ACVA ICD 10 code is a classification on the basis of which the most accurate diagnosis is made, indicating the specific area of cerebrovascular accident. This scale is accepted all over the world and helps the patient to seek help with a ready-made diagnosis in a clinic in any other country. In this case, the doctor at the foreign medical center will fully understand the previously made diagnosis and quickly select the necessary therapy.
In this scale, there are 10 types of diseases with codes from I 60 to I 69. Let's consider each type separately.
Description of the disease
An ischemic stroke occurs due to obstructions in the vessels that supply blood to the brain. Such obstacles can be fatty deposits and blood clots. The disease is based on 3 pathologies associated with circulatory disorders - ischemia, stroke, and heart attack.
Reference: ischemia is the insufficiency of blood supply to an area of tissue or organ, and stroke is the death of brain tissue due to impaired blood flow due to ischemia or rupture of blood vessels.
What is ONMK according to ICD 10?
Receive a free consultation at our center: Request a call back Send us your medical documents Our medical team prepares a preliminary proposal for you You choose the best option For yourself On the date agreed upon with you, we will organize an appointment at the clinic You (with our help) purchase tickets, book a hotel , order a transfer, an interpreter and begin treatment abroad. We help you at all stages of diagnosis and treatment, as well as after your return home
ACVA ICD 10 code - allows you to make an accurate diagnosis, which will take into account the exact affected area. This gradation corresponds to the international level, which facilitates the transfer of patients between clinics in different countries, and in the event of discharge abroad, the doctor will immediately read the report and prescribe effective treatment.
According to this classification, there are 10 types of pathologies corresponding to the codes I 60 - I 69. Let's talk about them in more detail.
Strokes
This term refers to rupture of an artery followed by hemorrhage. This is a very dangerous condition in which the cerebral cortex is damaged by a growing hematoma with subsequent loss of function. According to ICD 10, there are three codes corresponding to stroke:
- I 60 - indicates hemorrhage into the space that is located between the membranes of the brain, called subarachnoid. According to further gradation, it includes five varieties (0-4) depending on the vessel whose rupture caused the stroke. The next digit is written after the period;
- I 61 – damage to parenchymal tissue. This means that the vessel has ruptured inside the hemispheres or brain stem, damaging the white or gray matter. Further classification also includes five types depending on the location of the lesion;
- I 62 – stroke, the localization of which could not be identified. The doctor is sure that the patient has a hemorrhage, but it is impossible to determine the location and area of the lesion for a number of reasons. Includes three subclasses.
The consequences of stroke of the hemorrhagic type are described in the headings of ICD 10 - these are residual effects after hemorrhage, which often lead to disability. These are very dangerous conditions, during which there is a high mortality rate; about a third of patients die in the first 5 years of life.
Heart attacks
This is an acute condition characterized by blockage of the lumen of the artery or its sharp spasm, followed by impaired circulation and the appearance of an area of tissue necrosis (scientifically called necrosis).
Code 63 corresponds to the ICD 10 code for stroke of ischemic type, the gradation is as follows:
- thrombosis of arteries in the neck and base of the skull - corresponds to the number 0, embolism - 1, unspecified rupture - 2;
- thrombosis of cranial arteries - coded 3, embolism - 4, unspecified etiology - 5;
- vein rupture – 6;
- unknown and other heart attacks are marked with numbers 8 and 9.
All of the listed sub-clauses of the classification are placed after the dot; if, for example, the veins are damaged, the code will look like this: I 63.6. Heart attacks are very dangerous; according to statistics, about 80% of all strokes are ischemic. Such patients are hospitalized in the intensive care unit and are under the supervision of a doctor.
Blockages and spasms of blood vessels without heart attack
In clinical practice, there are often cases where disruption of blood flow does not cause necrotic changes. According to ICD 10, such conditions are included in two large groups:
- I 65 – includes damage to the carotid, vertebral and basilar arteries emerging from it;
- I 66 – this code indicates spasm or embolism of the cerebral and cerebellar arteries.
Nerve cells are very sensitive and quickly die due to oxygen starvation and lack of nutrients. But the brain is structured in a unique way; it contains the so-called “Circle of Willis” - these are “spare” connections between arteries, thanks to which blood can flow through bypass vessels. That is why sometimes obstruction does not lead to cerebral infarction.
Let us note the main reasons that can create an obstruction in the artery:
- Spasm is a narrowing of a vessel due to contraction of its muscles, resulting in a decrease in its capacity. Usually the cause is neurogenic;
- Narrowing - differs from the previous version by violating the anatomical integrity of the vascular wall in a certain area. Such changes are irreversible;
- Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot on the artery wall, which gradually increases in size and creates an obstruction;
- Embolus - circulates along with the blood, enters a vessel of a smaller caliber and causes its blockage. Usually this is a detached blood clot or atherosclerotic plaque.
The listed reasons often lead to cerebral infarctions or the development of severe conditions after stroke, having a certain code according to ICD 10.
Remaining classification
We have listed the main gradation of cerebrovascular disorders, which are often encountered in clinical practice. Let us note the remaining pathologies, concomitant diseases and conditions after stroke, which correspond to their code according to ICD 10:
- I 64 – set when it is not possible to distinguish hemorrhage from ischemia;
- I 67 – cerebrovascular pathologies not related to strokes and heart attacks;
- I 68 – cerebrovascular accident in other diseases;
- I 69 – complications of stroke.
Evaluate the quality and detail of the information
Loading…
Source: https://Evexia.ru/nauchnaya-rabota/poleznye-sovety/chto-takoe-onmk-po-mkb-10/
Spinal stroke
A spinal stroke is a rare but dangerous pathology in which there is a disruption of the blood supply to the spinal cord.
When compared with cerebral stroke, spinal stroke is less likely to cause death, but often causes severe disability . According to the frequency of detection among other diseases, spinal stroke is diagnosed in 1% of cases.
The development of pathology begins with pain in the lumbar region, lameness, and problems with urination. Then the limbs become numb and their sensitivity is lost.
Types by TOAST
Currently, the generally accepted classification of pathogenetic subtypes of ischemic stroke is the TOAST classification.
There are five types of ischemic stroke: due to atherosclerosis of large arteries (atherothromboembolic), cardioembolic, due to occlusion of a small vessel (lacunar), stroke of another established etiology, and stroke of unknown etiology.
- Atherothrombotic attack. It is provoked by atherosclerosis of a medium or large artery.
- Lacunar. Occurs against the background of hypertension, diabetes, affecting small arteries.
- Cardioembolic. It becomes a consequence of blockage of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) by an embolus.
- Ischemic stroke , developing as a result of rare causes - increased blood clotting, hematological diseases, dissection of the arterial wall, etc.;
- Of unknown origin. Pathology occurs for unknown reasons.
Heart attacks
A heart attack develops against the background of blockage or rapid narrowing of the main vessel, which leads to disruption of blood flow and death of entire sections of organs - necrosis.
Number 63 according to the ICD 10 code of ischemic stroke contains the following additional classification:
- 0 – blockage of an artery by a thrombus in the neck and near the skull, 1 – a cluster of emboli, 2 – a rupture in an unspecified area;
- 3,4,5 – blockage of an artery in the area of the skull with a thrombus, emboli and unknown accumulation, respectively;
- 6 – violation of the vein wall;
- 8, 9 – unspecified and other types of heart attacks.
These clarifications in the form of numbers are indicated through a dot. Let’s say that if a patient has venous bleeding, the doctor diagnoses I63.6. Heart attacks account for about 80% of all ischemic cerebrovascular accidents. If a heart attack is detected, the patient is sent to the intensive care unit for intensive monitoring by specialists.
Periods
A stroke, as impaired blood circulation in an area of the brain, is distinguished by the timing of its onset.
In total, doctors distinguish 5 stages of stroke:
- the most acute period – the first 72 hours;
- acute period – up to 28 days;
- early recovery period – up to 6 months;
- late recovery period – up to 2 years;
- residual effects – after 2 years.
In most cases, ischemic strokes occur suddenly and develop rapidly, causing the death of brain tissue in a period from a couple of minutes to a couple of hours.
Classification by affected area
The classification of cerebral infarction also takes into account the location of the lesion. Taking into account localization, the following strokes are distinguished.
Right-handed
The consequences affect the motor functions of the left side of the body, with a poor prognosis for recovery (sometimes up to paralysis). Psycho-emotional indicators remain almost normal;
Left-handed
Speech and the psycho-emotional sphere suffer, but motor functions can be fully restored . After such a defeat, the patient can only use simple phrases and individual words; he cannot form or perceive complex ones.
Cerebellar
The result is impaired coordination of movements, nausea to vomiting, and dizziness. After 24 hours, the cerebellum presses on the brain stem, the person’s facial muscles become numb, coma often begins, and death often occurs;
Extensive
It is detected against the background of the cessation of blood supply to a large area of \u200b\u200bbrain tissue. Swelling appears, then paralysis with a poor prognosis for recovery.
Important: despite the fact that stroke occurs more often in older people, there is a risk of the condition occurring at any age.
Therefore, prevention and a healthy lifestyle come to the fore.
Minor ischemic stroke
A minor stroke, or microstroke, is characterized by the disappearance of pathological symptoms (paresis, speech and vision impairment) within 3 weeks.
After this period, the person can return to their normal lifestyle.
The causes of the condition are the same as with a regular stroke - atherosclerosis plaques, blood clots in blood vessels, hemorrhages . It is important not to ignore a small stroke, as it signals problems with the blood vessels of the brain. If you do not take action, you can expect a real stroke in the future with the consequences described above.
You can differentiate a micro-stroke from a hypertensive crisis by numbness of the limb, a feeling of pins and needles, and blurred speech . Such symptoms will not be detected during a hypertensive crisis. If the symptoms described above disappear within 21 days, we can confidently say that the person has suffered a minor ischemic stroke.
In children
An acute disruption of the blood supply to the brain in a child leads to a stroke. Precursors and symptoms of pathology in children differ from similar signs in adults. A problem can be suspected by squint, rapid eye movements, instability of body temperature, convulsions, tremors of the limbs, hypo- or hypertonicity of muscles.
A sharp decrease in blood pressure, hearing problems, nausea to vomiting, painful headaches, dizziness - all this may indicate a stroke in a child. In infants, it is more difficult to identify the pathology, but there are several signs - the baby often cries, changing his voice, or tenses his facial muscles, in addition, he reacts sharply to light and sound.
Ischemic stroke with hemorrhagic impregnation
The hemorrhagic form is considered the most severe type of stroke, with a mortality rate of up to 90%.
The condition begins against the background of a hypertensive crisis, stress, and excessive physical exertion. If ischemic stroke is more often detected in old age, then hemorrhagic stroke is detected in young and mature people, more often in males.
Great psycho-emotional stress causes apoplexy even in 18-year-old people.
A stroke with hemorrhagic impregnation is otherwise called diapedetic hemorrhage. In this condition, fluid effusion from damaged vessels into the surrounding space is observed.
The fluid accumulates and permeates the brain tissue, resulting in reactions that provoke brain swelling and compression of the nervous structures to a critical state.
What does ONMK mean according to ICD 10? – Evexia
ACVA ICD 10 code is a classification on the basis of which the most accurate diagnosis is made, indicating the specific area of cerebrovascular accident.
This scale is accepted all over the world and helps the patient to seek help with a ready-made diagnosis in a clinic in any other country.
In this case, the doctor at the foreign medical center will fully understand the previously made diagnosis and quickly select the necessary therapy.
In this scale, there are 10 types of diseases with codes from I 60 to I 69. Let's consider each type separately.
Blockage and narrowing of blood vessels without heart attack
Sometimes it happens that problems with blood flow do not lead to tissue necrosis. In the ICD 10 scale, these pathologies occupy two codes with many additional clarifications:
- I 65 – this code describes a disorder in the vascular network of the vertebral, carotid and basilar arteries;
- I 66 – this describes vasospasm or accumulation of emboli in the arteries of the brain or cerebellum.
The tissues of the nervous system instantly react to any lack of nutrition and die. However, the brain, a very complex and sophisticated structure, has an additional vascular network that can deliver blood bypassing damage. This grid is called the “Circle of Willis”. If the escape route is activated, cerebral infarction does not occur.
There are several conditions that can cause blood flow in your arteries to slow.
- Spasm (or vasospasm) is a decrease in the lumen inside a vessel due to increased muscle tone, which leads to a decrease in blood flow. This deviation is neurogenic.
- Narrowing - the wall of the vessel changes in a specific area, as a result of which its tightness is broken.
- Thrombosis – blood clots accumulate on the inner arterial wall and over time can cause slow blood flow.
- Emboli are compactions of various substances that move through the circulatory system with the bloodstream and can cause congestion in small vessels. As a rule, plaques or blood clots act as emboli.
The above conditions often provoke the development of cerebral infarction or complex conditions after stroke, having a certain code according to ICD 10.
Clinic
The symptoms of an ischemic stroke usually manifest themselves abruptly, literally in a matter of seconds or minutes. Rarely, signs appear gradually over a couple of hours or days. The clinical picture depends on the location of the brain damage.
This may be blindness in one eye, weakness or paralysis of a limb, inability to understand the speech of others, or inability to speak.
There may also be double vision, body weakness, disorientation in space along with dizziness.
Important! If the symptoms listed above occur, you should immediately call an ambulance - the sooner help is provided, the more favorable the prognosis.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures aimed at making a diagnosis are reduced to the following examinations:
- taking an anamnesis, physical and neurological examination, identifying concomitant diseases that can provoke ischemic stroke;
- laboratory tests (coagulogram, blood biochemistry, lipid analysis);
- ECG;
- blood pressure measurement;
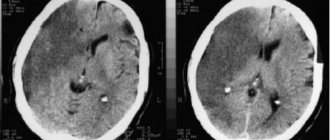
- CT or MRI of the brain to identify the location of the lesion, size, period of formation.
Diagnostics is aimed at determining the affected area, differentiating it from epilepsy, tumor, hemorrhage and other diseases with a similar clinical picture.
Treatment
Therapy is aimed at maintaining the basic functions of the body (breathing, heart and blood vessels).
If cardiac ischemia is detected, antianginal drugs are prescribed, as well as drugs to improve the pumping function of the heart, antioxidants, glycosides, etc.
Procedures are performed to prevent swelling and structural changes in the brain.
Treatment should restore blood circulation to the affected area, support metabolism and prevent damage to brain tissue. It can be medicinal, non-medicinal, or surgical. Within a couple of hours after a stroke, thrombolytic therapy is administered, which can restore blood flow to the brain.
Patients are prescribed a special diet that excludes fatty foods, sugar and salt, flour and smoked foods, canned food and marinades, ketchup, eggs, and mayonnaise. The emphasis is on fruits and vegetables, vegetarian soups, and dairy products. Bananas, dried apricots, citrus fruits, apricots are useful.
Remaining classification
Above is a key classification of problems with blood flow in the brain, which reflects the most commonly diagnosed conditions. Let's consider what other cases, diseases and complications of stroke there are, which are covered by separate codes on the ICD 10 scale:
- I 64 – placed if the clinical picture is unclear and the patient has symptoms of both an ischemic attack and hemorrhage.
- I 67 – the disease is associated with impaired blood circulation in the brain, but is neither a heart attack nor a stroke.
- I 68 – disturbance of blood flow in the brain as a consequence of another disease.
- I 69 – complications after cerebrovascular accident.
Recovery
Rehabilitation after a stroke includes neurological therapy, sanatorium treatment, and observation in a dispensary. The objectives of rehabilitation include restoration of functions (speech, movements), social and mental assistance, and prevention of complications. Taking into account the course of the disease, the following regimes alternate:
- Strict bed rest , excluding active movements.
- Moderately wide, allowing independent turning in bed and sitting up.
- Ward . Involves moving around the ward, basic self-care (eating, washing, dressing).
- Free.
The duration of each regimen depends on the severity of the condition and the degree of neurological defects.
Consequences and prognosis
After a stroke, there are various complications, from minor to very severe.
The most common consequences are listed below:
- mental disorders. We are talking about depression, fear of being a burden, disabled. The patient may become fearful or aggressive, the mood changes dramatically;
- impaired sensitivity of the face and limbs . Nerve fibers need more time to recover than motor muscles;
- movement disorder. The limbs may not fully return to normal. Because of this, difficulties arise when dressing, holding cutlery, and walking (you will have to use a stick);
- cognitive impairment. Consequences manifest themselves in the form of forgetfulness (your name, telephone numbers and addresses, childish behavior);
- speech disorder. The patient has difficulty finding words and sometimes expresses himself incoherently;
- impaired swallowing. A person chokes on solid and liquid food, which can lead to aspiration pneumonia and sometimes death;
- impaired coordination. Manifested by unsteady walking and dizziness. Possible fall due to sudden movement or turn;
- epileptic seizure. Occurs in 10% of patients after a stroke.
The prognosis depends on the degree of damage to brain tissue, the type of stroke, proper treatment, age and concomitant diseases.
Symptoms of acute cerebrovascular accident
Before the onset of stroke, precursors may appear in the form of short-term neurological disorders. In 75% of cases, an ischemic episode occurs during sleep. Symptoms appear over several minutes or hours and may gradually increase. An increase in blood pressure is typical on the first day of the disease. Patients are concerned about the following complaints: headache (90%), weakness (75%) and/or numbness (70%) in one half of the body/limbs, decreased vision (30%), speech impairment (45%). 15% of patients may deny the presence of weakness/numbness in the limbs.
A neurological examination reveals a general cerebral syndrome, contralateral hemiplegia, hemianesthesia, homonymous hemianopsia, adversion of the head and concomitant deviation of the eyes, central paralysis of the face, tongue on the contralateral half of the lesion, motor-sensory aphasia, alexia, acalculia. Anosognosia, a disorder of the body diagram, is determined by damage to the non-dominant hemisphere.