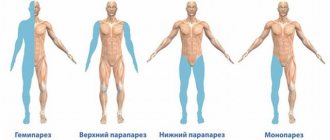
Tetraparesis is a pathological disorder characterized by decreased motor activity of the arms and legs. The long course of this pathology leads to changes in the condition of the limbs, the occurrence of contractures, muscle atrophy, severe pain or complete loss of motor functions.
The mechanism of development of the disease, as a rule, is formed as a result of damage to the central and peripheral nervous system.
Tetraparesis occurs as a result of pathological processes in the brain stem, hemispheres of the brain or in the cervical spine. In a more acute form, it occurs after a spinal injury, after an internal cerebral hemorrhage, for example, after a stroke, or due to abnormal metabolic processes in the brain.
Due to damage to the upper cervical vertebrae in the acute period of injury, flaccid paralysis of the limbs and impaired respiratory and pelvic functions occur. In case of injury in the cervical spine, death can occur, since vital structures of the body are disrupted.
Factors provoking paresis
Tetraparesis should be classified into two groups:
- acquired - occurs as a result of spinal injury, after cerebral hemorrhage, with the development of a malignant or benign formation, encephalitis, polyneuritis;
- congenital - occurs as a result of complications during pregnancy.
Disruption of the central or peripheral nervous system, which leads to the development of this symptom, develops under the influence of such factors:
- cerebral palsy;
- cervical spine injury;
- polyneuropathy;
- Landry-Guillain-Barre syndrome;
- Krabbe disease;
- occlusion of cerebral arteries;
- myasthenia gravis;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- dropsy of the brain;
- complications of surgery on the brain or spine.
Diet
Patients who do not have impaired swallowing can take regular food and sit on a common table. If a child can chew and swallow independently, his diet should consist of vegetables, fruits, eggs, nuts, meat, fish, cereals, but prepared food must be crushed (pureeed) to make it easy to swallow.
It is necessary to ensure that the diet contains a sufficient amount of protein products (meat, fish, cottage cheese, cheese and other dairy products, eggs) and complex carbohydrates, since rehabilitation treatment requires an increased supply of protein and energy. Fats must be present in the diet - butter and cold-pressed vegetable oils (olive, sesame, flaxseed).
Severe swallowing disorders require special nutrition adapted to the child’s characteristics, since problems with eating gradually lead to a deficiency of essential substances and energy. In such children, protein deficiency and energy deficiency progress. If swallowing continues, the child is additionally given formula through a tube (sipping method). Modern enteral nutrition is a mixture with an optimal composition of nutrients, vitamins, macro- and microelements.
There are dry mixtures ( Nutrien standard ), which need to be prepared by diluting with water, or ready-made mixtures - Nutrizon standard , Nutrien standard , Nutrizon energy and others. Children 3-5 years old with nutritional deficiencies are prescribed formulas for premature infants up to one year old. In severe cases, patients need special nutrition - enteral tube or parenteral.
Varieties of symptoms
Tetraparesis occurs:
- Spastic . It manifests itself as increased muscle tone in the arms and legs, which leads to stiffness of movement. This mechanism may occur due to increased intracranial pressure, for example, with cerebral palsy or encephalopathy. As a result, depletion of the cerebral cortex may develop, which contributes to mental underdevelopment.
- Central . Occurs when both hemispheres, the brain stem, or the upper spinal cord are damaged.
- Reflex . It is characterized by hypertonicity and hyperreflexia in the limbs in the presence of normal muscle strength. This condition is usually accompanied by pathological reflexes.
- Mixed . There is varying intensity of muscle tone in the arms and legs. In other words, hypotonicity and hypertonicity can occur simultaneously.
- Lethargic . There is weakness and severe partial loss of sensation in the limbs.
Diagnostics
A set of laboratory and instrumental studies helps doctors establish the root cause and confirm the preliminary diagnosis – tetraparesis. After a thorough history collection - when the patient felt weakness in the limbs, what preceded this, previous illnesses, harmful factors in the workplace, the doctor will conduct a visual examination of the person and select the optimal diagnostic procedures for him.
In most cases, diagnosing tetraparesis involves assessing information from the following examinations:
- radiography of bone structures of the extremities;
- ultrasound examination of soft tissues, as well as internal organs;
- electroneuromyography;
- blood tests - general with biochemical;
- PCR studies of human infections;
- myelography;
- according to individual needs - if the information is unclear or dubious, a computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging scan will be required.
In some cases, for example, with severe tetraparesis, a specialist can give his medical opinion at the initial consultation, after assessing the reflexes. However, in order to establish the true provoking factors, it will be necessary to perform all of the above examinations.
Clinical picture
With cerebral palsy, which is most often accompanied by spastic tetraparesis, the child’s cerebellum is damaged.
As a result, the child cannot hold his head up, sit down, stand, or generally move around without assistance.
Also, depending on the location of the brain lesion, mental retardation and decreased intelligence are detected.
Very often, tetraparesis is accompanied by other congenital diseases - dropsy of the brain and underdevelopment of the bone structure of the skull.
General signs of pathology include:
- pronounced decrease in motor function of the limbs;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- change in the shape of the limbs;
- dysfunction of the pelvis;
- muscle spasticity;
- muscle pain;
- complete loss of activity in the arms and legs after some time;
- irritation of the spinal diaphragm, and as a result - hiccups, shortness of breath, cough.
Prevention
Considering that the main cause of paresis in children is cerebral palsy, its prevention includes:
- improving the health of adolescents and women of childbearing age;
- treatment of sexually transmitted infections when planning pregnancy;
- regular examinations and timely detection of pathology in pregnant women;
- timely diagnosis of coagulopathies in expectant mothers;
- prevention of premature birth;
- adequate obstetric care;
- proper resuscitation, adequate care and use of hypothermia in newborns, timely treatment of hyperbilirubinemia .
In adults, the following are important:
- prevention of injuries (traumatic brain injuries and spinal injuries);
- timely treatment of hypertension , which, if left untreated, is complicated by cerebral hemorrhage;
- exclusion of alcoholism and poisoning by alcohol substitutes.
Spasticity - as a special form of paresis
The most common form of this condition is spastic tetraparesis. Characterized by a decrease in motor activity.
In this case, an increase in muscle tone occurs, and it is because of this that stiffness and “disobedience” of the arms and legs appear, as well as severe painful sensations.
After some time, spasticity leads to pathological changes in the joints, deformation of the limbs, and in some cases even the torso.
There is a dysfunction of not only skeletal muscles, but also smooth muscles, which in turn leads to disruption of respiratory and pelvic functions.
Spastic tetraparesis is accompanied by other signs of damage to the nervous system. Intellectual impairment of various degrees is observed in almost 90% of all cases.
In addition to these symptoms, there are signs of damage to the cranial nerves, against the background of which hearing, vision, and strabismus occur. Also, in rare cases, epileptic activity may be diagnosed, accompanied by seizures.
Spastic tetraparesis is most severe in the presence of double hemiplegia - significant damage to the upper extremities. This syndrome can be accompanied by oligophrenia - a severe degree of debility, as well as imbecility and idiocy.
Spastic tetraparesis with double hemiplegia is characterized by the following symptoms:
- impaired motor function of the arms and legs;
- asymmetry of muscle tone;
- delayed speech and mental development;
- severe damage to the muscles of the face and the muscular girdle of the upper half of the body.
In some cases, a type of disease such as triparesis may develop, i.e. one limb remains completely healthy and functions normally.
With cerebral palsy, spastic tetraparesis is diagnosed in two forms - lower paraparesis and tetraparesis in more than half of the cases. Spastic syndrome develops against the background of damage to extrapyramidal fibers in the brain.
Due to this, there is a sharp weakening of inhibitory control over the segmental apparatus of the spinal cord. This accompanies the activation of the pathological stretch reflex. It provokes an increase in muscle tone, because in response to stretching, the muscles begin to contract.
Consequences and complications
With paralysis and paresis, complications arise from the musculoskeletal system:
- joint contractures;
- pathological attitudes;
- arthrosis;
- formation of vicious poses;
- muscle atrophy.
Joint contractures are secondary and their severity depends on the severity of the disease and the age of the patient. At first, contractures develop reflexively (from muscle contraction against the background of prolonged excitation), and then become permanent due to degenerative changes in the muscles, ligaments and tendons. The combination of various contractures forms a vicious posture in patients. Motor installations are manifested by a forced position of the limb due to excessively high muscle tone. An example of a propulsion system is the equinus position of the foot, which is formed due to the traction of the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. With Little's disease, the patient often falls and therefore receives injuries (hematomas, fractures).
Complex of therapeutic measures
Treatment of tetraparesis should be comprehensive and carried out in a hospital setting. Conservative, neurosurgical, orthopedic methods and rehabilitation are used.
Therapy is carried out to achieve the following goals:
- reduction of spasticity;
- prevention of dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system;
- formation of the correct motor stereotype.
Conservative treatment primarily includes two main aspects:
- Drug therapy - prescribed drugs, for example, Baclofen and Botulinum toxin, help reduce the spastic effect, resulting in increased impulse conduction and improved metabolic processes in the brain, while increasing the number of passive movements of the limbs.
- Physical therapy – focuses on movements, exercises and poses that strengthen muscles.
The treatment package also includes:
- reflexology;
- hirudotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- exercise therapy;
- massage;
- gymnastics on special simulators;
- kinesitherapy.
Surgery
For more effective correction of spastic tetraparesis, surgical treatment is required. The operation is performed to restore the functions of a specific damaged area.
An orthopedic procedure corrects contractures and stretches muscles. Plastic surgery of muscles and tendons is also performed. This correction method brings very good results.
Forecast
Functional recovery depends on the severity of the damage to the nervous system. In this regard, compensation of neurological disorders, partial compensation, or the formation of persistent syndromes are ultimately possible.
A quarter of patients move independently, while the rest cannot do without walkers or wheelchairs. With good treatment, children with paraplegia or hemiplegia survive to adulthood and live almost normal lives. The effectiveness of rehabilitation for spastic diplegia depends on how severe the motor impairment is and how much intelligence is preserved. If active rehabilitation has been carried out since early childhood, a person can acquire a profession. If mental abilities are preserved, then they are well adapted in social life. In the presence of epileptic seizures, the prognosis worsens.
With tetraplegia, accompanied by impaired swallowing and the need for feeding through a gastrostomy tube, life expectancy is sharply reduced. Hereditary diseases affecting the pyramidal system ( Strumpel's disease ) progress slowly and have a favorable prognosis for life. However, the ability of patients to work is limited at the onset of the disease, and is lost as it progresses.
Rehabilitation period
Of great importance in the treatment of spastic tetraparesis, in particular with cerebral palsy, are rehabilitation measures, the task of which is to improve the physical condition of the child and adapt him to living conditions as much as possible. Rehabilitation includes the following methods:
- Occupational therapy – develops motor skills and sense of touch, regulates movement and orientation. Fine motor skills also develop separately. In occupational therapy, play methods, techniques of physical contact, holding, and copying are used.
- Speech therapy exercises . The purpose of the classes is to develop correct pronunciation. Special methods can eliminate the problem of non-verbal communication and swallowing reflex disorders. Also, thanks to these programs, coordination and hearing are improved, and previously formed speech disorders are eliminated.
- Aquatherapy . Helps relieve pain symptoms by relaxing spastic areas, as well as strengthen muscles. This treatment has a beneficial effect on the emotional state of the child. The procedure is carried out by lowering the child into the water using special chairs. The water temperature should be approximately 35 degrees.
- Hippotherapy . A very effective method in which the horse serves as the therapeutic agent. This procedure stimulates motor reflexes and increases activity. Sometimes therapy gives very good results when the child gradually learns to sit in the saddle and control a horse independently.
Treatment tactics
Complex therapy should be started immediately from the moment the preliminary conclusion of a specialist is confirmed - tetraparesis has actually developed in a person. Of course, in a hospital setting there are more opportunities to combat pathological symptoms. Therefore, for children, treatment of tetraparesis is preferred in neurological departments of hospitals.
The stages of alternating medicinal effects on the nervous system, physiotherapeutic procedures and massage replace each other. It is necessary to understand that it will take years of hard work to restore active movements. This is especially true for pediatric practice.