External hydrocephalus of the brain is considered a disease of newborns, but the disease also occurs in adult patients. The development of hydrocephalus is caused by impaired absorption or outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. At the Yusupov Hospital, neurologists use modern diagnostic methods that make it possible to establish the causes, form of the disease and severity.
For mild hydrocephalus, conservative therapy is carried out aimed at reducing intracranial pressure and improving the function of nerve cells in the brain. Neurosurgeons at partner clinics perform surgical interventions that eliminate the cause of the disease. After surgery, patients’ quality of life improves and impaired nerve functions are restored.
What is hydrocephalus?
The trophism of nervous tissue is ensured by the continuous circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. Cerebrospinal fluid moves along a certain path within the cerebral structures, participating in metabolism. Liquor protects tissue from mechanical stress, provides stable concentrations of electrolytes, acid-base balance, and acts as an immunobiological barrier.
Hydrocephalus is a pathological condition characterized by disturbances in the production, outflow and/or circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, its excessive accumulation, often with an increase in the level of intracranial pressure. The disease is characterized by neurological symptoms. Over time, hydrocephalus leads to the development of secondary changes. Synonym: dropsy of the brain. Uncontrolled course of the disease is fraught with death.
Manifestations of dropsy:
- attacks of cephalalgia (headache);
- fluctuations in blood pressure;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- urinary incontinence;
- unsteadiness of gait;
- mental disorders (dementia, etc.);
- in young children - a progressive increase in head size, a symptom of the setting sun, etc.
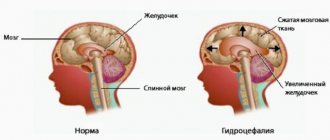
Schematic representation of the ventricles of the brain normally and with internal hydrocephalus.
In the early stages of the development of pathology, changes occur in the brain, but there are no neurological symptoms. Manifestations arise against the background of organic processes in the cerebral substance, circulatory disorders, and atrophy of individual areas.
Hydrocephalus is a sign of the disease, because is a complication of the latter. The idiopathic form of the pathology practically does not occur. Hydrocephalus and its causes are identified using neuroimaging methods. MRI is considered the most informative.
The pathology is most often diagnosed in children in the first 3 months of life. The disease also occurs in adults, especially after 60 years. Reasons for the development of hydrocephalus:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- tumors;
- vascular pathologies;
- infectious diseases;
- previous neurosurgical operations;
- strokes and hematomas;
- developmental abnormalities of the central nervous system.
Treatment tactics for cerebral hydrocephalus depend on the type of disease. If the course is favorable, drug therapy is prescribed. If the drugs are ineffective and there is a high risk of complications, surgical intervention is performed urgently.
3.Endoscopic operations for occlusive hydrocephalus
Of course, this serious disease requires effective and timely treatment. Patients suffering from this pathology usually undergo the following endoscopic operations:
- aqueductoplasty;
- ventriculocystocysternostomy;
- endoscopic implantation of shunt systems;
- ventriculocisternostomy (perforation) of the bottom of the third ventricle of the brain.
Today, doctors consider perforation of the floor of the third ventricle to be the best option in the treatment of hydrocephalus.
. The essence of this surgical intervention is to create an anastomosis (an artificial passage in the form of a small hole) between the ventricular cavities. This measure can provide additional opportunity for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. This operation is performed using a ventriculoscope - a special optical device that allows the operating surgeon to control all manipulations with endoscopic instruments performed within the ventricular system.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Types of hydrocephalus
Depending on the cause of development, hydrocele of the brain can be congenital or acquired. Based on the distribution of cerebrospinal fluid, pathology is classified into types:
- external;
- internal (mono-, bi-, tri- or tetraventricular);
- mixed.
Based on the mechanism of development, hydrocele of the brain occurs:
- open (communicating);
- closed (occlusal).
Internal triventricular occlusive hydrocephalus on MRI in the frontal and sagittal planes: the left image shows a giant cystic-solid formation, which was the cause of obstruction of the cerebrospinal fluid ducts at the level of the aqueduct of Sylvius
What is the danger of the disease?
The consequences of dropsy largely depend on the age at which the disorders occurred and the development of complications:
- Infants experience high excitability, sleep disturbances, and increased muscle tone. The most severe manifestation is developmental delay and mental deviations.
- Preschoolers show aggression, stutter, develop strabismus, and experience developmental delays.
- School-age children experience memory loss and headaches. The learning process is difficult.
- In adults, epilepsy, increased excitability, and hallucinations appear.
The danger of the disease in adulthood is the development of mental disorders, motor functions and motor skills. If urgent measures are not taken, the patient becomes disabled.
Will an MRI show hydrocephalus?
With magnetic resonance imaging, layer-by-layer images of the anatomical area being studied are obtained. When examining the scans, the doctor sees the brain matter and identifies abnormalities. MRI clearly shows hydrocephalus. The method is informative in the early stages of the disease, even if the patient does not have characteristic symptoms. Detailed images allow doctors to identify dropsy of the brain, determine the type, and diagnose concomitant diseases.
Hydrocele of the brain on coronal MRI scanning
Symptoms
The main signs of hydrocephalus in children are accelerated head growth and an enlarged, disproportionate skull. In newborns, the following symptoms of non-occlusive hydrocephalus occur:
- tense fontanel;
- frequent tilting of the head;
- downward displacement of the eyeballs, strabismus;
- pulsating rounded protrusions in places where the bones of the skull are not fused.
Adult patients with hydrocephalus complain of a feeling of heaviness in the head and headaches that get worse in the morning. They may experience high or low blood pressure, palpitations, sweating, nausea, and vomiting in the morning. Increased fatigue and fatigue, nervousness develops. The gait is disturbed, the condition worsens when the weather changes. Over time, urinary incontinence and paresis of the lower extremities develop. At a late stage of the disease, intelligence is impaired and the ability to self-care is lost.
To determine the form and severity of hydrocephalus, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a comprehensive examination of patients, including computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, fundus examination, craniography, and ultrasound. Doctors perform a lumbar puncture and collect 40 ml of cerebrospinal fluid for laboratory testing. Improvement in the patient's condition after the procedure indicates a good prognosis for recovery after surgery.
Signs of hydrocephalus in adults according to MRI
Manifestations of pathology in photographs can be direct or indirect. The first are associated with the expansion of the cerebral ventricles (III, IV and lateral (in the initial period - in the area of the anterior horns and body)), aqueduct and/or subarachnoid space (convexital, in the area of the basal cisterns, Sylvian fissures, etc.). Indirect signs on MRI scans:
- interventricular index over 0.5;
- periventricular edema with intense dropsy;
- downward displacement of the hypothalamus;
- local protrusion of the roof of the lateral ventricles, etc.
Additionally, tomograms determine the cause of cerebral hydrocele—the underlying disease.
Reasons for the development of pathology
The human brain consists of soft tissues located in the skull. To protect against damage, cerebrospinal fluid circulates in the cavity - the liquid fills the internal ventricles and grooves. When a person is healthy, the inflow and outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is balanced. The performance of its functions does not affect the patient’s health. If disturbances occur due to the development of tumors, injuries and infections, intracranial pressure increases and the process of cerebrospinal fluid movement is disrupted, causing changes in brain function and neurological manifestations.
Hydrocephalus can develop due to a stroke or tumor development.
Treatment of the disease
To effectively solve the problem of excess cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricular system of the brain, drug therapy and surgical intervention are used. Treatment with pharmaceutical drugs is aimed at eliminating the initial stages of the disease. Their list includes medications whose action is aimed at reducing ICP, removing excess fluid, and also improving the nutrition of brain cells. In case of diagnosing acute or chronic forms of pathology, surgical operations are prescribed. These include:
- external ventricular drainage, which makes it possible to ensure the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and administer blood thinners;
- cerebrospinal fluid shunting, based on the removal of excess volumes of cerebrospinal fluid using a system of valves and tubes in the patient’s body cavity, including the atrium, peritoneum, etc.;
- endoscopic plastic surgery of the interventricular foramen, aimed at freeing the natural outflow pathways of cerebrospinal fluid from the lateral ventricles.
The form and stage of development of the pathologist determines the method of treatment.
Diagnostic methods of determination
The clinical picture in patients with hydrocephalus is so obvious that it allows the specialist to suspect the occurrence of the disease already during the initial examination. Next, the doctor needs to diagnose the form of pathology and the root cause that led to dropsy. Instrumental diagnostic methods come down to methods such as X-ray examination, ultrasound, computer or magnetic resonance scanning.
On a traditional x-ray, thinning of the bone tissue of the skull, divergence of the sutures, the formation of small intra-shell cavities, and asymmetry of the skull are clearly visible. An ultrasound examination reveals an increase in pressure in the head area. Upon examination by an ophthalmologist, degeneration of the optic nerve, loss of peripheral fields and decreased visual function are diagnosed.
During any type of tomography, the type of anomaly, the location of the root cause and intrauterine developmental anomalies are determined. If the source of compression of the cerebrospinal fluid system is a tumor process, the nature of the formation and the degree of its ingrowth into the tissue are revealed. If the pathological phenomenon is caused by a disorder in the vascular network, MRA of the vessels is prescribed. Additional information can be obtained by studying the composition of the cerebrofluid, which is taken by puncture. The same method is also used to identify an infectious pathogen that causes an inflammatory process.
How to deal with pathology?
Drug therapy is effective for acquired dropsy. The root cause is treated, diuretics are used to reduce the amount of fluid in the body.
The congenital type of anomaly is treated with surgery to get rid of the anatomical defect or tumor object. If it is not possible to restore the normal outflow of the substance, an artificial bypass is performed to remove excess water from the cranial cavity. This procedure can be carried out repeatedly.
Diet
The patient's nutrition should be aimed at improving the water-salt balance. Foods that cause fluid accumulation should be excluded from the diet. Instead, vegetables and fruits, steamed meat, and cereals are introduced into the menu.
It is important to lead a healthy lifestyle, exercise with moderate exercise, and walk a lot. Following these recommendations will help maintain the patient's mental and mental fitness.
Dropsy is a serious disease that does not go away on its own. The patient requires qualified specialist assistance for life. The disease is in an advanced stage and cannot be treated.
Which doctor should I contact?
Hydrops is treated by neurosurgeons. When you contact the RAS clinic in Moscow, you will be provided with qualified, effective assistance: they will conduct an examination, prescribe tests, make a diagnosis, and determine an effective treatment strategy.
If any symptoms of neurological diseases appear, you must immediately make an appointment with a neurologist to prevent the situation from worsening. We invite you to a consultation with a neurologist in Moscow at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Registration can be made by phone or using the feedback form on the website.
What is the disease characterized by?
The function of nourishing the brain and protecting it from concussions is performed by the liquid that washes it - cerebrospinal fluid. Excessive accumulation or disruption of outflow causes the development of moderate external hydrocephalus.
Some neurologists say that this disease can only appear in children and is a congenital pathology. Of course, there are quite a lot of newborn babies who suffer from dropsy. But it is not necessary to unequivocally classify hydrocephalus only as a congenital pathology.
In adults, the disease is difficult to diagnose. The patient may be treated for an entirely different mental or neurological condition without suspecting hydrocephalus. Dropsy is a dangerous disease that can provoke various neurological disorders.
Moderate hydrocephalus often has two stages of development. The acute stage is characterized by the appearance of signs of the disease that caused hydrocephalus. During the chronic stage, symptoms appear that indicate brain pathology itself.
Diagnostics
The following diagnostic methods are used:
- The beginning of the examination is characterized by a detailed history taking. The onset of symptoms, the nature of their course, and the presence of primary pathology are determined.
- Neurological examination. The specialist determines intracranial hypertension and focal symptoms.
- Ophthalmological examination. The condition of the fundus and optic nerves is determined. Ophthalmoscopy, perimetry, and visometry are performed. Visual fields and visual acuity are examined.
- Echoencephalography. Determines intracranial hypertension, enlarged ventricles, and movement of brain tissue.
- Neuroimaging. In infants, it is performed using neurosonography through the fontanel. Adults are diagnosed using an MRI of the brain. In this way, developmental pathology and the location of the block of liquor vessels are determined.
Competent differential diagnosis excludes subarachnoid hemorrhages. In young children, it is important to exclude macrocrania, which is a hereditary feature.
Prevention of hydrocele of the brain
Observation and examination of a pregnant woman will help identify abnormalities in the development of the fetus and promptly treat the infectious disease. Women whose close relatives suffer from hydrocephalus require special attention.
Caring for the fetus will protect it from intrauterine injuries and diseases. Newborns at risk require observation by a specialist.
It is necessary to protect young children from traumatic brain injuries and protect them from neuroinfections. This will also prevent the development of the disease in adults.
Congenital hydrocephalus stops its development, but is not cured. Treatment for older children may be beneficial. It depends on the severity of the disease, timeliness and quality of treatment.