Mental disorders in older people are accompanied by severe behavioral and mental disorders, complete loss of working capacity, and self-care skills. However, even the most modern treatment methods can only slow down the progression of the disease. The specialists of the Leto clinic offer not only supportive therapy for senile dementia , but also the possibility of round-the-clock medical supervision in a comfortable hospital equipped with everything necessary.
Causes of the disease
The etiology of senile dementia is associated with various pathological processes in the body. This:
- complications of traumatic brain injury;
- previous strokes;
- deterioration of cerebral circulation;
- neurological pathologies (neoplastic brain tumors, central nervous system infections);
- hypothyroidism, severe deficiency of cyanocobalamin, folic acid;
- deterioration of liver, kidney, and respiratory tract functions;
- intoxication due to alcohol abuse, drug use, adverse reactions of some potent drugs;
- aging-related changes in hormonal levels and metabolism;
- hereditary predisposition, etc.
Measures to prevent dementia
- Physical exercise. Physical exercise can be considered the basis for the prevention of senile dementia. It is difficult to find another method that would have the same complex effect on the body. Therefore, modern doctors primarily recommend not memorizing poetry or solving crossword puzzles, but physical activity that is appropriate for the patient’s age.
- The protection of nerve cells during physical exercise is partly explained by the release of neurotrophic factor, a decrease in cortisol, and a positive effect on the vascular system. At the same time, physical exercise itself does not improve the cognitive status of a healthy person, but it prevents its decline with age.
- Diet. Proper balanced nutrition provides sufficient protection to brain neurons and prevents the development of inflammatory processes. The model diet for the brain is usually called the Mediterranean-type diet (low consumption of meat and dairy products, inclusion of fish, vegetables and fruits in the diet). It has been proven that following this diet reduces the risk of vascular disorders, reduces plasma glucose concentrations and serum insulin, and reduces insulin resistance, markers of oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Social engagement. Social activity helps prevent depressive states, and therefore increases the cognitive reserve of the brain. In addition, involvement in social life ensures the preservation of brain neurons.
- Gaining new knowledge. Constant study of previously unfamiliar information to a certain extent contributes to maintaining the ability to adequately think.
What is senile dementia in older people
In the development of senile dementia of the brain, the following stages are distinguished:
- preclinical, characterized by mild forgetfulness, slight difficulty and slowing of basic mental reactions;
- mild dementia, in which mental changes become obvious and noticeable to others, although working capacity is partially preserved;
- moderately severe senile dementia: symptoms of the disease progress, memory rapidly deteriorates, orientation in time and space is impaired;
- severe dementia with complete loss of self-awareness, everyday self-care skills and severe mental disorders.
In modern psychiatry, there are several options for classifying the disease (primary, secondary, mixed, etc.). But it is generally accepted to divide senile dementia into several syndromes:
- Alzheimer's type;
- Pick's disease;
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease;
- dementia with Lewy bodies;
- Huntington's disease;
- dementia due to parkinsonism.
By and large, the main symptoms of various forms of the disease, prognosis and treatment principles differ slightly. The pathogenetic mechanisms of development differ (in particular, the area of brain damage), the age at which the first signs of pathology appear (for example, Pick syndrome manifests itself at 45–50 years), and the etiology (in Huntington’s, a genetic predisposition is clearly visible).
Symptoms and signs of senile dementia - dementia
The first symptoms and signs of senile dementia (dementia) may go unnoticed by relatives, because they are so easy to attribute to age. However, not all so simple. To slow down the process of disintegration of a person as an individual, you need to take these signs as a bell that you urgently need to see a doctor. Main manifestations:
- memory deteriorates, a person forgets what needs to be bought or done, does not learn new information;
- does not want to do everyday activities, go to work;
- tries to control everything and indicate what needs to be done;
- cannot find his way in an unfamiliar place;
- cannot conduct a normal dialogue, does not listen attentively to the interlocutor, chooses the wrong words;
- intellectual abilities deteriorate;
- the logical chain in the expression of thoughts is disrupted;
- stinginess, greed, quarrelsomeness may appear, previously unusual for a person;
- sexual preoccupation may arise;
- prolonged depression, tearfulness;
- manifestation of aggression;
- gradual loss of physical strength associated with the inability to carry out household chores, hold objects in one's hand, eat and dress independently.
These signs depend on the type and stage of dementia. The fewer symptoms of dementia a person has, the easier it is to help him. After all, with the appearance of each new sign, it becomes more and more difficult to provide a person with a full life. Doctors at the Alco-Center clinic deal with issues of prevention, diagnosis and treatment of senile dementia.
Clinical picture of senile dementia
It occurs in old age and is characterized by progressive mental disorders and the gradual development of total disability. On average, 4.5–5% of people over 65 years of age suffer from the disease ; women are diagnosed twice as often.
A specific symptom is the so-called “senile psychopathization.” What does it mean? Signs of rigidity and coarsening of the personality, narrowing of interests and horizons in general come to the fore in the patient’s behavior and actions. Responsiveness, the ability for emotional empathy, and sympathy are lost. Typical:
- gullibility and suggestibility, the patient quickly succumbs to the influence of others, and we are talking about complete strangers, which is often used for fraudulent purposes;
- wariness, mistrust and suspicion towards relatives and friends;
- absent-mindedness, inattention, forgetfulness;
- changes in behavior: the patient may constantly walk around his home, checking door and window locks, listen to extraneous sounds, not sleep, fearing burglars;
- sleep disorders: insomnia at night and irresistible drowsiness during the day (a person sometimes falls asleep while eating, while talking, etc.);
- disinhibition, sexual promiscuity (in severe cases, attempts at sexual violence are not excluded);
- frequent falls, fainting, tremors, shuffling gait (typical of Lewy syndrome);
- speech disorders (the occurrence of stereotypies, when the patient repeats the same thing several times with the same intonation, reluctance to speak, etc.);
- impaired coordination of movements, etc.
One of the main symptoms of senile dementia is memory impairment. At the initial stage of the disease, the ability to remember is partially preserved, but over time, it becomes more and more difficult to consolidate new information. Fixation amnesia gradually develops (the patient does not remember recent events), then the patient ceases to navigate in time, in the surrounding space, and at the final stage of the disease, in his own personality. Memory loss occurs in the reverse order, and sooner or later a moment comes when a person, in principle, does not remember anything about himself.
False recognitions are common. A kind of “shift into the past” is possible: a person considers his children to be brothers/sisters or parents, says that he is in school, etc. This is due to the fact that relatively recently acquired events are forgotten, and earlier episodes from life come to the fore.
Sometimes senile delirium develops, but unlike senile and other forms of psychosis, in this case the awareness of what is happening is impaired not due to hallucinations, but due to a general distortion of the perception of reality.
At the terminal stage of senile dementia, the patient is completely immobilized, mainly lies in the fetal position and leads an almost vegetative lifestyle. But there are no neurological disorders (in particular, various automatisms).
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, doctors at the Leto Mental Health Center use a variety of tests and techniques to assess cognitive function. In addition, the following studies are required:
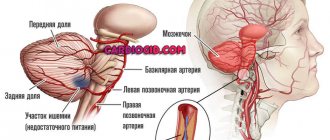
- CT and/or MRI of the brain (if necessary, with contrast);
- Dopplerography and ultrasound;
- analysis for biomarkers of hereditary forms of senile dementia (Alzheimer's, Huntington's, etc.);
- assessment of vitamin levels, hormonal levels, metabolism;
- ECG, EchoCG, etc.
Consultations with related specialists to assess general health are also indicated.
Cost of services
| CONSULTATIONS OF SPECIALISTS | |
| Initial consultation with a psychiatrist (60 min.) | 3,500 rub. |
| Repeated consultation | 2,500 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychiatrist-narcologist (60 min.) | 3,500 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychologist | 2,500 rub. |
| Consultation with Gromova E.V. (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| PSYCHOTHERAPY | |
| Psychotherapy (session) | 6,500 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (5 sessions) | 25,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (10 sessions) | 48,000 rub. |
| Group psychotherapy (3-7 people) | 3,500 rub. |
| Hypnosis (1 session) | 10,000 rub. |
| Hypnotherapy course (5 sessions) | 45,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy session with E.V. Gromova (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| TREATMENT IN A HOSPITAL | |
| Ward for 4 persons | 8,500 rub./day |
| Ward for 3 persons | 9,500 rub./day |
| Ward for 2 persons | 11,500 rub./day |
| Ward for 2 persons Comfort | 12,500 rub./day |
| Ward 1 bed VIP | 16,500 rub./day |
This list does not contain all prices for services provided by our clinic. The full price list can be found on the “Prices” , or by calling: 8(969)060-93-93. Initial consultation is FREE!
Principles of treatment
Properly selected therapy can significantly increase the patient’s life expectancy and slow down progressive mental disorders. For senile dementia the following is prescribed:
- cholinesterase inhibitors to normalize the balance of neurotransmitters;
- glutamatergic drugs are one of the few drugs that have proven therapeutic efficacy in senile dementia;
- neuroprotectors that improve blood supply to the central nervous system and the energy function of neurons;
- antioxidants;
- tranquilizers and neuroleptics (with exacerbation of pathology);
- drugs for the correction of concomitant diseases and symptomatic treatment.
A balanced diet rich in B vitamins and antioxidants is also recommended. Psychotherapy is effective only in the initial stages of the disease for the correction of behavioral disorders. At later stages of the disease, the patient has no contact, and sessions with a psychologist are not productive; hospitalization is indicated.
At home, it is very difficult to provide proper care and treatment procedures to a person with senile dementia. This requires complete dedication on the part of relatives - they often have to sacrifice their families, personal lives and interests in order to care for a virtually incapacitated patient. In our clinic, the patient will feel as comfortable as possible under the supervision of qualified doctors, junior medical staff and experienced nurses. For more detailed advice, call us at 8(969)060-93-93 .
Treatment of dementia at the Preobrazhenie clinic
Dementia cannot be cured completely, but it is possible to eliminate the signs of the disease and stop the progression of the disease. One of the appropriate treatment options for dementia is therapy at the Preobrazhenie specialized clinic (Moscow), which deals exclusively with the pathology of the psyche and nervous system.
Certified specialists at the Preobrazhenie Clinic are ready to provide assistance both in an inpatient and outpatient setting. The practice of providing medical services at home is also provided.
The clinic employs doctors with predominantly the highest professional category and extensive practical experience in the treatment of psychiatric and neurological diseases. In the case of various manifestations of dementia, several specialists, psychiatrists, neurologists, therapists, psychologists, and chiropractors, take part in the treatment process.
Drug treatment for dementia
First, a full diagnosis of the patient is carried out, and then effective comprehensive treatment is prescribed. Antidementia and antiparkinsonian drugs, psychotropic drugs that relieve symptoms of psychosis, antidepressants to stabilize mood, sleeping pills to improve sleep and other medications are usually prescribed.
- Vitamin complexes;
- Tranquilizers;
- Blockers of certain receptors;
- Nootropic drugs;
- Medicines that improve blood circulation in the brain.
We teach relatives how to properly care for such patients, conduct cognitive and other types of psychotherapy with the patients themselves for better adaptation in the family and the world, select a diet taking into account all existing diseases, conduct physical therapy sessions and physical therapy to improve the person’s condition. The Preobrazhenie Clinic provides full-fledged professional care for patients diagnosed with dementia.
The prognosis of the disease is conditionally favorable: with a professional approach, the development of the disease can be stopped for months and years.