Head injuries, intoxication, stroke and many other causes can lead to pathological inhibition of the central nervous system and the development of coma.
A condition in which the patient balances between life and death is called third-degree coma. The development of a coma can be caused by various factors. The first place is occupied by direct damage to brain tissue due to stroke, trauma, infectious process, epilepsy. Toxic substances that accumulate due to liver or kidney failure, infection, alcohol poisoning, and drug poisoning also damage the brain. Metabolic changes in any pathology, imbalance of hormones, and brain hypoxia can lead to coma.
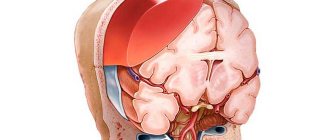
Damage to the nervous system is based on bilateral diffuse damage to the cortex and brain stem with the reticular formation. This area maintains the tone of the cortical sections; its shutdown leads to inhibition of the central nervous system.
Impaired consciousness: mechanism of occurrence
After damage to the central nervous system due to a traumatic brain injury, a person loses the ability to respond to any external stimulus. The psycho-emotional state is completely disrupted, the victim cannot contact the people around him. Coma sets in.
Coma due to TBI is characterized by the immersion of a person in a specific state, which is associated with inhibition of certain areas of the central nervous system. The victim does not respond to pain, bright light and loud sound, and has no reflexes.
Consciousness is impaired when certain parts of the brain that are responsible for speech, thinking, wakefulness, and reasoning are damaged. Based on the degree of damage, loss of consciousness can have different durations:
- mild traumatic brain injury (for example, bruise): loss of consciousness does not occur or lasts no more than 5 seconds;
- moderate injury (for example, open head injury): duration of disturbance of consciousness – 2 hours-2 days;
- severe injury: deep coma and vegetative states occur.
Coma after TBI is not a separate disease, but only a consequence of damage to the central nervous system. If there is a severe general condition that threatens a person’s life, he may be placed in an artificial coma. This condition allows you to cause a controlled decrease in the activity of reflexes and vital functions.
An artificial coma involves the introduction of special medications into the body. In this case, the respiratory function is performed by a ventilator.
Main symptoms and signs of coma
The process of coma development can be either almost instantaneous or gradual. This can be a time period from several minutes to several days. Symptoms of comatose states may vary depending on the underlying disease. A very important point is the timely recognition of the condition preceding the onset of coma. In some cases, in addition to loss of consciousness, symptoms include changes in the color of the skin, the presence of unusual odors in the air exhaled by the patient, a decrease or increase in body temperature, as well as pressure. X-ray, laboratory and instrumental examinations make it possible to clarify the diagnosed coma.
Characteristic symptoms
Coma after traumatic brain injury is primarily characterized by impaired consciousness. All symptoms of this condition can be divided according to the degree of its severity:
- Superficial disturbance of consciousness. The person falls into deep sleep. When trying to talk to the victim, he may open his eyes and sometimes start a conversation. Speech with punctuation. The patient can make slight movements of the limbs.
- Ordinary coma. The patient is able to make sounds, unintentionally open his eyes and make sudden movements with his hands. The doctor can fix the victim’s limbs with special devices to prevent physical harm.
- Deep coma. Reflexes, mobility and respiratory function are completely absent. There is no reaction to pain, just like there is to the light of the pupils.
How long can a coma after an accident last? Heart Treatment
From ancient Greek “coma” is translated as “deep sleep”. While a person is in a coma, the nervous system is depressed.
This is very dangerous, because this process progresses and failure of vital organs is possible, for example, respiratory activity may stop.
While in a coma, a person stops responding to external stimuli and the world around him; he may have no reflexes.
Stages of coma
Classifying coma according to the degree of its depth, we can distinguish the following types of this condition:
- Prekoma. While in this state, the person remains conscious, but there is slight confusion in actions and lack of coordination. The body functions according to the concomitant disease.
- Coma 1st degree. The body's reaction is very inhibited even to strong stimuli. It is difficult to find contact with the patient, but he can make simple movements, for example, turning over in bed. Reflexes are preserved, but are very weakly expressed.
- Coma 2nd degree. The patient is in a deep stage of sleep. Movements are possible, but they are performed spontaneously and in a chaotic manner. The patient does not feel touch, the pupils do not react to light in any way, and respiratory function is impaired.
- Coma 3rd degree. Deep state of coma. The patient does not respond to pain, the reaction of the pupils to light is completely absent, reflexes are not observed, the temperature is low. Disturbances occur in all body systems.
- Coma 4 degrees. A state from which it is no longer possible to get out. The person has no reflexes, the pupils are dilated, and the body is hypothermic. The patient cannot breathe on his own.
In this article we will take a closer look at the condition of a person in a penultimate degree coma.
Coma 3rd degree. Chances of survival
This is a very dangerous condition for human life, in which the body cannot practically function independently. Therefore, it is impossible to predict how long the unconscious state will last.
It all depends on the body itself, on the degree of brain damage, and on the age of the person. Coming out of a coma is quite difficult; as a rule, only about 4% of people are able to overcome this barrier.
Moreover, even if the person has regained consciousness, most likely he will remain disabled.
If you are in a third-degree coma and return to consciousness, the recovery process will be very long, especially after such serious complications. As a rule, people learn to speak, sit, read, and walk again. The rehabilitation period can take quite a long time: from several months to several years.
According to studies, if in the first 24 hours after the onset of a coma a person does not feel external irritants and pain, and the pupils do not react to light in any way, then such a patient will die.
However, if at least one reaction is present, then the prognosis is more favorable for recovery.
It is worth noting that the health of all organs and the age of the patient who has developed a 3rd degree coma play a huge role.
Chances of survival after an accident
About thirty thousand people a year die as a result of road accidents and three hundred thousand become their victims. Many of them become disabled as a result. One of the most common consequences of a road accident is traumatic brain injury, which often causes a person to fall into a coma.
If, after an accident, a person’s life requires hardware support, and the patient himself has no reflexes and does not respond to pain and other stimuli, a 3rd degree coma is diagnosed.
The chances of survival after an accident that leads to this condition are negligible. The prognosis for such patients is disappointing, but there is still a chance of returning to life.
It all depends on the degree of brain injury as a result of the accident.
If a stage 3 coma is diagnosed, the chances of survival depend on the following factors:
- Degree of brain injury.
- Long-term consequences of TBI.
- Fracture of the base of the skull.
- Fracture of the cranial vault.
- Fracture of the temporal bones.
- Concussion.
- Trauma to blood vessels.
- Brain swelling.
Probability of survival after a stroke
A stroke is a disruption of the blood supply to the brain. It happens for two reasons. The first is blockage of blood vessels in the brain, the second is bleeding in the brain.
One of the consequences of cerebrovascular accident is coma (apoplectiform coma). In case of hemorrhage, a 3rd degree coma may occur. The chances of surviving a stroke are directly related to age and the extent of the damage. Signs of this condition:
- Lack of consciousness.
- Change in complexion (becomes purple).
- Loud breathing.
- Vomit.
- Trouble swallowing.
- Slowing heart rate.
- Increased blood pressure.
The duration of the coma depends on a number of factors:
- Coma stage. In the first or second stage, the chances of recovery are very high. With the third or fourth, the outcome is usually unfavorable.
- Condition of the body.
- Patient's age.
- Equipping with necessary equipment.
- Patient care.
Signs of third degree coma during stroke
This condition has its own distinctive features:
- Lack of response to pain.
- The pupils do not respond to light stimuli.
- Lack of swallowing reflex.
- Lack of muscle tone.
- Reduced body temperature.
- Inability to breathe independently.
- Bowel movements occur uncontrollably.
- Presence of seizures.
As a rule, the prognosis for recovery from a third-degree coma is unfavorable due to the absence of vital signs.
Probability of survival after neonatal coma
A child may fall into a coma in the event of a deep disorder of the central nervous system, which is accompanied by loss of consciousness.
The reasons for the development of coma in a child are the following pathological conditions: renal and liver failure, meningoencephalitis, brain tumor and trauma, diabetes mellitus, water and electrolyte imbalance, cerebral hemorrhage, hypoxia during childbirth and hypovolemia.
Newborns fall into a comatose state much more easily. It is very scary when a third degree coma is diagnosed. A child has a higher chance of survival than older people. This is explained by the characteristics of the child’s body.
In the case when a 3rd degree coma occurs, the newborn has a chance of survival, but, unfortunately, it is very small. If the baby manages to get out of a serious condition, severe complications or disability are possible. At the same time, we must not forget about the percentage of children, albeit small, who managed to cope with this without any consequences.
Consequences of coma
The longer the unconscious state lasts, the more difficult it will be to get out of it and recover. A 3rd degree coma can occur differently for everyone.
The consequences, as a rule, depend on the degree of brain damage, the length of time spent in an unconscious state, the reasons that led to the coma, the health of the organs and age. The younger the body, the higher the chances of a favorable outcome.
However, doctors rarely make a prognosis for recovery, since such patients are very sick.
Despite the fact that newborns recover from a coma more easily, the consequences can be very sad. Doctors immediately warn relatives how dangerous a 3rd degree coma is. Of course, there are chances of survival, but at the same time a person may remain a “plant” and never learn to swallow, blink, sit and walk.
For an adult, a prolonged stay in a coma is fraught with the development of amnesia, the inability to move and speak, eat and defecate independently.
Rehabilitation after a deep coma can take from a week to several years.
In this case, recovery may never occur, and the person will remain in a vegetative state for the rest of his life, when he can only sleep and breathe independently, without reacting in any way to what is happening.
Statistics show that the chance of a full recovery is extremely small, but such events do happen. Most often, death is possible, or in case of recovery from a coma - a severe form of disability.
Complications
The main complication after a coma is a violation of the regulatory functions of the central nervous system.
Subsequently, vomiting often occurs, which can enter the respiratory tract, and stagnation of urine, which can lead to bladder rupture. Complications also affect the brain.
Coma often leads to breathing problems, pulmonary edema and cardiac arrest. Often these complications lead to biological death.
The feasibility of maintaining body functions
Modern medicine makes it possible to artificially maintain the vital functions of the body for quite a long time, but the question often arises about the feasibility of these measures. This dilemma arises for relatives when they are informed that the brain cells have died, that is, in fact, the person himself. Often a decision is made to remove artificial life support.
Coma is a very serious phase of the disease, which is completely unpredictable. After all, it has not yet been clearly studied what a person feels during a coma, and what its duration depends on. Also, no one can predict what the consequences of such a difficult development of events will be.
The word "coma" translated from Greek means "deep sleep, drowsiness." It is characterized as loss of consciousness, a sharp weakening or loss of reaction to external stimuli, extinction of reflexes, etc.
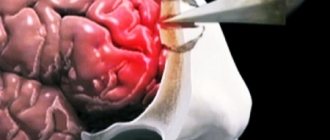
Coma develops as a result of inhibition in the cerebral cortex, spreading to the subcortex and other parts of the nervous system. As a rule, the main reason for the development of coma is a violation of blood circulation in the brain due to a head injury, inflammation affecting the brain, etc.
Causes of coma
The causes of coma can be very diverse.
For example, a person may become immobilized and unconscious due to severe damage to both the head and brain, a serious viral infection such as meningitis, a lack of oxygen to the brain for a long time, or poisoning from any drugs or chemicals. , as a result of alcohol intoxication, etc.
Of course, you should not think that if any event from the specified list occurs, this will immediately lead to the development of a coma. Each person has an individual risk of developing a pathology such as coma.
In general, the mechanism for the appearance of coma as a result of one of these reasons is quite simple: part of the brain cells wipes off and stops functioning, as a result of which the person loses consciousness and falls into a coma.
Types of coma
Coma is divided into several different degrees depending on the severity of the patient's condition. As a rule, it is divided into 3 main types:
- deep;
- just a coma;
— superficial.
In general, coma in medicine is divided into 15 degrees. However, from them, about 5 most basic ones can be distinguished, which as a result are reduced to 3 main states.
In the first case, we are talking about a situation when the patient does not come to his senses at all and does not react in any way to any stimuli. At the same time, he does not make sounds, does not react to the voice or touch of even those closest to him.
In a normal coma, the patient may make some sounds and even open his eyes spontaneously. However, he is not conscious.
Superficial coma is characterized by the fact that the patient, while unconscious, can open his eyes in response to a voice. In some cases, he can even pronounce certain words and answer questions. True, the speech is most often incoherent.
Exit from a comatose state is characterized by a gradual restoration of the nervous system and brain functions. As a rule, they return in the order of their oppression. First the pupils begin to react, then consciousness returns.
Consequences
On average, a coma lasts 1-3 weeks. However, there are often cases when it lasts for a longer time - people can lie unconscious for years.
The patient's return to consciousness occurs gradually. At first he comes to his senses for a couple of hours, then this time increases more and more. As a rule, the body goes through several different stages during this time. And the consequences will depend on how he copes with the load placed on him.
Since the brain is affected during a coma, one should be prepared for the fact that the patient may not recover many vital functions. For example, quite often people cannot walk, talk, move their arms, etc.
Naturally, the severity of the damage directly depends on the degree of coma the patient was in. For example, after a superficial coma you can come to your senses an order of magnitude faster than after a normal one. The third degree, as a rule, is characterized by almost complete destruction of the brain.
This means that there is no need to expect good recovery results.
Among the most common problems faced by a person who has been in a coma are memory impairment, decreased attention, and various changes in behavior (lethargy, aggressiveness, etc.). Sometimes relatives do not even recognize the person close to them.
Also, after a coma, many patients take a long time to restore everyday skills. For example, they cannot eat on their own, wash themselves, etc.
One of the signs of a person's recovery and recovery after a coma is the desire for some kind of activity. However, in this case, you should not be overly happy and immediately give the patient maximum loads - too abrupt a return to normal life can have a negative impact on his condition and lead to a noticeable deterioration in well-being.
Naturally, you should be prepared for the fact that you will have to spend a lot of effort on recovery. The list of important rehabilitation measures includes gymnastics (to restore motor skills), maintaining hygiene, proper nutrition, walks, adequate sleep, taking medications and regular consultations with a doctor.
What are the consequences of coma
| ddm2003 |
| Status: OfflineYarila |
Source: https://doctor-serdce.ru/koma-posle-avarii-skol-ko-mozhet-dlit-sya/
Treatment during coma
Once a diagnosis of coma due to traumatic brain injury has been made, appropriate treatment is begun. First of all, measures are taken to increase blood flow to the brain. Emergency treatment begins already in the ambulance.
Artificial ventilation is used and medications are introduced into the body to help normalize blood pressure. It requires the introduction of drugs that improve the functioning of organs such as the liver and kidneys.
In case of respiratory arrest, the emergency doctor inserts a special tube into the tracheal cavity, which is a conductor of oxygen air coming from the breathing apparatus.
Since, while in a coma, a person cannot eat on his own, nutrients are administered by tube. To prevent secondary infections of the urinary tract and lungs, powerful antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Pseudocomatose states
Coma state 4 must be differentiated from other conditions that are accompanied by similar symptoms:
1. Locked-in syndrome. Damage to the motor tract leads to paralysis of the muscles of the limbs, neck and face, and is a consequence of blockage of the main artery or tumor of the bridge, a demyelinating process. Patients cannot move or pronounce words, but understand speech, blink, and move their eyes.
2. Akinetic mutism. Stroke, injury to the thalamus, midbrain, caudate nucleus, motor and sensory pathways are damaged, paresis or paralysis of the muscles of the limbs develops, and speech is lost. A person can open his eyes, sometimes perform some movements or pronounce words in response to a painful stimulus. But wakefulness takes place without the participation of consciousness. After recovery, the patient remains amnesic.
3. Abulia. The lesions are located in the temporal lobes, midbrain and caudate nucleus. The ability to move and speak is impaired. Sometimes patients can emerge from this state and respond adequately to stimuli, and then return to their original state.
4. Severe depression. Accompanied by a state of stupor, complete immobilization and loss of contact are possible. The condition develops gradually. Diagnostic CT or MRI does not reveal signs of brain damage.
5. Hysteria. People with pronounced affective behavior after a traumatic situation experience complete immobilization and withdrawal. There are no signs of organic damage to brain structures.
Rehabilitation period
Not all cases of impaired consciousness require a long rehabilitation period. According to statistics, recovery from a coma caused by diabetes, high doses of drugs or alcohol does not last long. In such cases, impaired consciousness is present before the toxic substance is eliminated from the body.
Coming out of a 3rd degree coma after a TBI or 1st degree equally requires rehabilitation measures. First of all, measures are taken to restore brain function. Not in every case, amnesia develops, but there is a deterioration in memory and attention.
How do you recover from a coma after a TBI? During this period, the ability to sit and walk without assistance and available means is lost. Confusion of consciousness is observed, the person loses orientation in space. The following specialists help correct such disorders caused by prolonged impairment of consciousness:
- neurologist (helps restore speech);
- psychologist (normalizes the psycho-emotional state);
- occupational therapist (helps improve motor skills);
- neurologist, physiotherapist, etc.
When recovering from a coma after a TBI, there is no need to immediately subject the patient to physical and mental stress on the first day. Rehabilitation should take place gradually. How many months or years it will take to fully restore the activity of the central nervous system, and what the prognosis will be, depends on the severity of the traumatic brain injury.
Rehabilitation after a coma consists of assisting the patient in all everyday activities: eating, going to the toilet and showering. Developmental games are required to help restore motor skills, memory, and speech. It is important to normalize your diet so that it includes all useful vitamins and microelements.
To restore muscle tone, massage procedures are prescribed, which are carried out in a specialist’s office and subsequently at home. During the massage, you can use any essential oil. The procedure also helps improve blood circulation. The main condition is continuity of therapy, even if the first positive changes are visible.
Rehabilitation after a coma
There is a position according to which timely and high-quality treatment can significantly help the body cope with this condition. Initially, to maintain vital functions, the patient is provided with the ability to breathe and function of the cardiovascular system. Next, all the necessary studies are carried out aimed at identifying the disease - the cause of the development of coma. It is the research results that determine further treatment, prescription and use of medications. When a patient comes out of a coma, treatment of the underlying disease not only does not stop, but complications are also prevented. In the future, rehabilitation measures are prescribed.
Complications
If the central nervous system was affected at the time of the traumatic brain injury, complications are likely to occur. Coma is one of them. With severe TBI, the consequences can be so serious that the patient will no longer be able to care for himself, stand up, or sit. In such cases, outside help and special medical equipment will be required.
Coma is not always accompanied by such severe consequences. In some cases, a person quickly recovers from injury and impairment of consciousness, and basic functions and reflexes return to normal.
The most common consequences of coma include amnesia or incomplete memory loss, impaired concentration, loss of the ability to independently care (eating, taking water procedures, etc.).
Being in a lying position for a long time, a person may begin to suffer from bedsores, which require other specific therapy using medications.
Recovery after a coma
Rehabilitation after a coma becomes extremely important: a set of measures that can help you get closer to or return to your previous way of life. Everything is subject to calculation - from the load level to the program itself. The Clinical Brain Institute has been successfully dealing with these problems for quite a long time. We are ready to offer effective rehabilitation programs developed with special care, which are selected individually for each patient. Our specialists, being professionals in their field, are also very responsive and attentive people, which is something that patients so often lack!
What is the prognosis and chances of survival?
It all depends on the stage of the coma. The danger also increases if it is not the brain cells that are affected, but the stem structures. In this case, it is not the brain metabolism that needs to be corrected, but rather it needs to be restored after an injury or tumor.
- In the first stage of coma, a person comes to consciousness in a short time in 99% of cases. At the same time, the body also recovers quickly.
- In stages 2 and 3, the probability of waking up from a coma and dying in this state is approximately the same. Whether patients come out of this state and how long they remain in it depends on the care, treatment and health of the patient before the coma.
- Comatose state 4 degrees in almost 100% of cases ends in death.
The consequences of a stroke are ambiguous for both men and women: for some it is death or severe disability, for others it is a completely normal life, with some changes in habits and activities. Read articles from our experts about how long they stay in hospital and intensive care, why swelling of the brain and limbs occurs, legs hurt or walk poorly, and seizures appear.