Our expert - neurologist Elena Yuryeva.
This injury is considered mild - not a brain injury, after all! However, with a concussion, multiple microbruises, numerous minute perivascular edema and hemorrhages occur, the functions of the nerve cells of the brain are disrupted, and their nutrition deteriorates. And sometimes all this can result in immediate and long-term complications: increased intracranial pressure, severe headaches, decreased visual acuity.
Article on the topic Concussion: how to recognize and what to do
Signs of a concussion
It is quite difficult for a person far from medicine to recognize a concussion in a victim, especially if the injury is not too serious and does not have obvious external signs. It is worth noting that not all symptoms appear immediately. Some may make themselves felt several hours after the incident.
In addition, each degree of concussion (there are only three) also manifests itself in its own way. It turns out that you just need to understand whether there is a concussion and decide on further actions. The following are typical signs of a concussion.
Primary symptoms:
- noticeable external injuries, nosebleeds;
- Strong headache;
- loss of consciousness;
- inhibited reactions, loss of orientation in space;
- visual and hearing impairments;
- unsteadiness in the legs.
Primary symptoms appear immediately or within a few minutes after the injury. In a mild form, they may not appear immediately or not be expressed. One of the listed symptoms is enough to understand that the injury is more serious than a bruise that does not pose a significant threat to health.
If your fears are confirmed, you need to take the necessary measures and, before the ambulance arrives, provide first aid for a concussion to the victim.
Secondary symptoms:
- dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased body temperature;
- feeling of weakness;
- pale complexion;
- loss of appetite;
- sleep disorders.
Depending on the severity of the concussion, the time for secondary symptoms to appear varies from 20 minutes to several hours after the incident. It turns out that first aid for a concussion is no longer relevant - treatment is needed. In this situation, you will be required to provide the victim with conditions under which his condition, if not improved, then at least will not worsen.
Less common symptoms:
- trembling of the eyeballs, inability to focus;
- confusion, inappropriate answers;
- amnesia, which can be either short-term or long-term.
The signs listed above occur in rare cases and are not always symptoms of a concussion, therefore they are considered in conjunction with the others. However, they are serious and require monitoring and urgent action.
Rehabilitation at home
For a quick recovery, the patient must follow all the doctor’s instructions and ensure complete rest. In addition, herbal sedatives can be used to minimize the effects of hitting your head. However, before using them, you must coordinate your appointment with your doctor. The following traditional medicine recipes are popular:
A decoction of motherwort, mistletoe and mint herbs softens the effects of a concussion.
- a collection of motherwort, mistletoe and mint herbs (in equal proportions), as well as lemon balm (3/4 doses) are brewed with boiling water and allowed to brew for several hours. The product is consumed 3 – 4 times a day, half a glass at a time;
- mix valerian, mint, lemon balm and hops and pour boiling water for 20 minutes. The decoction is drunk at night;
- Bee pollen, which is consumed in a course for 1 to 2 months, accelerates recovery.
If there is a disturbance in brain activity due to a concussion in a child or adult, consultation with a doctor is required. Mild injuries can be treated at home. The patient is provided with complete rest and lack of physical activity.
Degrees of concussion
First aid for a concussion depends on the severity of the injury. How serious the situation is can be seen from the obvious signs.
Mild degree
A mild degree can be determined in the first hour after hitting the head. In some situations, a short-term loss of consciousness occurs for up to 5 minutes, but it may not exist. After 20 minutes, the person’s condition returns to normal: he can speak clearly, walk independently and navigate in space. Subsequent symptoms usually appear within 24 hours.
Average degree
Moderate, like mild, is not always accompanied by fainting, which in rare cases can last more than 5 minutes. Immediately after an injury or return of consciousness, the patient experiences a severe headache, is unable to clearly explain what happened, has difficulty speaking and orienting himself in space.
Severe degree
The most dangerous situation both at the time of the incident and for the state of health in the future. As a rule, it is accompanied by fainting, but in rare cases a person can remain conscious all the time.
The victim does not remember what happened to him. When trying to stay on his feet, he falls, and in some cases he cannot even stand up. As a result of disruption of most brain functions, he is unable to speak clearly and describe his state of health. It is accompanied by noise in the head and ripples in the eyes, severe nausea and weakness.
The worst sign of severe severity may be bleeding from the ears during a concussion. This fact indicates a skull injury, which can be either open or closed.
What to do after a head injury
Mild concussions are treated at home. To do this, the victim is recommended to follow the following rules:
- Bed rest: the first few days after injury are key, so it is necessary to maintain a daily routine and rest and get out of bed only when absolutely necessary;
- calm environment around: after a head blow, the patient should be in a state of complete rest, not turning on the TV, music, computer, phone (this regime should be followed for about a week);
- taking medications as prescribed by a doctor: for frequent headaches, often occurring after skull injuries, painkillers are prescribed.
What is first aid for a concussion?
It is important to understand that no action you take will change the severity of the injury already received, but can alleviate its consequences and significantly speed up the healing process. There are also cases in which it is more advisable to do nothing until the ambulance arrives.
What should she be
Now we will talk about emergency measures, that is, about desirable actions on the part of people who are close to the victim and who do not have medical education. After calling an ambulance, everything must be done to alleviate the patient’s general condition.
General recommendations include the following:
- providing the patient with peace;
- ensuring proper ventilation if located indoors;
- abstaining from active actions (you should not try to get a person to talk, put him on his feet, give him something to drink, feed, etc.);
- eliminating noise and harsh light source.
These steps are recommended for all types of concussions, brain injuries, and contusions. Then it all depends on the specific case and additional symptoms.
Immediate measures
A concussion, even a mild one, only at first glance seems to be a completely harmless phenomenon for health. In fact, ignoring pathology can lead to serious consequences associated with brain dysfunction, ophthalmological problems, and hearing. If you receive a traumatic brain injury with alarming symptoms, first of all, you need to call an ambulance.
If signs that appear during a concussion are observed, then first aid from a nearby person can prevent undesirable consequences. Elementary but correct actions before the arrival of doctors will ensure a quick and complete recovery of the injured person. The arriving team will already provide professional first aid (PMA) or hospitalize him if necessary.
What should you do if you suspect a concussion? In general, first aid includes the following measures:
- After calling an ambulance, an examination is carried out to identify wounds.
- A state of complete rest is ensured for the victim. If he is conscious, then it is necessary to lay him in a horizontal position, raising his head slightly. In case of unconsciousness, the person lies on his side, his legs are bent at the knees, his hands are placed under his head. One condition must be met - complete rest is ensured, but the victim is not given the opportunity to fall asleep for 40-60 minutes or until the doctor arrives.
- Eating any food is not allowed and drinking is excluded.
- Provides access to fresh air. For normal breathing, the top buttons are unbuttoned and all constricting elements of clothing are removed. A window opens in the room.
- A cold compress is applied to the head. You can use water frozen in the refrigerator or a cloth soaked in cold water.
- Any external influence is completely excluded - TV, music, telephone, computer, any sharp sounds.
- If there are open wounds, they are disinfected and a bandage is applied.
- Constant monitoring of the victim's condition is ensured.
Help for moderate cases
If the patient is in a supine position, he cannot be lifted - this will be done by ambulance workers. The best thing to do is to carefully place a flat pillow or a sheet or towel folded several times under his head. The use of a high pillow is unacceptable, since there is a possibility of additional injuries to the neck or spine.
If the patient has lost consciousness, reviving him using ammonia, splashing water and similar methods is strictly prohibited: a sudden movement of the head as a result of awakening can cause additional brain damage.
Vomiting can start at any moment, so carefully turn the victim's head to the side so that as a result of the possible release of vomit, he does not choke or choke.
Help for severe cases
Providing first aid for severe concussion must be competent and timely. The faster the patient gets into the hands of qualified specialists, the faster his health will be restored. Maximum non-interference will be required from you.
If you lose consciousness, do not, under any circumstances, try to revive the victim. Do not try to rotate it or change its position - this is dangerous. Open windows and doors to improve air circulation in the room or vehicle if the incident occurs in an enclosed space. If you are outdoors, try to protect the victim from direct sunlight in an accessible way.
In case of rain or cold, do not try to dress him, but cover him with a blanket or your own outerwear, if possible. Monitor your symptoms carefully: the more detailed information the ambulance team receives, the more timely and qualified their assistance will be.
Possible consequences and complications of traumatic brain injury
Severe concussions, accompanied by compression of brain tissue, circulatory disorders, rupture of capillaries, hematoma at the site of impact, can provoke serious complications in the victim:
- speech impairment of varying severity;
- confusion and confusion;
- temporary or permanent amnesia;
- violation of innate skills and reflexes.
After minor head injuries, the patient is likely to have persistent headaches, often occurring several years after the concussion. If signs of complications appear, it is necessary to consult with doctors such as a neurologist, psychotherapist, or neurosurgeon.
Any head injury is a dangerous condition for a person’s life and health. A concussion always has a strong impact on the body and is often accompanied by serious consequences. Timely, competent first aid, a thorough examination by doctors and complete rehabilitation can reduce the risk of complications and speed up the patient’s recovery rate.
Bleeding from the ear due to severe concussion
Here you need to act extremely carefully, since we are talking about traumatic brain injury. It is likely that the upper spine was also damaged, so the patient’s head position must be stable.
Do not try to provide him with a more comfortable position, place a pillow on him or transfer him to a soft surface: the patient can only be carried on a hard stretcher and this should be done by ambulance workers.
In any case, you won’t be able to stop bleeding from your ears during a concussion on your own, but blood loss can lead to the most undesirable consequences. In this situation, every minute counts. When you call the ambulance, describe the situation in detail. A resuscitation team may need to be dispatched.
Medical care for concussions
Medical care for head injuries is provided only in a hospital setting. The only action on the part of emergency personnel is to treat the wound or stop bleeding, if any. Other treatment methods are permissible only after a thorough diagnosis.
Taking medications, including painkillers, is possible only with the permission of the attending physician: there are patients who are allergic to certain categories of medications, and, in addition, there are cases when taking medications can blur the symptoms and complicate the diagnosis. It follows from this that self-medication is strictly prohibited.
Second video
There is also an interesting video of head screwing up . Watch, gain experience, try - and you will succeed!
Did you like the article? Leave your comment. Your opinion is very important to me.
If you liked the site, you found something interesting in it, applied it and got the result - AND YOU WANT TO LIVE IN A FLOW OF GRATITUDE,
support the site by sending any amount to Yandex wallet No. 410011662319725
What to do after a concussion
The recovery period after injury lasts from one to three weeks. In elderly patients and people suffering from other diseases, the treatment process may be delayed. In order for the patient to return to a full life as quickly as possible, during sick leave he must follow the following recommendations:
- follow the schedule for taking medications prescribed by the doctor;
- refrain from listening to music, watching movies, working on the computer, reading and activities that require visual concentration, such as small crafts, crossword puzzles, online games, etc.;
- maintain bed rest, avoid sudden movements;
- do not be nervous, exclude the possibility of any, even the most minor stress;
- get as much rest as possible - sleep and rest in this case are the best medicines;
- follow a diet, eat foods rich in vitamins, refrain from “heavy” foods such as fatty meats, mushrooms, etc., since the body spends too much energy to digest them;
- regularly ventilate the room, since fresh air not only promotes a speedy recovery process, but also alleviates symptoms;
- eliminate sources of bright light - it irritates the eyesight;
- talk on the phone as little as possible (ideally, don’t talk at all);
- Do not play sports under any circumstances, avoid any activity.
As an aid, with the permission of the attending physician, you can use relaxing herbal decoctions and other folk remedies - this will certainly help the patient with a concussion and alleviate his condition.
Treatment of injury
After providing first aid for a concussion, treatment is carried out either in a medical facility (for severe injuries) or at home. During rehabilitation therapy in a hospital, medications are selected by the attending physician. It is also necessary to follow the instructions if the patient is undergoing rehabilitation at home. In this case, it is necessary to provide the patient with the following conditions:
- no stress and complete rest. Bed rest is indicated for several days after brain damage. Those around must provide the victim with comfortable conditions that do not require leaving the bed;
- absence of external stimuli. The patient is advised to rest, which should not be disturbed by noise from the TV, computer, etc.;
- the use of painkillers and other medications prescribed by the attending physician.
The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the concussion. Symptoms may go away within a few days or may persist for 3 to 4 weeks.
What to do in case of complications
Complications can arise in two cases: if the treatment rules were not followed, or as a result of an unfortunate combination of circumstances, the patient received an additional injury or health problem.
Complications are as follows:
- sleep disturbance;
- confusion;
- lack of appetite;
- hearing and speech impairment;
- frequent vomiting;
- severe tinnitus and unbearable headaches;
- hallucinations;
- problems with wound healing (if any) or new bleeding;
- blood from the nose;
- blood pressure disorders;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- new loss of consciousness.
In this situation, we are no longer talking about the rules of first aid for a concussion. Self-medication is strictly unacceptable, since both the health and life of the patient are at risk. It is necessary to contact a physician who has previously observed the patient and is familiar with his clinical picture. Most likely, urgent hospitalization will be required. Further recommendations from medical personnel may be individual.
How does osteopathy help treat concussions?
A concussion is a mild form of brain damage. It is believed that the basis for the manifestation of a concussion is a disruption of connections between nerve cells, mainly functional.
In terms of frequency of occurrence, concussion ranks first in the structure of traumatic brain injuries. The causes of concussion include both road traffic accidents and domestic, industrial and sports injuries; Criminal circumstances also play a significant role.
Symptoms of a concussion
Immediately after a concussion there may be
one-time vomiting
· slight increase in breathing,
Increased or slowed heart rate
but these indicators will soon normalize. Blood pressure quickly returns to normal limits, but in some cases it can persistently increase - this is due not only to the injury itself, but also to the stress factors accompanying it. Body temperature during a concussion remains normal.
Upon restoration of consciousness, typical complaints are headache, dizziness, weakness, tinnitus, flushing of the face, sweating, discomfort and sleep disturbance. There is pain when moving the eyes, divergence of the eyeballs when trying to read.
With a concussion, the general condition of the victims usually improves quickly during the first, and less often, the second week. However, it should be taken into account that headaches and other subjective symptoms can last much longer for various reasons.
Age-related features of manifestations
The pattern of concussion is largely determined by age factors.
In infants and young children, concussion often occurs without impairment of consciousness. At the time of injury - sharp pallor of the skin (primarily the face), rapid heartbeat, then lethargy, drowsiness. Regurgitation occurs during feeding, vomiting, anxiety, and sleep disorders are noted. All manifestations disappear within 2-3 days.
In young (preschool) children, a concussion can occur without loss of consciousness. The general condition improves within 2-3 days.
In the elderly and elderly, primary loss of consciousness due to concussion is observed much less frequently than in young and middle age. At the same time, pronounced disorientation in place and time often manifests itself. Headaches are often pulsating in nature, localized in the occipital region; they last from 3 to 7 days, differing in significant intensity in people suffering from hypertension. Frequent dizziness.
Diagnosis of concussions
When diagnosing a concussion, it is especially important to take into account the circumstances of the injury and information from witnesses to the incident. Traces of trauma on the head and factors such as alcohol intoxication, the psychological state of the victim, etc. can play a dual role.
Various functional studies (electroencephalography, ophthalmoscopy, ultrasound intracranial Dopplerography, etc.) can indirectly contribute to the objectification of a concussion. The most informative is an otoneurological study (preferably using electrogustometry, audiometry, electronystagmography).
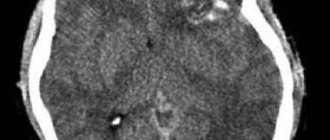
There are no fractures of the skull bones during the concussion. Pressure and composition of cerebrospinal fluid without deviations. M-echo is not shifted.
Computed tomography in patients with concussion does not reveal traumatic abnormalities in the state of the brain matter (the density of gray and white matter remains within normal limits - 33-45 and 29-36 H, respectively) and cerebrospinal fluid-containing intracranial spaces. Magnetic resonance imaging data for concussion also do not reveal any damage.
Treatment of concussions
First aid for concussions
First aid for a victim with a concussion, if he quickly regains consciousness (which usually occurs with a concussion), is to give him a comfortable horizontal position with his head slightly elevated.
If the person who has received a concussion continues to be unconscious, the so-called rescue position is preferable - on the right side, head thrown back, face turned to the ground, left arm and leg bent at right angles at the elbow and knee joints (fractures of the limbs and spine must first be excluded) . This position, ensuring the free passage of air into the lungs and the unhindered flow of liquid from the mouth to the outside, prevents breathing problems due to the retraction of the tongue, the flow of saliva, blood, and vomit into the respiratory tract. If there are bleeding wounds on the head, apply a bandage.
All victims with a concussion, even if it seems mild from the very beginning, must be transported to an emergency hospital, where the primary diagnosis is clarified. Victims with a concussion are placed on bed rest for 1-3 days, which is then, taking into account the characteristics of the course of the disease, gradually extended over 2-5 days, and then, in the absence of complications, discharge from the hospital for outpatient treatment is possible (lasting up to 2 weeks ).
Drug therapy
Drug treatment for concussion is aimed mainly at normalizing the functional state of the brain, relieving headaches, dizziness, anxiety, insomnia and other complaints.
Typically, the range of medications prescribed upon admission includes painkillers, sedatives and sleeping pills, mainly in the form of tablets, and, if necessary, injections. Among the painkillers (analgin, pentalgin, baralgin, sedalgin, maxigan, etc.), the most effective drug for a given patient is selected. They do the same for dizziness, choosing one of the available medications (Belloid, Bellaspon, Platyfillin with papaverine, Tanakan, Microzer, etc.).
Valerian, motherwort, Corvalol, valocordin, as well as tranquilizers (Elenium, Sibazon, phenazepam, nozepam, rudotel, etc.) are used as sedatives. To eliminate insomnia, phenobarbital or reladorm is prescribed at night.
It is advisable to carry out a course of vascular and metabolic therapy for a faster and more complete recovery of brain dysfunction. A combination of vascular (Cavinton, Stugeron, Sermion, Teonicol, etc.) and nootropic (Nootropil, Encephabol, Aminolon, Picamilon, etc.) drugs is preferable. As options for possible combinations, a daily dose of Cavinton, 1 tablet three times a day, can be presented. (5 mg) and nootropil 2 caps. (0.8) or stugeron 1 tablet. (25 mg) and encephabol 1 tablet. (0.1) for 1-2 months.
To overcome frequent asthenic phenomena after a concussion, the following are prescribed: Pantogam 0.5 3 times a day, Cogitum 20 ml 1 time a day, Vasobral 2 ml 2 times a day, multivitamins and polyminerals such as Unicap-T, Vitrum " and so on. 1 tab. 1 per day. Tonic preparations include ginseng root, eleutherococcus extract, lemongrass fruit, saparal, and pantocrine. In elderly and senile people who have suffered a concussion, anti-sclerotic therapy is intensified. They also pay attention to the treatment of various concomitant diseases. To prevent possible deviations in the successful completion of a concussion, clinical observation is required for a year by a neurologist at the place of residence.
Forecast
With adequate adherence to the regimen and the absence of circumstances aggravating the injury, a concussion ends with the recovery of the victims with full restoration of their ability to work.
A number of patients, after the acute period of concussion has passed, experience a weakening of concentration, memory, depression, irritability, anxiety, dizziness, headaches, insomnia, fatigue, and increased sensitivity to sounds and light. 3-12 months after a concussion, these signs disappear or are significantly smoothed out.
However, in 3% of patients after a concussion, moderate disability occurs if the recommended treatment regimen and behavior are not followed. This can lead to an extension of the recovery period and the occurrence of various consequences: asthenic syndrome, vegetative-vascular dystonia, insomnia and other disorders. Alcohol abuse may lead to the development of epileptic seizures.
Repeated concussions
If the head injury was accidental, the risk of re-injury is not so great. If the victim’s life is closely connected, for example, with sports, the likelihood of getting a new concussion increases significantly.
A mild degree of injury, although not desirable, does not pose a significant threat to human health in the future. As for moderate and severe concussions, having recovered from it, it is important to understand that the brain is already injured and additional stress is extremely dangerous for it.
The consequences of repeated concussion can be as follows:
- irreversible changes in the functioning of the auditory and visual organs;
- causeless and frequent headaches;
- partial or complete memory loss;
- increased nervous excitability;
- sleep problems;
- dementia.
What exactly the consequences may be depends more specifically on the previously damaged brain area, since it is this area that is now the most vulnerable. In other words, if the patient experienced short-term memory loss during the first concussion, then the second time it may take longer to recover. The same applies to hearing, vision, coordination of movements, etc.
This means that you need to make every effort to protect yourself from future injuries. In some situations, this requires a complete lifestyle change, for example, giving up sports or driving. Extreme entertainment is also dangerous. As for sports exercises, their selection should be individual, taking into account previous trauma.
Prevention
Regardless of whether you have had a head injury or concussion in your life, you need to take care of your health and follow safety measures. If you drive a car, do not forget to fasten your seat belt - it is this that most often becomes a guarantee of head safety, since it protects you from hitting the windshield.
If you ride a motorcycle, roller skates, skateboard or snowboard, do it with a helmet. Even if an accident occurs, first aid for a head injury or concussion will be provided to you much faster, and the injury itself will be milder.