Ischemic stroke: general characteristics
The nosological description of ischemic stroke includes three different pathologies that characterize the localization of the circulatory disorder:
- ischemia – lack of blood flow in a local area of an organ;
- heart attack - organ damage caused by a lack of blood supply;
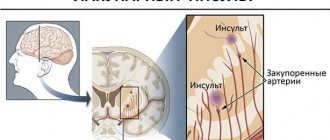
- stroke is a disturbance in the blood supply to one of the areas of the brain, caused by progressive ischemia of one of the vessels and accompanied by necrosis (death) of brain cells.
Another name for ischemic stroke – cerebral infarction – fully corresponds to the ongoing pathological processes in the brain. It is important to note that tissue destruction occurs even after normal blood flow is restored.
That is why a person who has suffered a stroke needs qualified medical supervision and subsequent rehabilitation.
Among the causes leading to ischemic stroke, two groups can be distinguished:
- unmodifiable , i.e. untreatable (for example, genetic predisposition, age-related risks);
- modifiable , the influence of which can be controlled (bad habits, excess weight, diabetes, high cholesterol, sedentary lifestyle and others).
Many adverse factors can be corrected or minimized by following the rules of a healthy lifestyle.
Types of stroke
Ischemic stroke is a pathological syndrome , the manifestations of which vary depending on the type of disease. If we consider the mechanism that led to the development of pathology, we can distinguish five types of stroke:
Atherothrombotic
Atherothrombotic stroke - its development is based on atherosclerosis, in which blockage of a vessel in large or medium arteries is caused by cholesterol “plaques”; This condition often develops at night during sleep.
Cardioembolic
Cardioembolic stroke - caused by a special type of blood clot - an embolus, which forms in various heart diseases (arrhythmia, endocarditis, heart disease) and blocks the arteries of the brain; the condition is sudden and develops during wakefulness.
Lacunar
Lacunar stroke - occurs when small vessels are damaged; most often develops in patients with hypertension or diabetes mellitus.
Hemodynamic
Hemodynamic stroke - caused by impaired blood movement through the vessels (for example, when pressure decreases), as a result of which the brain does not receive enough essential nutrients; most often develops in patients with concomitant vascular pathology.
Unknown origin
Stroke of unknown origin - it is not possible to identify the cause of the disease.
Periods of stroke
Ischemic stroke has an individual course for each patient. However, the rapid development of the pathological process is one of the common features inherent in people who have suffered this serious condition.
Sometimes the count is not in hours, but even in minutes, since brain tissue is destroyed very quickly.
There are five periods of stroke:
The first period - the most acute - lasts no more than 3 days. Timely medical care, consisting of administering thrombolytic drugs to the patient, can slow down the pathological reaction and even eliminate it.
If medical measures are successful, then doctors talk not about a stroke, but about a transient ischemic attack (a less dangerous condition that responds well to treatment).
The second period - acute - lasts from 3 days to 4 weeks. This is an important time to diagnose the extent of brain damage, as well as relieve symptoms of the disease.
This is followed by recovery periods: early (up to 6 months) and late (up to 2 years). At this time, a set of rehabilitation measures and procedures is carried out aimed at restoring the lost functions of areas of the brain (if this is possible).
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine: symptoms and treatment
After this comes a period of residual effects that will accompany the person and make themselves felt throughout his life.
Based on the speed of spread of the lesion and intensification of symptoms, experts distinguish the following types of ischemic stroke:
- transient ischemic attack - a small area of the brain is affected, blood circulation is disrupted for no more than a day; the prognosis is favorable;
- minor stroke – attacks of ischemia are severe and can last up to 3 weeks;
- progressive stroke - symptoms do not appear immediately, but gradually increase over several hours or even days; full recovery is impossible;
- extensive ischemic stroke – symptoms are most pronounced and last for a long time; the prognosis is unfavorable.
The possibility of a favorable prognosis is also influenced by the severity of the ischemic stroke.
With mild severity, there are few or only minor symptoms. The prognosis is favorable, rapid recovery is possible.
The average degree is characterized by many signs depending on the location of the lesion. A person’s consciousness does not change, in contrast to severe damage, in which large areas of the brain are involved in the pathological process and many functions suffer.
A sick person requires mandatory hospital treatment followed by a course of rehabilitation.
When a cerebral infarction occurs, certain areas of the brain that are responsible for certain mental and neurological functions are affected. There are several types of stroke depending on the area affected.
Classification
Depending on the nature of the damage, there are:
- Hemorrhagic.
- Ischemic.
- Subarachnoid.
According to the degree of brain damage:
- Extensive. This type of stroke affects multiple lobes of the brain. This is manifested by the loss of several body functions, depending on which parts of the brain are damaged. For example, paralysis and loss of speech.
- Focal. Affects only one zone. One function is lost (for example, vision).
- According to the degree of severity , they are distinguished: mild; moderate severity; heavy.
Types of ischemic stroke
Right-sided ischemic stroke
Right-sided ischemic stroke leads to impairment of motor functions on the left side of the body. Recovery is very slow. One of the most unfavorable consequences is paralysis of the left side.
In addition, there may be speech impairment, as well as loss of concentration and short-term memory.
Signs of a stroke on the right side may include:
- inhibition of reactions,
- body numbness,
- paralysis of the body and facial muscles on the left side.
Left-sided ischemic stroke
In left-sided ischemic stroke, speech functions are primarily affected, while motor functions are only slightly affected. Speech is restored with great difficulty.
When Broca's center is damaged, a person is able to speak only in single words and simple sentences. Other signs include disturbances in perception, difficulty moving and poor coordination.
The main complication of this type of stroke is deviations in the mental sphere, primarily from emotional manifestations. Memory loss and disorientation in space and time may also occur.
Cerebellar stroke
Cerebellar stroke leads to persistent impairment of motor coordination. In addition, at the initial stage of the lesion, the patient may experience attacks of nausea and vomiting, and frequent dizziness.
As the cerebellum begins to compress the brain stem, other symptoms (numbness of the facial muscles) are added, after which the person falls into a coma. The mortality rate for cerebellar stroke is extremely high.
Brainstem stroke
The most dangerous type of ischemic stroke is a brainstem stroke, since it is in the brainstem that the centers responsible for the most important systems of the body’s functioning are located – the respiratory and cardiac ones.
If they are defeated, the chances of recovery are almost zero. Symptoms of this type of stroke are the inability to navigate in space, loss of coordination, dizziness, and nausea.
Major stroke
A major stroke affects large areas of the brain, where there is an almost complete disruption of blood circulation, up to its absence. Brain swelling occurs. Complete paralysis sets in. There is practically no chance of recovery.
Clinical picture
The clinical picture of ischemic stroke includes cerebral and focal manifestations. Ischemia is not always characterized by general cerebral signs: headaches, nausea, vomiting, impaired consciousness from stupor to coma.
The focal symptoms of ischemic stroke depend on the area affected and the specific vessel.
| Artery | Brain area | Stroke Clinic |
| Middle cerebral artery | Lateral surface of each hemisphere, motor functions of the upper limbs | Weakness and loss of sensation in the face, neck and arm (and to a lesser extent in the leg) on the opposite side of the body, loss of half the visual fields of both eyes, impaired tongue movement, speech understanding |
| Anterior cerebral artery | Frontal lobe | Changes in mental status, impaired emotionality and fluency of speech, activity of the grasp reflex, impaired ability to concentrate and think, weakness more in the legs than in the arms on the opposite side of the body, sensory disturbances, gait disturbances and urinary incontinence |
| Vertebrobasilar artery | Damage to the brainstem, cranial nerves, cerebellum | Dizziness, nystagmus, diplopia, visual field deficit, swallowing disorder, dysarthria, impaired facial sensitivity, syncope, ataxia |
| Posterior cerebral artery | Depending on whether the entire bed or cortical branches are affected. | Loss of half the visual field of the eye on the opposite side, cortical blindness, visual agnosia (impaired perception), changes in mental status and memory. If the cortical branches are affected - blindness, the lower thalamic branches - burning pain. |
The clinical picture of a stroke depends on the damage to certain areas of the brain. Blocking of the area of the middle cerebral artery on the left side is associated with speech impairments, and on the right side – with changes in behavior, absent-mindedness, slackness, and memory impairment. Speech restoration is difficult in patients with lesions of Wernicke's and Broca's areas - global aphasia.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke
Typically, an ischemic stroke develops quickly, in just a few minutes. The deterioration of the condition may begin suddenly against the background of complete health. In old age, a gradual increase in the manifestations of stroke is possible over two days.
In order to recognize this life-threatening condition in time, you need to clearly know what symptoms indicate it.
There is a special test that helps identify early signs of cerebral infarction: you need to ask the person to smile or show his teeth, raise his hands and say a few phrases.
When a stroke begins, it is not possible to perform these actions: the patient’s face is asymmetrical or distorted, he is not able to raise two arms at once (one arm will be lowered), speech is unclear.
If there are one or more signs, then the person should be taken to the hospital as soon as possible and given medical assistance. The first 3 hours are considered the most important for the provision of medical care and a further favorable prognosis.
The variety of symptoms of ischemic stroke depends on the location of the site of damage in the brain. So, if there is a blockage of a vessel located in the front of the neck, then the patient will be bothered by numbness or immobility of an arm (or leg) on one side of the body, speech difficulties, blurred vision in one eye, up to blindness.
Phosphogliv or Karsil, which is better? Doctors' opinion
If blood circulation is impaired in the vessel along the back of the neck, symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, weakness throughout the body, double vision and blurred vision, feeling hot and sweating may occur.
How is ischemic different from hemorrhagic?
To understand the difference between these two types, it is necessary to understand more carefully what they are.
An ischemic stroke , simply put, is when blood, due to a blood clot or other obstruction, does not flow to the brain tissue, as a result of which the tissue is weakened and does not “work.”
A hemorrhagic stroke is when part of the brain dies and the blood that should go there goes to the other side of the brain. Because too much blood accumulates, the vessels dilate and burst, causing bleeding in the brain.
The difference between them is easily perceptible. It should also be noted that with the second type of stroke the patient does not have the opportunity to live long, and with the first type he can even survive the first and second stroke if his health is in good condition. But even with excellent physical and moral condition, the third stroke will be severe.
Symptoms of transient ischemic attacks (TIA)
Symptoms of ischemic stroke may be similar to those of transient ischemic attacks , however, the latter are milder and have a good chance of survival and restoration of lost brain functions.
Often transient ischemic attacks precede cerebral infarction, but can also be its consequence.
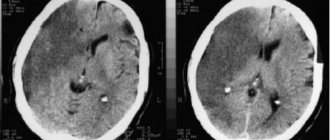
The clinical picture of TIA when performing an MRI or CT scan of the brain does not suggest the presence of a lesion, and the duration of neurological symptoms does not exceed 24 hours.
The following methods are used in the differential diagnosis of ischemic stroke and TIA:
- clinical and biochemical blood test;
- electrocardiogram (ECG);
- echocardiography (EchoCG) of the heart;
- Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck using Doppler.
Recovery
In order for the patient’s recovery to be more effective, it is important to observe regularity when carrying out rehabilitation measures. To regain lost functions, you may need the help of a physical therapist and speech therapist. Therapeutic gymnastics can improve motor skills.
It is important to monitor a person’s mental state. Patients who have had a third stroke are at high risk of developing post-stroke depression. This should not be allowed, since people with depression are less responsive to rehabilitation and have a higher risk of death than patients without mental disorders.
Features of stroke diagnosis
Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to quickly and clearly identify the signs of an incipient stroke and promptly begin a set of measures to relieve its symptoms, which in the future helps prevent serious complications and reduce mortality from this disease.
The main methods for diagnosing ischemic cerebral stroke include:
- examination of blood and its most important indicators (clinical and biochemical blood tests, study of lipid composition, detailed coagulogram);
- conducting an ECG and measuring blood pressure;
- MRI or CT scan of the vessels of the brain and neck (to accurately determine the location and size of the affected area and the condition of nearby vessels);
- examination of the patient by a neurologist, collecting anamnesis, identifying concomitant diseases that affect the development of cerebral infarction and the effectiveness of treatment.
In a hospital setting, differential diagnosis of ischemic stroke and other diseases with similar symptoms is carried out, primarily transient ischemic attacks, as well as epilepsy, brain tumors and other diseases.
Why does it occur
The main causes of stroke are:
- Rupture of a blood vessel in the brain as a result of thrombosis or the formation of an aneurysm (an abnormal formation with thin walls).
- Vascular pathologies (vessels with thinned walls that arise as a result of a disease or genetic abnormality).
- Narrowing of the lumen of the vessel or its complete thrombosis as a result of fouling of the vessel walls with adipose tissue.
How to restore vision after a stroke
Stroke is a pathology associated with the rupture of a cerebral vessel or its blockage.
Thrombosis occurs in people who have undergone heart surgery or suffer from cardiovascular diseases and increased blood clotting. Stroke occurs most often at night or early in the morning. The risk group includes:
- elderly people and cocaine addicts;
- diabetics;
- overweight persons ;
- smokers;
- women protected by oral contraceptives.
Middle-aged people are most often susceptible to hemorrhage. A stroke occurs in the daytime after heavy physical exertion or stressful situations.
The main causes of hemorrhage are hypertension, sudden changes in blood pressure, diabetes, vascular aneurysm, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Consequences of ischemic stroke
Cerebral infarction causes a variety of adverse effects and complications, which depend on the location and size of the affected area and vary in severity, duration and ability to recover. The larger the lesion, the less chance of complete restoration of lost functions.
The most common consequences of ischemic cerebral stroke can be divided into several groups:
- speech disorders - observed quite often, especially in patients who have suffered a left-sided stroke; may manifest itself in the inability to pronounce words and general unintelligibility of speech, difficulty naming objects, problems with reading and writing;
- motor impairments - can be either partial or complete, up to paralysis; localized in a specific area (or even half) of the body; manifest themselves in impaired mobility, weakness; this type of complication complicates a person’s self-care skills and makes him dependent on the help of other people;
- impaired sensitivity in certain parts of the body - sometimes can remain for a long time, even when motor functions are restored (this is due to the fact that the nerve fibers responsible for conducting nerve impulses are restored very slowly);
- disorders in the cognitive and emotional-volitional spheres - weakening of intellectual abilities, problems with memory and attention, frequent mood swings, decreased communication skills;
- mental disorders - decreased emotional background, sleep problems, decreased appetite, depressive states, even thoughts of suicide.
In addition to the listed complications, patients may experience symptoms such as impaired coordination and unsteady gait, difficulty swallowing food, especially hard food, epileptic seizures, blurred vision, the risk of developing pneumonia, thrombosis of the extremities and other consequences that negatively affect the quality of life.
Separately, it is worth noting the risk of recurrent stroke. Unfortunately, about a third of patients who have suffered a stroke are subject to a second attack, which inevitably entails a serious threat to life and health.
Third stroke: prognosis and chances, consequences, symptoms, 3 signs – About Blood
Stroke, previously considered a problem exclusively for older people, has been rapidly increasing in age for several years now. More and more people, suffering from even minor heart problems, are at risk for a stroke. To avoid it, not only the prevention of heart disease is necessary, but also fundamental changes in a person’s lifestyle.
Description of the disease
It is known that blood supply to the brain is the most important and one of the most difficult tasks of the human body.
This organ requires a lot of energy and nutrients, being the center of the functioning of all other systems, and if it is deprived of this energy, a natural failure will occur, critical for human life.
Such a failure is called a stroke. This is a sudden stop of blood circulation in the brain , which leads to loss of consciousness and paralysis of varying degrees of severity.
If you do not provide proper assistance to a person during a stroke, death is extremely likely. If in the case of the first stroke the patient has some time to receive help, then the second or other subsequent times (and stroke recurrences occur often) the chances will be much less.
The most common causes of stroke:
- Cardiovascular diseases. The heart is primarily responsible for blood supply. If its functioning is impaired, the risk of stroke increases to the maximum
- Increased blood cholesterol levels. Cholesterol is harmful because it forms plaques in the blood vessels - “plugs” that interfere with the flow of blood and can almost completely block the ducts at a critical moment
- Diabetes. This disease thins the walls of blood vessels, making them fragile and thin, less flexible. Because of this, ruptures occur, leading to insufficient supply to the brain
- Increased blood clotting. Blood that is too thick in comparison with general medical standards tends to coagulate and form clots, which also form “plugs” for blood vessels
- Bad habits. Alcohol, smoking, drugs - all this, in addition to general intoxication of the body, greatly affects the blood vessels, weakening them.
IMPORTANT! Not the cause, but a prerequisite for a possible stroke is advanced obesity. This disease leads to at least the first three items on the list above.
Danger
- Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely remove the consequences of such a serious shock from the body.
- Modern medicine is able to save a person experiencing a stroke for the first time in most cases, but the problem does not end there.
- It is present even after a course of rehabilitation, because the patient is primarily at risk of having cerebral stroke , and within the current year or several subsequent years.
It is not only the patient who is to blame for the relapse, who, having recovered from a critical state, continues his past life without any positive and preventatively useful changes.
A stroke causes irreparable damage to the brain and cardiovascular system , which cannot be restored with medications, exercise sessions and rest. The resources of the human body are not infinite, and a stroke brings their depletion closer by 3-10 years.
If a first stroke causes such damage, one can only imagine what a second stroke can do. If after the initial case, with the most favorable outcome and if all medical prescriptions are followed, the patient can live on average from 8 to 12 years, then after a relapse, the average life expectancy drops to 2-3 years.
Repeated ischemic stroke
- Ischemic stroke is the most common clinical case of stroke, affecting mainly elderly people (after 60 years).
- Occurs due to the rapid death of brain cells as a result of oxygen starvation due to the vessels not being able to function properly.
- Saving a person from repeated ischemic stroke is very difficult, but still easier than from other types.
- Accompanying diseases such as diabetes and heart problems are not uncommon and significantly complicate treatment.
- The prognosis for ischemic stroke is still more encouraging than for hemorrhagic hemorrhage.
- The ICD 10 code for ischemic stroke is 163, which is also suitable for recurrence.
Repeated hemorrhagic stroke
A hemorrhagic stroke is essentially a bleeding in the brain. A critical condition, survival from which is much more difficult than in the case of an ischemic stroke. The causes are radically different: they are chronic hypertension or hypertension, various blood diseases and cerebral atherosclerosis .
The body rarely experiences such a shock twice, especially in a short time. The only thing that smooths out the situation a little is that this type of stroke mainly affects people who have not reached old age. An even stronger body can withstand a stroke more easily.
Probability of occurrence
A stroke is a consequence of diseases that have been and have been developing in the patient’s body for more than one year. After rehabilitation, these diseases will not disappear anywhere, which means they will provoke a second attack. That is why even exemplary patients who take care of their body after an illness, do not violate the recommendations and take preventive medications, are at risk.
How long does it take for a relapse to occur?
For some, another stroke occurs within the first year after the first. For others, the second blow falls two or three years later.
If a person suffered a stroke after the age of 45-50, then the likelihood of the disease returning is very high.
What frightens doctors most is not the possibility of relapse itself, but how quickly it can happen. About 30% of recurrent strokes occur within one year of the first. Of course, such a load most often turns out to be lethal - about 70% of cases end in the death of the patient.
This does not mean that there is no point in engaging in prevention - the patient has the power to delay a relapse or get rid of this possibility for good.
Causes
In addition to the obvious reasons such as depleted brain cells, blood vessels and heart, there are simpler circumstances.
For example, if a patient suffers a stroke due to excess cholesterol, the risk of a repeat event will not disappear until the level of the dangerous substance is reduced.
If a patient suffers from heart disease, then it is worthwhile to work hard to prevent it, since now every time a heart problem will increase the risk.
Also, sometimes patients, having got out of the hospital ward, think that nothing threatens them anymore and that the danger has completely passed. They return to the previous way of life, which led them to the stroke, do not eliminate diseases, suffer from bad habits and do not strengthen the body with physical activity - cardio jogging or gymnastics.
IMPORTANT! Infectious diseases, especially those leading to inflammatory processes, can increase the likelihood of a stroke. Getting rid of such diseases, as well as any others that impair the immune system when a stroke is dangerously close, is necessary first of all.
Age can be a very significant reason. It is difficult to do anything about worn-out organs and organ systems; unfortunately, modern medicine has not yet reached such a level. Elderly and elderly people should be especially careful not to encounter the disease again.
Signs
Recognizing a stroke in time is very important. If in the first case you will have several tens of minutes to get your bearings and provide assistance, then in the second case you will not have even this time.
A repeated blow to weakened cells will occur quickly and suddenly.
Main symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- numbness of the facial muscles (a simple test will help here - the patient should be asked to smile and if he cannot, then this is definitely a stroke);
- disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus, loss of coordination;
- loss of ability to speak coherently or at all;
- loss of vision clarity;
- faintness, weakness.
With such symptoms, a person must be hospitalized immediately, as minutes count. Only a professional who quickly responds to a call can save a life in the event of a second stroke.
Consequences
Medicine does not stand still, so in about a third of the total number of clinical cases it is possible to save the patient. But if after the first stroke it is possible to maintain the usual rhythm of life even for an elderly person, after a relapse such chances are reduced by half or three times.
Such strong repeated shocks to the brain, which is actually a very vulnerable organ, cannot but leave an imprint on the human body. Since most active brain cells are destroyed by strokes, many body functions will be irreversibly impaired.
Possible consequences of a repeated cerebral stroke include:
- partial or complete loss of the ability to move independently;
- deterioration in the functioning of the senses (hearing, vision, taste perception, etc.);
- loss of some thinking and mental abilities, memory impairment.
IMPORTANT! These changes do not happen on their own. Depends on which specific areas of the brain are affected or bypassed by the disease. Damaged parts of the brain are very difficult to restore, often impossible.
The likelihood of a quick death due to an even greater load on the cardiovascular and nervous systems increases significantly.
Forecast for life
Doctors' prognoses for patients who have survived such a critical situation twice are usually disappointing. This is not surprising, since the body's resources are running out after the damage has been done.
Giving a general time frame for everyone, equating people who are different in terms of genetic data, lifestyle, health and financial status is difficult and pointless. The main thing is the patient’s desire to stabilize his condition, as well as the most accurate and strict adherence to all medical recommendations.
Having created all the recommended conditions for rehabilitation for the patient, all that remains is to hope for the stamina and residual resources of the body, which will help prolong life as much as possible.
It is even more difficult to give a life prognosis to older people. Due to the wear and tear of the body, it is often disappointing.
Source:
Prognosis for a third stroke
Stroke is widespread throughout the world. It is the third leading cause of death according to WHO. Among brain diseases associated with changes in blood vessels, the proportion of second and third strokes is more than 30%.
The reasons for the development of repeated cerebrovascular accidents and the prognosis for those who have suffered a third stroke are discussed below.
Who has a third stroke?
People who have had a stroke twice, especially if they managed to fully recover, eventually stop paying attention to their health. Even experiencing repeated circulatory disorders does not force you to constantly take the necessary medications and quit bad habits. The probability that a third circulatory disorder will occur, despite the previous two, is about 50%.
After two strokes, the patient may be more careless about his health, which entails the likelihood of another
The main group of patients who have a higher chance of developing this pathology are people who have suffered mild transient circulatory disorders or micro-strokes. Often, patients do not pay due attention to small signs of cerebrovascular accident and, as a result, after two transient attacks, develop another stroke.
Its development is due to the fact that the body retains the mechanisms that led to impaired cerebral circulation:
- the body's tendency to form blood clots;
- atherosclerotic changes in cerebral vessels;
- the presence of chronic diseases that provoke stroke - this is, first of all, hypertension and diabetes.
In such a situation, a person does not have enough internal reserves to prevent the onset of the next ischemia. Each subsequent brain injury is more difficult to tolerate by the body than the previous one. With each new cerebrovascular accident, the number of people living five years or more after a stroke decreases.
To illustrate these words, let’s turn to statistics:
- Every year in Russia, up to 450 thousand people experience various forms of cerebrovascular accident for the first time, 80% are ischemic strokes, 20% are various types of hemorrhagic.
- In the first 20 days, 35% of people with this disease die, and in the first year, about another 15% of patients die.
- People who survive the first year after a cerebrovascular accident live from 8 to 10 years. These patients do not have severe neurological impairment.
- After the third ischemia, 20% of patients die in the first month.
Source: https://igl-clinic.ru/analizy/tretij-insult-prognozy-i-shansy-posledstviya-simptomatika-3-priznaka.html
Prognosis for life with ischemic stroke
When making a prognosis after a stroke, the main factors that medical workers rely on are:
- Size and localization of brain tissue lesions. Recovery after a cerebral infarction can proceed much faster if the affected area is relatively small and the lesion does not affect vital brain centers.
- A type of stroke. High mortality rates accompany atherothrombotic and cardioembolic forms of cerebral infarction, and the lowest – lacunar.
- Patient's age. The older the patient, the more unfavorable the prognosis for him.
- Accompanying illnesses. If the patient has diseases that caused the development of a stroke (for example, atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension), then the risk of recurrent blood clot rupture and blockage of the vessel is very high. Accordingly, the prognosis for such patients is not very favorable.
- Time factor. The outcome of an ischemic stroke will also largely depend on the speed of medical care provided and the duration of rehabilitation.
Ulkavis or De-Nol, which is better, reviews from doctors
The main percentage of deaths occurs in the first two days from the onset of the disease; in the next 30 days, about a quarter of patients die (mainly from developed complications). Surviving patients acquire various forms of disability, which, however, may disappear with timely rehabilitation.
The survival rate of patients after a cerebral infarction gradually decreases with each passing year: if at the end of the first year of the disease about 70% of patients survive, then after 10 years - no more than 25%.
Help before hospitalization
If relatives, friends or just strangers have a suspicion that a person has had a stroke, then you need to provide all possible help and immediately call an ambulance. When the blow hits the house, then the person who answers the call needs to be told that the person has had a stroke and needs to insist on it. You could even say that this verdict was given by a familiar doctor. This is the main condition that guarantees that a team of qualified specialists will arrive and they will have everything necessary for quick assistance and an effective remedy will be in the doctor’s suitcase.
There is no guarantee that the ambulance that arrives will have a sufficient number of strong men capable of transporting the patient. You need to take care of this yourself. You can turn to your neighbors if you don’t have enough strong hands. Paramedics may demand payment from relatives for transporting their loved one. Such an act should be recorded on camera and dealt with when the patient is out of danger. But there is no need to argue with payment before transporting to the hospital and pay to fraudulent orderlies.
In the ambulance, doctors provide intensive therapy; they do not wait for the patient to arrive at the hospital; they give the person the drug that is required. Doctors can apply bandages, tourniquets, and connect it to honey. equipment to help immobilize the limbs.
If the patient has lost consciousness after a stroke and is paralyzed, you need to provide him with a normal flow of air, free his neck, untie his tie or scarf, unbutton his shirt on his chest, open the window so that the room is filled with fresh air.
The head is placed on the pads and raised. It is necessary that the tongue does not stick in the mouth, this is checked if the patient is vomiting, it is necessary that the masses do not interfere with breathing, the person does not choke or choke on them. If the disease strikes while eating, you need to remove food and dentures from your mouth, if the patient uses them. If a person is vomiting, turn his head to the side, because vomiting may recur.
If a patient has problems with swallowing after an acute stroke, glycine should be used in the amount of 2-3 tablets, they are placed under the tongue. After they are completely absorbed, the procedure is repeated and another 2-3 pieces of glycine are added. It is acceptable to give a person 10 tablets, that is, 1 gram of the drug. It is important to lower the patient's blood pressure if it is elevated. This is determined by measurement. You can lower your blood pressure with the help of medications or by immersing your feet in hot water. Competent first aid will help maintain a person’s health and well-being.
Rehabilitation after ischemic stroke
Rehabilitation measures after a stroke are designed for a long period.
The basic principle is a gradual complication and increase in the load on the patient’s body, using gentle treatment regimens :
- strict bed rest - at the very beginning of the development of the pathological condition, sudden movements and movements are contraindicated for the patient, but in caring for him, medical personnel use means aimed at preventing bedsores, wiping, turning over, elements of breathing exercises;
- moderately extended bed rest - the patient is allowed minimal physical activity (turning over independently, taking a sitting position, eating independently);
- ward mode - independent or with the help of medical personnel movement within the ward, use of special rehabilitation equipment (walkers), gradual transition to self-care;
- free mode.
The rehabilitation that people go through after a stroke consists of several stages and begins in the department where the patient was hospitalized (usually the neurology department).
At the end of the acute period, transfer to the rehabilitation department of a hospital or specialized sanatorium. Next, outpatient observation is connected to the clinic at the place of residence.
Rehabilitation measures after a cerebral infarction include:
- therapeutic exercises (physical therapy) and massage;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- taking medications prescribed by a doctor;
- dietary nutrition;
- compliance with the daily routine.
Many rehabilitation activities can be carried out at home.
How is the treatment carried out?
Treatment consists of several periods: resuscitation measures, intensive and general therapy, home regimen, and recovery phase.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
In the first stages, treatment is carried out within the walls of the clinic in the intensive care or resuscitation room.
How to provide first aid for a stroke
The disease develops as a result of impaired blood circulation.
In case of hemorrhagic stroke, the following measures are taken:
- Stopping hemorrhage. For this purpose, drugs that increase blood clotting are used.
- Removing swelling from brain tissue.
- Restoring normal pressure.
The patient is on bed rest (bed with a raised headrest and a bolster under the feet, a heating pad with ice on the head).
For treatment the following are used:
- medications to lower blood pressure;
- drugs to increase clotting ;
- means to restore or improve circulation around the affected area.
Therapy for the treatment of ischemia has the opposite direction:
- The use of drugs aimed at dilating blood vessels in the brain.
- Use of thinners .
- Administration of anticoagulant .
- The use of diuretics for hypertensive patients to avoid the formation of edema.
General therapy includes:
- Use of sedatives .
- The use of medications that restore vascular tone.
- Actions to restore or maintain damaged brain cells.
Memory recovery after stroke
The consequences of a stroke do not disappear without a trace, but manifest themselves in the form of neurological deficits.
Surgical intervention is usually performed if there are certain indications:
- Persistent cerebral edema
- The presence of hematomas located on the sides, as well as hemorrhage in the cerebellum.
- Identifying symptoms that the resulting hematoma is compressing the brain.
- High level of probability of recurrent hemorrhagic stroke.
It should be noted that the operation is prescribed for young or middle-aged people. The optimal time for the operation is the first two days after the stroke.
The accumulated blood is removed by cutting the head and gaining access to the brain or using a puncture.
Surgery for ischemia is less common. It is performed for thrombosis of the main vessels.
Treatment of ischemic stroke
In the treatment of stroke, the most important for the possibility of restoring lost brain abilities are the first 3 hours from the onset of symptoms.
In a hospital setting, after diagnosing the patient’s condition, it is possible to carry out thrombolytic therapy , the essence of which is the intravenous administration of special drugs that can dissolve blood clots.
However, after 4.5 hours from the onset of the pathological condition, this method of treatment loses its effectiveness and is not prescribed.
Even before hospitalization, emergency physicians provide the patient with so-called basic therapy aimed at stabilizing the patient’s condition (normalizing the cardiovascular and respiratory systems).
Basic therapy includes:
- maintaining water and electrolyte balance,
- normalization of tissue metabolism,
- control of body temperature and blood pressure,
- monitoring heart contractions.
In the presence of concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular system, the following may be prescribed:
- angioprotectors,
- anticoagulants,
- cardiac glycosides,
- antioxidants,
- and other means.
Specific treatment for a stroke consists of restoring impaired blood circulation in the affected area ( thrombolytic therapy ) and preventing new thrombus formation ( anticoagulant therapy ).
The therapeutic effect is achieved by taking medications and surgical treatment methods (according to health indications).
Primary, secondary prevention
You can prevent a stroke by following simple rules:
- reduce salt intake, increase potassium intake. Dried apricots, grapes, nuts, sunflower seeds, bananas, buckwheat, and broccoli contain a lot of minerals;
- DASH diet. The basic principles are to increase the consumption of vegetables, fruits, low-fat dairy products, and unsaturated fats. Limiting saturated lipids (red meat, cream, fatty cottage cheese, cheese, lard);
- increase physical activity: at least 150 minutes/week of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes/week of intense aerobic exercise;
- normalize weight;
- quit smoking, including passive smoking;
- limit or eliminate alcohol;
- maintain blood pressure by taking medications and lifestyle changes at a level of less than 140 mmHg. Art. for systolic, 90 mm Hg. Art. for diastolic pressure;
- take aspirin (with a 10-year risk of stroke of 6-10%);
- Regularly undergo an ECG for all patients over 65 years of age;
- control diseases that can cause a brain attack: atrial fibrillation, diabetes mellitus, congenital, acquired pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- reduce cholesterol levels to healthy levels;
- preventive operations for significant narrowing of large vessels.
Nutrition for patients after a stroke
A special diet after a stroke requires: limiting the consumption of salt and sugar, avoiding spicy, fatty and fried foods, various smoked foods, pickles and marinades. The main goal is to promote the recovery of the body and prevent new attacks of the disease.
Meals should be frequent ( at least 5-6 times a day ), but in small portions. It is recommended to include fresh vegetables and fruits rich in fiber, cereals, dairy products and lean meats and fish in your diet.
First courses are best made vegetarian and not too thick . Foods with a high potassium content (dried apricots, bananas, citrus fruits) and those that can remove free radicals from the body (blueberries, cranberries) can be of great benefit.
for patients after a stroke to drink a lot of fluids to avoid the formation of edema. As a rule, doctors recommend drinking no more than one liter of fluid per day.