Angelman syndrome ("happy puppet" syndrome, "parsley syndrome") is a fairly rare neurogenetic disease associated with chromosomal abnormalities.
According to approximate data, per one thousand newborns there is one child with this pathology. Patients experience physical and intellectual developmental delay, sleep disturbances, seizures, sudden movements, and frequent, causeless laughter.
Children with this pathology always look very happy.
History of the study of the disease
The disease is named after Harry Angelman, a British pediatrician who first differentiated this syndrome in 1965. Then it was called happy puppet syndrome, but today this term is not used, as it was considered disparaging.
Dr. Angelman had treated several children with similar symptoms and suspected a common diagnosis. It was not possible to prove the diagnosis and obtain accurate data at that time due to the lack of technologies that are available today. The doctor reflected his guesses in an article entitled “Children of Puppets.”
At that time, the publication did not arouse much public interest, and was soon forgotten. It was remembered again in the eighties, when the necessary research methods appeared. Scientists have found that most children suffering from the syndrome are missing a small part of chromosome 15.
Pathogenesis and causes
This defect occurs due to deletion (loss of a piece of genetic material) of a segment of chromosome 15. Other causes are often cited as unipaternal disomy (inheritance of two paternal copies of a chromosome, instead of copies from both parents), translocation or mutation of a single gene.
The syndrome can also appear as a result of a mutation in a gene involved in ubiquitin metabolism.
Most patients with this pathology do not have a family history of genetic abnormalities. However, for a certain percentage of patients this syndrome is inherited. The risks become higher if the parents have chromosomal abnormalities. An interesting fact is that if a child with this syndrome is born in a family, then the probability of having another child with the same pathology is 1%.
The appearance of Angelman syndrome is quite spontaneous, and almost any family can have a child with this disease. There are no specific statistics on the number of children with this syndrome.
According to various estimates, the number of newborns with doll syndrome ranges from one in ten thousand to one in twenty thousand. Scientists suggest that in reality this number is much higher.
Angelman syndrome - what is it?
This pathology is a congenital disease. It develops in utero. This disorder was first described by a British pediatrician, Dr. Harry Angelman, in 1965. Back then, patients with this diagnosis were called “doll children.” The disease itself was called “happy puppet syndrome.” This disease has other names. One of them is Parsley syndrome. This pathology is accompanied by delayed physical and mental development, walking on straight legs and laughing for no reason. Outwardly, patients with this diagnosis look like dolls.
Angelman syndrome - causes
To this day, scientists are studying the factors that provoke the development of this pathology. Angelman syndrome develops more often, if genetics are disturbed. In other words, the likelihood of its occurrence increases when one of the parents has chromosomal defects. However, Angelman syndrome, Parsley syndrome, and the laughing doll syndrome can also appear spontaneously in a baby whose parents are completely healthy.
The following factors have a teratogenic effect on a child:
- bad habits of a pregnant woman;
- long-term use of psychotropic drugs by parents;
- strong feelings of the expectant mother, provoked by grief or excessive stress;
- an inflammatory process that affects the reproductive system of a pregnant woman;
- stay of the expectant mother in a zone of increased radiation radiation.
Angelman syndrome - type of inheritance
This pathology occurs due to a disturbance in the process of chromosome division. Angelman syndrome has a karyotype of 46 XX or XY. Defects are found in the 15th chromosome. The mutation manifests itself as follows:
- Deletion
is the loss of a piece of chromosome. Patients with this disorder suffer from severe mental retardation. These children in most cases cannot walk or talk. In addition, such patients are often overcome by epileptic seizures. - Duplication
is the appearance of extra genes. If Angelman syndrome is diagnosed, patients are more likely to die in infancy. Sometimes such people survive until puberty. - Inversion
is a defect in which part of a chromosome is missing. In this case, the genes are located in the reverse sequence. - Translocation
- part of a chromosome is attached to another. - Uniparental disomy
is a disorder in which a child inherits two copies of the father's set of chromosome 15. He does not receive maternal benefits.
Genetic mutations increase the risk of developing the disease
The appearance of Angelman syndrome is associated with the presence of various chromosomal abnormalities in the parents of the unborn child. Among such deviations are usually called:
- chromosome trisomy - the presence of one or more extra chromosomes in the chromosome set;
- inversion - a turn of one of the chromosome sections by 180 degrees, while part of the chromosome is skipped, and the genes are arranged in the opposite order;
- microdeletion , which is the result of rearrangement of the Y chromosome and the exchange of sections between chromosomes, a small number of chromosomes is observed, and one of the genes may be missing;
- deletion – lack of one of the chromosome sections;
- translocation - transfer or attachment of a section of one chromosome to another chromosome;
- duplication - copying part of chromosomes, resulting in excess genetic material;
- ring chromosome - there is no genetic material at the ends of the chromosome, while the newly formed ends are connected in the form of a ring.
Article on the topic: Treatment of colds in children and adults with medications, folk remedies and physiotherapy
Gene mutations that can cause the syndrome
Symptom groups
Angelman syndrome is usually diagnosed between the ages of 3 and 7 years, when symptoms become severe. A newborn child with the syndrome does not differ from healthy children, however, during the first months of life, problems with feeding appear, children slowly gain weight, problems with sleep, and delays in the development of motor skills are observed.
All symptoms of parsley syndrome are divided into several types. They have a relationship with the neuralgic, mental and physical condition of the patient:
- Physical symptoms include vision problems (strabismus, optic atrophy), tongue protrusion, wide mouth, large distance between teeth, head size proportionately smaller relative to the size of other parts of the body, albinism and hypopigmentation, inflexion of the leg joints when walking (hence the comparison with puppets), scoliosis.
- Neurological symptoms include tremors in the limbs, a range of sleep disorders, hysterical fits, the intensity of which is high at the age of three and gradually decreases as they grow older, problems in the communication process (delayed speech development), hyperactivity and attention deficit.
- Psychological symptoms are usually expressed in overly emotional behavior (always happy appearance, friendliness), severe mental retardation.
Clinical picture in detail
Different patients may exhibit different symptoms. This difference depends on the degree and type of chromosomal abnormality.
Signs can be divided according to the frequency of their manifestation in children with Angelman syndrome:
- Symptoms that appear in all patients . These include severe functional developmental delay, behavioral deviations (laughter and smiling for no reason, a state of happiness, increased excitability, decreased concentration). Also, absolutely all patients experience impaired motor functions, impaired balance, tremors, a predominance of nonverbal skills over verbal ones, and speech disorders.
- Symptoms characteristic of 80% of patients . Stunted growth leading to disproportion of the head relative to other parts of the body. This often leads to the development of microcephaly. Children under three years of age often experience epileptic seizures, then they become less frequent or disappear altogether. Electroencephalogram results are often abnormal, with low-level waves having increased amplitude and temporal dynamics.
- Symptoms that occur in less than 80% of patients . Such manifestations include strabismus, decreased ability to control tongue movements, problems with swallowing, hypopigmentation of the eyes and skin, albinism. Many patients experience increased activity of tendon reflexes. In early childhood, many people have problems with eating and sleeping. Manifestations also include drooling, tongue protruding, and constant thirst. External signs also include the presence of a flat back of the head and smooth palms.
As you grow older, the manifestations of the syndrome change. Sleep disorders, hyperactivity, and seizures are less common. Adults with Angelman syndrome appear younger than their peers.
Puberty occurs a little later than in individuals who do not have this pathology. Patients can have their own children, but there is a high risk of transmitting the disease to their offspring.
Many adult patients suffer from uncontrollable urination. Often there are difficulties with motor skills, which leads to the need to wear clothes without zippers and buttons. Among adult patients, there is a problem of excess weight, so it is necessary to monitor compliance with a special diet.
Children perceive oral speech well and understand the content of almost all conversations, but rarely respond. They often refuse to take part in the conversation and use several dozen words in their speech.
Symptoms
The first signs of Angelman syndrome appear towards the end of the child's first year of life. Symptoms become more obvious after reaching the age of two. The syndrome is characterized by polymorphic clinical manifestations. Patients can be recognized immediately. Such children have a characteristic appearance.
- Features of the appearance of a sick child: discrepancy between a small head and a normal body, large mouth, constant smile, wide interdental spaces, narrow lips, protruding wide tongue, malocclusion, flat back of the head, smooth palms, pointed chin, hypopigmented skin, strobism, scoliosis, walking on straight legs.
- Violation of psycho-emotional development is manifested by mental retardation, excessive fussiness, friendliness, causeless laughter, and euphoria.
- Neurological symptoms: limb tremors, ataxia, incoordination, loss of balance, muscle hypotonia, sleep disorder, hysteria, speech impairment, hyperactivity and hyperexcitability, learning difficulties.
- Movement disorders: poor control over the movement of the tongue and its unreasonable protrusion, difficulties with swallowing and sucking, arms raised or bent while walking, frequent drooling, irrepressible thirst, excessively active chewing movements, impaired fine motor skills, epilepsy.
Children with Angelman syndrome are prone to nonverbal communication: they perceive oral speech, but cannot express their thoughts. They practically do not participate in the conversation, since their vocabulary consists of 10-20 words necessary in everyday life. Patients have stereotypies - repeated flapping of arms, twisting of hands and frequent clapping of hands, as well as other actions that are not typical for healthy people. A shaky gait is accompanied by sharp twitching of the arms, which makes the person look like a puppet. Patients feel more comfortable in water and do not tolerate stuffy rooms and high temperatures.
With age, the clinical picture of the disease changes significantly. Convulsions and seizures occur less and less often or disappear completely. Patients become calmer and their sleep improves. Men and women with this syndrome have a youthful appearance that hides their true age. They experience puberty on time, and may even have children.
Symptoms of the pathology in adults include impaired fine motor skills and urinary incontinence. Patients cannot cope with buttons and zippers on clothes, but at the same time they can easily use a fork and spoon. They are friendly, loving and affectionate. Obesity is a common disorder among adult patients, especially women. People with Angelman syndrome are prone to autonomic and somatic disorders. They do not tolerate hot weather well and often suffer from constipation and esophageal reflux.
Since the disease is congenital, all of these anomalies can appear immediately after childbirth. Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to identify the syndrome in utero and prevent the birth of a sick child.
Video: examples of children with Angelman syndrome
Diagnosis and timely detection
Doll syndrome can be diagnosed before the baby is born by conducting a genetic study of the fifteenth chromosome.
Article on the topic: Use of Cortexin for the treatment of children: instructions and reviews
Diagnosis can be invasive or non-invasive. An invasive research method has existed in medicine for a long time, but is quite risky, since it requires penetration into the uterus and collection of amniotic fluid.
The non-invasive method involves testing the mother's blood and testing the baby's DNA. Based on this study, conclusions are drawn about the presence or absence of certain deviations.
Diagnosis is also carried out on newborns who exhibit disturbances in muscle tone and delays in the development of speech and motor skills.
It is necessary to monitor the baby’s facial expression, behavior, expression of emotions, and movements. If a baby has difficulty bending the limbs, tremors, chaotic and sudden movements of the limbs are observed, then it is worth seeking advice and help from specialists.
Often, the diagnosis of Angelman syndrome is made between the ages of 3 and 7 years, when a clear manifestation of the signs of this disease can be noticed. Depending on the extent of damage to chromosome 15, manifestations can vary in severity: some patients even have difficulty speaking, while others can lead an independent life.
Necessary diagnostics
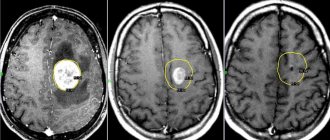
Confirming the presence of a problem begins with taking a history and examining the child. As a rule, suspicion of Angelman syndrome arises due to the specific behavior and appearance of the patient. However, to make an accurate diagnosis, genetic tests will be required. The examination of the child also includes standard blood tests, which make it possible to exclude other possible disorders that are accompanied by the development of a similar clinical picture. Computed and magnetic resonance imaging is also widely used to obtain layer-by-layer photos of bone structures and the brain. Such studies are necessary in the presence of neurological symptoms.
Improving the condition and life of patients
Angelman syndrome is a genetic disease; today there are no methods for restoring chromosomal abnormalities, and treatment is impossible. However, there are a large number of ways to reduce symptoms, which makes the condition of such people easier.
In each specific case, the rehabilitation program is developed individually, according to the symptoms and condition of the individual patient. Experts identify four main areas of therapy:
- Taking antiepileptic drugs and anticonvulsants . These medications help control and reduce the frequency of attacks caused by the disease.
- Therapeutic exercise – helps develop fine motor skills and solve other problems of the musculoskeletal system. Children with chromosome abnormalities develop more slowly than their healthy peers, and this requires patience on the part of the family.
- Sign language . Patients with marionette syndrome speak little, but use sign language quite successfully. Education should start from a very early age.
- Behavioral therapy . This program allows you to provide correct and effective education to children who have disabilities and will help cope with hyperactivity and attention deficit.
Many doctors note the similarities between children suffering from autism and Angelman syndrome. American scientists have achieved success in treatment, namely the use of intravenous injections with the hormone Secretin. The positive effect is expressed in reducing signs of unwanted behavior, as well as improving communication skills.
Treatment
Methods for correcting chromosomal disorders are not yet known to medical science, so there is no treatment, but it seems quite possible to make life easier. Symptom relief is carried out through the use of special programs developed individually taking into account specific symptoms. There are four steps to follow.
- Taking anticonvulsants and antiepileptic drugs to reduce the frequency and control of seizures that accompany Angelman syndrome.
- Physical therapy and training can eliminate problems with movements, including fine motor skills. Slower development against the background of the disease in question can be slightly accelerated, but parents must be patient.
- Sign language must be learned with the child from early childhood. For such people, communication plays an important role, so this method of communication will be useful.
- Behavioral therapy allows you to make the education process effective and correct. Increases concentration and overcomes hyperactivity. Creating a family and making friends becomes quite possible after completing the program.
European doctors note the similarity between autism and the pathology in question. The similarities are expressed by obsessive movements, communication problems, impulsiveness and a tendency to use inappropriate things. It is possible to combine methods of working with autistic children and children who exhibit Angelman syndrome.
Film “Maxim’s Mom.” A special child diagnosed with Angelman Syndrome.
Features of education and adaptation
As a child with this pathology grows up, the symptoms change, become less intense, or, on the contrary, more intense, old ones may disappear and new ones may appear. The prospects for the patient's condition largely depend on the conditions that surround the patient.
A friendly environment, an atmosphere of love and affection gives the patient a chance to become at least partially an independent person. With proper care, the symptoms of the disease become easier over time. Life expectancy for people with Angelman syndrome is average. It is necessary to remember about regular examinations, proper nutrition, and compliance with treatment conditions.
Educating a child at school requires the use of inclusive programs. However, in Russia and the CIS countries today these programs are not widely practiced. Such children need a special approach, including learning to concentrate. An important requirement is also the ability of the educational institution to provide medical assistance during a seizure.
In our society at the moment, people with chromosomal disorders are treated with caution and fear. In recent years, various events have been actively carried out aimed at disseminating knowledge about such diseases, as well as at developing tolerance in society.