Pinchuk Elena Anatolyevna
Deputy chief physician for medical work, kmn, neurologist, doctor of physical and rehabilitation medicine
Kritskaya Olga Pavlovna
Neurologist, highest category
Maltseva Marina Arnoldovna
Neurologist, specialist in the field of extrapyramidal pathologies, doctor of the highest category
Shabunina Ekaterina Mikhailovna
Neurologist, category 2
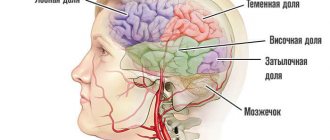
One third of the total mass of the human cerebral hemispheres is in the frontal lobes. If blood circulation is disrupted in this particular part of the brain, then, first of all, all cognitive (cognitive) processes suffer.
The main causes of impaired blood flow in the vessels of the frontal lobes of the brain are exacerbations of hypertension, atherosclerosis, some congenital pathological diseases of blood vessels, poor blood clotting, and a tendency to thrombus formation. All this leads to a stroke. Depending on its mechanism of action, a stroke can be ischemic or hemorrhagic. Further, in turn, the stroke leads to the development of frontal syndrome. It is important to note that stroke is not the only cause of this disease. However, symptoms may
Features of damage to the right hemisphere of the brain
A right-sided accident, unlike a left-sided impact, has a longer recovery period. With the help of the right hemisphere, a person is able to navigate in space, perceive the world around him, process familiar information, as well as feel and touch.
Thrombosis, embolism and significant spasm of cerebral vessels in the right hemisphere completely or partially paralyze the left side of the body. Short-term memory is impaired - the patient remembers events of the past well, without recording what is happening in the present.
IMPORTANT! The center of speech is located in the right hemisphere of left-handers, so after suffering a stroke they often lose the ability to communicate.
With an ischemic stroke of the right hemisphere, patients lose the feeling of their limbs, do not identify them as parts of their body, or it seems to them that they have more arms and legs.
Vision disorders
ACVA may be accompanied by partial or complete loss of vision. In the first case, blind spots (spots) arise, in the second - blindness. Symptoms depend on the location of the lesion.
Human vision is normal and with cataracts
Cataract is a clouding of the lens, in different parts of which opaque spots appear, reducing the clarity of vision. Problems with blood vessels (atherosclerosis), which become the cause of stroke, can lead to disruption of the nutrition of the lens, creating conditions that predispose to the occurrence of cataracts. This, however, is not the main reason. The exact mechanism of cataract occurrence has not been reliably established.
Clouding of the lens leads to blindness. In the early stages, cataracts can be treated conservatively. This allows you to slow down its progression, but sooner or later surgery becomes inevitable. A radical method of treating cataracts is lens replacement.
Another possible consequence of a stroke is visual hallucinations. Damage to the occipital lobe, the formation of sclerosis or cysts in this area may be accompanied by irritation of the nerve centers of the visual analyzer. The result is hallucinations. They may disappear on their own with treatment that improves blood flow and recovery processes in the brain. If hallucinations are severe, tranquilizers may be prescribed. We should not forget that stroke can also lead to mental disorder. Its symptoms are also often hallucinations.
Causes
The factors leading to a stroke in either hemisphere are identical.
Factors that provoke stroke:
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- obesity;
- increased blood cholesterol levels;
- physical inactivity;
- taking combined oral contraceptives;
- emotional and physical overload;
- chronic diseases of the heart, blood vessels and kidneys.
Often, ischemic stroke of the right hemisphere is preceded by traumatic brain injury and congenital or acquired aneurysms of the brain vessels.
What is ONMK?
Acute cerebrovascular accident (ACVA) is a broad concept that includes stroke and transient events (TIA, microstroke). Mention of attacks dates back half a millennium BC. e. Although the disease has been known since ancient times, it has never been managed. The main cause of the disorder is vascular pathology. Few people pay attention to their condition, so the number of victims is growing year by year.
A stroke occurs suddenly. It manifests itself as focal or cerebral neurological symptoms – cerebrovascular pathology. Translated from Latin, insultus means blow, attack. In fact, the disease, before manifesting itself in an acute form, warns about itself in advance:
- short-term attack (TIA, hypertensive cerebral crisis);
- headaches;
- numbness of the limbs;
- a kind of visual impairment.
Remember the proverb: if only I knew where to fall, I would have laid out straws. A stroke is just such a case: the body signals, lets you know, but few people take the warnings with due seriousness. For which he subsequently pays with an insidious illness.
Cerebrovascular pathology is a change, lack of oxygen, leading to an ischemic attack, microstroke or stroke.
Diagnostics
Typical symptoms of a right-sided stroke are impaired motor function and difficulty swallowing. Nervous regulation in the human body has a “crosswise” principle, so the occurrence of a right-sided brain catastrophe leads to paralysis of the left side of the body. It is worth noting that the victim’s left arm may be characteristically bent.
It is difficult for such a patient to walk, paralysis, numbness and loss of sensation on the left side are possible. The patient has difficulty eating, the swallowing reflex is impaired, and swelling of the left side of the face may also be present.
IMPORTANT! In case of a stroke, the doctor has only 4.5 hours to save the patient’s life, so it is worth knowing the algorithm of actions for the preliminary diagnosis of this disaster.
To make sure you have a stroke, you need to ask the person:
- raise both arms at the same time;
- smile;
- say your name.
Signs of a right-sided stroke:
- I can’t smile, the left corner of my mouth is drooping.
- Unable to raise both arms at the same time, left hand does not obey.
- Cannot pronounce his name clearly.
If a person cannot perform the above steps, an ambulance must be called. Before she arrives, you need to put the victim on his back, place a pillow or any soft object under his head, and also ensure access to oxygen.
Respiratory damage after stroke
Prolonged bed rest can lead to the development of pneumonia. Other reasons are food particles getting into the respiratory tract, mechanical ventilation (especially long-term).
Pneumonia is a dangerous condition, as it is not always diagnosed in a timely manner and, against the background of a general weakening of the body, is difficult to treat. A patient in a coma cannot make any complaints, so it is not immediately possible to suspect pneumonia. However, successful treatment cannot protect against recurrent disease. Pneumonia can recur if risk factors for its development are not eliminated.
The presence of other respiratory pathologies also increases the likelihood of the disease. Pneumonia after stroke primarily affects patients who have previously had or are currently suffering from lung diseases.
Diagnosis is fraught with difficulties due to the severity of the consequences of stroke (speech disorders, depression of consciousness). Therefore, treatment of pneumonia often begins late, which increases the likelihood of complications. It is much better to pay attention to prevention and prevent this condition. What should you do for this? Breathing exercises, postural drainage and sanitation of the respiratory tract in patients on mechanical ventilation prevent the development of pneumonia. An effective method of prevention is early activation of the patient. In this case, the cause for the occurrence of congestive pneumonia is eliminated.
Treatment methods
A favorable prognosis for recovery from this disease requires knowledge of adequate treatment at the stage of resuscitation therapy.
The primary goal of rehabilitation therapy is to return the brain to its previous activity.
Treatment of ischemic stroke of the right hemisphere is complex and is based on basic and specific methods.
Basic treatment includes monitoring blood pressure so that its fluctuations do not aggravate the situation. An important component is monitoring body temperature.
It is necessary to maintain breathing, ensure the functioning of the heart and other important functions. Therapy also focuses on relieving symptoms of nausea, seizures and tachycardia.
At the same time, treatment or prevention of possible complications is carried out. The peculiarities of the treatment of right-sided stroke are that it is aimed at eliminating the causes that caused it. This becomes possible thanks to the use of drugs that are individually prescribed by the attending physician.
The administration of medications is carried out by taking medications in courses.
Doctors prescribe the following drugs:
- improving blood supply to the brain;
- nootropic drugs that help restore higher mental functions;
- accelerating metabolism at the cellular level;
- complex with sedative effects;
- antidepressants (in case of depression).
IMPORTANT! Using medications on your own initiative without a doctor’s prescription is extremely dangerous and can lead to irreparable consequences even during the recovery period.
Kinds
If the neurological deficit regresses within 24 hours, it is a transient disorder, a transient ischemic attack (TIA). Despite the fact that the person’s condition returns to normal, it is urgent to prevent recurrent, acute manifestations of the disease.
Warning manifestations of the disease include a small stroke, which lasts up to three weeks.
Do not neglect such signals, take care of strengthening and cleansing blood vessels, normalizing blood pressure and blood counts, undergo research, and begin preventive treatment. Otherwise, there is a high probability of relapse, but in a more life-threatening form.
There are three main types of stroke: ischemic, hemorrhagic and subarachnoid (SAH). More often they are divided into two types: infarction and hemorrhage in brain tissue. The ischemic form is five times more common than the hemorrhagic form.
What is ischemic stroke?
This is the most common type of stroke. Diagnosed in 75% of patients. Ischemia or cerebral infarction, which is the same thing, refers to an area to which blood has stopped flowing, and with it the necessary oxygen. Without nutrition, brain tissue dies within three hours. Due to necrosis, neuron cells die, and it is impossible to return them to their previous state. What is dead cannot be restored. Therefore, stroke patients rarely achieve full recovery.
If you notice signs of a brain stroke, call an ambulance immediately. Restoration of body functions largely depends on timely treatment. Don't miss the first three golden hours while your nerve cells are alive.
What causes a cerebral infarction?
The cause of a cerebral stroke is blockage or narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels. Depending on the location where the thrombosis formed and the nature of the damage, the physical condition of the patient and the success of treatment depend. The rheological state of the blood and the pathology of the main arteries eventually lead to ischemia and necrosis of areas left without oxygen.
Fatty degeneration of the walls of blood vessels - atherosclerosis - does not occur suddenly. This is facilitated by a number of diseases, in which it is necessary to more carefully monitor the state of the cardiovascular system and undergo periodic examinations. At the first symptoms of TIA, treatment should be started. People at risk are:
- With rheumatic pathology, cardiac arrhythmia and conduction disorders.
- Having diabetes.
- Having suffered a myocardial infarction.
Reference: Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease, pathological changes in blood vessels, loss of elasticity due to the formation of a dense substance on the walls - cholesterol or other deposits. The lumen gradually narrows until it completely blocks the blood duct. It appears as focal plaques or plaque that thickens the tissue of the arteries.
Types of ischemic stroke
Depending on the nature of the source that caused cerebral infarction, there are 5 types of this category of stroke. The exact characteristics and diagnosis of the disease are determined by the doctor after a thorough examination. It is absolutely forbidden to do this on your own or take medications at your own discretion. An error can lead to a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition or death.
Etiopathogenesis according to the type of ischemic infarction
| № | Subtype of ischemic stroke | Characteristics of brain | Cause of the disease |
| 1 | Atherothrombotic – 34% | It appears in stages, after a precursor - TIA. Most often affects large and medium-sized arteries. Vasoconstriction occurs gradually. | Atherosclerosis Embolism |
| 2 | Cardioembolic – 22% | Blockage of the lumen by an embolus. It appears suddenly. The damage is extensive. Localization – middle cerebral artery. There may be a component of hemorrhage. | Pathology of heart valves, arrhythmia Formation of blood clots |
| 3 | Hemodynamic – 15% | The onset is gradual or sudden. Localization is often adjacent. Occurs due to abnormalities of cerebral vessels, septal stenosis of the arteries. | Low blood pressure. Decrease in heart volume, bradycardia |
| 4 | Lacunar – 22% | Damages small perforating arteries. It starts gradually and lasts for hours. The size of the lesion is no more than 1.5 cm. Accompanied by atactic hemiparesis. | High blood pressure |
| 5 | Hemorheological microocclusion | Neurological deficit is poorly expressed. Hemorheological changes in the hemostasis and fibrinolysis system are noted. | No vascular diseases |
| 6 | No definition | It is difficult to give an exact definition. Symptoms of multiple signs of stroke, of different origins. | The cause is unknown |
Reference: Embolism is a blockage of blood vessels with gaseous bubbles, fat, clots from damaged tissue, foreign particles that should not exist in the normal state of blood and lymph. Clusters that block the lumen are called emboli.
Hemorrhagic stroke
Non-traumatic intrathecal hemorrhage and subarachnoid hemorrhage are often classified as one type of stroke - hemorrhagic. In both cases it is a cerebral hemorrhage. The attack occurs suddenly, and the usual preceding symptoms of a cerebral stroke may be absent. Most often the cause is hypertension, cerebral atherosclerosis or blood diseases.
Pathological vascular permeability causes diapedesis of plasma and erythrocytes. In this situation, the blood clotting factor is of great importance. If necessary, drugs are administered to stop the bleeding, or urgent surgery is performed so that ischemia does not spread to a large area of the cerebral cortex.
Manifestation
With nervous or physical stress, there is a threat of increased stress on the blood vessels, which the body cannot cope with. This is why a brain stroke occurs. For example, the pressure jumped sharply and the vessel burst. A hemorrhage has formed, which can be either extensive or minor. The main risk group (85%) are hypertensive patients. Signs that a blow has occurred are:
- Sharp pulsating pain, with a feeling of boiling water pouring into the head.
- Uncontrollable vomiting and nausea.
- Disorientation in space.
- Slurred speech.
- Loss of consciousness.
In 90% of cases, the hemorrhage zone is localized in the cerebral hemispheres: in the anterior part. Less commonly, the brain stem or cerebellum is affected - pain occurs in the occipital area, the back of the neck. As a rule, the vessel ruptures. Diapedetic disorder does not occur often. A hemorrhagic stroke can occur even in a child; the main age of victims is from 35 to 65 years. Extensive damage to brain cells and delayed seeking medical help lead to death.
Statistics: Up to 40% of patients survive. More than half die from a second stroke. Disability occurs in 30% of patients. The average life expectancy is 10 to 15 years after impact. With timely medical care, the chances for a long existence, while maintaining the basic functions of the body, increase.
Recovery
Recovery after a right-sided ischemic stroke is aimed at returning motor and speech functions, as well as restoring the visual and tactile apparatus.
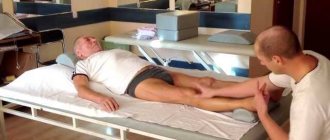
The recovery program includes methods of influencing paralyzed limbs; the patient is also re-taught to walk, eat, maintain personal hygiene, dress, etc. It includes areas such as kinesiotherapy (movement therapy), speech and memory training, dietary nutrition, medication, physical therapy, and massage.
The basic list of rehabilitation measures after a right-sided stroke includes:
- massages that relieve muscle hypertonicity and restore lost sensitivity;
- Exercise therapy – to restore motor functions of the limbs;
- acupuncture , physiotherapy, medicinal baths - activate nerve impulses in paralyzed limbs, establish their relationships with the brain center;
- speech therapist (for speech disorders);
- psychologist - preventing the development of depression and setting the mood for recovery.
The duration of recovery after a stroke is individual for each patient.
Folk remedies
Brain functions cannot be restored by traditional medicine. Herbal medicines can only have an auxiliary value. And even in this case, their use should be coordinated with the attending physician, since even a seemingly harmless herbal preparation can cause serious complications of an allergic nature.
In no case should you replace traditional medicine with drugs prescribed by a doctor - understand correctly, all traditional medicine does not have even a basic evidence base.
But it’s very good to use herbs and infusions as supporting agents - especially if it is necessary to provide a slight sedative effect.
[adsp-pro-1] [adsp-pro-2]
Stroke
Consequences
Almost always, after a right-sided ischemic stroke, a person will face consequences.
Some of them can be cured, but others he will have to live with permanently.
Paralysis
A right-sided blow leads to a decrease in motor activity and strength in both limbs on the left side of the body.
The arm and leg are constantly bent, the patient can sit, but cannot move his limbs freely and without assistance, walking, grasping objects with the hand, and fine motor skills are impaired.
We invite you to watch a useful video on the topic:
Behavior disorder
Often, after a right-sided blow, behavioral disorders such as frivolity, decreased criticism, agitation, swagger, loss of tact, aggression appear; the patient may often use obscene expressions and excessively use inappropriate sentences. Frequent depression, dissatisfaction or joy for no reason are also possible.
Memory impairment
Patients remember past events well, but forget current or recently occurring ones. Possible lapses in memory , disorientation in one's own personality, time and location . The patient does not remember his recent actions, does not recognize the faces of people close to him.
Impaired spatial perception
It is difficult for a person to estimate the size of an object, the distance to it, it is difficult to dress independently , because... he cannot easily determine where exactly any part of the body is located.
Visual impairment
Visual impairment or blindness, double vision in the left eye. The head and left eye are turned to the left.
Weakening of mental abilities
A sharp decline in cognitive ability, loss of once acquired skills, dementia, inability to perceive expressions in a figurative sense, everything is taken literally.
Sensory impairment
There is an exacerbation or distortion of skin sensitivity, and painful sensations occur when touched. Loss of sensation of one's own limbs and their spatial location.
What signs warn of an initial stroke?
Due to the onset of a stroke, a sufficient amount of oxygen ceases to flow into the brain, resulting in the death of those cells where the disorder occurred. Therefore, in order to avoid the development of a pathological process, it is important to call an ambulance if:
- Presence of headaches.
- Symptoms of recurrent migraine.
- Distortion of auditory perception in the victim.
- Low ability to remember and reproduce information.
- Lack of correction and speed in performing motor actions.
If a stranger or one of your close relatives begins to have similar symptoms or complaints, go with him to the hospital or call a doctor at home. After all, restoring the brain of a sick person after a stroke without timely medical intervention can greatly harm him and become a very terrible threat for him.
Prognosis for life and recovery
Factors influencing recovery:
- age;
- degree of damage to brain tissue;
- quality of treatment, first aid and rehabilitation provided.
Life statistics after a stroke:
- 75% survive the first days after an ischemic attack;
- 50% of them die earlier than 2-3 months after the disaster;
- 18-20% of survivors experience a second strike , which is much more difficult than the first and reduces the chances of survival;
- up to 95% of survivors remain disabled.