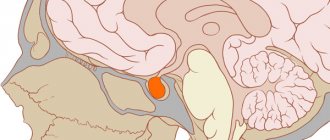
Microadenoma, which appears in the anterior pituitary gland, is a benign brain tumor that is small in size (diameter up to 10 mm). In the general structure of pituitary tumors, the share of adenomas is about 80%, in the structure of all brain tumors - about 15%. The pituitary gland is an important element of the endocrine system, which itself produces hormones and is involved in regulating the activity of other glands.
It is located in the bony formation of the skull, which is called the sella turcica. Produces hormones that regulate metabolism in the body, growth processes, and reproductive function. Pituitary microadenoma often appears as a result of pathologically accelerated division and growth of gland cells.
Types of disease
The pathological condition is distinguished depending on the symptoms into specific and nonspecific. The first provokes specific manifestations that can help a specialist immediately diagnose damage to the pituitary gland. The second is manifested by signs that are characteristic of many brain pathologies, and therefore significantly complicate diagnosis.
In addition, there are hormonally active and hormonally inactive tumors. The former provoke an increase in the production of one or another hormone, the latter suppress these processes. Which also leads to violations.
Additionally, doctors divide microadenomas into several types depending on which hormone production is disrupted.
| Variety | Peculiarities |
| Prolactinoma | This type is most often diagnosed in women, as it leads to excessive or insufficient production of the hormone prolactin, which is responsible for the production of breast milk. The pathology can be acute or occur in a latent form, provoking only unexpressed manifestations. It is worth noting that the disease can manifest itself not only in young patients, but also in mature women |
| Somatotropinoma | Such tumors in most cases are hormonally active, that is, they provoke excessive production of the hormone somatotropin. This substance in the body is responsible for growth, that is, when there is an excess amount of it, osteocytes divide and an increase in human growth, and especially his limbs |
| Corticotropinoma | Such tumors provoke disruption of the adrenal glands, namely, they stimulate the production of hormones that lead to other disorders. In most cases, when this type of neoplasm develops, Itsenko-Cushing's disease is diagnosed. |
| Gonadotropinoma | These tumors are considered less common and affect not only women, but also men. The main feature of this formation is considered to be a disruption of the reproductive system. In this case, infertility most often develops |
| Thyrotropinoma | This type of tumor is quite common, especially among women, and provokes intense work of the thyroid gland with the release of large amounts of thyroid-stimulating hormone. The pathology is quite easily diagnosed, but often specialists cannot immediately identify the cause |
Any type of pathology leads to the development of disorders. Sometimes several areas of the pituitary gland are affected in a patient. In this case, the symptoms are mixed, and the diagnosis is complicated.
Features of the development of microadenoma
The pituitary gland is one of the endocrine glands. It is located at the base of the brain and is responsible for metabolic processes, human growth and physical development. Microadenoma is understood as hyperplasia (growth) of individual areas of the pituitary gland, which generally leads to an enlargement of the entire gland. The neoplasm most often occurs in women between 20 and 40 years of age, although it is also often diagnosed in children and adult men. Many doctors believe that its development in women is facilitated by hormonal changes associated with bearing a child and breastfeeding.
Microadenoma is a tumor no more than 1 cm in diameter.
Microadenomas are benign formations, but untreated disease can lead to a significant deterioration in quality of life.
It begins to grow most often in the anterior portion of the pituitary gland - the adenohypophysis. The formation of hormones itself does not produce hormones, but can lead to their excessive production or, conversely, to a decrease in secretion.
Stages and degrees
Pituitary microadenoma (symptoms in women depend on the type of pathology) occurs in several stages. However, it is worth noting that the severity of symptoms depends on the type of tumor and other characteristics of the body. There are initial, progressive and advanced stages of the pathological process.
Prolactinoma at the initial stage manifests itself in the form of discomfort in the mammary glands, as well as symptoms from the nervous system. At the progressive stage, the manifestations worsen, discharge from the mammary glands appears, and the menstrual cycle is disrupted. An advanced degree of pathology is accompanied by disorders of internal organs and systems.
The initial stage of somatotropinoma manifests itself in a change in the patient’s height if she has not yet reached 23-25 years of age. At the same time, growth increases quite rapidly, which indicates the transition of the pathology to a progressive degree.
If a woman is over 25 years old, her height does not change, but the size of the limbs, namely the hands and feet, as well as individual parts of the face, such as the nose and chin, increases. At an advanced stage, deviations from the muscular and skeletal system appear, and motor activity decreases.
When diagnosing gonadotropinoma, the symptoms manifest themselves almost equally at the initial, progressive and advanced stages. The patient's menstrual cycle is disrupted, problems with conception are observed, and general symptoms of the nervous system and digestive organs appear.
A mild degree of corticortropinoma manifests itself in the form of a slight upward deviation in body weight, as well as changes in appetite. At the progressive stage, the symptoms worsen, which is explained by a violation of the distribution of fat in the body. The advanced stage is characterized by obesity and the development of complications from the digestive and cardiovascular systems.
If a patient is diagnosed with thyrotropinoma, at the initial stage the disease hardly manifests itself. Minor changes in the heart and digestive system are possible.
The progressive degree is accompanied by changes in body weight and serious disturbances in the functioning of the heart. In advanced cases, exhaustion, metabolic disorders and severe complications associated with excessive production of thyroid-stimulating hormone are observed.
Classification of microadenoma
Based on the degree of change in hormone secretion, pituitary adenomas are divided into inactive and hormonally active. It is the first type of neoplasm that may not manifest itself for a long time and is often discovered by chance during examinations for other diseases. Hormonal adenomas are divided into:
- Corticotropin
. Secretes adenocorticotropic hormone. - Prolactinoma
. The production of prolactin is disrupted. - Somatotropin
. There is an increase in the production of somatotropic hormone. - Thyrotropin
. The secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone increases. - Gonadotropin
. The amount of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones increases.
Inactive types of adenomas include tumors of chromophobe etiology and oncocytoma. Microadenomas are also classified according to their location in the sella turcica:
- endosellar - located inside;
- endosuprasellar - the main part is located at the apex of the sella;
- endoinfrasellar - descend from the sella turcica;
- endolaterosellar - grow through the side walls.
Classification, first of all, is necessary for the correct selection of treatment for pathology.
Symptoms
Depending on the type of pathology, the patient may experience severe symptoms. Prolactinoma is accompanied by suppression of the ovulation process in a woman’s body, as well as a significant decrease in libido, up to the development of aversion to sexual intercourse. Additionally, clear or whitish liquid may be released from the mammary glands in varying quantities.
The patient's menstrual cycle is disrupted, and breaks between menstruation can reach 3 months. Sometimes the patient’s periods completely disappear for a fairly long period.
This type of microadenoma also leads to disruption of the adrenal glands, which provokes hair growth on a woman’s body in atypical places, for example, on the face. In addition, fat and carbohydrate metabolism in the body is disrupted, which leads to obesity, even with proper nutrition.
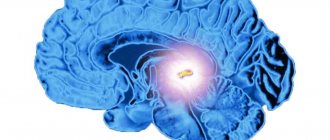
Somatotropinoma manifests itself in the form of other symptoms. The most pronounced is acromegaly , that is, an increase in the size of the hands, feet, as well as the nose, ears, and chin. Often the patient’s entire face becomes large and heavy. As a result of such changes, a woman’s appearance changes, the skin becomes jaundiced, excessively oily or dry.
Changes in somatotropinoma (pituitary microadenoma)
Additionally, not only the limbs and face become enlarged, internal organs suffer, in most cases the liver and pancreas. This leads to disorders of the digestive tract in the form of lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, and indigestion. If the pathology affects the patient at a young age, gigantism develops.
The symptoms of corticotropinoma are somewhat similar to those of prolactinoma. The patient experiences decreased libido, increased body weight, and male-pattern body hair growth. Additionally, striae, or stretch marks, appear on a woman’s body.
Their color can be red or burgundy, which depends on the characteristics of the organism. The patient develops symptoms of the heart and blood vessels in the form of tachycardia and increased blood pressure. In addition, a decrease in glucose tolerance and the development of diabetes mellitus is possible.
Common symptoms of the disease include depression, sleep disorders, and a weakened immune system.
Thyrotropinoma leads to a woman’s sudden weight loss, as well as tachycardia and fluctuations in blood pressure. There is redness of the facial skin, as well as increased work of the sweat glands.
When examining blood, an increase in glucose levels is noted, as well as trembling of the hands and the whole body. In advanced stages, an enlargement of the thyroid gland is observed, the volume of the woman’s neck also increases, and a goiter appears.
Common symptoms of any type of disease include menstrual irregularities, headache, weakness and depression. In addition, the patient’s appearance always changes, rashes appear, areas of irritation on the skin, and the skin tone becomes grayish or yellowish.
Consequences of the appearance of a tumor in the medullary process
The pituitary gland of the brain, whether the tumor is benign or malignant, causes constant pain in the frontal, temporal and infraorbital region. It is accompanied by constant nausea, blurred vision and does not depend on body position, and also poorly responds to analgesics. If the meninges rupture due to excessive pressure of the tumor on it, the pain stops.
But this does not solve the problems. After all, further growth of tumors will put pressure on the optic nerves, which will lead to defects, and then to the complete death of the optic nerves and blindness. Sometimes only one eye goes blind. The upward growth of the adenoma leads to pressure on the hypothalamus. The signs of this process are:
- temperature fluctuations;
- sleep disturbance;
- emotional shifts.
At the same time, the tumor affects the ventricles of the brain, which can cause dropsy. Pressure on the temporal and frontal lobes can cause seizures, double vision, or optic nerve palsy. The adenoma grows gradually, and its symptoms appear one after another.
Adenohypophysis, what is it, causes, treatment.
But in some cases, sudden hemorrhage and apoplexy are also possible. Such complications lead to complete atrophy of the pituitary gland and serious visual impairment.
Reasons for appearance
Pituitary microadenoma (symptoms in women can be expressed with varying degrees of intensity) appears as a result of various factors, regardless of the type of pathological condition.
The most common reasons:
- Stressful situations, disturbance of emotional balance.
- Chronic vitamin deficiency.
- Chronic sleep disorders that provoke neurological disorders.
- Congenital anomalies of brain development.
- Severe traumatic brain injuries.
- Artificial termination of pregnancy or frequent childbirth.
- Infectious diseases affecting the brain.
- Long-term use of hormonal contraceptives.
- Pathologies of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland, provoking the production of hormones that can disrupt the functioning of the pituitary gland.
- A hereditary predisposition to multiple adenomatosis increases the likelihood of developing a tumor in the pituitary gland.
- Hormonal disorder of unspecified origin.
- Congenital anomalies of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland.
The risk of developing the disease increases in patients who suffer from disorders of the hypothalamus. In each case, the disorder is triggered by several factors. Usually the root cause is identified during diagnosis.
Causes of tumors hypothesis
At present, the exact causes of the formation and development of tumors have not been established. Possible reasons experts include:
- negative factors affecting the body during pregnancy;
- use of hormonal medications - this usually occurs to eliminate another disease;
- receiving mechanical injuries to the skull (open, closed), hemorrhage in the brain, causing inflammation;
- past infectious diseases - meningitis, which is easily transmitted by airborne droplets;
- heredity - mutated genes are inherited;
- the appearance of tumors as a result of stress.
Diagnostics
The disease is not so easy to diagnose, because the symptoms fit many disorders.
For examination, the specialist uses several methods:
- A general examination and interview of the patient helps to assess her condition, identify the most acute manifestations and establish a presumptive diagnosis. The specialist listens to complaints to find out about the time of onset of the disease, the conditions for the manifestation or disappearance of symptoms. Based on the survey data, further examination is scheduled. The survey is conducted in a public clinic and does not require payment from the patient.
- Biochemical and clinical blood tests are carried out in private and public clinics, the cost usually does not exceed 500-600 rubles. The study allows you to see general disorders and signs of inflammation. It is especially important to determine blood glucose levels and prothrombin time indicators.
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands costs approximately 800-1500 rubles. depending on the city and complexity of implementation. The examination is carried out in private rooms equipped with appropriate equipment. During diagnosis, a specialist can see abnormalities in the structure of organs, the presence of tumors or other signs of the disease.
- Blood analysis The level of thyroid and adrenal hormones is also carried out in public and private clinics. In private the price is usually no more than 1000 rubles. Diagnostics makes it possible to detect abnormalities in organs and the degree of neglect of the disease. Blood is taken from a vein and then sent to the laboratory for testing.
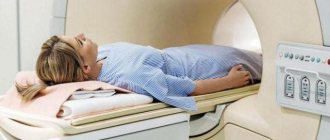
- MRI of the brain , as well as internal organs, is considered the most effective diagnostic method, since it can detect even minimal tumors, abnormalities of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland. During diagnosis, the patient is placed in a horizontal tomograph. The specialist examines the necessary organs layer by layer and then draws up a conclusion. The study is carried out in specialized clinics and costs approximately 3,000-8,000 rubles.
Based on the examination data, the doctor makes a final diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
What are pituitary tumors
One of the diseases of the pituitary gland is its tumors. A tumor of the pituitary gland of the brain is a neoplasm that affects the production of hormones by the gland. Some tumors lead to overproduction, while others lead to underproduction. In most cases, these pathological formations are benign (prolactinoma); the likelihood of their occurrence increases in adulthood.
By size, adenomas are classified into: pico-, micro-, macroadenomas and giant adenomas.
The peculiarity of pituitary adenomas is that they are localized only on the gland and do not spread to other organs and tissues, unlike malignant pituitary tumors, which quickly and aggressively grow into neighboring tissues.
Based on the type of cells that make up the tumor, tumors are classified into hormone-producing and non-hormone-producing tumors.
Prevention
It is almost impossible to completely eliminate the risk of developing pathology. However, you can reduce the likelihood using simple methods. It is recommended to normalize the work and rest schedule, try to avoid stressful situations and overwork.
Additionally, it is necessary to balance the diet, include vegetables, fresh fruits, as well as herbs and meat. Patients taking hormonal medications should visit their doctor regularly and also have their blood taken to determine their hormone levels. This will allow deviations to be detected at an early stage.
Women with diseases of the hypothalamus, thyroid gland and adrenal glands should also visit an endocrinologist regularly, because any complication can lead to the formation of microadenoma. When the first signs of a disorder appear, you should immediately visit a doctor.
How is pituitary microadenoma diagnosed?
Microadenomas in the anterior pituitary gland secrete hormones. They are considered functional adenomas and are usually discovered earlier than others because the elevated hormone levels cause hormonal imbalance and noticeable changes in the body. Therefore, approximately 50 percent of pituitary adenomas are diagnosed when they are less than 5 millimeters in size.
In contrast, adenomas larger than 10 millimeters (macroadenomas) usually do not secrete hormones and are found when they compress nearby brain structures or cranial nerves.
To confirm the diagnosis, hormonal blood and urine tests, as well as brain imaging studies, are used. The most accurate diagnostic test is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) , performed with or without contrast material.
A complete endocrine ( hormonal) examination consists of assessing the function of the pituitary gland - determining the presence of deficiency or overproduction of hormones. Necessary hormonal blood tests include assessment of cortisol (cortisol and ACTH), thyroid function ( free T4 and TSH growth hormone production luteinizing hormone (LH) and estrogen levels prolactin levels .
Treatment methods
Medicines and folk remedies are used to treat the patient. If therapy is ineffective, surgery is performed.
Medications
Pituitary microadenoma (symptoms in women can significantly reduce the quality of life) at the initial stage can be treated with medications from different groups. The regimen is drawn up individually depending on the type of disease.
The most effective means:
- Bromocriptine – a means for normalizing hormonal levels, prescribed for prolactinoma, somatotropinoma.
The tablets help suppress the active production of prolactin and improve the patient’s condition. Take 0.5 tablets 2-3 times a day for 4-8 weeks. The duration of the course is always individual; sometimes a longer dose is required until the adrenal glands are fully restored. The medicine is very effective and requires proper dosing. Price – from 240 rub. - Alactin is another tablet medication to suppress prolactin production. Prescribed for prolactinoma of varying severity. The product is effective; you should take 1 tablet 1-2 times a day for 2-4 weeks. If necessary, the course is extended. The price of the medicine is from 500 rubles.
- Octreotide is a highly effective injectable medication prescribed for the treatment of prolactinoma, somatotropinoma, stops the progression of acromegaly and improves the patient's condition. Treatment lasts from 2 to 4 weeks, the patient receives 1 to 5 ml of medication daily, depending on the degree of neglect of the condition. The drug is administered intravenously, subcutaneously or intramuscularly. The cost of the product is from 1600 rubles.
- Chloditan is a drug for the treatment of corticotropinoma and some other types of pathology. The drug does not help completely cure the disease, but suppresses the activity of the adrenal glands. The daily dosage is 2-3 g, it must be taken 3-4 times during the day. The course duration ranges from 3-6 weeks. The drug is effective. The cost of the drug is from 1000 rubles.
- Digoxin is a medication used to normalize heart rhythm, help improve heart function and prevent complications. It is highly effective, but is used only as part of complex treatment. The patient is administered 1 ml of medication intravenously per day, repeated for up to 14 days in a row. The cost of the product starts from 100 rubles.
- Enalapril is a drug for normalizing blood pressure that is effective. It is prescribed to almost all patients, since when the pituitary gland is damaged, an increase in indicators is observed. You need to take from 1 to 3 tablets per day, depending on the severity of the symptom. The duration of the course is 2-3 weeks, some take the pills constantly. Price - from 50 rub.
Depending on the other manifestations of the disease, various medications are used to suppress them. Drugs are selected individually, but in most cases they do not help completely cure the disease.
Traditional methods
Pituitary microadenoma (symptoms in women often resemble other disorders) cannot be treated with folk remedies, but homemade formulations can be used to relieve severe symptoms.
- Shilajit solution is considered a good immunostimulating and general strengthening agent. You can get it by dissolving 2 g of powder in 2 liters of boiled water. After dissolving the product, you need to take 100 ml of the product 3 times a day. Course duration is 10-14 days.
- Chamomile decoction – a good remedy for normalizing digestion and suppressing nausea. You can prepare the composition from 1 liter of water and 20 g of dry herb, cook for 5 minutes, leave for at least 1 hour, filter. Take the finished product 150 ml per day.
- Aloe juice strengthens the immune system and has a beneficial effect on the heart, blood vessels and digestive tract. It must be taken on an empty stomach, 1 tbsp. l. You can prepare the product by chopping fresh leaves of the plant and then squeezing it through cheesecloth. Continue therapy for 2 weeks in a row.
Any folk remedy cannot act as the only method of treatment.
Other methods
Among other methods of therapy, only surgery to remove the pituitary tumor can be distinguished. The manipulation is considered minimally invasive, since removal is carried out through the nose using an endoscope.
The operation requires general anesthesia, but the recovery period does not exceed 7 days. After removal, the patient is under the supervision of a specialist for 2-3 days. After 2-3 weeks, he is re-examined to assess the effectiveness of the operation.
There is also another method of tumor removal that eliminates the need for endoscopic intervention. A radiosurgical knife is used, which is a beam of rays that penetrates the pituitary gland and affects the tumor. As a result, the tumor gradually and independently decreases without causing pain or other discomfort to the patient.
Possible complications
In advanced cases, the patient develops various complications.
The most common ones are:
- Diabetes.
- Incurable infertility
- Risk of miscarriage a few weeks after conception.
- Serious hormonal imbalance.
- Uncontrolled arterial hypertension.
- Tumors of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland.
- Exhaustion of the body.
- Muscle atrophy and complete immobility of the patient.
- Severe osteoporosis.
- Accidental fractures due to light load or careless movement.
Only proper treatment will help prevent complications.
Pituitary microadenoma is a serious disease accompanied by various disorders. Symptoms appear in women after a slight growth of the tumor and significantly worsen the quality of life. However, experts note that such tumors are easier to treat, and relapses occur less frequently, especially if you consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Article design: Vladimir the Great