0
Author of the article: Marina Dmitrievna
2017.10.22
8 288
Vessels
More and more often we hear about the risk of stroke. This condition has become an all too common cause of death in older adults. A stroke is a disorder of blood circulation in the brain that leads to the death of nerve cells. The cause of this condition can be either a blood clot or a ruptured vessel. 80% of all cases that lead to stroke are due to the formation of a blood clot that prevents normal blood flow to the brain. The result of the disease can be paralysis.
Stroke
Recovery after a stroke is long, since a person may lose the ability to talk, move, eat independently, etc. The severity of such consequences depends on the speed of providing medical care immediately after the stroke. Paralysis can be avoided when the patient is taken to the hospital within an hour after the stroke and medical therapy is started.
Causes of paralysis
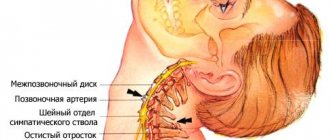
Paralysis of the right half of the body occurs if a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke occurs in the left cerebral hemisphere.
This is due to the crossing of nerve fibers - the cells of the left hemisphere are responsible for the work of the right half of the body.
The disease is characterized by the rapid development of paralysis following damage to the vessel.
The causes of right-sided paralysis are divided into controllable and non-controllable. The first group consists of factors that can be controlled by the person himself. The second group includes external factors, as well as congenital anomalies.
Controllable causes:
- Excess animal fats in food and increased cholesterol formation;
- Uncontrolled arterial hypertension;
- Overweight;
- Long-term use of glucocorticoids;
- Diabetes.
Non-modifiable reasons:
- Anomalies in the development of the left cerebral vessels (anterior, middle and posterior cerebral arteries);
- Atherosclerosis of the left internal carotid artery;
- Renal hypertension;
- Burdened heredity;
- Tortuosity of the vertebral arteries.
Therefore, if after a stroke some part of the body is paralyzed, then the patient himself may be to blame for not leading a healthy lifestyle, and the consequences in this case are much more serious.
What to do if the right side is paralyzed due to a stroke
Right-sided strokes are much more common than left-sided strokes. Paralysis of the right side indicates that the left hemisphere of the brain is affected. The prognosis in this case will be much more favorable.
First of all, this is achieved due to the fact that a diagnosis can be made quickly and treatment can begin. If the right side is paralyzed during a stroke, then the diagnosis is very easy to make - almost always this pathology is accompanied by a violation of speech functions.
It is this indicator that allows you to identify the problem almost accurately.
Characteristic signs
Paralysis develops soon after the blood supply to the brain is disrupted.
Regardless of which artery was damaged, the disease is accompanied by both general and local symptoms.
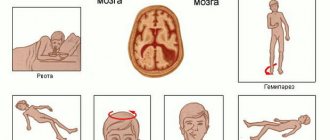
General symptoms:
- Dizziness, headache;
- Nausea and vomiting that do not bring relief;
- Loss of consciousness with possible aspiration of gastric contents;
- Drop in blood pressure, rapid pulse.
Paralysis begins from top to bottom. Its first manifestations are associated with damage to the motor cranial nerves:
- Loss of facial muscle tone;
- Drooping of the right eyelid and corner of the lips;
- Paralysis of half the tongue;
- Inability to speak, chew or swallow;
- Paralysis of the right eyeball.
Following damage to the cranial nerves, paralysis of the muscles of the head and neck occurs:
- Difficulty turning and tilting the head;
- When asked to squint or smile, the patient cannot comply with the command.
Paralysis of half the body indicates thrombosis of large arteries such as the internal carotid, vertebral, and basilar. Immobilization develops within 0.5-3 hours, depending on the depth and severity of the lesion. The loss of motor ability is of a descending nature with the parallel addition of ataxia (gait disturbance), tremor, and vestibular disorders.
After paralysis of the neck muscles, the process sequentially proceeds to:
- Muscles of the right half of the shoulder girdle and arm;
- Muscles of the trunk (intercostal muscles are affected last);
- The right half of the pelvis and the entire lower limb.
REFERENCE. In rare cases, a stroke attack lasts for hours or days. This is due to such a phenomenon as “increasing thrombosis” - gradual blocking of the vessel wall. In this case, the symptoms increase within 3-5 days and are accompanied by various disorders of intellectual functions, perception of the surrounding reality, and consciousness.
What to do if the right side is paralyzed due to a stroke? –
Receive a free consultation at our center: Request a call back Send us your medical documents Our medical team prepares a preliminary proposal for you You choose the best option For yourself On the date agreed upon with you, we will organize an appointment at the clinic You (with our help) purchase tickets, book a hotel , order a transfer, an interpreter and begin treatment abroad. We help you at all stages of diagnosis and treatment, as well as after your return home.
Often, after a stroke, a diagnosis of “stroke, paralysis of the right side of the body” is made - this is a serious complication of cerebrovascular accident, which indicates a lesion left hemisphere of the brain. Such syndromes lead in frequency of occurrence; this is explained by the peculiarities of the anatomy and physiology of the vascular system.
Etiopathogenesis
The main mechanism for the development of paralysis is stroke - damage to the artery with blood escaping beyond the vascular bed. As a result, a hematoma is formed, which gradually grows and compresses the brain tissue. Vital neurons die, loss of function is noted, control of skeletal and smooth muscles decreases, and sensitivity disappears.
This condition is predisposed to:
- Eating disorders – the main role is played by a lack of calcium in the diet, which strengthens the walls of the arteries. In these cases, cardiologists repeat “where it’s thin, that’s where it breaks.” Weakened brain vessels that are prone to damage can cause a stroke;
- Hypertension – the situation is aggravated by increased blood pressure, which can damage weakened blood vessels. In older people, there is a lack of calcium, which can cause artery rupture;
- Compounded heredity - according to recent studies, there is a predisposition to vascular diseases, especially hypertension and strokes. The mechanism has not been fully studied; insufficiency of the neurohumoral mechanism and weakness of the vascular wall are assumed;
- Obesity - this condition is accompanied by a lack of minerals, an increase in blood pressure, which increases the likelihood of developing a stroke with subsequent paralysis;
- Cardiovascular diseases - valve malformations, heart failure, atherosclerosis and thrombosis predispose to cerebral hemorrhage;
- Endocrine diseases - diabetes comes first, leading to hypertension and hemorrhages. Sometimes the causes are hypothyroidism, pathologies of the adrenal cortex;
- Bad habits - nicotine weakens the walls of arteries and increases cholesterol levels in the blood. Natural alcohol in minimal dosages is useful, but an excess of surrogate or drunkenness often ends in stroke and paralysis.
The listed factors can provoke both left and right paralysis. According to statistics, the latter option is observed more often, which increases the patient’s chances of survival due to timely diagnosis.
Types of paralysis
After a stroke, the doctor’s main task is to determine the presence of paralysis and its type. All hemorrhages on the right and left sides are divided into two categories:
- Peripheral paralysis is the most favorable variant of the disease, characterized by partial loss of function. The patient's motor neurons are damaged, which leads to loss of sensitivity and a decrease in complex and purposeful movements.
- Central paralysis - indicates hemorrhage in the motor areas, as a result of which the right arm and leg are completely amputated. Such patients are unable to care for themselves and there is a high risk of disability.
Signs of right-sided paralysis
If there was a stroke in the left hemisphere, the patient’s right side of the body is affected, the muscles of the limbs are paralyzed and there is no speech. These are the main differences between this condition. Patients also develop the following symptoms:
- Common symptoms are headache, nausea, vomiting and weakness. They appear in the first few days and are considered the body’s response to damage to brain neurons;
- Loss of movement - with central paralysis, the right limbs are flaccid, there is no sensitivity, the patient cannot perform any actions with the right arm and leg. If peripheral neurons are affected, the patient experiences tremor, and some movements are difficult on the same side;
- Reduced memory – there are difficulties in remembering sentences; in severe cases, it is difficult for a person to repeat individual words;
- Paresis of the right facial nerve - this branch innervates all facial muscles on its side. In the absence of control, the muscles relax, the patient’s corner of the mouth and lower eyelid “hang”;
- Spontaneous contractions of some skeletal muscles on the right - usually the arm is bent at the elbow joint, the leg is straightened, and inward rotation of the foot is noted.
The listed symptoms are observed a few minutes after hemorrhage. As health deteriorates, the patient develops stress, accompanied by depression and difficulties in communication.
Consequences of right-sided paralysis
In severe cases, right-sided lesions lead to irreversible complications that develop as a result of massive hemorrhage or violation of treatment rules. We list the most common conditions:
- paralysis of both arms and legs;
- lifelong speech dysfunction;
- disturbance of thinking, memorization, social behavior;
- the appearance of bedsores;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases against the background of reduced physical activity;
- enuresis and fecal continence disorders.
The doctor’s task is to create conditions that ensure full recovery after a stroke on the right side, which will minimize the development of complications.
Treatment
The therapeutic program is aimed at restoring blood circulation and nutrition in the affected area, preventing vascular disorders and recurrent strokes. Treatment includes the use of medications, rehabilitation and prevention measures.
Drug therapy
If the right side is paralyzed due to a stroke, you should start with drug therapy. The drugs of choice are:
- Antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants (Curantil, Warfarin) - thin the blood and improve its passage through the arteries. The use of these drugs is effective for atherosclerosis, thrombosis or vascular spasms;
- Diuretics (Hypothiazide, Veroshpiron) – remove excess fluid, prevent cerebral edema and hypertensive crisis;
- Antispasmodics (Papaverine, Vincamine) - relax blood vessels and improve blood circulation;
- Agnioprotectors (Parmidin, Alprostan) – have a beneficial effect on the arteries, preventing the development of spasms;
- Nootropics (Piracetam, Actovegin) - improve brain function. They are taken for a long time, including the rehabilitation period.
The doctor prescribes medications based on the patient’s condition. In severe cases, a complete list is written out, and daily blood pressure monitoring is carried out.
Rehabilitation
The main goal of recovery after a stroke is the return of movements on the right side, speech and memory. You should start with a diet, supplementing the procedures with massage, physical therapy and a visit to a speech therapist (comprehensive rehabilitation).
Diet
Diet is necessary to improve blood circulation and maintain immune resistance. A well-chosen table should contain everything necessary for the regeneration of damaged tissues, but not overload the weakened body.
The basic rules for the diet are as follows:
- exclusion of smoked and fatty foods;
- meat can only be eaten with the approval of a doctor, in small portions and pureed. The menu includes only lean varieties;
- enrich your diet with vegetables and fruits;
- exclude coffee, strong tea, soda and alcohol;
- food should be fractional, in small portions.
For seriously ill patients, the menu is prepared by a nutritionist, taking into account the state of the body and the necessary energy costs.
Massage
This method is aimed at preventing bedsores and is used from the first days of paralysis. The right side of the body is warmed up, after which blood circulation and tissue trophism are improved, and mobility in the joints is restored.
To eliminate the effects of paralysis, a standard warm-up includes:
- stroking - from the periphery, along the blood flow;
- rubbing – carried out more intensively, similar to the previous method;
- vibration movements – in the area of soft tissues;
- The procedure ends with stroking.
To prevent new bedsores from arising, it is recommended to massage daily, regularly change the patient’s position and rub the skin with alcohol (if there are no wounds).
Exercise therapy
Physical therapy is used 2-3 weeks after the attack, taking into account positive dynamics. Its main tasks are:
- prevention of muscle atrophy;
- improvement of neuromuscular conduction;
- restoration of motor coordination and self-care ability.
To create a complex, it is better to consult a doctor; the doctor selects an individual program, taking into account the lost functions and functioning of the limbs.
Visit to a speech therapist
To restore speech, daily training is required, which will be supervised by a specialist. The patient is given homework, including systematic exercises.
The objectives of such therapy are:
- restoration of oral speech;
- rehabilitation of writing;
- normalization of speech memory.
It is very important that a person not only learns to speak, but also understands the speech of others. Experts recommend that patients not isolate themselves, but constantly contact people.
Evaluate the quality and detail of the information
(7 4,43 of 5) Loading...
Source: https://Evexia.ru/nauchnaya-rabota/poleznye-sovety/chto-delat-esli-pri-insulte-paralizovalo-pravuyu-storonu/
Consequences of paralysis
The consequences are more pronounced in cases where a large cerebral vessel was damaged, or treatment was started inadequately and at the wrong time. The following consequences are possible:
- Persistent facial expression disorders, drooping eyelids;
- Swallowing and chewing disorders;
- Decrease in intelligence;
- Movement coordination disorder;
- Loss of control over pelvic functions (defecation, urination);
- Partial memory loss, speech, reading and writing impairments.
Often, if the right side of the body is paralyzed, speech is completely absent. This complicates the recovery process.
Disability with this disease reaches 30%.
Why does the disease occur?
In the case of the development of paralysis during a stroke, various diseases act as unfavorable factors. The list of possible reasons includes:
- arterial hypertension in case of uncontrolled flow;
- atherosclerotic changes in the vessels of the brain or vessels of the cervical spine;
- some diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- suffered a severe stressful situation, as well as as a consequence of a hypertensive crisis.
The cause of the disease may be the presence of certain problems with blood clotting, certain endocrine disorders. Stroke is often diagnosed in people with global capillary damage; the risk of its occurrence is increased by a sedentary lifestyle and taking hormonal medications.
Irreversible changes in the cerebral cortex and its trunk also occur during prolonged oxygen starvation.
When the lesion is located in the left hemisphere of the brain, symptoms appear on the right. A speech disorder is considered a dubious sign, since it mainly affects left-handed people.
Treatment and recovery of the paralyzed side
Treatment should be organized before hospitalization.
The first measures begin at home or during transport to the hospital and include:
- Providing access to oxygen;
- Control of breathing and blood circulation;
- Maintaining blood sugar levels (since the brain feeds on glucose) - intravenous administration of glucose;
- Thrombolysis (measures to dissolve blood clots) - administration of thrombolytic drugs;
- Prevention of cerebral edema (diuretics);
- Replenishment of fluid losses (administration of saline solution, blood substitutes according to individual schemes).
Inpatient therapy is based on therapeutic measures and maintenance of vital functions.
Mode: bed. The patient is in the intensive care unit and then transferred to a neurological hospital;
Nutrition: parenteral and through a tube. They use special protein-carbohydrate mixtures, amino acid solutions, and glucose.
Therapeutic measures:
- Prevention of recurrent thrombus formation (antiplatelet agents, thrombolytics);
- Strengthening the walls of blood vessels (vascular drugs, nicotinic acid);
- Maintaining brain functions (nootropics);
- Blood pressure control (hypertension medications, beta blockers);
- Stabilization of concomitant diseases (antiarrhythmics - for arrhythmia, statins - for atherosclerosis, insulin - for diabetes).
Restorative procedures
Rehabilitation should begin as early as possible.
This is due not only to the possibility of faster recovery, but also to the prevention of complications.
The most common complications for bedridden patients are:
- Loss of body weight;
- Bedsores;
- Depression;
- Pneumonia.
Rehabilitation should be gradual and carried out in a hospital , at home and in a rehabilitation center. The main procedures for restoring lost abilities are massage and passive (later active) exercises on the side that is paralyzed. If the patient is cared for by loved ones or social workers, they should learn the basics of rehabilitation from professional rehabilitation therapists.
Useful video on the topic:
Massage
The massage is carried out to prevent muscle atrophy; it has the following features and rules:
- All types of tonic or specific massage are prohibited;
- You can massage only with stroking movements;
- Full body massage is not recommended.
REFERENCE. The session should begin with one area (including the healthy half), for example, the head. After a few days, the cervical-collar area is connected, then the arms, back, and legs. Massage on the front half of the body is not performed.
Exercises
In the first 2-3 months, only passive exercises are performed.
They consist in the fact that the caregiver himself carries out the exercise , and the patient does not make active efforts to perform it.
Types of exercises:
- Slow tilts of the head to the right and left;
- Bending the elbows, circular movements in the forearm, turning the wrist;
- Vibration and breathing exercises;
- Bending the legs at the knee, turning the bent leg left and right.
Subsequently, classes on fine motor skills are added. The patient must eat independently and perform simple hygiene procedures. Washing and walking are carried out together with the caring staff.
During treatment and rehabilitation, paralysis may go away completely or partially. Depending on the dynamics, after about six months they begin active exercises. They include:
- Group walks;
- Simple exercises in a sitting position (torso bending);
- Exercises with a gymnastic ball;
- According to the patient’s condition, exercise in the pool (but not active swimming).
Second stroke in 2013. Right arm and leg do not work
insultu-net.ru
Hello, Alexander! I accidentally saw your correspondence on the site and decided to write in the hope that you could help me with something.
The story of my problem will be long, I hope you will understand everything. In my position, I have no one to rely on, so I turned to you.
First stroke - hemorrhagic in 1995
In May 1995, I suffered a hemorrhagic stroke (the first), was hospitalized immediately, stayed there for almost a month, was discharged to recover at home, my mother and my children and husband looked after me, pretty soon I recovered almost completely, they gave me 1 gram. disability.
I was not completely examined, nothing, our hospital in Ust-Kut at that time apparently was not equipped with the necessary equipment, so I recovered as best I could, I read on the Internet how to be treated.
And only after 11 years I was able to get out to the Region. hospital, went to get checked by a vascular surgeon, and I also have lymphedema and at the same time checked with a neurologist (attached an extract).
Second stroke. Consequences
And in 2013, the second stroke struck, here I myself refused hospitalization, and the doctor on duty did not insist, he said it was already going away, took a receipt and I safely met the stroke at home, I did not call the doctor.
I understand that it’s my own fault, I should have insisted on first aid. Then, later, I called a neurologist friend, she prescribed a system, injections, agreed with the nurse, she came and treated me. I invited a massage therapist 2 times, she gave me a massage, she did some exercises herself, but somehow it didn’t go away.
After a stroke, the right leg does not work well, the arm does not work
As a result, my right hand doesn’t work, it’s bad, I move with a cane to the kitchen, the toilet, along the walls, leaning against the walls, my speech is not affected at all, my memory too, only my right arm and leg, tactile sensitivity is preserved, I feel hot, cold, pain with a wound in the arm, maybe it’s because of a cyst? Tell me, what can I do or wait patiently for the outcome?
Possible reasons
Hello. You developed problems with your right arm and leg after your second stroke (repeated). It’s a pity that I didn’t get examined after the first one. Hemorrhagic I., especially under the age of 50, is a reason to exclude anomalies in the structure of cerebral vessels. Arteriovenous malformations and aneurysms are common causes of intracerebral hemorrhage.
And not just hemorrhages. For example, a growing aneurysm can cause acute cerebrovascular accident
You wrote that you consulted a vascular surgeon. Did he recommend cerebral angiography for you? This is MR angiography or CT angiography. This would make it possible to assess the structure of the vascular bed of the brain. And regarding lymphostasis, did you find the cause? There may also be a problem common to the causes of ischemic I.
Stroke in the basal ganglia
You had a stroke in the area of the basal ganglia - the place where the nerve pathways pass as tightly as possible. This means that even with a small lesion, a large portion of the nerve pathways responsible for conducting nerve impulses is affected. At the same time, higher nervous functions (speech, memory, counting, logic) are not affected.
A cyst is a consequence of the death of nerve cells and its replacement with cerebrospinal fluid. The reason is what happened in 2013.
Forecast
What to expect next. You still have hemiparesis, about which you can read more here. Spastic - accompanied by an increase in muscle tone. The higher the tone, the more damaged the motor pathways are. Rehabilitation is definitely needed.
As for the prognosis after the second stroke - the full return of muscle strength is a difficult question - more likely no than yes, after 5 years. But it is possible to improve the mobility of your right arm and leg. This requires exercise therapy under the supervision of a physical therapist.
A set of exercises that you will perform independently and under his supervision. The movements will train and improve mobility and dexterity of the limbs. This will affect your confidence when walking and moving around the house.
And it is important to assess muscle spasticity. If spasticity is high, the issue of muscle relaxants needs to be addressed. These are drugs to reduce muscle tone. If they are not effective, then discuss with your doctor the issue of botulinum therapy.
If you find the article useful, share it on social networks. I would be grateful [upto]
Sincerely, neurologist Postnikov Alexander Yurievich
Source: https://insultu-net.ru/vtoroy-pervyy-insult-posledstviya-ne-rabotaet-pravaya-ruka-i-noga-prognoz-problemy/
Prognosis for paralysis
The prognosis is determined by the size of the paralyzed area, the affected area of the brain, the person’s age and the presence of complications. If thrombolysis was started in the first 6-12 hours from the moment of the attack, the prognosis for life and health is relatively favorable. Paralysis in such patients can disappear within 3-4 months.
IMPORTANT. If the stroke was accompanied by collapse, coma, or breathing problems, the prognosis is less favorable. This group of people is characterized by persistent lifelong impairments, paralysis goes away partially or not at all.
Massage treatment
To speed up the healing process and improve blood circulation in the brain, you can use massage. Foot massage after a stroke (and the whole body) is performed using:
- Stroking. With a relaxed palm they slide over the surface of the skin, collecting it into large folds. At first, the strokes should be superficial, but gradually their depth should be increased. They should capture fatty tissue and muscle. The specialist’s hand should move in a zigzag, spiral pattern. With this massage you can tone the body and, by removing the top layer of cells, improve blood circulation and tissue nutrition.
- Rubbing. This increases tissue elasticity and reduces swelling due to fluid movement. You need to rub the skin using your fingertips, the base of your palm, or your hand clenched into a fist.
- Kneading. This is a type of passive gymnastics. During the procedure, the muscle is grabbed, pulled, and compressed. There is also some effect on the blood vessels. Kneading helps increase the elasticity and tone of muscle fibers. Therefore, in the presence of spastic changes, the procedure is prohibited.
- Vibrations. The specialist performs oscillatory movements with a relaxed hand on the affected part of the patient’s body. The massage is performed at different speeds and amplitudes. Therefore, the result may be different. If the vibration is strong, then muscle tone decreases, and if it is high, it increases. Movements are usually performed from right to left.
Similar treatment can be carried out at home. It is carried out independently by loved ones, by hiring a specialist or using massagers.
Relatives of the victim should perform massage on the affected side, gradually moving to other areas. After a stroke, people only have:
- palmar surface, anterior part of the shoulder and forearm;
- pectoral muscle;
- the anterior surface of the thigh and the back of the lower leg;
- muscles of the sole.
These areas can only be massaged superficially, by stroking or lightly rubbing. For other areas, intense movements are suitable.
When massaging a patient in a supine position, you need to place a pillow under your head and a bolster under your knee. To prevent a healthy limb from moving, it can be secured with weights.
The process of recovery after a stroke is difficult and lengthy, but if the victim himself and his relatives make every possible effort, the result will be positive.
Care and psychological support
Patient care must be continuous and comprehensive. Activities include:
- Organizing high-calorie meals and monitoring the patient’s intake of food;
- Assistance during hygiene procedures;
- Changing clothes once every 3 days and changing bed linen once a week;
- Regular change of vessel;
- Applying heating pads to the patient’s feet;
- Assistance with mobility;
- The use of moisturizers (since the skin of patients is dry and prone to atrophy);
- Walk at least 40 minutes a day.
Until the patient is able to move independently, he should be turned over in bed every 2 hours (prevention of bedsores).
Psychological support for patients helps speed up recovery and prevent depression.
The main measures are aimed at eliminating isolation and patient education:
- It is necessary to explain to the person the importance of full therapy;
- For rehabilitation, group rather than individual classes are preferable.
Relatives should not just visit the patient, but organize joint leisure time with him (reading books, walking, talking). This will help a person feel not cut off from their usual life.
How to learn to use a walker
As soon as the patient learns to stand confidently on his feet without support, he can begin to take his first steps. You can’t do this without an assistant, since he must belay from the paralyzed side to prevent a fall.
The patient should place the assistant's hand on the neck and rest his knee on the assistant's knee. Having fixed the joint, you can take the first step.
The assistant’s task is not only to support the patient, but also to control the correctness of his gait. When the patient moves with the help of a walker, it is necessary to ensure that the placement of the foot, rotation of the knee and hip joint are correct.
WE RECOMMEND SEEING: Medications for microstroke of the brain
The whole process has several features:
- The patient cannot fully grasp the assistant's hand, since it is weakened.
- To take a step, he needs to throw his leg forward, which leads to the helper's leg catching.
- It is much more convenient to support the patient from a healthy part of the body, but the knee joint will not be fixed and the patient will not be able to hold on to the wall with his healthy hand.
The main purpose of using a walker is to gain the ability to bend the leg in all joints, otherwise the patient will constantly cling to the floor with his foot. The assistant should remind the person that the leg should be raised higher and bent at all joints.
High boots that fix the ankle joint will help facilitate movement. The affected arm should be secured with a scarf so that it does not sag during movement and the head of the humerus does not come out of the socket. During exercise, you should monitor the patient’s heart function and give him rest.
Once the patient can move with the help of a walker without assistance, he or she can begin to walk independently. This is done with the help of a cane, holding on to the walls, moving a chair in front of you. But it is important to ensure that the load is evenly distributed. You cannot spare the sore leg by relying more on the healthy one.
Conclusion
With timely and adequate treatment, patients can be rehabilitated within 6-9 months. Regardless of how long the recovery takes, patients must adhere to certain recommendations throughout their lives:
- Monitor blood sugar and cholesterol levels;
- Change your diet (replace meat with fish, eliminate processed foods and baked goods, reduce salt intake);
- Be attentive to changes in your condition;
- Control urination, bowel movements and sleep duration;
- Continue taking medications to treat concomitant diseases.