The danger of hypotension of cerebral vessels and its treatment
Hypotension or decreased blood pressure occurs due to decreased tone of blood vessels.
Due to decreased tone and reduced blood flow, the consumption of nutrients and oxygen by cells decreases. One of the first of all organs and systems to suffer from this is the brain.
Oxygen deprivation of the brain causes most of the symptoms experienced by people with low blood pressure.
How does hypotension of cerebral vessels manifest?
With this condition, several options for the development of the disease and clinical symptoms are possible, therefore, cerebral vascular hypotension has the following types:
- In the brain, the tone of the smallest arteries decreases, which ultimately leads to a forced increase in blood flow in them. The walls of small blood vessels become stretched and cause headaches. Headaches are localized in the back of the head or temples.
- In the brain, the tone of the veins is significantly reduced, resulting in a disruption of the outflow of venous blood. Patients diagnosed with hypotension feel this especially acutely in a lying or sitting position, when the head is lowered down. In these body positions, the outflow of blood from the veins is naturally disrupted, causing a decrease in pressure. A characteristic symptom is a bursting headache, which usually appears in the morning.
- In some cases, patients are bothered by migraine-like pain, which usually appears in one half of the head. In addition to headaches, symptoms such as nausea, darkening before the eyes, and sometimes vomiting occur.
Normally, the outflow of blood from the venous bed of the brain vessels occurs when a person awakens. At night, during sleep, the tone of the veins is reduced, and a certain amount of venous blood accumulates in them.
When getting out of bed, a person begins to move, which causes contraction of skeletal muscles and the pushing of venous blood into the bloodstream.
This, in turn, causes an increase in the tone of the veins and a slight increase in blood pressure.
In hypotensive patients, venous hypotension is manifested by headaches in the morning, which disappear after some physical activity and do not bother patients during the day. However, towards evening, such patients again experience a decline in activity, fatigue, decreased performance and drowsiness.
Very often, patients with hypotension feel that their well-being is dependent on weather conditions, and sometimes they begin to anticipate a change in weather and atmospheric pressure.
When the weather changes, such patients are usually irritable, susceptible to negative emotions and mood swings, and are depressed for a long time.
Very often they have sleep disturbances - in some patients it is insomnia, and in others it is increased drowsiness.
Problems with the blood supply to the brain in response cause other problems, primarily with the heart. During the day, patients note pain in the chest and in the heart area, disturbances in rhythm and heart rate. A characteristic and excellent sign of such pain is its appearance in a state of complete rest, without physical activity.
Following this, problems arise with the volume of air inhaled, since the amount of blood flow and oxygen in the blood also decreases in the lungs. As a result, patients often take a deep breath, explaining that they do not have enough air.
With venous hypotension, symptoms such as numbness of the arms or legs, a feeling of “crawling”, coldness of the upper and lower extremities, and increased sensitivity to high and low temperatures may occur.
Hypotension of cerebral vessels, if chronic, can cause a decrease in potency and libido in men, as well as menstrual irregularities in women. This occurs due to the fact that the regulatory centers of many organs and systems are located in the brain.
Treatment and therapy
To treat hypotension of cerebral vessels, an integrated approach and combination therapy are used. A course of treatment is usually prescribed to patients only after examination by a cardiologist and neurologist. After examining the patient and collecting anamnesis, a full clinical examination should be carried out, which includes the following tests:
- General and biochemical blood tests.
- Study of blood viscosity and coagulation rate.
- Dopplerography of cerebral vessels.
- Angiography of blood vessels.
Patients with hypotension should follow a diet, lead a healthy lifestyle, move more, and exercise. Among the medications used in the treatment of cerebral vascular hypotension, the following methods are used:
- Medications containing caffeine are used as first aid. They are used for a short period of time because they have only a symptomatic effect, but they are not used for permanent therapy.
- Nootropic drugs are used as maintenance therapy, which include aminalon, nootropil, phenibut and others.
- For depression and migraine-like pain, the drugs encephabol, stugeron, tanakan are prescribed, which accelerate blood flow and tone the walls of blood vessels.
- Herbal preparations have a good therapeutic effect for hypotension, of which ginseng root, Rhodiola rosea extract, Eleutherococcus tincture, liquid Leuzea extract and others are often used.
- Treatment with amino acids is used as nutrition and building material for blood vessels, many of which have the properties of neurotransmitters (substances that transmit signals between cells of the nervous system). Among the amino acids, glycine, glutamic and gamma-aminobutyric acids are used.
(: 1 , 5,00 out of 5)
Source: https://TvoeLechenie.ru/kardiologiya/opasnost-gipotonii-sosudov-golovnogo-mozga-i-eyo-lechenie.html
Classification of arterial hypotension
Among the many attempts to systematize the disease, the classification proposed by the domestic doctor N.S. is convenient for doctors. Molchanov. Its division takes into account the reasons why hypotension develops in women, men and children. In addition, it provides an opportunity to expand and clarify the diagnosis. Happens:
- Physiological hypotension. It is usually accompanied by symptoms of bradycardia and a rare (compared to normal) pulse. But such a condition does not cause any complaints in humans. There is no pain in the heart, weakness in the lower extremities, or dizziness. This form of hypotension, in turn, is divided into a disease, as a variant of the norm for a particular patient, a decrease in blood pressure in people accustomed to intense physical activity, and compensatory hypotension, which develops in a person in a high-mountain climate with thin air.
- Pathological hypotension may be associated with heart failure and other disorders of the vascular, endocrine or nervous system.
Methods for normalizing vascular tone
The human circulatory system is represented by arterial, venous vessels and capillaries. The anatomical structure of the vascular walls determines their tone, on which the blood supply to a particular organ and the level of blood pressure depend.
Review from our reader Victoria Mirnova
I recently read an article that talks about the drug Choledol for cleaning blood vessels and getting rid of CHOLESTEROL. This drug improves the general condition of the body, normalizes the tone of the veins, prevents the deposition of cholesterol plaques, cleanses the blood and lymph, and also protects against hypertension, strokes and heart attacks.
I’m not used to trusting any information, but I decided to check and ordered a package. I noticed changes within a week: the constant pain in my heart, heaviness, and pressure surges that had tormented me before receded, and after 2 weeks they disappeared completely. Try it too, and if anyone is interested, below is the link to the article.
Read the article –>
What is vascular tone?
Vascular tone is the degree of tension in the vascular walls, which is supported by their smooth muscle layer. The smooth muscle layer in the vascular walls of arteries, veins and capillaries has different severity:
- in the arteries it is most pronounced, due to which it is able to resist blood pressure and constantly maintain their lumen;
- in the veins the smooth muscle layer is thin, therefore it is not able to resist blood pressure and maintain the lumen of the veins;
- There are no smooth muscles in the capillary walls.
Structure of blood vessels
Vascular tone is maintained by two mechanisms of its regulation:
- Neurogenic (under the influence of nerve impulses);
- Myogenic (with spontaneous contraction of smooth muscles of vascular walls).
In case of injuries, operations, strokes, disorders of the autonomic nervous system, intoxication, some infectious and endocrine diseases, the neurogenic regulation of vascular tone may be disrupted.
Then the smooth muscle fibers of the vascular walls take over the provision of constant blood flow. This self-regulation is called basal vascular tone. Basal vascular tone is provided by the myogenic regulation mechanism.
There are such types of vascular tone disorders as hypotonicity and hypertonicity.
Hypotonicity (hypotension) of blood vessels
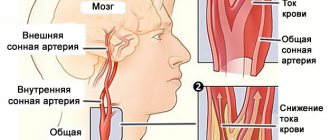
Vascular hypotonia (hypotension) is a decrease in the tension of the vascular wall, as a result of which there is a decrease in the speed of blood flow and a drop in blood pressure. Symptoms of hypotonicity differ depending on the type of vessels and the organ they supply with blood. Arteries and veins of the brain are often susceptible to hypotension.
Decreased tone of small cerebral arterial vessels leads to increased blood flow to the brain. During cardiac systole, the walls of the arteries are stretched, which leads to a throbbing headache.
A decrease in the tone of small cerebral veins provokes a violation of the outflow of venous blood from the brain. The veins and venous sinuses of the brain act as a depot for blood.
In a lying position, when the head is lowered below the body, physical activity or emotional stress creates conditions for even greater difficulty in the outflow of blood from the brain.
This explains the bursting nature of headaches that appear in patients with cerebral hypotension in the morning.
Hypertonicity (hypertension) of blood vessels
Hypertonicity (hypertension) of blood vessels is an increase in the degree of tension of the vascular walls, as a result of which their resistance to blood flow increases. This is accompanied by an increase in blood pressure.
As a result of spasm of the vascular walls, a narrowing of the vascular lumen occurs, which leads to a decrease in the minute volume of blood passing through them. The resulting blood deficiency leads to hypoxia, and in the case of significant narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels - to tissue ischemia.
The most dangerous consequences are the hypertonicity of cerebral vessels, as a result of which the blood supply to the brain deteriorates and its functions are impaired.
How to normalize cerebral vascular tone?
Normalizing the vascular tone of the brain means influencing the mechanisms of its regulation.
Therapeutic tactics depend on the type of tone (hypotonicity or hypertonicity) and consist of:
Reader Recommendation:
To clean VESSELS, prevent blood clots and get rid of CHOLESTEROL, our readers use a new natural drug recommended by Elena Malysheva. The preparation contains blueberry juice, clover flowers, native garlic concentrate, rock oil, and wild garlic juice.
Read more…
- Non-drug treatment.
- Drug therapy.
- Surgical interventions.
Non-drug methods
Non-drug methods of normalization do not depend on the type of tone and include:
- rejection of bad habits;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- correct work and rest schedule;
- increasing time spent in fresh air;
- reduction or elimination of stressful situations for the body (overwork, lack of sleep, overheating, hypothermia, harmful working conditions, stress);
- inclusion in the diet of vegetables, herbs, fruits, berries, nuts, vegetable oils, fish and seafood, lean meats, low-fat dairy products, whole grains (bread, cereals);
- limiting the consumption of salt, smoked foods, fatty and fried foods, hot seasonings, tea, coffee, alcoholic and carbonated drinks;
- contrast water procedures (baths, showers, foot baths);
- dosed physical activity, gymnastics;
- massage;
- herbal medicine;
- aromatherapy;
- autogenic training.
Drug therapy
The use of medications for cerebral vascular hypertonicity or hypotonicity should occur exclusively as prescribed by a doctor and only after its cause has been established. Self-medication in this case can lead to undesirable consequences.
The goal of drug treatment is to improve blood supply to the brain and prevent vascular accidents. When vascular tone increases, it is necessary to prescribe drugs that relax their walls and expand the lumen of blood vessels. When vascular tone is reduced, agents are used that can raise it.
When treating vascular tone disorders, it is necessary to understand that drugs that increase or decrease it are means of symptomatic, not etiological therapy. Only eliminating the cause of the increase or decrease in vascular tone can relieve the patient from the symptoms and consequences of vascular pathology.
To improve blood flow in the brain, depending on the type of cerebral vascular tone disorder, drug therapy may include:
- For hypertension: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - NSAIDs (Aspirin, Paracetamol, Ibufen, Voltaren);
- myotropic antispasmodics and anticholinergic blockers (Drotaverine, Papaverine, No-shpy, Dibazol, Spasmomena);
- diuretics (Furosemide, Veroshpiron);
- theophyllines (caffeine sodium benzoate, theophylline);
nootropic drugs (Piracetam, Glycine, Vinpocetine, Cinnarizine);
In severe cases of impaired cerebral vascular tone, it is possible to prescribe potent prescription drugs:
- benzodiazepines (Sibazon, Valium, Diazepam);
- antidepressants (Amitriptyline, Fluoroacyzine, Imipramine);
- barbiturates (phenobarbital);
- ergot alkaloids (Ergotamine, Ergometrine, Sermione).
Surgical interventions
Sometimes the only way to eliminate the cause of vascular hypertension is surgery. The question of the need for surgical treatment of vascular pathologies of the brain is decided collectively: by the attending neurologist or therapist and a vascular surgeon or neurosurgeon.
Source: https://ProInsultMozga.ru/sosudy/kak-povysit-tonus-sosudov-golovnogo-mozga.html
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism. Methods of its treatment and therapy
Arterial and venous pressure in the human brain is not a constant value. Due to necessity, it can vary within significant limits.
Yes it is. After all, it is the autonomic system that controls vascular tone. By and large, this phenomenon is functional, and no irreversible, serious disease occurs. Unpleasant symptoms may simply appear, indicating that the type of reaction “selected by the vessels” at a given time does not meet the requirements.
For example, there are two types of vascular dystonia: hypertonic (hyperkinetic) and hypotonic (hypokinetic). In the case of a shift to the hypotonic side, the ability to quickly increase blood flow with a sharp increase in mental load is impaired. In the opposite case, the tendency to vasospasm provokes constant muscle tension in the vascular muscles, which can lead to symptoms of chronic ischemia.
The Ministry of Health says the new drug will normalize blood pressure forever.
The symptoms of angiocerebral dystonia are varied. You should not assume that since there is a disorder with the blood vessels “in the head”, then the symptoms will also relate to the head. Let us remember that during a stroke, the focus of ischemia is also in the brain, but the leg may be paralyzed. Without going into details, we will simply list these signs:
- episodes of noise and ringing in the ears;
- attacks of dizziness;
It should be remembered that in some cases, a temporary lack of “pressure” of blood flow can produce symptoms that interfere with mental work: absent-mindedness, yawning, difficulty or even inability to concentrate on a task, apathy and lethargy occur.
Treatment approaches
Modern therapy for cerebral angiodystonia should be functional in nature, since vascular disorder is a completely reversible phenomenon, and its treatment should not begin immediately with potent drugs. The most likely measures at the first stage of treatment of cerebral angiodystonia are:
- Compliance with the work and rest regime. Sometimes just giving up sitting at the computer at night and normalizing the rhythm of life leads to very good results. But, as practice shows, this is very difficult to achieve. People are ready to take “handfuls” of medications just to avoid having to work on themselves.
- Walking, active lifestyle, being in the fresh air.
- Quitting bad habits, especially smoking, which causes chronic vascular spasm over time, not to mention drugs, which are very common among young people.
- Stop abuse of stimulants, such as green tea, coffee, Coca-Cola.
- Relaxation. Warm baths, relaxation techniques, and massage help with this.
- Careful observance of the bedtime ritual; When waking up, it is better not to get up immediately, otherwise the unpreparedness of the vascular bed to increase pressure can provoke collapse.
Taking medications
Taking medications must take into account the type of dystonia:
- For the hypertensive type, sedatives and mild soothing herbal infusions are preferable.
- For the hypotonic type, the use of adaptogens is indicated - drugs that stimulate vitality (tincture of ginseng, golden root, eleutherococcus).
Further therapy should only be carried out by a doctor. There are many modern medicinal methods for treating cerebral angiodystonia, but the best way is to normalize the tone of one’s own blood vessels without drugs.
Oleg Tabakov shared his secret to successfully combating high blood pressure.
A number of reasons can provoke spasm of cerebral vessels, which increases their tone. A prolonged absence of the relaxation phase impedes blood flow, resulting in severe pain.
The appearance of any ailment is always due to some factors. The disease cannot develop in a vacuum. There are more than enough reasons for such a pathological condition as cerebral vasospasm. All of them can be divided into two main groups: medical and so-called household.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_zCrldvVZR8
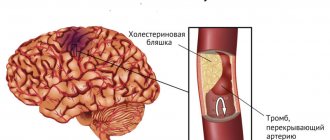
• Atherosclerosis. The progressive narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels is caused by the deposition of cholesterol plaques on their walls;
• Osteochondrosis of the upper spine. As a result of degenerative changes in the processes of the vertebrae, a narrowing of the openings through which the arteries pass to the brain occurs;
• Vegetative-vascular dystonia. Dysfunction of the nervous system can contribute to both a prolonged spastic state of cerebral vessels and their prolonged dilation, causing impaired blood flow;
• Endocrine disorders. Problems with the thyroid gland or complications of diabetes often provoke disruptions in the blood supply to tissues. With spasm of cerebral vessels, the causes may be physical or mental fatigue, lack of sleep, systematic stressful situations, as well as long-term static, most often sedentary, work. Smoking, alcohol, and poor nutrition play a very important role in disrupting vascular tone.
Weather conditions have a significant impact on the contraction of the walls of arteries and veins. Fluctuations in atmospheric pressure cause a specific reaction in the cerebral vessels in many people. Some of them can sense an approaching weather change in advance by a gradually increasing headache.
The main symptom of impaired cerebral vascular tone is periodic headache. It can occur suddenly, in the event of a sudden onset of spasm. If the tone does not change so quickly, the intensity of the pain increases gradually. This allows you to take the necessary measures to prevent the body’s condition from deteriorating. With cerebral vascular spasm, the symptoms depend on the speed of its onset and duration.
A gradual deterioration in blood flow, in addition to increased pain, is accompanied by a number of specific symptoms. This is approaching nausea, a feeling of lack of air, rapid heartbeat, paleness of the face. If the spasm begins at night, sleep becomes restless and intermittent. As a result, upon awakening, a feeling of “overwhelm” occurs, which leads to irritability or, on the contrary, to apathy.
With a sharp spasm of cerebral vessels, symptoms usually manifest themselves as sudden pallor, sweating, numbness of the lips, and coldness of the extremities. The headache is of significant intensity and has a different character, most often squeezing or pressing. Often this condition is accompanied by dizziness and vomiting, after which some improvement in well-being may occur.
Periodically occurring spasm of cerebral vessels significantly worsens the quality of life. In addition, it is dangerous for the development of complications, the most dangerous of which is ischemic stroke. Long-term disruption of the blood supply causes different consequences, depending on the affected area.
If a spasm of cerebral vessels occurs, treatment should be aimed primarily at normalizing blood flow. This is achieved by using vasodilators and antispasmodics. They help reduce vascular tone, improve tissue nutrition, and relieve pain. After carrying out such measures to relieve cerebral vascular spasm with essential drugs, it is extremely important to find out the cause of its occurrence. To do this, you need to undergo an examination that will allow you to find “weak spots” in the body.
Spastic headaches can be relieved through acupressure. To do this, apply pressure to points located in the temporal fossa, on the bridge of the nose, in the middle of the eyebrows and on their inner corners.
Like any disease, vascular spasm is easier to prevent than to deal with its consequences. The best preventive measure is an active healthy lifestyle. It provides for a balanced diet, reasonable physical activity, and normalization of sleep and wakefulness. Plants such as viburnum, chokeberry, hawthorn and many others are very useful as a means of preventing cerebral vasospasm. Decoctions and infusions prepared from them strengthen the walls of arteries and veins, and also help remove cholesterol plaques.
(NPNKM) develop more often against the background of hypertension, atherosclerosis, and vegetative dystonia. The basis for diagnosis is a combination of two or more of the following complaints: headache, dizziness, tinnitus, memory impairment, decreased performance, sleep disturbance.
Symptoms exist for a long time or often occur in conditions that require increased blood supply to the brain or lead to disruption of cerebral hemodynamics (intense mental or physical work, stuffy room, alcohol intake, etc.). In addition, there may be some slowness in solving intellectual problems.
Treatment of NPNCM
A special role belongs to drugs that have a combined effect on blood supply and metabolism of the brain, as well as on central hemodynamics and rheological properties of blood. Cavinton (vinpocetine) 0.005 g is used; cinnarizine (stugeron) - 0.025 g; xanthinol nicotinate (teonicol, complamin) - 0.15 g; parmidine (anginine) - 0.25-0.5 g; sermion - 0.005-0.03 g; tanakan - 0.04 g - 3-4 times a day.
In cases of increased cerebral vascular tone in the spastic type of REG, antispasmodic and vasoactive agents are recommended.
It is advisable to prescribe aminophylline 0.15 g 3 times a day. As a result, as a rule, the general condition of patients improves, headaches and dizziness decrease or disappear, and positive changes in rheographic and Doppler sonographic parameters are noted.
Problems with cerebral vascular tone
The human brain (BM) is involved in the regulation of all processes occurring in the body. For an organ to function normally, it must receive the amount of oxygen it needs. The latter enters the GM through blood vessels that are in normal tone.
In the case when the tone increases (or decreases), a narrowing of the lumen of the vessels is observed, due to which the blood flow is disrupted and a spasm develops.
We will tell you how to increase vascular tone, however, the information is provided for informational purposes and is not a guide to action.
What are its features
Vascular tone refers to the tension of the walls, which is ensured under the influence of smooth muscles. The latter has different severity, based on where it is located (arteries, veins, capillaries):
- the greatest severity is seen in the area of the arteries: smooth muscles provide high resistance to blood pressure and constantly maintain the arterial lumen;
- the least pronounced is in the area of the veins: the layer cannot resist the pressure of the blood flow and maintain the venous lumen;
- there is no smooth muscle in the capillaries.
The tone of cerebral vessels (brain) is maintained by 2 mechanisms: neurogenic (nerve impulses) and myogenic (spontaneous contraction of the smooth muscle layer).
Trauma, surgery, stroke, pathologies of the ANS (for example, vegetative-vascular dystonia), intoxication syndrome, the development of certain diseases of infectious and endocrine etiology often become causes of disruption of neurogenic regulation of tone. In this case, the smooth muscle muscles contained in the vessels take over the implementation of normal blood circulation. This process is called basal tone. It is provided through the myogenic regulatory mechanism.
Types of changes in vascular tone
The tone of cerebral vessels can be decreased or increased. In the first case, there is hypotonicity, in the second - hypertonicity, the features of which are different.
Hypotonicity
Hypotonicity or hypotension is a decreased vascular tone, which is expressed in a decrease in blood flow volume and a drop in pressure in the arteries. When the tone of small vessels decreases, the flow of blood into the organ increases. The walls of the arteries are stretched during contraction of the ventricles of the heart (one of the states of the organ's muscle), thereby causing throbbing headaches.
If the tone of the small veins located in the brain decreases, there is difficulty in the outflow of blood from the organ. It is in the area of veins and venous sinuses that the largest volume of blood is localized.
When a person is lying down, when the head is below the level of the neck (when bending forward or throwing it back), during physical exertion and emotional overload, blood flow is further disrupted, causing bursting headaches.
Hypertonicity
Hypertonicity of cerebral vessels is an increase in their tone, that is, the degree of wall tension, which causes an increase in resistance to blood flow. Hypertonicity is characterized by an increase in blood pressure and the occurrence of corresponding symptoms.
Hypertonicity, like hypotonicity, can occur against the background of the following pathological conditions of the body:
- constant lack of sleep and overwork;
- abuse of invigorating drinks (coffee, tea, etc.), alcohol, smoking;
- long stay in a stuffy room;
- frequent emotional experience, stress;
- development of hormonal disorders;
- VSD;
- development of atherosclerosis or osteochondrosis;
- heart and kidney diseases.
Spasm of the walls of blood vessels contributes to the narrowing of the lumen of the latter, causing a decrease in the volume of passing blood. Hypoxia develops, and with significant narrowing of the lumen, tissue ischemia.
Symptoms
The signs and characteristic manifestations of increased and decreased vascular tone are significantly different.
Problem in newborns
Pathologically altered vascular tone in infants is a dangerous phenomenon, which, if treatment is not started in a timely manner, can be fatal or cause the child to be assigned a disability group.
The most common consequence of insufficient oxygen supply to the brain with impaired vascular tone is cerebral ischemia. In this case, brain cells are inhibited due to insufficient blood supply, including oxygen. In approximately 40% of cases, the newborn dies.
To date, there is no specific treatment for cerebral ischemia in infants. Despite this, maintenance therapy can be started, which helps prevent complications and reduce the intensity of clinical manifestations.
Oxygen starvation can begin while the fetus is in the womb or during labor. During the prenatal period, this process is influenced by the following factors:
- alcohol and smoking abuse by a pregnant woman;
- development during pregnancy of an infectious disease, pathology of an endocrine nature, ARVI;
- age of the pregnant woman (before 18 years and after 35);
- high degree toxicosis in the third trimester.
Problems during labor also affect the condition of the baby’s brain. This:
- large fruit;
- use of drug stimulation of labor;
- premature birth;
- complications during childbirth, including birth injuries;
- entwining the fetus with the umbilical cord.
Basic treatment
How to improve vascular tone? Treatment methods may differ depending on whether a person has a decrease or increase in tone. To determine the tone, appropriate studies are carried out (rheoencephalography, etc.), based on the results of which a final diagnosis is made (hypotension or hypertension).
Additional treatment
Therapy for pathologically altered tone in an adult or child can be supplemented with folk remedies, which are considered absolutely safe. In addition, they are not inferior in effectiveness to generally accepted medications, and are much cheaper, if not free at all. To prepare them, just have simple ingredients on hand:
- herbs (chamomile, linden, St. John's wort, etc.): throughout the day it is recommended to drink not ordinary tea, but an infusion or decoction of medicinal herbs;
- garlic, honey, lemon: consuming such products helps normalize vascular tone and eliminate spasms;
- garlic and alcohol, from which an infusion is prepared, taken orally, 2 drops at a time, diluted with milk: chop 2 heads of garlic, pour in 200 ml of alcohol, leave for 1 week, strain;
- walnuts (partitions): pour a handful of partitions with hawthorn infusion, leave for 1 week, take 1 tsp orally. before eating;
- horse chestnut and vodka: grind a handful of chestnuts in a meat grinder, pour in 200 ml of vodka, leave for 1 week, strain, take 5 ml orally on an empty stomach.
To eliminate vascular spasm, you can wipe your face and neck with ice cubes made from decoctions or infusions of medicinal herbs. The latter can be added to baths when bathing or used as compresses.
In any case, treatment for altered (increased or decreased) cerebral vascular tone should be prescribed by a doctor. The cause of the changes is taken into account, as well as concomitant diseases and the general condition of the patient. There is no need to self-medicate, which rarely leads to recovery.
Source: https://vsepromozg.ru/ozdorovlenie/tonus-sosudov-golovnogo-mozga
Hypotension of cerebral vessels: clinical picture and treatment
Hypotension of cerebral vessels is a state of low blood pressure due to decreased tone of blood vessels. Reduced blood flow leads to a lack of nutrients and oxygen in the head vessels. As a result, a number of unpleasant symptoms appear.
Manifestations of hypotension of cerebral vessels
Depending on the development of the disease and the clinical picture, the following types of cerebral vascular hypotension are distinguished:
1) Decreased tone of the smallest arteries in the brain leads to an increase in blood pressure in them. The walls of blood vessels stretch. Headaches appear in the back of the head or temples.
2) Reduced tone of the veins in the brain causes a violation of the outflow of venous blood. The patient feels this acutely when lying down or sitting, when he lowers his head down. A characteristic symptom is a bursting headache in the morning.
3) Some patients complain of pain localized in one part of the head. Nausea, vomiting, and darkening before the eyes are added to these.
Normal outflow of venous blood in the brain area occurs when a person awakens after a night's sleep. During rest, the veins relax and some blood accumulates in them.
When a person gets out of bed and begins to move, his muscles contract, and venous blood is pushed into the channel. This leads to an increase in the tone of the veins and a slight increase in blood pressure.
With venous hypotension, you have a headache in the morning. After some physical activity the pain goes away. The patient feels relatively well during the day. But in the late afternoon, you feel tired, lose activity, drowsiness appears, and performance decreases.
Clinic of cerebral vascular hypotension
The clinical picture of the disease is varied. Some patients are persistently haunted by one symptom. Others experience a range of symptoms.
How to recognize hypotension?
1) Headache.
Some patients may experience headaches for several days in a row. The pills don't help. Sometimes there is a dependence of pain on the time of day, work done, fluctuations in atmospheric pressure, overeating, overwork, etc.
Headache with excessive pulse stretching of the arteries is localized in the temples and crown, in the back of the head, and has a pulsating character. When the outflow of venous blood from the skull is disrupted, the head hurts in the back of the head. The pain is pressing and growing.
2) Dizziness, apathy, excessive fatigue and weakness, fainting, staggering when walking.
These manifestations are possible due to insufficient blood supply to the brain. As a result, oxygen starvation and lack of nutrients develop.
3) Dependence of well-being on weather conditions and atmospheric pressure.
Changes in weather in patients with hypotension are reflected in irritability, an abundance of negative emotions, mood swings, depression, and sleep disturbances. Some people just can’t get enough sleep, others suffer from insomnia.
4) Pain in the heart area, cardiac arrhythmia.
Insufficient blood supply to the brain affects the patient's cardiac activity. Pain behind the sternum appears in a state of complete rest. That is, it is not associated with either physical or mental stress.
5) Feeling of lack of air.
Problems with the blood supply to the brain lead to impaired blood flow in the lungs. Patients often take deep breaths and yawn. For the same reason, their vision becomes dark, they experience fainting, and their legs “don’t obey” when suddenly changing position from horizontal to vertical.
Characteristic signs of venous hypotension:
- numbness of the limbs;
- “pins and needles” feeling in the arms and legs;
- cold hands and feet;
- increased sensitivity to cold and heat.
Signs of chronic hypotension:
- decreased libido and potency in men;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle in women.
The full functioning of many organs and systems depends on the normal functioning of the brain. Malfunctions inside the skull lead to malfunctions in the body.
Treatment of cerebral vascular hypotension
A cardiologist and neurologist confirms the diagnosis and prescribes treatment. First, the patient needs to undergo the following tests:
- general blood test plus biochemical;
- blood test for viscosity and coagulation rate;
- angiography of cerebral vessels;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels.
Treatment of the disease is complex.
1) Healthy lifestyle, special diet plus exercise. And, of course, daily walks in the fresh air.
2) To relieve symptoms - medications containing caffeine.
3) To maintain vascular tone - nootropic drugs.
4) For depressive states and migraine-like pain - drugs that activate blood flow and strengthen the walls of blood vessels (Tanakan, Stugeron, Encephabol).
5) To normalize the psychological state - sedatives of plant origin (tincture of Eleutherococcus, ginseng root, Rhodiola rosea, etc.).
6) To strengthen blood vessels - amino acids.
Let us repeat once again: treatment of cerebral vascular hypotension should be comprehensive.
Source: https://TvoyAybolit.ru/gipotoniya-sosudov-golovnogo-mozga.html
Symptoms of hypotension
The symptoms and treatment of hypotension are determined by the therapist. There are several signs that help diagnose the disease:
- increased sweating;
- severe pallor of the skin; low body temperature up to 36°C;
- painful pulsations in the head;
- increased heart rate;
- drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- impaired thermoregulation of the body.
All this leads to decreased performance. This manifests itself not only in physical weakness, but also in a decrease in brain activity. With increased physical activity, people with hypotension may experience increased pulse and heart rate, and sometimes discomfort in the heart area and shortness of breath.
Arterial hypotension is cyclical. Its exacerbation is clearly manifested in the spring-summer season or after infectious diseases or stressful situations. But this is only if the body is predisposed to low blood pressure. A doctor can determine symptoms and treatment after conducting a comprehensive examination.
Hypotonicity of cerebral vessels
Hypotension or decreased blood pressure occurs due to decreased tone of blood vessels. Due to decreased tone and reduced blood flow, the consumption of nutrients and oxygen by cells decreases.
One of the first of all organs and systems to suffer from this is the brain. Oxygen deprivation of the brain causes most of the symptoms experienced by people with low blood pressure.
How dangerous is hypertension and how to recognize its symptoms?
Source: https://profalmazperm.ru/gipotonus-sosudov-golovnogo-mozga/
Symptoms of hypotension
Symptoms of low blood pressure, if the disease is caused by physiological reasons, most often are practically not felt by the person himself. In other cases, manifestations can be varied. For example, with orthostatic hypotension, which clearly demonstrates itself during a sharp transition from a horizontal to a vertical position:
- dizziness occurs;
- weakness appears;
- gait becomes unsteady;
- visual impairment occurs;
- changes in the activity of the heart appear.
Manifestations of panic and even fainting are possible.
In the primary or essential form, the following symptoms of hypotension in women are added to those listed above:
- frequent headaches and fatigue;
- anxiety;
- depressive states;
- numbness of the limbs, increased sweating, frequent flashes of hot and cold.
Men may additionally experience problems with potency.
With secondary hypotension, the symptoms of the underlying disease clearly manifest themselves.
Read about the effect of coffee on blood pressure here. A list of herbs for treating cerebral vessels can be found here.
What is cerebral vascular hypertonicity - treatment
28.06.2018
Vascular tone is the tension of the vascular walls maintained by the muscular wall in these vessels. This is a factor that determines the blood supply to brain tissue.
The tone of the muscle wall maintains a certain tension, allowing the lumen of the vessel to maintain the required diameter. Thanks to the muscular walls of the cerebral vessels, the brain tissue is protected from a lack or excess of blood, therefore, in a healthy body, the blood supply to the brain does not depend on pressure changes in other parts of the body.
However, with diseases of the internal organs or disorders of the nervous system, the tone of the arteries and veins may change: the muscle wall goes into a state of spasm - the lumen of the vessel decreases, and the supply of blood to the neurons decreases. This leads to tissue hypoxia, when the brain does not receive the proper amount of oxygen and nutrients. Vascular hypertonicity provokes functional and organic disorders in the brain.
What it is
Hypertonicity is a change in the tone of a vessel, in which the lumen of the latter decreases due to spasm of the smooth muscles of the arteries, and vice versa, if the tone decreases, this is called hypotonicity.
Increased tone can be of a physiological or pathological nature.
In the first variant, vascular tone naturally increases during temporary functional states, when a normal amount of adrenaline is released due to internal (pain, fear) and external (sharp loud sound) factors. Physiological hypertonicity will never lead to disorders in the long term and is considered a positive temporary condition.
Pathological hypertonicity of cerebral vessels is formed as a result of diseases of internal organs, glands and metabolic disorders. Severe arterial spasm can lead to ischemic stroke (acute cerebrovascular accident), which results in irreversible organic changes in tissue and subsequent loss of intellectual and motor capabilities.
Causes
The following reasons lead to spasm of cerebral arteries and veins, which are divided into psychological (neurological, psychiatric), somatic (bodily) and indirect.
Psychological reasons:
- Anxiety disorder, accompanied by excitement, fear due to constantly elevated levels of adrenaline.
- Vegetovascular dystonia. The disease is characterized by an imbalance between the functioning of the autonomic parts of the nervous system. In this disease, blood vessels spasm for no obvious reason.
- Stress, neuropsychic tension.
- Sleep disturbance: insomnia, taking a long time to fall asleep.
- Personality pathologies: psychopathy, accentuation. This is predominantly a hysterical, emotionally labile and cycloid personality type.
Somatic causes:
- Arterial hypertension - as a primary disease - a persistent increase in blood pressure over 140/80 for more than two weeks.
- Atherosclerosis is the presence of fatty deposits on the walls of the arteries.
- Inflammation of the walls of blood vessels.
- Diseases involving systems: rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus or scleroderma.
- Diseases of the endocrine organs: pheochromocytoma is a tumor of the adrenal glands that sharply stimulates the glands and provokes the release of huge amounts of adrenaline.
- Dystrophic diseases of the musculoskeletal system: cervical osteochondrosis, spinal hernia.
- Hyperthyroidism. What it is? This is a disease of the thyroid gland, in which the release of T3-T4 hormones increases, which increases the sensitivity of blood vessels to adrenaline and norepinephrine.
- Inflammation of the tissue of the nerve ganglia of the sympathetic parts of the autonomic nervous system.
- In children, cerebral ischemia is observed due to pathologies during pregnancy and complicated childbirth. As a rule, a child’s pathology is diagnosed immediately in the maternity hospital.
Indirect reasons that increase the likelihood of hypertension:
- smoking;
- large doses of caffeine: more than three cups of coffee per day; caffeine temporarily stimulates the release of adrenaline into the blood;
- diabetes;
- heredity;
- age: from 50 years old, mostly men;
- prolonged stay in stuffy, unventilated rooms;
- weather sensitivity.
Treatment
Complex therapy of the disease, how to restore brain function and how to increase the body’s performance:
- Treatment of the underlying illness that led to a disorder of brain tone.
- Psychohygiene: dosed mode of work and rest.
- Get a good night's sleep: remove bright light sources (phone, laptop) away from you an hour before bedtime.
- Aromatherapy. You can use scented sticks or scented oils.
- Balance your diet: reduce salt and alcohol intake.
- Drug treatment. Medicines that lower blood pressure: valerian, captopres or captopril.
- Folk remedies:
- rosehip tea;
- take a warm shower or bath.
Source: https://sortmozg.com/bez-rubriki/gipertonus-sosudov-golovnogo-mozga
A decrease in blood pressure and vascular muscle tone is
Vascular tone
is the tension of the vascular wall, which is created by the contraction of its smooth muscle cells and changes the diameter of the lumen of the vessels. Changes in vascular tone are the main mechanism for regulating peripheral and regional vascular resistance. Muscle-type vessels (small arteries and veins, arterioles and venules, sphincters) are capable of active changes in tone. There are two types of vascular tone, fundamentally different in the mechanisms of its regulation.
Central (neurogenic) tone
regulated by the autonomic nervous system. The innervation of blood vessels is mainly carried out by the sympathetic nervous system. Most vessels of internal organs and skin contain α-adrenergic receptors. Through them the vasoconstrictor effect of the nervous system is carried out. The vessels of the brain and myocardium contain mainly beta-adrenergic receptors, through which the vasodilator effect occurs.
Peripheral (basal) tone
- tension in the vascular wall, which persists after complete denervation of the vessels. This indicates that there are other vasomotor mechanisms besides the nervous system. Basal tone is regulated by the influence of vasoactive tissue metabolites, endothelial factors, biologically active substances and hormones. In addition, so-called myogenic regulation plays an important role.
Myogenic regulation of vascular tone
(Beilis-Ostroumov effect) is based on the reaction of vascular smooth muscle cells to stretching. Fluctuations in blood pressure change the stretching of the vascular wall and smooth muscle cells. With an increase in blood pressure, the stretching of smooth muscle cells increases, but in response to stretching, they contract and the tone of the arteries increases, they narrow, and vascular resistance increases. Thanks to this mechanism, an increase in blood pressure is accompanied by a contraction of the smooth muscles of the arterioles of the organs, as a result of which hyperperfusion of the organs is prevented. On the contrary, with a decrease in blood pressure, the stretching of the vascular wall weakens, vascular smooth muscles relax, which allows maintaining regional blood circulation under these conditions.
Metabolic regulation of vascular tone
aims to maintain proper perfusion and metabolism in organs. Most metabolites of energy metabolism have pronounced vasodilating activity. These are adenosine, CO2, lactic acid, H+ and others. In an intensively working organ, metabolic products accumulate, resistive vessels dilate and perfusion of the organ increases. The same mechanism operates when metabolic products accumulate due to decreased blood flow to the organ.
Endothelial regulation of vascular tone
is carried out due to the production of biologically active substances with vasomotor activity by endothelial cells. The endothelium produces compounds with a dilator and constrictor effect on the tone of resistive vessels. The most important endothelial vasodilator is nitric oxide.
Source