| Nymphomania | |
| A patient suffering from nymphomania (illustration from A. Morison’s book “Physiognomy of Mental Illnesses”, 1843) | |
| ICD-10 | 52.752.7 |
| ICD-9 | 302.89302.89 |
Nymphomania
(ancient Greek νύμφη - bride + μανία - passion, madness; lat. nymphomania) or
andromania
(ἀνήρ,
gen.
ἀνδρός - man) - excessive sexual desire in women;
a type of hypersexuality. Characterized by constant sexual dissatisfaction and erotic fantasies, an incessant search for new partners and, due to the disinhibition of sexual behavior, casual sexual relations. Sometimes the term “nymphomania” is used in a figurative sense to denote forms of sexual behavior in women that are not approved by society, or to express the negative attitude of Puritan morality towards the sexual activity of women. Women suffering from nymphomania are called nymphomaniacs
.
The ability to better control one's behavior in selecting a sexual partner distinguishes other people from people suffering from nymphomania. Nymphomania (in the past considered a consequence of “rabies of the uterus”) is manifested by pronounced impulsive, often uncontrollable, obsessive desires for a variety of sexual contacts with different partners. At the same time, there is a high degree of indistinguishability of the sexual object: often the gender, age and appearance of the “handy” partner have little meaning. Nymphomania, as a rule, is associated with failure to achieve orgasm (nymphomanic frigidity), so sexual intercourse does not bring complete satisfaction. Excitement in true nymphomania is subjective in nature, without adequate physiological reactions from the genitals. The obsessive nature of sexual desire without involving the genital organs in the process of excitation indicates the presence of psychopathology, in contrast to pathological hypersexuality with organic brain lesions. It is this circumstance that distinguishes nymphomania from banal promiscuity arising from other reasons (for example, mental retardation, schizophrenia, asociality, etc.).
What is nymphomania in women?
In short, the term “nymphomania” refers to increased sexual desire in women, which also occurs among representatives of the stronger half of humanity. In Western medicine, this problem in both sexes is simply called “hypersexuality,” since when it comes to the intimate side of life, it is difficult to establish the boundaries between normality and pathology. The desire for sexual intimacy with a partner several times a day, if the woman controls her behavior, cannot be considered a symptom of nymphomania.
Additional Information. Who a nymphomaniac is, how nymphomania develops in women, and what consequences this disorder can lead to is well described in the feature film “Nymphomaniac” by Danish film director Lars von Trier.
Still from Lars von Thier's erotic drama “Nymphomaniac”
Even in the modern, sexually liberated 21st century, nymphomaniacs have a hard time. It is difficult for them to build close relationships with someone, because if a person is completely absorbed in thoughts of his sexual satisfaction, no partner will stay with him for a long time. Due to their pathological dependence on sex, nymphomaniacs risk losing their jobs, since they prioritize leisure with the opportunity to have sexual intercourse with someone, rather than their work and business obligations.
How to recognize a nymphomaniac: main signs
One of the primary signs of nymphomania is a continuous, uncontrolled desire to find a new sexual partner. In second place after this is constant excitability, which is atypical for a woman’s normal behavior. That is, sexual desire arises even when looking at the opposite sex or thinking about it.
Symptoms of nymphomania
If a nymphomaniac has a permanent partner, then she will satisfy her sexual needs with him, while showing complete selfishness. A nymphomaniac wants to get satisfaction in any way. If sexual hunger is not satisfied with a regular partner, then an active search for a new one begins.
Attention! Manifestations of nymphomania can be very dangerous for a woman’s life, since on a psychological level she loses her feeling of disgust. Under the influence of continuous sexual desire, the mind becomes completely clouded. The desire to obtain sexual satisfaction does not stop a nymphomaniac from the risk of acquiring serious sexually transmitted diseases and even AIDS.
An obsessive desire to experience new sensations and pleasure with a new sexual partner is an integral characteristic feature of nymphomania. In general, the following typical symptoms of nymphomania are distinguished:
- A woman is constantly looking for sexual partners; she cannot stop at just one man.
- Repeatedly having sex with a partner brings dissatisfaction.
- Sexual desire is uncontrollable.
- Sexual preoccupation and constant thoughts about sexual intercourse.
- External indicators and personal characteristics of a man do not interest a woman at all, the only goal is sex.
- A constant need for a new sexual relationship; in its absence, hysteria or other mental disorders occur.
Causes of nymphomania
Attention! Women who have been diagnosed with nymphomania are first advised to undergo a long course of treatment with a psychologist or psychotherapist, since the problem is of a mental nature.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
The disease is diagnosed by a sex therapist if the woman comes to the appointment on her own. Nymphomaniacs who deny the fact of pathology significantly complicate the possibility of diagnosis. After all, in order to determine nymphomania, a woman must pass a special psychological test. In the process of answering questions, the main problem that worries the patient will be identified. If the test cannot accurately establish a diagnosis, then an additional sex therapist can prescribe instrumental and laboratory tests that provide the opportunity to confirm the disease.
Video - Nymphomania
Types of nymphomania
Infantility in women - what is it, signs, how to get rid of it
Modern science identifies four types of disorders:
- Congenital nymphomania, when erotic desire arises in girls at a very young age. Such girls have their first sexual experience earlier than their peers, and quickly begin to engage in promiscuous sex.
- Acquired form of the disorder. Symptoms of the disease can appear at any age as a result of mental disorders, disruption of the endocrine and reproductive systems (pregnancy, childbirth).
- Menopausal nymphomania. It occurs in women during menopause and is associated with hormonal changes. The growth of libido in adulthood is extremely difficult for the fair half of humanity, because a husband of the same age with fading potency is no longer able to satisfy the increased sexual needs of his wife, and it is much more difficult for an already middle-aged woman who has lost her former attractiveness to find a young and ardent lover.
- Imaginary nymphomania. It is diagnosed when behavior characteristic of the disease manifests itself in mentally and physiologically healthy women. For example, numerous sexual contacts are interpreted by such girls as “victories” and are used for self-affirmation and raising self-esteem.
How to distinguish true nymphomania from imaginary one?
True nymphomania, from the point of view of most experts, is quite rare; according to statistics, one in five thousand women suffers from it.
A nymphomaniac constantly thinks about sex, she is practically unable to control herself. Sexual desire haunts her around the clock, and she tries to satisfy it at the slightest opportunity, and the degree of acquaintance with a potential partner, his social status, age, etc. are completely unimportant for her. The peculiarity of real nymphomania is that during sexual intercourse a woman never receives complete release. It is the search for satisfaction that pushes her into promiscuous relationships. If a woman still controls herself, conducts some kind of selection of partners and everything is fine with orgasms, then we can only talk about increased libido.
Causes of the disorder
Midlife crisis in women - what time does it start, how to survive it
Experts say the main reason for the development of the syndrome is psychological problems and trauma. In women who have experienced sexual violence, the protective mechanism of the psyche is activated. The traumatic incident is devalued, memories of it are completely distorted. The victim prefers to consider himself the initiator of unwanted sexual intercourse and confirms the truth of his version of events by entering into new meaningless sexual relationships.
The cause of unruly behavior may be a previous experience of sexual violence.
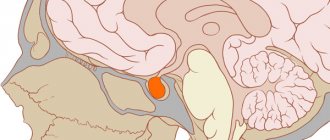
Important! In some cases, nymphomania is a sign of severe mental illness (schizophrenia, manic-depressive psychosis, hysteria with hyperthymic manifestations) and organic brain lesions, ovarian tumors.
Childhood and adolescence of a nymphomaniac
In childhood, both girls and boys are interested in building their bodies. In addition to studying their own genitals, they can ask the opposite sex to show theirs. This is the norm within the framework of child development. In this way he understands the world.
One can suspect the pathology of hypersexuality when a girl uses indecent expressions that refer to the genitals or the act itself. May constantly touch his genitals. It is also important to pay attention to the general mental state: frequent mental agitation, negative emotions predominate.
The cause may be psychological disorders described above. As well as lack of parental attention. In the latter case, hypersexuality is both an attempt to attract him and to provide attention to oneself. Over time, however, this may pass.
During adolescence, interest in sex, erotic fantasies and dreams are a manifestation of normal physiological development. But if a girl engages in early sexual intercourse of her own free will, or rubs her genitals on a chair during school hours, this is a manifestation of pathology.
Symptoms of the disorder
Psychopathy - signs in women, how to understand by behavior
True nymphomania is a rather rare phenomenon. According to statistics, only one woman in 5 thousand suffers from the disorder. However, it is not so difficult to understand that a person has a real problem.
Daily life is extremely difficult due to the inability to switch from erotic fantasies to productive activities. In the presence of the opposite sex, a nymphomaniac experiences excitement, begins to flirt, make advances, and hint at her availability.
The attraction is constant, obsessive. Provokes the patient to enter into numerous sexual relationships, just to satisfy a burning desire. Appearance, age, status of the partner, the presence or absence of romantic feelings for him do not matter at all. Moreover, in pursuit of orgasms, a nymphomaniac may ignore basic hygiene rules and contraceptive methods.
Nymphomania can cause attraction to completely unsuitable men
The number of sexual acts is limited, roughly speaking, only by the resistance of the vagina to abrasion. Sexual intercourse with one man is usually not enough to satisfy your needs. If a woman cannot find a lover, she actively resorts to masturbation and same-sex relationships.
In sex, he behaves extremely selfishly, as he is in an eternal pursuit of satisfying his obsessive need for release. So a man, having noticed signs of nymphomania in a girl he knows, should not rush to rejoice. It may not be difficult to persuade a nymphomaniac to have intimacy, but it is unlikely that you will be able to get pleasure with her in bed.
Who is nymphomania in girls? Some symptoms of hypersexuality are pronounced in girls during puberty. However, they are temporary and have nothing to do with true nymphomania. Adolescence is not only a process of hormonal explosion, but also the formation of value ideas and self-knowledge. At this time, girls become reacquainted with their bodies, begin to realize their feminine attractiveness and simply experience the power of their charms on those around them.
What's happening?
Nymphomania is female hypersexuality, a pathological increase in sexual desire and an increase in the ability to experience orgasm.
The origin of this term is quite poetic. According to ancient Greek myths, nymphs lured men into the forest to satisfy their lust. Nymphomania also has a more mundane name - “rabies of the uterus.” This designation belongs to Plato, who assumed that the uterus is a kind of beast that has settled in a woman’s body and longs to perform reproductive functions. When he fails to conceive for a long time, he becomes furious and begins to wander throughout the body, bringing the woman to all sorts of ailments. Now such ideas are nothing more than a myth. And yet, nymphomania causes suffering not only to the women themselves, but also to their sexual partners. The nymphomaniac herself, with multiple orgasms, cannot achieve sexual satisfaction, and her requests to her partner exceed his capabilities.
Treatment of nymphomania
Treatment for the disorder depends on the causes of its occurrence. For example, with increased testosterone production, antiandrogens are used. Also, based on the diagnostic results, individual psychotherapy sessions and antidepressants may be prescribed.
Note! When a person does not have serious life goals or achievements, he may go in search of sexual adventures. Anything to get rid of boredom, feelings of loneliness and the sense of meaninglessness of life.
Hypnosis has also proven itself to be effective in blocking unhealthy impulses and directing a person’s energy in a more constructive direction.
You can try to treat nymphomania with folk remedies: make special soothing infusions from herbs. For example, infuse 2 tablespoons of hop cones in 400 ml of boiling water and drink half a glass three times a day before meals and one glass at night.
If you have nymphomania, you should avoid foods that stimulate libido.
Avoiding meat, onions, garlic, and sugar will also help to significantly reduce obsessive sexual desire. They affect the chemical composition of vaginal discharge and can cause inflammation and itching, which is mistaken for arousal.