What is ischemic cerebral infarction
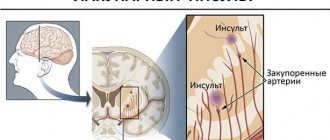
The condition is the destruction of organ tissue, formed due to insufficient blood flow to the cells. The main cause of the disease is ischemic stroke - partial or complete blockage of blood vessels. Due to damage to neurons, the functions of the central nervous system are impaired. Symptoms of the pathology include temporary muscle paralysis, headache, decreased visual acuity and impaired consciousness. Without treatment, death can occur.
A cerebral infarction cannot be called an independent disease. Softening of tissues is a consequence of impaired blood supply to the organ that occurs during an ischemic stroke. In this case, the degree of damage to the central nervous system and the severity of the patient’s condition depend on the area of formation of the vascular blockage. Neurologists include hearing loss, decreased visual acuity, paralysis of the limbs, and impaired thinking as common complications of stroke.
Extensive cerebral infarction is the second most common cause of death. The mortality rate is increasing every year. Elderly people suffering from chronic cardiovascular diseases are at risk. Timely treatment of atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus and other ailments is the main way to prevent neurological disorders of ischemic nature.
Causes
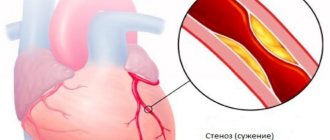
A common cause of infarction occurring in the brain is atherosclerotic damage to the cerebral arteries (about 95% of cases), which leads to thrombosis or embolism (clogging of the vascular lumen with an embolus - a particle that is not normally characteristic of blood) of the vascular bed. Cardiogenic (provoked by disruption of the cardiovascular system) embolism often becomes the cause of the development of ischemic processes.
The pathogenesis of the formation of a heart attack involves stenotic (provoking narrowing of the vascular lumen) processes and a violation of the neurohumoral regulation of the tone of the arterial wall. TIA (transient ischemic attack) is a marker indicating a high risk of developing a heart attack. Statistics show that 40% of patients with a history of TIA develop a stroke within a 5-year period. Provoking factors:
- Arterial hypertension.
- Hyperlipidemia (increased concentration of lipid fractions in the blood).
- Diabetes.
- Atrial fibrillation.
Risk factors: previous small heart attack, age over 50 years, migraine status, lack of physical activity, excess weight. At risk are patients with diseases of the hematopoietic system, heart failure, other pathologies of the heart and elements of the circulatory system, abuse of alcoholic beverages, and smokers.
Deterioration and weakening of cerebral blood flow correlates with vascular pathologies, including atherosclerosis, varicose veins located in the lower extremities, vasculitis (systemic inflammatory damage to the walls of blood vessels), vascular malformations and other diseases of the elements of the circulatory system.
Features of the organ's work
The brain is the main part of the central nervous system, responsible for providing vital functions of the body. This organ not only controls the functioning of internal organs, but also supports cognitive abilities, including thinking, memory and emotions. The medulla is formed by a huge number of cells (neurons), connected to each other using long and short processes. Clusters of cells represent brain nuclei that perform specific functions, and bundles of neuron processes form pathways connecting different parts of the central nervous system.
Maintaining brain function is impossible without a constant flow of blood. Cells need oxygen to release energy. Even a short-term delay in blood flow can lead to a heart attack because neurons are unable to store oxygen. Pathological changes appear in the first minutes after the formation of a vascular blockage. The cells of the central nervous system cannot regenerate, so rehabilitation options are limited.
First aid
The first measures to prevent irreversible consequences and death should begin in the very first minutes after the attack.
Procedure:
- Help the patient lie down on a bed or any other surface so that the head and shoulders are slightly higher than the level of the body. It is extremely important not to rub the victim too hard.
- Get rid of all items of clothing that compress the body.
- Provide maximum oxygen, open windows.
- Apply a cold compress to your head.
- Use heating pads or mustard plasters to support blood circulation in the extremities.
- Rid the oral cavity of excess saliva and vomit.
- If the limbs are paralyzed, then you should rub them with solutions based on oil and alcohol.
Video about cerebral infarction and the importance of providing proper first aid:
Classification
Doctors classify acute cerebral ischemia according to the reasons for the formation of the pathology.
Main types:
- lacunar cerebral infarction - destruction of brain tissue due to blockage of a small artery;
- a heart attack that forms due to dissection of the vessel wall, increased blood clotting, or another, more rare disease;
- atherothrombotic infarction - brain damage resulting from the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque;
- cardioembolic stroke - a delay in blood flow to neurons that occurs due to heart disease;
- unspecified cerebral infarction; this diagnosis is made when several mechanisms of ischemia are identified.
Other types of classification are focused on the area of neuronal damage. So, an infarction of the cerebellum of the brain or another part of it may occur. Determining the type of lesion is important for successful treatment and evaluation of prognostic data.
Formation mechanism
A variety of neurological disorders that appear during a heart attack are formed due to disruption of the vital activity of neurons in various parts of the brain. Immediately after the delay in oxygen supply, a cascade of biochemical changes occurs in the cells. Depletion of energy sources leads to disruption of cellular transport. The concentration of sodium in neurons increases, resulting in a large amount of water entering the cells. Cellular edema appears in the first minutes after blood flow deteriorates.
Process stages:
- The most acute stage of neuronal damage in the first 72 hours after vascular occlusion.
- An acute stage of organ damage that persists for a month.
- The period of recovery of the central nervous system, the duration of which varies from several months to two to three years.
- Residual complications that persist throughout the patient's life.
The main mechanism of damage to intracellular structures of the brain is a massive influx of calcium into neurons. Excessive penetration of this substance into cells is accompanied by the activation of enzymes that destroy the most important organelles. At the same time, the process of tissue softening is constantly progressing: toxic substances are released from one destroyed neuron, affecting neighboring cells.
Mechanism of development of cerebral infarction
Within several hours after the occurrence of an ischemic stroke, the barrier function of blood vessels is impaired. Proteins, along with fluid, enter the extracellular space, resulting in increased swelling of the organ. In the following days, severe swelling is the main cause of damage to healthy tissue. Activation of the immune system acts as a negative side factor that increases the disruption of blood flow in the vessels. In addition, in 5% of cases, cerebral ischemia is complicated by hemorrhage. Hematomas form in the organ, compressing the tissue.
How does the pathology differ from hemorrhagic stroke?
There is another type of cerebrovascular accident called hemorrhagic stroke. Dangerous neurological disorders in this case are caused by damage to the vascular wall and the penetration of blood into the intercellular space. This type of disease is also characterized by biochemical changes leading to cell death, but the mechanism of formation of the disease is different. Hemorrhagic stroke is formed due to blood thinning, traumatic brain injury, high blood pressure and other conditions complicated by rupture or thinning of the vascular wall.
Development mechanism
Acute cerebrovascular accident is formed as a result of the influence of one or more key factors.
Among them:
- Atherosclerosis. The scourge of modern man. The disease occurs in two forms. Formation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of arteries. The result of excess circulation of fatty compounds in the bloodstream.
It occurs frequently, the process is determined by nutrition, lifestyle, and to a large extent also by metabolic characteristics. Which are inherited from parents and ancestors going back generations.
Correction is carried out at an early stage, then it is more difficult to cope with the problem.
The second possible form is spontaneous vascular stenosis, arterial spasm.
As a rule, this is the result of an irrepressible craving for smoking and consumption of large amounts of tobacco. Treatment in such a situation comes down to giving up the bad habit and using drugs to normalize microcirculation.
- Thrombosis. The essence remains the same. The lumen of the vessel supplying the brain becomes insufficiently wide. However, the reason is different. If in the first case a plaque forms, which grows gradually, in this situation the cause of the disorder is a blood clot. A blood clot containing fibrin.
Depending on the size, the formation can block part of the artery or completely block it. In the latter case, a hemorrhagic form of cerebral infarction (stroke) may develop. When the vessel ruptures, hemorrhages begin, and a hematoma occurs.
This type of condition is much more dangerous than ischemic. When tissue death occurs as a result of insufficient nutrition.
- Blocking the supply of oxygen to the brain. As a rule, it is observed in cases of poisoning with toxic substances: hydrocyanic acid vapor, carbon monoxide, and under the influence of neurotoxins. All body systems suffer. Often the patient dies before a heart attack occurs. But not always.
Then the process moves progressively. Violation of trophism (nutrition) as a result of small lumen of blood vessels leads to cerebral ischemia.
How pronounced depends on what the hemodynamics (blood flow) is at the moment. The more blood flows in, the less noticeable the abnormalities are. In case of total blockage, rupture of the vessel and heavy bleeding cannot be avoided.
After a disorder of cerebral nutrition and breathing, a period of pronounced clinical symptoms begins. Depending on which area is most affected, focal symptoms develop.
There is always a neurological deficit: problems with speech, vision, hearing or intelligence. The correction is carried out as part of rehabilitation; this process lasts for years.
The end result is permanent disruption of brain activity or death of the patient. A stroke never goes away without consequences. “Correcting” the results of the violation will take a long time and persistently, not always quite successfully.
Reasons for development
Ischemic infarction is a complication of acute or chronic cardiovascular pathology. The main condition for the formation of the disease is a partial or complete disruption of blood flow through the vessels of the brain. If the decrease in blood flow is not sufficiently pronounced, the patient develops chronic ischemia of the organ.
Immediate reasons:
- Progressive atherosclerosis. A fatty plaque forms on the walls of the vessel, slowing down the movement of blood. The gradual growth of the plaque can lead to blockage of the vessel by 50-75%. Also, the plaque can break away from the vessel wall and block a small cerebral artery. Neurologists call this condition thrombotic occlusion.
- Formation of blood clots in the cardiac cavity followed by embolism of the cerebral artery. In the heart, a blood clot forms due to abnormal heart rate and inflammatory processes. Cardioembolic cerebral infarction occurs.
- Disturbance in the movement of blood in the cerebral vessels, appearing against the background of narrowing of the arteries. This mechanism of stroke formation may be associated with an increase in blood pressure and deformation of the cervical spine, complicated by compression of the arteries.
- Coagulation diseases characterized by increased blood clotting. In this case, a blood clot can form in any vessel.
- Inflammatory and infectious processes in arteries and veins. Ischemia in this case is formed due to narrowing or thrombosis of the vessel.
The listed negative factors can affect the condition of various blood vessels. In 3% of cases, patients experience a venous infarction, accompanied by stagnation of blood and swelling of brain tissue.
Treatment options
In most cases, people who have serious problems with the vessels of the carotid system require immediate hospitalization. Treatment in a hospital under the supervision of a doctor usually gives a good effect, thanks to which the patient has every chance of fully recovering and recovering.
Doctors dealing with vascular pathologies may prescribe the following medications to the patient:
- thrombolytic drugs (used for ischemic strokes to dissolve a blood clot within the first three hours after an attack);
- antihypertensive drugs (to lower blood pressure);
- anticoagulants (necessary to thin blood clots);
- drugs to lower cholesterol levels;
- means for normalizing heart rhythms;
- medicines to restore brain cells and neurons.
In some cases, the only treatment method is surgery to remove plaques and blood clots blocking the vessels.
Risk factors
Doctors consider not only the direct mechanisms of heart attack formation, but also various forms of predisposition to this pathological condition. Risk factors associated with lifestyle, individual and family history of the patient are taken into account. First of all, these are cardiovascular diseases that affect the blood supply to the brain. Metabolic pathologies that can directly or indirectly affect the functioning of blood vessels also play a huge role in the development of the disease.
Identifying risk factors plays a key role in prevention. Many negative influences can be easily eliminated by changing your lifestyle. Screening examinations are performed to detect predisposition to ischemic stroke. This is a diagnosis of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases, carried out even in the absence of any complaints from the patient. Screening is necessarily included in the medical examination program.
Lifestyle influence
The functioning of the heart and blood vessels directly depends on dietary preferences, physical activity, psychological well-being and other aspects of a person’s life.
Key risk factors:
- improper diet - excess fats and simple carbohydrates in the diet contribute to the development of atherosclerosis;
- obesity - excess fat deposition increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases;
- low physical activity - a sedentary lifestyle negatively affects the blood supply to organs and venous outflow in tissues;
- bad habits - drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking are risk factors for atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension.
All of these forms of predisposition are highly preventable. It is necessary to change your lifestyle as early as possible, since pathologies of the heart and blood vessels are increasingly being diagnosed in young people. In addition, preventing heart attacks in older people is less effective.
Medical factors
Pre-existing diseases play an important role in the development of a heart attack.
The main ones:
- increased levels of fats and fat-like substances in the blood - hyperlipidemia occurs due to consumption of junk food and metabolic disorders;
- increased blood pressure - chronic arterial hypertension increases the risk of stroke by 50%;
- heart disease, accompanied by irregular heartbeat and tissue inflammation - these are various forms of arrhythmia, endocarditis and other ailments;
- diabetes mellitus - constantly increased concentration of glucose in the blood negatively affects the condition of the vascular walls;
- unfavorable family history - if the patient’s close relatives suffered from vascular pathologies, the individual risk of stroke increases;
- brief cessation of breathing during sleep (many people suffering from sleep apnea do not have any complaints).
Almost all of these pathological conditions are much more often detected in men and women over the age of 50, so screening for cardiovascular disorders is mandatory for older people.
Causes
In fact, the reasons why one or another form of cerebral infarction develops are largely the consequences of various pathological conditions of the human body.
But among the main causes of stroke are :
- atherosclerotic changes;
- the presence of thrombosis in the veins;
- systematic hypotension;
- disease with temporal arteritis;
- damage to large intracranial arteries (Moya-Moya disease);
- subcortical encephalopathy of a chronic nature.
Smoking provokes thrombosis, so the bad habit must be forgotten if health problems are suspected.
Taking hormonal contraceptives also slightly increases the risk of cerebral infarction.
Watch the video that talks about the main causes of the disease:
Clinical picture
Symptoms of a cerebral infarction occur rapidly. First, general cerebral disorders appear, manifested by drowsiness, weakness, dizziness and short-term loss of consciousness. Later, symptoms of damage to a specific part of the central nervous system appear.
Signs of cerebral infarction
Additional symptoms:
- temporary loss of speech;
- unilateral or bilateral decrease in visual acuity;
- hearing impairment;
- paralysis of the facial muscles, manifested by an asymmetrical smile, drooping eyelid of one eye and other anomalies;
- impaired mobility of the upper or lower extremities;
- Strong headache;
- gait disturbance;
- inability to understand someone else's speech.
To quickly detect characteristic signs of illness, the patient must be asked to smile, raise both hands up and say any word.
Symptoms and signs
a stroke immediately makes itself felt: a person suddenly begins to experience unbearable headaches, which most often affect only one side, the skin of the face during an attack acquires a pronounced red tint, convulsions and vomiting begin, breathing becomes hoarse.
It is noteworthy that the seizures affect the same side of the body as the side of the brain that was affected by the stroke . That is, if the location of the lesion is on the right side, then the cramps will be more pronounced on the right side of the body and vice versa.
However, there are cases when the attack as such is completely absent , and only some time after the stroke, which the patient might not even suspect, numbness is felt in the cheeks or hands (one of them), the quality of speech changes, and visual acuity decreases.
Then the person begins to complain of muscle weakness, nausea, and migraines. In this case, a stroke can be suspected if there is a stiff neck, as well as excessive muscle tension in the legs.
Complications that arise
Negative consequences of deterioration of cerebral circulation occur already in the first days after a heart attack. Some complications resolve on their own within a few months after treatment, but a significant portion of the neurological symptoms persist.
Common complications:
- muscle paralysis, manifested by impaired mobility of the limbs, changes in gait and facial expressions;
- speech disorders and difficulty swallowing food;
- memory loss and decreased intelligence.
Many of the negative consequences of the disease are associated with a specific area of damage to the nervous system. A cerebral infarction of the right hemisphere makes it difficult to perceive objects located on the left side of the visual field, leading to the development of apathy and depression. The consequences of a cerebral infarction of the left hemisphere are more often manifested by impaired memory and intelligence.
Diagnostics
If a cerebral infarction is suspected, it is urgent to differentiate the pathology from hemorrhagic stroke and transient ischemic attack (they have similar symptoms, manifestations and complications). It is also necessary to clarify the area of the lesion (right or left hemisphere, midbrain or medulla oblongata, brainstem, cerebellum, etc.). The main diagnostic methods are:
- MRI.
- CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) analysis.
- Dopplerography.
- CT (computed tomography).
- Angiography.
During the diagnostic process, doctors must also detect concomitant diseases that could lead to the development of ischemic stroke.
Diagnostic measures
Neurologists are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of pathologies of the central nervous system. If stroke symptoms occur, the patient is hospitalized. The doctor in the emergency department clarifies complaints, studies individual anamnesis and conducts a general examination. Assessing the neurological status helps the specialist detect specific signs of impaired blood supply to the brain. Accurate diagnosis is impossible without instrumental examinations.
Cerebral artery embolism and complications of this condition are detected using computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. These highly informative visual diagnostic methods make it possible to assess the degree of damage to organ tissue. Using volumetric images of the brain, the neurologist identifies changes caused by the release of fluid into the intercellular space. Tomography is performed not only during the initial diagnosis, but also during further treatment.
Laboratory research
To establish the cause of the disease and assess the severity of the patient's condition, laboratory diagnostic results will be required. First of all, a biochemical blood test is prescribed. Blood coagulation is examined to determine the cause of blood clot formation. Metabolic disorders, such as diabetes, are also detected by biochemical blood tests.
Diagnostic methods
To identify the first pathological changes in blood vessels or to diagnose a person with an already developed and progressive disease, doctors need to conduct a series of examinations.
For an accurate diagnosis, patients may be prescribed:
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, neck, chest;
- electrocardiography;
- carotid angiography (x-ray examination with the introduction of contrast agents into the vessels);
- ultrasound examination with Dopplerography, etc.
A comprehensive examination of the vascular system of the neck, head and brain will allow the doctor to get an idea of the condition of the arteries and make a decision on the treatment of the pathology.
Treatment of cerebral infarction
A patient with signs of cerebral circulatory disorders is hospitalized in the intensive care unit. During the acute period of illness, the main task is to maintain vital functions. Drug therapy is prescribed to destroy blood clots and thin the blood. Thrombolysis drugs and other drugs are administered intravenously.
Routine therapy is carried out using intravenous solutions of electrolytes and medications to prevent the formation of new blood clots. The use of neuroprotective substances makes it possible to preserve healthy neurons. If the patient cannot swallow food on his own, feeding is performed using a feeding tube.
In the intensive care unit, the patient is constantly examined for timely elimination of stroke complications and monitoring the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment. If there is a significant decrease in the concentration of oxygen in the blood and the impossibility of spontaneous breathing, intubation is performed, followed by the connection of an artificial lung ventilation device.
Surgical measures
Invasive treatment methods are prescribed if there are appropriate diagnostic indications. Various interventions make it possible to restore cerebral circulation faster and more effectively.
Methods used:
- Intravascular thrombolysis is the administration of drugs that destroy a blood clot directly into a cerebral artery. To do this, the doctor places a catheter in an artery in the groin area, and then gradually moves the tube into the cerebral vasculature.
- Stenting is an endovascular intervention necessary to restore blood flow in a damaged artery. Using a catheter, the surgeon destroys the blood clot and expands the vascular lumen.
- Decompressive craniotomy is the creation of a small hole in the cranial vault to reduce intracranial pressure and restore cerebral circulation. This procedure reduces the risk of death in severely ill patients.
Surgical treatment shows better results in cases of delayed hospitalization and the presence of large blood clots.
Treatment
The treatment process is particularly influenced by many factors simultaneously:
- Localization of the pathological focus in the head (depending on which part of the brain and what functions were impaired, appropriate therapy is prescribed).
- The volume of the pathological focus, the prospects for its development or self-removal (here it is important whether compression of adjacent tissues occurs).
- Current condition of the patient (normal wakefulness, stupor, stupor, coma).
- Individual characteristics of the patient (age, presence of chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, relapses, micro-strokes or transient ischemic attacks in history).
The patient's likelihood of survival will depend on these factors. When edema develops and the patient is unconscious, there is a high probability of death. Modern medicine is able to cure patients in a coma, but not in all cases.
Traditional therapy includes the use of various drugs and medications. Medications allow you to maintain the functioning of vital functions at a normal level, as well as prevent the development of somatic diseases. In particular, the macropreparations and micropreparations used (depending on the indications and doctor’s prescriptions) are necessary for the following:
- Bringing basic respiratory functions back to normal (if this is not possible, doctors perform long-term artificial ventilation).
- Supporting the normal functioning of the heart and cardiovascular system as a whole, adjusting blood pressure levels if indicated (especially important for elderly patients).
- Regulation of homeostasis processes (glucose levels, acid-base balance, water-salt balance, etc.).
- Maintaining normal body temperature (allows an increase to no more than 37.5o C).
- Reducing the size of swelling in the brain structures (if it develops). The ideal is to completely get rid of it in the first few weeks of treatment.
- Elimination of manifestations and symptoms of the disease as they appear.
- All necessary preventive measures that will prevent complications from occurring (bedsores, thrombosis, pneumonia, fractures, pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, etc.).
If the patient has sclerotic and atherosclerotic changes (which usually occurs against the background of problems with lipid metabolism), then during his stay in the intensive care unit or hospital the patient is prescribed statins. Treatment with their help should be carried out both after discharge during the recovery period and during rehabilitation (regardless of whether manifestations of sclerosis and atherosclerosis remain or not).
During therapy, it is especially important to take medications (antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, etc.) aimed at restoring blood flow mechanisms in the pathological area. But often even the most powerful drugs cannot give the desired effect.
- The issue of using anticoagulants is particularly acute. When using them, it is necessary to constantly monitor the degree of blood clotting in the patient, as well as to prevent the development of a number of complications.
- Antiplatelet agents (the most famous drug of the group is Aspirin) are one of the most important therapeutic agents in the treatment of cerebral infarction.
In each individual case, the drugs for treatment are selected by the doctor strictly individually. In the situation of cerebral infarction, there are no universal solutions that could suit most patients. Therapeutic tactics are selected in accordance with many criteria.
Considering the high severity of developing complications, the special location of the pathological focus and other factors, doctors may also decide to perform an operation. Surgical intervention for ischemia is a common solution all over the world, therefore, if indicated, surgery is mandatory. Timely surgery under appropriate conditions can reduce mortality.
Treating cerebral infarction at home using folk remedies is strictly prohibited.
Forecast and recovery
Cerebral infarction caused by thrombosis of cerebral arteries or vascular stenosis ends in the death of the patient in approximately 20% of cases. At the same time, the provision of surgical and therapeutic care in the first hours after the onset of the disease is characterized by a relatively favorable prognosis. Further quality of life depends on the results of rehabilitation therapy.
Rehabilitation should be aimed at restoring lost functions of the nervous system and preventing the development of additional complications. A neurologist and a rehabilitation specialist work with a patient who has suffered a stroke. Therapeutic exercise helps restore the functions of the musculoskeletal system. Electromyostimulation has a good effect on muscle function. To correct cognitive and emotional disorders, the patient may need to work with a psychotherapist.