrations, text tips.
In the case of children, you should always take into account that the baby may not complete tasks not out of stubbornness, but only because he is not able to follow the parent’s instructions.
A calm atmosphere is also important. In stressful situations, aphasics become lost, showing noticeably worse results than when relaxed.
At any age, it is important to have fun while exercising - otherwise, you cannot expect any improvements. It's better to take a break than to overcome and suffer.
Aphasia after a stroke can be very diverse, depending on the degree of damage. If one part of the brain is damaged, the disease is called partial, for example, this is Broca's aphasia. In this case, a similar set of tasks will be of undoubted benefit.
With more significant disorders, total aphasia is likely - the person continues to think as before, but communication is lost in all its manifestations (gestures, words, drawings, text). It is almost impossible to overcome this at home; treatment of aphasia after a stroke with complete loss of speech requires the supervision of doctors and regular inpatient examinations.
Remember: aphasics of all ages really need the support of family and friends. They fully retain the ability to think, just, unfortunately, they are not quite able to formalize this verbally. Share news with the patient, watch your favorite movies together, go for walks and have fun. This will both preserve and help the relationship. Restoring speech in aphasia is not only monotonous exercises, but also ordinary live communication.
What to do if there is a patient with aphasia in the family
Relatives of a person who has suffered a stroke should be patient and prepare for a long, difficult road to rehabilitation. It is not easy to restore speech functions with sensorimotor aphasia, but you cannot give up prematurely. An extremely positive attitude of the patient, his determination and desire to work on himself will play an important role in recovery. First of all, the patient must be sure that he is not a burden to his environment, and feel the love of his closest and dearest people.
To regain speech after a stroke, you must follow all the recommendations of specialists and regularly perform speech therapy exercises. Yes, the rehabilitation process does require significant effort, but the main thing is not to despair! Even minimal changes will become an incentive to continue treatment and recovery.
Sensory aphasia
Sensory aphasia has many synonyms for its name: receptive, fluent, acoustic-gnostic, Wernicke's aphasia, or simply word deafness.
The pathology consists of damage to the auditory zone of the cerebral cortex, namely Wernicke's area. The pathology is based on the difficulty of recognizing the sound composition of a word. The key defeat in this type of aphasia is the lack of understanding of the meaning of a word, while a person can freely repeat words and hear them, the whole point is the lack of understanding of their meaning. With severe damage to Wernicke's area, the audible speech of another person is perceived as white noise. Wernicke's aphasia occurs due to a defect in the superior temporal gyrus. In this case, the auditory analyzer, namely the primary auditory field, is damaged. In this case, the native language is perceived by the person as a foreign language. Since the cortical centers of the auditory analyzer are damaged, the experience of speech perception is lost, hence the second name of the pathology - speech deafness. Almost always, together with damage to the primary auditory field, the sensory centers of speech are affected.
Types of pathology
In accordance with the characteristics of its course, several types of aphasia are distinguished:
- Motor type . This is a speech disorder in which a person has difficulty pronouncing words. The patient can fully pronounce sounds. The patient normally perceives and understands speech addressed to him. In severe forms of the pathological process, speech is completely absent.
- Total view . It is a severe speech impairment after a stroke. With pathology, the patient does not perceive speech addressed to him and cannot pronounce it.
- Sensorimotor type . The patient cannot perceive speech. His hearing is intact and he can speak. In some cases, during a conversation, the patient confuses words. The patient does not remember the names of objects and phenomena.
- Semantic view . The ability to produce speech with this type of pathology is preserved. The person does not understand complex lexical structures. He confuses endings and prepositions when pronouncing words.
There are several types of aphasia that are recommended to be identified in order to prescribe effective treatment.
Mechanism of development and symptoms
The brain is characterized by the presence of several centers that are interconnected. When they work correctly, a person correctly understands and reproduces speech, can fully analyze complex speech structures, and constructs sentences correctly. Nerve fibers connect with each other all the centers that are located in the temples, crown and center of the brain .
When a stroke occurs, a certain area of the brain dies. This leads to damage to nerve fibers, so a person cannot understand and reproduce speech. During the period of aphasia after a sensory stroke, the patient experiences corresponding symptoms.
Such a pathological process is accompanied by a misunderstanding of speech addressed to the patient. People also cannot understand sayings and proverbs. With aphasia after a stroke, patients claim that everyone around them speaks an incomprehensible language. The patient can construct simple sentences with meaning.
With mnestic aphasia, a person understands only a few phrases from the sentence that is addressed to him. He begins to pronounce the first words of a sentence and forgets what he is talking about. During the course of the pathological process, patients speak very slowly and carefully select their words . The patient may replace some words with others that do not fit the meaning.
With acoustic-mnestic aphasia, a person reads subheadings in books and newspapers, the meaning of which he does not understand. Difficulties arise in describing the events happening around. It is difficult for a person to call objects by their proper names.