Lumbodynia is a chronic or acute disease that causes lower back pain. The pathology can be periodic and can occur in both children and adults. Most often, lumbodynia syndrome is diagnosed in people with a physically active lifestyle, as well as in those who, due to their occupation, are forced to remain in one position for a long time. The opinion that lumbodynia is an independent disease is erroneous. Rather, it is a kind of signal from the body about hidden health problems. Failure to promptly identify and treat these ailments can lead to disability.
What is lumbodynia?
The human musculoskeletal system includes the spinal column, as well as the surrounding muscles, tissues, nerve endings, and ligaments. When pathology occurs in any of these structures, pain occurs in the back, which can be accompanied by sharp, pulling or aching sensations lasting up to 3 months. Lumbodynia is a type of pain syndrome characterized by muscle spasms and limited movement in the lumbar region. In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), pathology is numbered 54.5. Important!
Lumbodynia and lumbago are different types of pain despite the similarity of their symptoms.
Causes and mechanisms of development
Diseases and conditions that cause lumbodynia can be divided into 2 large groups - vertebrogenic (that is, associated with the spine) and non-vertebrogenic (not associated with the spine).
Vertebrogenic factors that can cause lower back pain are:
- scoliosis (lateral curvature of the spine);
- osteochondrosis;
- spondylosis (degenerative changes in the vertebrae);
- intervertebral disc protrusion;
- intervertebral disc herniation;
- arthrosis of the intervertebral joints;
- musculofascial syndrome;
- spinal canal stenosis;
- non-infectious inflammatory diseases of the spinal column, in particular, ankylosing spondylitis;
- instability of the lumbar spine.
In these diseases, structures of the damaged musculoskeletal system may compress the roots of the spinal nerves with corresponding clinical symptoms.
Nonvertebrogenic lumbodynia can be caused by diseases that are absolutely unrelated to the spine, namely:
- osteoporosis;
- traumatic injuries of the spine;
- kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, hematomas of a traumatic nature);
- intestinal diseases;
- diseases of the reproductive system of men and women (uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, endometriosis and others);
- vascular diseases;
- benign and malignant neoplasms (both primary and metastatic);
- inflammatory processes of the abdominal organs, pelvis, muscles;
- infectious diseases, in particular herpes zoster.
Often, lumbodynia accompanies a woman during pregnancy. It occurs when the back muscles are weak and is caused by pressure on the mother’s lumbar region from the growing fetus.
Classification of lumbodynia
Lumbar spine pain can be of two forms:
- Acute - in this condition, the pain occurs suddenly and is acute in nature, often not associated with the spinal column (with the exception of disc protrusion). The cause of the pathology can be sudden movements, lifting weights in an awkward position, injury or hypothermia. Serious disturbances do not occur in the vertebrae themselves, but degenerative changes develop in the lumbar or sacrum area, at the peak of which severe pain occurs. In some cases, acute lumbodynia goes away on its own, but more often, if left untreated, it becomes chronic.
- Chronic - in this case, the pathology develops gradually and is associated with damage to the vertebral structures. This form can be identified when the pain radiating to the buttocks and lower extremities is quite weak, but does not go away for a long time, appearing periodically under the influence of external factors. When palpating the affected area, a person feels pain.
According to the nature of origin, lumbodynia is also divided into two types: Vertebrogenic - is the result of disorders of the spine. The following diseases can cause the development of this type of pathology:
- osteochondrosis - leads to wear of the spinal discs and pinching of nerve processes, stagnation of blood in the veins and swelling. This process is accompanied by autoimmune changes, which causes the development of an aseptic inflammatory process;
- protrusions and intervertebral hernia - cause compression of the nerve roots and severe lumbar pain;
- facet syndrome - in this condition, the spinal discs become thinner and the load on the vertebral joints increases, cartilage is destroyed and articular subluxation develops;
- muscle degenerative changes - associated with weakening of the muscle corset and increased load on joints and discs, while irritation of nerve receptors in tissues occurs;
- damage to the spinal ligaments - causes a weakening of the fixation of the spinal column, an increase in the space between the vertebrae and stretching of the spinal discs;
- narrowing of the spinal cord canal – leads to compression of the spinal cord. The pain may move to the gluteal region and the back of the thigh;
- cauda equina syndrome - associated with compression of a bundle of nerve endings as a result of tumors, hernias, injuries and inflammation. May lead to dysfunction of the pelvic organs and paralysis;
- spondylosis – as a result of this pathology, the spinal column and its discs are destroyed, the gap between the vertebrae decreases, and the spinal canal narrows;
- osteoporosis – leads to the loss of vertebrae’s strength properties, a decrease in the distance between them and pinching of the nerve roots;
- lumbosacral injuries - cause tissue swelling and compression of the spinal cord, as well as damage to ligaments.
Nonvertebrogenic – caused by lumbar diseases localized outside the spine. This form of lumbodynia can be caused by the following diseases of the internal organs:
- kidney pathologies - when the renal capsule is stretched or the urinary tract is injured, pain occurs in the lower back on one or both sides, accompanied by swelling;
- chronic pancreatitis, gastric ulcers - in the first case, a girdle pain is felt, in the second - a dull, aching pain, which is eliminated by taking antacids;
- diseases of the ovaries and uterus in women - cause pain in the lower abdomen;
- paravertebral tumors - they infringe on the tissues surrounding the spine and irritate the nerve roots.
Types of lumbodynia
There are two types of lumbodynia: acute and chronic.
Acute lumbodynia occurs suddenly after heavy lifting or sudden awkward movement. Most often, a person's metabolic processes in the spine are disrupted. Lower back pain decreases when lying down and increases with any movement. This form of the disease may resolve abruptly.
Chronic lumbodynia can be a continuation of the acute form or appear independently of it. The chronic form of the disease occurs due to arthrosis of the facet joints, myofascial syndrome, spondylolisthesis or spondylolysis, and vertebral instability. With chronic lumbodynia of the spine, treatment will be more difficult, due to the greater “neglect” of the situation.
Causes of lumbodynia
Common causes of the pathological condition include:
- Excessive physical activity. Pain occurs as a result of shortening and tightening of muscles, which causes strong pressure on the joints and the development of inflammatory processes in them.
- Injuries. They appear as compression fractures or dislocations of spinal discs as a result of displacement of spinal discs or rupture of ligaments and tissues during sudden lifting of heavy loads. Athletes in the heavy weight category may experience separation of the transverse process of the first vertebra of the lumbar region and rupture of muscle fibers.
- Staying in an uncomfortable position for a long time. Associated with professional activities, sleeping in an uncomfortable position, accompanied by muscle spasms.
- Pregnancy. During this period, there is a rapid gain in body weight and a strong load on the spine, as well as tissue swelling as a result of fluid retention
- Physical inactivity. Leads to poor blood circulation, loss of elasticity in the spinal discs and weakening of the muscle fibers that support the spinal column. In this case, there is a tightening of the ligaments connecting the vertebrae, as a result of which the distance between them decreases and the spinal cord is compressed.
- Scoliosis to a significant extent. Leads to displacement of the vertebrae, their activity above normal and the rapid loss of disc tissues of their properties. With incorrect posture, the load on the facet joints on one side increases - for this reason, an inflammatory process develops and pain occurs.
- Hypothermia. Leads to vasospasm and impaired blood circulation, and can cause an autoimmune inflammatory process in the joints.
- Excessive body weight. With obesity, the load on the spine and its discs increases, there is a lack of moisture and their thinning and loss of elasticity occur. In this case, the distance between the vertebrae decreases, resulting in pinching of soft tissues.
- Stress. During intense experiences, muscles spasm, blood circulation is disrupted, and pressure on the spinal structures increases.
- Age-related changes. They lead to muscle weakness, loss of fluid and elasticity in the discs, the development of degenerative processes in the joints, and poor posture.
Lumbodynia: symptoms and treatment in various ways
In addition to the main above-mentioned causes of pain, sudden movements, hypothermia, and uncomfortable body positions, for example, during sleep or a long trip, can also be identified. The pain in this case is aching, and the pain can be transmitted to the leg along the back of the thigh.
An increase in pain can be experienced with even the most insignificant movements, which then weakens and then resumes again. Having diagnosed a disease such as lumbodynia, symptoms and treatment should be determined exclusively by a specialist.
It should be remembered that improper treatment of pathology can develop into disability and completely deprive one of the ability to work.
Symptoms
Treatment for such an ailment is prescribed only by a doctor, despite the fact that some prefer to self-medicate with the help of folk remedies. However, in this option it is worth understanding that there are health risks, because an incorrect diagnosis can provoke greater inflammation of the spine and muscle tissue around it.
The features and symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- unilateral pain in the lumbar region;
- increased pain as a result of vigorous movements or prolonged stay in one position;
- improvement of the situation when taking a supine position;
- difficulty in straightening the body when bending over;
- difficulties in basic actions: washing, walking, ironing clothes, etc.;
- fatigue in the lumbar region.
As the disease progresses, it becomes permanent, the discomfort becomes more intense, intensifying even with laughter, coughing, etc. If you do not use the medicine prescribed by your doctor, you can spread the pain to the entire sacral area, legs and buttocks.
In the affected area, a specialist or the patient himself may detect muscle compactions that hurt when pressed, which is comparable to a mild electric shock. This phenomenon is called a symptom of muscle tension; the patient may even wince in pain when examining the source of discomfort. Therefore, if the disease lumbodynia is detected, the symptoms of which are determined by the doctor, treatment is prescribed after a complete diagnosis.
Some patients may have a positive Lasègue symptom, which is one of the indicators of tension. It is manifested by increased pain in the lumbar region and along the sciatic nerve when the doctor tries to lift the straightened leg of a patient lying on his back. If you bend your leg at the knee, relief comes and discomfort disappears.
Diagnostics
A neurologist must examine the patient to identify possible reflex disorders. Also in the diagnostic process, devices are used: X-ray, CT, MRI, myelography. And if necessary, the doctor may prescribe additional tests.
To eliminate other problems you will need:
- urine and blood tests;
- Ultrasound of the genital organs and peritoneum;
- blood biochemistry.
Treatment is medicinal
After receiving the necessary examination results, the doctor prescribes therapy. It will depend directly on the phase of the disease. If the period is acute, then NSAIDs are used, for example, Ibuprofen or Diclofenac.
The complex also uses chondroprotectors, which have an extremely positive effect on cartilage not only in the lumbar region, but also on the tissues of the whole body. Such drugs include Chondroitin. The doctor may also prescribe Beclafen, which is a muscle relaxant.
Dosage and duration are the responsibility of the doctor; the main thing the patient must do is follow all prescribed treatment rules. When the pain subsides, physical therapy, which includes electrophoresis, mud therapy, apitherapy, massages, swimming and more, would be advisable.
Surgical treatment
When lumbodynia occurs in a severe form and circulatory disorders, abscesses, and tumors in the spinal cord occur, then surgical treatment becomes inevitable. In this case, an operation is performed that involves fusion of the degenerative segment and the implant. This surgical intervention is called spinal fusion and is performed in case of unbearable pain due to unstable movement of the vertebra.
If the patient has intervertebral hernia, then the spinal disc is removed and an artificial one is placed in its place. This manipulation is called discectomy. But surgeons perform such an operation extremely rarely, because it can lead to a recurrence of lumbodynia.
Dikul's technique
Popular today is the Dikul method for pain. In this case, a specially designed load pattern is used, which returns mobility to the spine. Also, along with exercises, the correct drinking regimen, manual therapy, and acupuncture are used.
The course according to the methodology consists of 3 cycles, each containing 12 lessons:
- Stage 1 is marked by preparing the body for stress. Breathing exercises, yoga, and Pilates take place here.
- Stage 2 involves the restoration of muscles affected by the disease, increasing the tone of the soft tissues in this area.
- Stage 3 is aimed at increasing the mobility of the spine. This is where the active exercises begin. Also, each patient receives his own set of exercises depending on the complexity of the situation. These exercises can be done at home.
Recovery occurs individually for each person; you can be cured in 3 months, or you can repeat the course for several years in a row.
Symptoms of lumbodynia
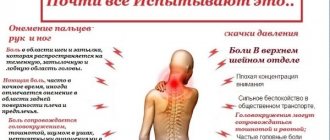
- Lumbar pain is usually felt on one side and can have varying degrees of intensity. When the spinal nerve roots are compressed, a very strong shooting pain occurs, which can result in immobility of a person. If there is aching pain, there is a suspicion of non-vertebrogenic lumbodynia.
- When bending over, coughing/sneezing, or during defecation, the pain syndrome intensifies.
- The range of movements decreases sharply, bending forward is almost impossible.
- Difficulties arise when trying to sit down, walking up stairs and crossing legs, and it is also difficult to straighten up from a bent position.
- There is a strong tension in the lower back muscles, it is very difficult to relax them.
- Palpation of the spine and surrounding tissues causes pain.
- Gate's symptom is positive - accompanied by sharp pain when trying to sharply bend the leg while lying on the back.
Diagnostic principles
The doctor finds out important information about the causes and nature of the disease by assessing the results of additional examination methods.
The doctor will suspect lumbodynia at the stage of collecting complaints and data from the patient’s life history and illness. An objective examination of the patient, in particular, a study of the neurological status, will convince the specialist that his guess is correct. To find out exactly what disease provoked the development of lower back pain, the doctor will prescribe the patient additional examination methods, among which the leading role belongs to imaging methods:
- X-rays of the lumbar or lumbosacral spine;
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging.
An x-ray will reveal gross changes in the structure of the spine: the presence of traumatic injuries, narrowing of the intervertebral spaces and bone growths around them, osteoporosis.
Computed tomography is more informative than radiography. This study allows you to obtain a clear layer-by-layer image of the spine and surrounding tissues and identify diseases such as stenosis (narrowing) of the spinal canal, disc herniation, and neoplasms.
The most informative method for diagnosing this group of diseases is magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI. It allows you to reliably diagnose changes in the spine and surrounding organs: muscles, blood vessels and nerves.
Diagnostic methods such as electromyography (EMG) and electroneuromyography (ENMG) can also be used. With their help, it is easy to detect disturbances in the transmission of nerve impulses through muscles and nerve fibers.
In order to detect tumors and the source of infection, the patient may be prescribed scintigraphy. This research method is based on the different absorption of a radioactive substance introduced into the body by healthy and pathologically altered tissues.
If there is a suspicion of compression (pinching) of a nerve root, thermography will help confirm or refute it. Using special infrared sensors, the temperature of two sides of the body is measured: up to the suspected site of damage and below it.
For the purpose of differential diagnosis of lumbodynia and diseases of the abdominal organs, ultrasound examination (ultrasound) can be used. If it is necessary to detect damage to any muscle, ligament or tendon, they are examined directly using this method.
To determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the body of an infectious or non-infectious nature that can cause lumbodynia, laboratory tests are carried out, in particular a general blood test, urine test, rheumatic test and others.
Diagnosis of lumbodynia
A preliminary diagnosis can be made based on the patient’s complaints and a story about the moment the pain syndrome appeared and its nature. Next, palpation of the lower back and spinal region, muscle corset and sacrum is performed. To exclude the presence of other diseases, a neurologist
prescribes the following examination methods:
- general and biochemical blood test, blood test for antibodies to various infections;
- radiography of the lumbosacral region of the spinal column;
- MRI or CT of the lumbar part - allows you to determine the presence of abnormalities in the development of the spine and assess the condition of the discs;
- Ultrasound of the peritoneal organs and reproductive system.
If necessary, a consultation with other specialists is scheduled - an infectious disease specialist, a gynecologist (urologist), a therapist.
Objective state of lumbodynia
When examining patients with lumbodynia, pain in the paravertebral points and spinous processes of the vertebrae is determined. Symptoms of tension are mild or moderate. Positive symptom of Lasegue, less often positive symptoms of Neri, Wasserman, Matskevich, Dejerine. Motor disturbances and changes in tendon-periosteal reflexes are often absent. There is no loss of sensitivity. When the thoracic spine is involved in the pathological process, doctors talk about thoracolumbodynia.
Treatment of lumbodynia
When treating lumbodynia, the main goal is pain relief; for these purposes, different methods are used:
- taking analgesics;
- muscle relaxants and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- manual therapy;
- acupuncture;
- vacuum therapy;
- spinal traction;
- physiotherapy;
- blockade of nerve endings.
As the acute pain symptom is eliminated, exercise therapy, osteopathy, and massage
. In parallel with this, it is necessary to reduce physical activity, reduce the load on the spine, and eliminate heavy lifting. Treatment of chronic lumbodynia should be complex and take a long period of time - simultaneously with the above methods of therapy, wearing a special bandage, using exercise equipment and physical rehabilitation methods are recommended.
Principles of treatment
First of all, the underlying disease that caused the pain in the lower back should be treated. Depending on the disease, patients with lumbodynia are treated by neurologists, therapists or orthopedists.
To alleviate the patient’s condition and speed up recovery, the patient is recommended to:
- Bed rest. During the acute period of illness, it will be much more beneficial for the patient to stay in bed for 3-5 days than to spend this time in queues at the clinic or in search of the necessary medications. Rest is an essential component of treatment, without which other types of therapy will not have the desired effect.
- Drug treatment:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or NSAIDs (meloxicam, rofecoxib, diclofenac, nimesulide and others); these medications help reduce the severity of the inflammatory process and reduce pain; drugs are prescribed in a short course - for 5-7, less often - more, days with mandatory stomach protection in the form of simultaneous administration of proton pump blockers (omeprazole, rabeprazole and others) with NSAIDs;
- muscle relaxants (as a rule, tolperisone is used, less often - sirdalud); relax spasmodic muscles, reducing the manifestations of the muscle tension syndrome described above;
- B vitamins (neurorubin, neurobion, milgamma and others); nourish nervous tissue, improving impulse transmission from neuron to neuron;
- diuretics (furosemide, torsemide); used in case of detection of tissue edema in the affected area; Also, a drug with a similar effect can include L-lysine escinate, which, in addition to its anti-edematous effect, has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect;
- drugs that improve blood circulation (pentoxifylline, nicotinic acid and others);
- antidepressants and, less commonly, anticonvulsants: in case of recurrent chronic lower back pain, when taken for a long time (6-10 weeks), these drugs act on the pain centers, reducing the severity of the pain syndrome;
- chondroprotectors (Mukosat, Dona, Rumalon and others) - affect the articular cartilage, activating metabolic processes in it, thereby partially restoring its structure and slowing down the progression of the disease; are used in long courses - 2-3-6 months 2-3 times a year.
- Physiotherapy and alternative medicine methods:
- massage;
- manual therapy (gentle techniques);
- reflexology;
- transcutaneous electrical stimulation;
- osteopathic techniques;
- ultrasound therapy;
- laser therapy;
- cryotherapy;
- kinesiotherapy;
- hirudotherapy;
- vacuum therapy;
- spinal traction;
- physical therapy (rightfully considered one of the most effective methods for eliminating chronic pain in the lower back - it helps strengthen the muscles of the back and abs);
- some other techniques.
It is worth noting that some of the above methods can be used to relieve pain in the acute period of the disease, while others can only be used when the main symptoms have been eliminated and the effect needs to be consolidated.
- Surgery. It is recommended for individual patients in cases where conservative treatment has not had the desired effect or drug methods cannot be effective for this disease.
Treatment of lumbodynia in St. Petersburg
A multidisciplinary medical center in St. Petersburg offers fast and high-quality treatment using modern equipment. Neurologists with many years of experience and a high level of knowledge will conduct an accurate diagnosis and select an individual course of therapy, which will avoid further complications and quickly relieve unpleasant symptoms. The clinic practices electronic patient registration, which guarantees European quality of service and the absence of queues. For consultation and to make an appointment, please contact the clinic staff at the numbers provided.
How to treat lumbodynia using traditional and alternative medicine
Physiotherapy procedures that are aimed at improving the patient’s condition and relieving him of pain are advisable in the treatment of the disease. Only a doctor can decide how to treat lumbodynia.
He also prescribes procedures, among which are:
- Diadynamic therapy , when the body is affected by pulsed currents of different frequencies and shapes. The procedure involves the alternate use of 2-3 types of currents. The number of procedures per course is 5-7, each manipulation takes about 10-12 minutes.
- Short-pulse electroanalgesia , where very short pulses are applied to the painful area. In this case, the pulse frequency can vary from 2 to 400 Hz. 10 procedures lasting 10 minutes are enough.
- Drug electrophoresis , in which the administration of a drug for pain relief occurs in combination with a direct electric current. The procedure takes 15-30 minutes, the course is 15-20 manipulations.
- Magnetic laser therapy , which by simultaneous exposure of the affected area to a laser and a magnetic field helps to improve the situation. The time for manipulation is 15 minutes, the course is up to 15 procedures.
- Magnetotherapy , where alternating and constant magnetic fields influence the body. Course - up to 20 procedures, 15-25 minutes each.
- Ultrasound therapy , where ultrasonic vibrations are used, the frequency of which ranges from 800 to 3000 kHz. The course is 6-14 manipulations for 12-15 minutes.
- Acupuncture therapy , during which impulses from needles pass into the painful part of the body. Such procedures are carried out for 15-45 minutes, the number of manipulations in the course is 3-15.
- Manual therapy is carried out by irritating the nerve endings. This procedure is performed either by special massagers or massage therapists. The course reaches 15 procedures. Repetition after six months is recommended.
How to treat lumbodynia is decided by a specialist, because there are also contraindications. They are neoplasms of both malignant and benign nature, infections of the spine and tissues, febrile conditions, abscesses in the area of influence.
Blockade for lower back pain
In addition, the doctor can decide how to treat the disease lumbodynia if there is unbearable pain in the lower back, which disrupts the rhythm of life and deprives the patient of working capacity. In such cases, a blockade is used, which consists of injecting a potent drug into the area of pain. This medication can quickly relieve suffering for a period of up to several days.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine is no less developed in the treatment of illness. But it is worth understanding that depending on how to treat the manifestation of lumbodynia, only the neutralization of pain may occur, while the cause is not eliminated.
To alleviate the condition, you can use the following recipes:
- Rub the sore spot with aloe juice three times a day.
- Make compresses from washed, dried and boiled horseradish leaves, wrapping them in a woolen product at night.
- Rubbing with pork fat also involves wrapping the sore spot with a woolen scarf.
- Using a heated ozokerite composition. Leave it until it cools down. Applications are made for 10 days, once a day. The thermal procedure is contraindicated in the presence of formations that are concentrated in the peritoneum or pelvis.
Pain may worsen if:
- do not monitor your posture while sitting or walking;
- do not do gymnastics, at least half an hour a day;
- injure and hypothermia the lumbar region;
- turn sharply, move, lift heavy objects;
- sleep on soft feather beds, it is better to give preference to a semi-rigid mattress;
- do not use a fixation belt when engaging in active sports, especially weightlifting;
- do not use the bandage from the 6th month of pregnancy (as prescribed by a doctor).
For prevention, it is important to remember the basic rules:
- maintaining posture;
- weight control for lifting;
- a balanced diet, eating at least 5 different vegetables and fruits every day;
- Remember about safety precautions not only at work, but also at home.
What it is
Lumbar pain can appear after hypothermia, physical exertion, sudden movement or a long stay in an uncomfortable position. It concentrates in the back or spreads to the thigh and the entire leg, going down its back surface and reaching the foot itself.
The pain is aching and dull, its intensity increases with walking, bending and turning the body. Even coughing, sneezing or laughing can trigger a painful attack. Over time, the back hurts less and less, which does not mean recovery.
After some time, the pain will definitely return. This happens until the cause of its appearance is eliminated. The danger of lumbodynia is that with the long-term existence of the pathology, the ability to work is sharply reduced, and disability is not excluded.
The vast majority of patients are people over 50 years of age. However, the disease occurs in children and adolescents. The peak incidence occurs between the ages of 10 and 12 in girls and from 13 to 17 in boys, that is, during the period when the body is actively growing.
The most common cause of lumbodynia is damage to the 4-5 lumbar vertebrae. The first three vertebrae are less vulnerable, which is due to the peculiarities of the distribution of the load on the spine.
Are lumbago and lumbodynia the same thing?
Lumbodynia must be distinguished from attacks of lumbago (sudden sharp, shooting pain in the lower back that occurs spontaneously and is not associated with physical activity or body position). This is important, since the principles of treatment for lumbago and lumbodynia may differ, so patients suffering from pain in the sacrum and lower back should know what to look for when visiting a doctor.
Difference between lumbago and lumbodynia
Lumbago and lumbodynia: what is the difference?
| Characteristic |
|
|
| Course of pain. | Chronic pain syndrome that does not go away for 3 months or longer (maybe a slight subsidence of symptoms with periods of regular exacerbation). | Acute, spontaneous pain that occurs suddenly and is usually not associated with physical or motor activity. |
| Duration of the attack. | The pain lasts for 10-12 weeks, is inconsistent and has multiple relapses. | From several minutes to several hours (less often – up to 1-3 days). |
| Relationship with environmental factors. | Occurs under increased loads (especially if the degree of load does not correspond to the person’s physical capabilities), sudden movements, and stress. | Pain with lumbago is rarely associated with physical activity, and the most common precipitating factor is hypothermia. |
What is it: pathogenesis and etiology
Lumbodynia is a chronic pain syndrome (most often with a progressive course), characterized by persistent pain in the lumbosacral segment of the spine. If the pain radiates to the gluteal muscles, coccygeal bone, thighs, lower legs and other parts of the lower extremities, along the location of the sciatic nerve, such an attack is called lumboischialgia.
Sciatica
In 80% of cases, lumbodynia is vertebrogenic, that is, it is caused by diseases of the spine. In some cases, it is not possible to accurately determine the cause of discomfort and shooting in the lower back, which may be the basis for examining the patient for rheumatoid and oncological factors.
Vertebrogenic lumbodynia
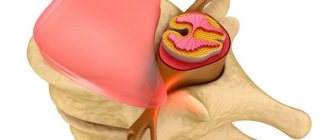
The occurrence of vertebrogenic lumbodynia is based on pinched nerve bundles that extend from the spinal nerve trunks into the central spinal canal.
The structure of the spinal nerve
During pinching, irritation of nerve receptors occurs, which leads to intense formation and transmission of nerve impulses and severe pain. The situation gets worse if the patient does not seek medical help at this stage. Nutrition in the tissues of the compressed nerve is disrupted, and the nerve root swells and becomes inflamed. It is these processes that underlie the pathogenetic mechanism of development of vertebrogenic lumbodynia, so we can say that timely diagnosis and early treatment of lumbar pain syndrome are the basis for the prevention of chronic attacks.