Traumatic brain injury (ICD-10 – S00-S09) is a whole complex of contact intracranial injuries. According to statistics, TBI is the third most common cause of death in our country (after oncology and cardiovascular pathologies). Injuries of this type occur in accidents and traffic accidents, while participating in sports competitions, during fights, during everyday falls and blows.
Almost always, after brain damage, the life of an adult or child changes completely. Again, according to statistics, approximately half of all those who have a traumatic brain injury recorded in their medical records are disabled. Such people need high-quality recovery and rehabilitation (which is often underestimated by patients and their relatives).
After receiving a severe or moderate TBI, after undergoing treatment and rehabilitation, not all people are able to lead a normal life. Many lost functions are restored over time, but some consequences of TBI haunt victims until the end of their days.
It is widely believed that in the absence of external damage, one can count on a favorable outcome. But any head injury is extremely insidious, therefore, if damaged, even if the person remains conscious and at first glance everything is fine with him, it is necessary to send him for a full examination to the hospital.
Varieties
TBI is differentiated into closed and open forms. With the open version, the skin of the head and the wide tendon plate with which the muscles are fixed are damaged. The damage reaches the skull bones or deeper tissues. If the dura mater of the brain is damaged, then the open form is called a penetrating wound. With a closed version of TBI, the skin may be damaged, but the connecting plate is not affected.
Brain damage is classified into categories depending on the degree of the defect that occurs: mild, moderate (moderate) and severe. The Glasgow Coma Scale, the most commonly used system for classifying the severity of traumatic brain injury, assesses a patient's level of consciousness on a scale from 3 to 15. Diagnosis is based on the results of verbal, motor and visual responses to stimuli. It is believed that an index of 13 and above is a criterion for a mild disorder, from 9 to 12 for moderate (moderately severe), from 8 and below severe.
HISTORY OF TREATMENT OF A PATIENT IN THE REUT CENTER AFTER SEVERE TBI
In 2015, a terrible story happened in the Romanian town of Brasov. A young woman, Yulia Ganeya, was hit by a drunk driver when she was 8 months pregnant. Yulia received a serious head injury and several leg fractures. So the 26-year-old girl found herself in a nervous-vegetative coma.
For a year she was treated in clinics in Bucharest and Bangkok. She underwent two stem cell transplants to stabilize her condition. In the fall of 2021, her husband brought Yulia for rehabilitation to the Israeli Reut Center. This is the only place where they agreed to accept a girl in such a serious condition. Over the course of a year, the best physiotherapists, rehabilitation specialists and occupational therapists in the country worked with Yulia.
Unfortunately, Yulia has not yet regained her speech or the ability to walk. But rehabilitation helped the girl make small movements with her head and eyes and learn to sit. The family does not lose hope that one day medicine will create a medicine that will help Yulia. Now all they can do is be near her and give her love and care.
Causes
Brain damage can occur in many ways. These injuries usually result from accidents in which the head hits an object. Trauma can result in brain damage if someone hits a person hard on the head.
Damage to cranial structures is a common occurrence in head impacts during car accidents. Such situations can arise due to industrial accidents, thermal and chemical burns. Symptoms of CMP may develop as a result of birth trauma. Similar disorders can be caused by a lack of oxygen, poisoning, hemorrhage in the cranial cavity or neuroinfection.
Are there any contraindications to the use of osteopathy?
Unfortunately, there is. These include: acute period of TBI; presence of osteoporosis; period after surgery on the skull or spine; chronic diseases in the acute phase; thrombosis; strokes; meningitis; mental illness; malignant neoplasms.
In conclusion, I would like to say that with the help of osteopathy it is possible to avoid a number of negative consequences of TBI, ranging from headaches to disability. The outcome, of course, depends on the motivation of the patient himself and the professionalism of the doctor. When choosing a specialist, check whether he is in the register of certified osteopathic doctors in Russia https://www.osteopathy-official.ru/rossiyskaya-osteopaticheskaya-assotsiatsiya/register-doctors/
Be healthy!
What happens with a traumatic brain injury
A mild form of TBI is characterized by one or more of the following symptoms:
- attack of short-term loss of consciousness;
- loss of memory for events immediately before or after the injury;
- any change in mental status at the time of injury;
- focal neurological deficit.
Very often in such cases, the victim looks good outwardly, without realizing that functional problems are developing. Some people suffer from the long-term effects of TBI, known as post-concussion syndrome (traumatic encephalopathy). Persons suffering from this syndrome experience severe headaches, dizziness, decreased performance, weakness, insomnia and intellectual impairment.
Most traumatic brain injuries result in widespread damage to brain structures. The brainstem, frontal and temporal lobes are particularly vulnerable to local injury from contusions due to their location near bony prominences.
In addition to regulating the basic functions of excitation and inhibition, the brain stem is involved in the processes of attention and short-term memory. Trauma in this area can also lead to autonomic dysfunction: disruptions in metabolism, thermoregulation, respiratory and cardiac activity.
The limbic system helps regulate a person's emotional status. Connected to the limbic system are the temporal lobes, which are involved in many cognitive skills such as memory and language. Damage to the temporal lobes is associated with a number of behavioral disorders.
The frontal lobe almost always suffers from injury due to its large size and location at the front of the skull. The frontal lobe is involved in many cognitive functions and is considered the center of control of emotions and behavior of the individual. Damage to this area can lead to decreased criticality and increased impulsivity.
Signs and symptoms
TBI can cause a wide range of functional short-term and long-term changes affecting cognitive, emotional, and behavioral areas.
As a result of brain damage, the following suffers:
- thinking (the process of modeling environmental patterns);
- attention (concentration and retention);
- memory (memorization, storage, reproduction of information);
- functions of the sense organs (vision, hearing, taste, smell, touch);
- speech activity (communication, expression and understanding of words);
- emotions and behavior (depression, anxiety, aggression, social unacceptableness).
Symptoms that may occur after a TBI:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- convulsions;
- loss of coordination of movements.
TBI can also cause epilepsy and increases the risk of conditions such as Alzheimer's-type dementia, Parkinson's disease and other brain diseases that become more relevant in old age.
Repeated mild brain injuries occurring over a long period of time (i.e., months and years after the initial episode) lead to cumulative neurological and cognitive deficits. Repeated moderate to severe TBIs occurring within a short period of time (i.e., hours, days, or weeks after the first event) can be catastrophic or fatal.
Periods, consequences and complications of TBI
The so-called traumatic disease includes three periods:
- Acute (duration 2 weeks – 2.5 months) – development of defense reactions to a damaging factor.
- Intermediate (duration 6 months – 1 year) – the process of lysis and repair in damaged areas.
- Long-term or final (duration 2-3 years, with complications - until the end of life) - completion of tissue degeneration and restoration of functions.
Complications of TBI in the acute phase:
- Impaired function of the respiratory system (respiratory depression and gas exchange disorders).
- Problems with central and regional (cerebral) circulation.
- Hemorrhagic complications (cerebral infarction, intracranial hemorrhage).
- Dislocation (displacement) of brain parts.
- Complications of a purulent-inflammatory nature: intracranial (abscesses, osteomyelitis, meningitis, encephalitis), extracranial (pneumonia, for example).
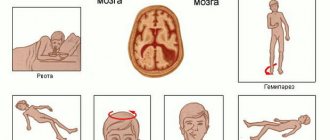
Possible consequences of TBI:
- Paralysis of the limbs (partial, complete) on one or both sides.
- Loss of vision, hearing, ability to speak, swallow, and breathe.
- Loss (weakening) of control over the function of the pelvic organs (the patient is not able to control the processes of urination and defecation).
- Tremor (shaking) in the limbs.
- Partial memory loss, deterioration of attention, changes in character and other consequences associated with higher nervous activity (usually after a coma).
In the long-term post-traumatic period, the development of epilepsy (acquired epilepsy), occlusive hydrocephalus, neuroses, and parkinsonism is possible. Also, cases of arachnoiditis and arachnoencephalitis (a disease of the central nervous system - serous (non-purulent) inflammation of the arachnoid membrane of the brain or spinal cord) are not uncommon.
Features of rehabilitation
If a person has suffered a traumatic brain injury, recovery and rehabilitation will be an important part of the treatment program. Rehabilitation can take different forms depending on the needs of the victim and may include physical therapy, vocational assistance, speech therapy, psychiatric care, psychotherapy, psychological correction and social support. All of these types of interventions are necessary to help the victim recover as quickly and fully as possible from the effects of the injury.
In the acute period after traumatic brain injury, rehabilitation is aimed at getting out of a coma and choosing a treatment strategy for a speedy recovery. With mild TBI, most patients recover quickly, but the effects of subsequent injuries can be devastating.
Complications of severe TBI that are functionally limiting and difficult to treat include heterotopic ossification, psychomotor agitation, and spasticity (involuntary movement and spasm of facial muscles). It should be borne in mind that the process of recovery from severe traumatic brain injury can be lifelong.
Psychotherapeutic techniques and exercise, along with pharmacological interventions, also aim to prevent long-term motor and cognitive impairment. In addition, rehabilitation of patients with traumatic brain injury targets long-term symptoms, including sleep disturbances, visuospatial deficits, cephalalgia, and cognitive dysfunction.
Employees of the Community for the Rehabilitation of Traumatic Brain Injuries of Irakli Pozharisky:
- help improve your ability to function fully at home and in the community;
- will reduce or completely eliminate mental and physical problems caused by TBI;
- provide emotional support;
- will tell you how to adapt to the changes that occur during recovery.
Rehabilitation carried out in the community of rehabilitation specialists Irakli Pozharisky can also help prevent complications of traumatic brain injury, such as:
- formation of blood clots (blood clots);
- pain syndrome;
- bedsores caused by prolonged lying in one position;
- breathing problems;
- drop in blood pressure when moving;
- muscle weakness and muscle spasms;
- problems with the intestines and bladder;
- deterioration of sexual function.
First aid and treatment
When a head injury occurs, the patient needs emergency care, on which not only his further treatment, but also his life may depend. If the victim has a serious head injury, the first thing to do is call a medical team.
In the case of head injuries, every minute can matter, so there is no time to waste and the following steps should be taken before medical professionals arrive:
- place the victim in a darkened room;
- provide access to fresh air by unfastening the collar, loosening the belt, opening the windows wide;
- if the victim is unconscious, the head must be turned to the side to protect the airways from vomit;
- Do not under any circumstances use any medications to reduce pain, this can have a negative effect on the brain and only worsen the situation;
- You can alleviate the victim’s condition and reduce pain by applying cold to the injured area;
- in case of an open injury, the wound surface must be treated with an antiseptic drug, for example, peroxide or chlorhexidine;
- after treatment, apply a sterile gauze bandage to the wound;
- if it is not possible to call an ambulance, you must immediately transport the victim to the nearest trauma center yourself.
Further treatment of the patient depends directly on the nature of the injury. Open TBIs can be penetrating or non-penetrating and are usually treated with surgery. Concussions and bruises are often treated with conservative methods using certain medications. In the first and second cases, treatment is carried out exclusively in the hospital under the constant supervision of doctors.
If a patient is diagnosed with a concussion, the doctor may prescribe bed rest for three days, followed by outpatient treatment for another six days, which will consist of the use of painkillers, multivitamins, as well as sleeping pills, sedatives and antihistamines. During treatment, patients are also given a solution of glucose and ascorbic acid, diphenhydramine and calcium chloride. The entire course of treatment lasts about two weeks, after which rehabilitation is prescribed, which also lasts for half a month.
What are the risks of rehabilitation measures after traumatic brain injury?
TBI rehabilitation performed by qualified and experienced professionals is unlikely to cause problems. But if you are not professionally literate, there is always a risk that parts of rehabilitation, such as physical or occupational therapy, could lead to new brain injuries or worsen existing symptoms. This risk occurs if rehabilitation measures are not carried out properly. This is why it is important to work closely with certified rehabilitation specialists who will take adequate measures to prevent worsening symptoms and prevent problems.
How to prepare for rehabilitation after a traumatic brain injury
Before rehabilitation can begin, the victim must receive nursing care and medication. At the first stage, assistance to the patient includes the following activities:
- emergency treatment by ambulance staff;
- intensive therapy;
- surgery if indicated;
- use of pharmacological agents.
Once the patient's condition is stabilized and not life-threatening, most people who have had a moderate or severe traumatic brain injury require rehabilitation. Patients may need to relearn basic skills such as walking or talking. The goal of rehabilitation interventions is to improve patients' ability to perform daily activities.
Rehabilitation therapy usually begins in the hospital. Recovery from a traumatic brain injury can continue in specialized rehabilitation centers or in public outpatient departments. The type and duration of rehabilitation is different for everyone, and depends on the severity of the TBI and what part of the brain was damaged.
Restoration of motor skills and functioning of the musculoskeletal system
In the case when, due to a head injury, paralysis or paresis begins to develop, seriously complicating a person’s ability to move independently, he needs the help of a rehabilitation specialist, physiotherapist, or massage therapist. In this situation, specialists can use all sorts of techniques that can help restore the usual tone of the muscles of the limbs, returning the previous sense of balance and balance. In case of such disorders, the massage therapist will massage not only damaged but also healthy limbs for the purpose of prevention.
Exercises prescribed by a specialist in physical therapy and a physiotherapist will help restore the previous coordination of the limbs, relieve the patient of cramps, trembling, and a feeling of weakness in the limbs. You need to understand that restoring such functions is a long and complex process that must be completely under the supervision of doctors. The positive impact of rehabilitation in this case is difficult to overestimate, because it is quite difficult to change something on your own after a TBI.
In situations where rehabilitation measures are started in a timely manner (simultaneously or immediately after treatment), there is a high probability that a patient after a serious injury will be able to move independently and perform simple self-care activities within a few weeks or months. In the absence of the necessary therapeutic actions, a worsening course of disorders may occur, contributing to the complete loss of the ability to walk or move the arms. This stage of pathology develops only in the complete absence of treatment and rehabilitation.
It is important to understand that tremors, numbness, convulsions, paresis, paralysis - all of this is associated with disorders of the nervous system, therefore, in addition to the help of physiotherapists and massage therapists, it is necessary to constantly be in contact with a neuropsychiatrist and psychotherapist.
In particularly complex and advanced cases, when traditional exercises and activities do not bring the desired effect, special equipment can be used in rehabilitation centers (for example, the Exart system, etc.). Such units can help activate the patient’s nervous system and muscles.
Rehabilitation of the patient should begin on the first day after injury, even if he is unconscious in intensive care.
Who takes part in rehabilitation
Specialists involved in the recovery and rehabilitation process:
A physical therapist is a doctor trained in physical medicine and rehabilitation who oversees and controls the entire process. He teaches targeted movements, teaches how to maintain balance, and helps with walking.
Speech therapist who specializes in speech restoration after traumatic brain injury. It helps a person improve communication skills and use assistive communication devices if necessary
A clinical psychologist who evaluates cognitive impairment and performance helps a person manage behavior. It introduces the patient to coping strategies and also provides information necessary for emotional and psychological well-being.
An vocational psychologist who evaluates the ability to return to work and related vocational opportunities. It provides the client with information resources to solve common workplace problems.
Occupational therapy
After basic speech and motor functions have been restored and psychological disorders have been eliminated, it is time for occupational therapy. Medical care in this case is aimed at eliminating complications associated with the problematic self-care and performance of the patient.
After receiving a head injury, many people lose the ability to perform certain independent actions (for example, they cannot go to the toilet, hold a spoon, pour water, etc.). To determine what the patient is currently capable of, doctors use special simulators, training rooms and premises. This approach allows you to practice basic skills under the supervision of an occupational therapist, rather than at home, where trial and error can be extremely time-consuming and ineffective.
What happens during rehabilitation after a traumatic brain injury
Each person's needs and abilities after TBI are different. By contacting the community of rehabilitologists Irakli Pozharisky, the client will have a rehabilitation program developed specifically for him. Many medical professionals and specialists will participate in this program.
An individual rehabilitation program may include any or all of these procedures:
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- breathing exercises;
- psychiatric correction;
- psychological support;
- psychotherapeutic intervention;
- speech therapy;
- social support.
Restorative procedures
To prevent pathologies due to a concussion, alleviate the patient’s general condition and reduce rehabilitation time, doctors additionally prescribe diet and exercise therapy. Therapeutic actions are selected so as to provoke beneficial effects without causing brain overload.
To prevent pathologies, victims are prescribed exercise therapy.
Diet
One of the most striking manifestations of the disease is headache. Often it becomes a consequence of increased intracranial pressure and cerebral edema. To combat the condition, it is necessary to limit the patient's salt intake. This automatically implies a ban on smoked meats, marinades, pickles, and most semi-finished products. Also, during the recovery period, you should give up strong tea, coffee, alcohol, fatty and fried foods, confectionery, spices and seasonings. Meals should be fractional, based on cereals, lean fish, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and dried fruits.
Physiotherapy
Exercise is an essential part of concussion treatment.
They are carried out both during the patient’s stay in the hospital and during home therapy. At the initial stage of the recovery process, intense physical activity is prohibited, only breathing exercises are allowed. Gradually, the patient’s regimen includes first passive and then gentle active exercises. Over time, the regimen includes swimming, race walking, and cycling. Often the cause of a concussion is a fall or inattention. When playing sports during the rehabilitation period after an injury, increased caution must be exercised. Until the victim has fully recovered, it is not recommended to perform activities that place stress on the head and neck. They are capable of inhibiting the functions of the central nervous system impaired as a result of injury.
Duration of rehabilitation
How long it takes to recover from a traumatic brain injury and how much follow-up care is required depends on how severely the brain is damaged and how well the patient responds to therapy. Some people can return to the same level of activity they did before their TBI. Other patients require lifelong care.
It is important to keep in mind that some long-term effects of damage to cranial cavity structures may take years to manifest. In the long term, the affected person may be at increased risk of developing problems such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia.
After rehabilitation, the center’s specialists will give important but simple instructions, including:
- symptoms and signs indicating that you should visit a doctor;
- possible delayed consequences;
- safety tips;
- recommendations for self-care and household organization;
- information regarding alcohol consumption.
Before agreeing to a diagnostic test or rehabilitation procedure, you should obtain information from employees:
- name of the test or procedure;
- the reason why the activity is recommended;
- what results can be expected;
- risks and benefits;
- what are the possible side effects or complications;
- place and time;
- other alternative methods;
- cost of manipulation.
Mental recovery
A concussion can cause the following mental disorders: apathy, hallucinations, mental disorders, temporary loss of reality.
Treatment of such mental disorders occurs with the help of drug therapy, and antipsychotics are also prescribed. Rehabilitation after a concussion with mental disorders can take from several months to several years.
In each individual case, the doctor selects a method for correcting the mental state for the patient. During the recovery period, the patient needs to spend time with strong emotional shocks (listening to loud music, watching horror films, going on rides, etc.).
Trauma can provoke the development of asthenia, which manifests itself in the form of a bad and changeable mood, the patient is constantly capricious, he is irritable, and nervous states may be observed. To eliminate such consequences, it is necessary to take the following medications: vitamin complexes, Eleutherococcus, Schisandra .
Rehabilitation after a concussion is an important period on which the process of recovery and the future state of health of the patient depends. If all requirements are met, medications prescribed by the attending physician and other therapy are used, no mental abnormalities should arise. However, it is worth noting that some complications may manifest themselves after a certain time after rehabilitation. At the first signs of any mental disorders, you should seek help from a specialist.
General Tips
After suffering a traumatic brain injury, after rehabilitation for at least six months, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- get enough good rest;
- do not take on previously habitual loads, increase your work or study time gradually;
- exercise caution and avoid situations where there is a risk of injury;
- do not engage in activities that require extreme concentration (for example, driving);
- avoid exhausting physical work;
- eat fully, balanced and in a timely manner;
- avoid information overload;
- write notes and place them in a visible place so as not to forget about upcoming tasks.
The patient may need help in the future to fully regain speech after traumatic brain injury. Therefore, you should not be afraid to contact specialists again if, after a period of relative well-being, existing problems reappear. The best option for people who have suffered from brain injuries is to undergo a complete physical examination twice a year. Completing this procedure on time will guarantee timely assistance to prevent serious problems.