Neuralgia pain
Regardless of the location of the damaged nerve, acute pain is considered a sign of this unpleasant condition. As a rule, it appears instantly and tends to intensify with any physical activity. The duration of the unpleasant sensation can be several minutes or several hours. At night, discomfort often increases.
The pain syndrome in neuralgia is localized depending on the location of the damaged nerve. In most cases, this is the intercostal zone, as well as the lower back, neck with discomfort extending to the clavicle area, and the frontal region with the peritemporal part of the head.
To eliminate the unpleasant factor in any situation, almost the same painkillers are used. For trigeminal neuralgia or another localization zone, medications are prescribed in the form of tablets, injections, etc.
Vitamin therapy
The use of medications is the main way to treat intercostal neuralgia. To treat the disease and the cause that caused it, the following is prescribed:
- pills;
- injections for intramuscular and intravenous administration;
- ointments, gels or creams.
Tablets are considered an ineffective treatment for intercostal neuralgia. In addition, they irritate the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract and cause adverse reactions. Erosive gastritis and stomach ulcers are possible harm from uncontrolled use of tablets.
To suppress inflammatory processes, replenish vitamins and minerals, and strengthen the immune system, it is necessary to take special complexes. Medicines with B vitamins are involved in blocking acute inflammatory processes that erupt in nerve tissues. Vitamin complexes relieve muscle spasms and neutralize the negative effects of medications used.
Medicines for muscle recovery
The use of antispasmodics and muscle relaxants for intercostal neuralgia relieves pain and shortens recovery time. By relieving muscle spasms during neuralgia, such medications prevent the development of relapse, improve the condition of muscle fibers, and increase the patient’s quality of life. Typically, therapy is limited to taking No-Shpy, Galidor, Mydocalm, and Clonazepam tablets.
In especially severe cases, antispasmodics and muscle relaxants are used in the form of injection solutions.
Medicines of this type for intercostal neuralgia exhibit a number of additional effects, eliminating tissue swelling and congestion in the affected area.
Therapy is often limited to taking No-Shpa.
Causes of the disease
The pathological process can affect any nerve ending in the human body. There are a number of factors that can cause neuralgia:
- Hypothermia.
- Diseases of the central nervous system.
- Severe ARVI.
- Infectious diseases.
- Spondyloarthritis (a systemic chronic disease of the spine, which is characterized by ankylosis of the sacroiliac symphysis, which, as it progresses, develops into a pronounced form of thoracic kyphosis).
- Osteochondrosis (a disease in which premature aging and destruction of intervertebral discs and then vertebrae occur).
- Spondylosis (a chronic pathology accompanied by deformation of the vertebral bodies, which, in turn, occurs under the influence of the proliferation of bone tissue).
- Allergic reaction.
- Intoxication with medications.
- Harmful industrial production.
- Inflammatory processes and malignant tumors.
- Compression of the nerve in a forced position.
- A large number of medical procedures in one area of the body.
Pain relievers
The primary goal of drug therapy is to relieve pain – the main symptom of the disease. Pills and injections help get rid of prolonged debilitating pain. For pain relief the following is usually prescribed:
- Spasmalgon;
- Spazgan;
- Analgin;
- Baralgin;
- I took it.
To relieve unbearable pain that occurs with swelling of nerve fibers and root compression syndrome, the following is used:
- Ketoprofen;
- Ibuprofen;
- Nise;
- Celebrex;
- Diclofenac.
Analgesics are used to relieve pain and prevent new attacks:
- Sedalgin;
- Panadol;
- Tylenone;
- Pentalgin.
These drugs are available in tablets, injection solutions, ointments and gels. They are taken in tablets. To quickly relieve pain, injections are given and IVs are placed.
The course of treatment with anesthetics is short, it does not exceed 4-5 days. They disrupt the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Painful sensations worsen the well-being of patients, plunge them into a state of prolonged stress, create a feeling of discomfort, and reduce the quality of life. Taking sedatives for intercostal neuralgia helps relieve nervous tension, relax skeletal muscles, and normalize the condition of the sick person.
They drink a sedative at night. It promotes good sleep, proper rest, and relieves nervous and muscle tension. Essential oils: lavender and peppermint have an excellent relaxing effect.
Features of drug treatment
Tablets and ointments for intercostal neuralgia are prescribed by a doctor if there are obvious indications for this. This is considered a persistent pain syndrome that is not relieved by local heating, compress or massage. The use of medications is often resorted to in cases of relapse of the disease or a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition. The patient is required to be prescribed vitamin therapy to prevent exacerbation of the condition or the development of new attacks.
The availability of medicines and information has led to the spread of self-medication. Previously, patients with chest pain went to see a doctor, and before his arrival they managed with improvised methods. Today, many people select medications themselves or with the help of a pharmacist, which often causes complications. It is necessary to refrain from drug treatment of any manifestations of intercostal neuralgia at least in some cases. Caution is necessary if the patient has a history of drug allergies, active somatic diseases, problems with the liver and/or kidneys. Tablets for neuralgia should not be given to children, pregnant women, or the elderly without a doctor’s permission.
Symptoms
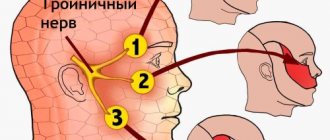
Damage to the trigeminal nerve causes severe acute pain in the face, which can occur at any time. Before the onset of the disease, the patient’s face begins to itch, goosebumps and numbness occur. The sharp pain continues for several hours.
With an intercostal lesion of the back, intense pain appears in the ribs, which worsens the situation with any physical activity, as well as coughing, sneezing or taking a deep breath. As a rule, the cause of the pathological process is considered to be osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine.
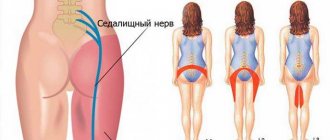
Damage to the sciatic nerve provokes pain in the buttock area, which radiates to the thigh, as well as the lower leg and toes. The pain becomes unbearable when moving, coughing or sneezing. The patient feels pain or burning in different areas of the limb. Such sensations lead to immobilization and do not allow you to stay in one position for a long time.
When the external cutaneous nerve of the thigh is damaged, local aching and prolonged pain, burning and numbness appear. The disease worsens with movement. Often the pain does not go away even after taking painkillers.
Occipital neuralgia provokes pain in the back of the head, which can move higher, localizing to the temples and eyes. The attack appears suddenly. It is possible that vomiting and increased pain may occur.
Postherpetic lesions appear in people who have the herpes virus in their bodies. The pain syndrome can be acute and intense. Develops suddenly, regardless of the exacerbation of the disease.
Without proper treatment, the disease can develop into neuropathy. With this pathological process, the tissue of the nerve and its sensitivity change. As a result of frequent attacks, a person develops a depressive state, as well as decreased immunity and suffers from insomnia.
What is intercostal neuralgia?
Intercostal neuralgia is a disease that does not occur on its own, but acts only as a symptom of other pathologies. When changes occur in the body that lead to irritation or compression of the peripheral nerves of the chest, girdle pain occurs at the site of the lesion. The causes of the disease can be different - from injury to the back or sternum to intoxication of the body and pathological processes in the tissues of the brain.
Most often, the symptom is the result of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine or other diseases of the axial part of the skeleton.
The main manifestation of intercostal neuralgia is pain. The sensations are burning, sharp, encircling. They are often accompanied by tingling and local numbness of the skin. The clinical picture worsens with the patient’s physical activity, coughing, sneezing, and sometimes even breathing. Before you start taking medications for neuralgia, you need to make sure the diagnosis is correct and exclude the development of heart failure. For this purpose, it is better to consult a doctor who will conduct all the necessary examinations. A simple test with nitroglycerin will help at home. Taking this medication will relieve heart pain, but will not have any effect on neuralgia.
The disease is aggravated by coughing.
Classification of painkillers for neuralgia
When treating neuralgic diseases, the patient first of all needs medications that can remove or reduce pain. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are often used for this. The range of such medications in pharmacies is very wide, so you cannot buy them on the recommendation of a pharmacy pharmacist or on your own - a doctor must select the optimal medicine for the patient.
A specialist can prescribe painkillers to the patient for neuralgia. Among such drugs are Nise, Baralgin, as well as Analgin or Movalis. These tablets should be taken three times a day after meals at the dosage recommended by your doctor. This treatment course usually does not last long, because long-term use of such medications can negatively affect the patient’s health. This is especially true for the gastrointestinal tract.
There are also more modern pills for neuralgia. They have a longer lasting effect on the body. Among these drugs is the medicine Melox Forte - it will be enough to take it once a day.
Local anesthetics relieve swelling and pain of a neuralgic nature. They are prescribed for temporary relief of acute pain. Reduce pain and eliminate muscle tension with ointments, gels, and injection solutions.
The drugs are applied or injected directly into the lesion. They are used to make blockades. Pain is suppressed with injections of Lidocaine, Novocaine or Xylocaine. The use of local anesthetics is limited in time. They are highly toxic agents that can cause great harm to the body. Unbearable pain is relieved with one-time blockades.
All analgesics are divided into non-narcotic and narcotic. The second group of painkillers can suppress the central nervous system. The active ingredients of narcotic drugs are based on changing the nature of the pain syndrome due to a direct effect on the brain.
Subsequently, not only does the pain “go away,” but also a feeling of euphoria arises. But, unfortunately, such medications carry a certain danger. They are addictive.
As a rule, narcotic drugs are used for myocardial infarction, burns and cancer. These medications contain codeine, morphine, and fentanyl.
Non-narcotic painkillers are divided into several groups:
- traditional;
- combined;
- from migraine;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- COX inhibitors;
- antispasmodics.
NSAID medications
Pharmacy products NSAIDs are non-steroidal drugs characterized by a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. With their help, it is possible to localize neuralgic syndrome, reduce the intensity of pain and attacks, and significantly improve the general condition of patients faced with a disease of the nervous system. Such properties of NSAID drugs, which have the ability to influence not only the inflammatory process, but also the thermal state of the sick person’s body, pain, play an important role in the treatment of pathology.
Drug therapy for neuralgia involves the use of a wide range of medications of this type. The most common of them include: Diclofenac, Ortofen, Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Piroxekam, Voltaren, Indomethacin. Such drugs and their analogues are available in the form of tablets and capsules. It is recommended to take them no more than 1-2 times a day. It is strictly forbidden to exceed the dosage prescribed by your doctor. Ignoring the recommendations of a neurologist can lead to the development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including ulcerative conditions of the mucous membranes of the stomach and duodenum, gastritis and other pathologies. The course of drug therapy based on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is 5-7 days.
In addition to the form of tablets and capsules, NSAID drugs are available in the form of rectal suppositories and injections. Ointments, creams, gels, and special patches are produced for external use. These include Diprilif, Voltaren, Ketonal, Nise, Diclofenac and other analogues with a similar composition. When using NSAIDs for external use, it is recommended to handle them carefully, carefully rubbing them into areas of pain, excluding pressing and massaging the inflamed areas. Special patches, which include Ketonal Thermo, are considered a modern alternative to applications with ointments, creams, and gels.
Methods of drug therapy
Inflammatory processes occurring in nerve fibers lead to swelling and pain. The swollen tissue puts pressure on the nerves. Pinched nerve roots are accompanied by pain. Relieving inflammation, eliminating pain.
Inflammatory processes are suppressed with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs:
- Ortofen;
- Diclofenac;
- Nimesulide;
- Ketoprofen;
- Voltaren;
- Movalis.
The products effectively relieve inflammation. If you use them correctly, according to the regimen given by the doctor, you can get a long-term stable remission. To eliminate inflammation, take a tablet 2 times a day, give an injection, or use rectal suppositories.
The body's susceptibility to drugs is almost the same. But they are best absorbed through the mucous membranes. Long-term treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs causes exacerbation of certain ailments (for example, gastritis or ulcers). They should not be used without a doctor's prescription.
Negative reactions
These drugs can cause certain adverse reactions:
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Flatulence.
- Peptic ulcer of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Migraine (severe pain that is localized in different parts of the head).
- Dizziness.
- Insomnia.
- Depressive disorders.
- Tinnitus.
- Hives.
- Quincke's edema.
- Rhinitis (runny nose).
The main group of drugs that are used for pain in neuralgia are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They not only eliminate noticeable discomfort, but also effectively eliminate inflammation.
In addition, this group of medications can reduce elevated body temperature, which occurs when peripheral nerves are damaged. What is the best pain reliever for neuralgia?
Injections with analgin
Intramuscular injections are considered one of the most effective ways to eliminate pain in various types of neuralgia. The effect of using injectable drugs manifests itself very quickly and has virtually no negative effect on the patient’s internal organs.
What are the strongest painkillers for neuralgia? Injections into the muscle. Analgesics that were administered by injection are absorbed by the body much faster than tablets. That is why when using them, it is imperative to follow the dosage and therapy regimen prescribed by the doctor.
The principle of drug use must also be observed, since certain medications require slow infusion to stimulate the active component, while others should be warmed to room temperature.
If emergency one-time administration is necessary, in the absence of the above painkillers, injections that contain analgin can be used for neuralgia. These include:
- "Spazgan".
- "Trigan."
- "Baralgin."
- "Analgin."
These drugs are usually used in combination with Diphenhydramine for pain relief in ambulances. But frequent use of painkillers for neuralgia is contraindicated, since there is an increased risk of agranulocytosis and other pathological changes in the blood.
Pills
Painkillers for neuralgia in tablet form are quite effective, but their use is not always permitted. If you have problems with the stomach and intestines, as well as impaired functioning of the liver and kidneys, it is not recommended to use such medications.
The most effective neuralgic drugs include:
- "Ketorolac".
- “Toradol.”
- “Ketokam”.
- “Dolak.”
- “Ketofril.”
- “Ketanov.”
- “Zaldiar.”
- "Flamax".
- “Ibuprofen.”
- "Nurofen".
- “Ibusan.”
- “Nalgesin”.
- “Brufen.”
- "Paracetamol".
Despite the high popularity of the analgesic drug Diclofenac, which also belongs to the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, it is better to avoid its use. This drug not only gives a short-term effect, but also significantly increases the likelihood of stomach and intestinal ulcers.
List of the best drugs for neuralgia
The main group of drugs used for neuralgia pain are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory tablets. They not only eliminate obvious physical discomfort, but also effectively reduce the inflammatory process. Also, this group of drugs can lower high body temperature that appears when peripheral nerves are damaged.
All existing painkillers used for neuralgia can be divided into several groups. According to the form of release and method of use, neuralgic drugs are as follows:
- pills;
- injections for injections;
- ointments and gels;
- candles.
Considering the speed of manifestation of the analgesic effect, as well as its duration, the more preferable medications for neuralgia are tablets, suppositories and injections for injections. Ointments and gels are mainly used as an additional auxiliary element. Their anti-inflammatory effect is significantly superior in quality to the ability of these drugs to eliminate spasms and pain.
Pills
Painkillers for neuralgia in tablet form are quite effective, but their use is not always possible. The presence of problems with the gastrointestinal tract, as well as liver and kidney dysfunction, are often direct contraindications to taking drugs of this type.
Ketorolac has many analogues and has an excellent analgesic effect.
The most effective tableted neuralgic drugs include the following drugs:
- Ketorolac. Analogues of this drug are tablets Toradol, Ketocam, Dolak, Ketofril and Ketanov;
- Zaldiar, which contains the active ingredients tramadol and paracetamol;
- Flamax;
- Ibuprofen. It is contained in various dosages by the painkillers Nurofen, Ibusan, Nalgesin, Brufen;
- Paracetamol.
Despite the high popularity of the painkiller Diclofenac, which also belongs to the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, it is better to avoid using it. This drug not only provides a short-lived and weak analgesic effect, but also significantly increases the risk of developing gastrointestinal ulcers.
A federal program to rid the population of musculoskeletal diseases has been launched! It's hard to believe, but an effective drug is funded by the Ministry of Health. Scary statistics show that banal crunching and pain in the joints often result in disability! To avoid this you need to take a cheap remedy...
Injections for injections
One of the most effective means of relieving pain for various types of neuralgia is intramuscular injections. The effect of taking drugs in this form manifests itself quickly enough and has virtually no negative impact on the patient’s internal organs and systems.
One of the most effective means of relieving pain for various types of neuralgia is intramuscular injections.
Painkillers administered by injection are absorbed by the body much better than tablets. That is why during their use it is necessary to follow the dosage and treatment regimen prescribed by the attending physician. The principle of drug administration must also be observed, since some analgesic anti-inflammatory injections require slow administration to activate the active substance, while others must be warmed to room temperature.
The most effective for damage to peripheral nerves are the following painkillers in the form of intramuscular injections:
- Ketanov;
- Lornoxicam and its analogue Xefocam;
- Toradol;
- Flamax;
- Meloxicam, an analogue of which is Movalis;
- Flexen.
If emergency one-time use is necessary, in the absence of the painkillers listed above, injections based on analgin can be used for neuralgia. These include Spazgan, Trigan, Baralgin and Analgin itself, which in combination with Diphenhydramine is used for pain relief in ambulances. However, frequent use of analgesics is unacceptable due to the high risk of developing agranulocytosis and other pathological changes in blood composition.
Ointments and gels
Anesthetic ointments and gels help activate the regenerative properties of tissues
This type of drug is used exclusively in combination with other painkillers in the form of tablets, injections or suppositories. As an independent pain reliever for neuralgia, ointments and gels are rather low in effectiveness. However, their long-term systematic use has a persistent anti-inflammatory and some antispasmodic effect.
The most effective ointments and gels that can eliminate pain from neuralgia are the following drugs:
- Ketoprofen;
- Nimesulide;
- Ketonal;
- Viprosan;
- Apizartron;
- Finalgon;
- Myoton.
Many of these drugs contain bee or snake venom. Based on this, before starting to use an ointment or gel that relieves inflammation and pain due to neuralgia, you should definitely consult a doctor and exclude all contraindications. In case of increased sensitivity of the patient’s body to most components of pain-relieving ointments and gels, he is most often prescribed Myoton, based on herbal components. However, its effectiveness is significantly lower than that of other drugs in this group.
In addition to the fact that these suppositories quickly relieve pain, they also effectively relieve inflammation and lower fever. But, despite the speed of the body’s reaction to rectal suppositories, they are rarely used in the treatment of neuralgia. The reason for this is the inconvenience of their use, including mandatory long-term bed rest.
In general, in the process of treating neuralgia, types of painkillers can be combined with each other to achieve a quick positive effect. However, strict medical supervision is a prerequisite for safe and effective therapy.
Have you tried all possible remedies, but the pain does not go away and prevents you from living a full life? Apparently yes, since you are reading these lines and not playing with your children and grandchildren.
The most effective painkillers for neuralgia are solutions for intramuscular injections:
- "Ketanov."
- "Lornoxicam."
- "Xefocam."
- "Toradol."
- "Flamax".
- Meloxicam.
- "Movalis".
- "Flexen".
Many drugs have been invented for neuralgic manifestations, but not all of them effectively relieve the symptoms that arise. Therefore, experts advise paying attention to the new generation of neuralgia pills. They have a more targeted effect, so they quickly relieve signs of pathology.
Among the new generation drugs the following can be distinguished:
- Menovazin;
- Ketorolac;
- Naproxen;
- Teaprofenic acid;
- Ketoprofen.
Of the painkillers of the previous generation, Diclofenac helps well with pain. It represents a group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The result is achieved after taking it by relieving inflammation from nerve tissue. However, not all old drugs can reliably relieve pain; for example, Celexib and Meloxicam are virtually useless for neuralgia. These medications are unable to completely suppress the pain attack and help only slightly alleviate the condition.
Previously it was believed that painkillers for neuralgia should be based on poison. This statement is only partly erroneous, since drugs like Apifor perfectly relieve the symptoms characteristic of the disease, but they have a huge number of contraindications.
How to treat intercostal neuralgia with physiotherapy?
We would like to immediately draw the attention of our readers that the article was written by a practicing neurologist, therefore all the information about painkillers for neuralgia presented in the article is reliable and relevant. And also does not contain any advertising or anti-advertising! Nevertheless, the article is for informational and educational purposes only; the doctor must be responsible for prescribing a particular drug individually! Therefore, in each specific case, a doctor’s consultation is required!
The principles of pain relief for acute neuralgia are quite diverse. For example, abroad, in developed countries of the European Union and in the USA, for persistent neuralgic and neuropathic pain, with a reasonable justification for the prescription, the patient can even receive narcotic analgesics - for example, in the form of a patch containing fentanyl. It is glued to the patient’s body and can significantly improve the quality of life in cases of severe insomnia due to persistent pain.
In the photo - a very popular painkiller in Western countries (fentanyl patch)
Naturally, these are exceptional cases. Let us list the main groups of drugs that have an analgesic effect and can be successfully used for various types of neuralgia.
There are a number of exceptions when painkillers are not able to help because they do not have a point of application. Thus, with trigeminal neuralgia, taking drugs for analgesic purposes does not produce any effect - for this disease, anticonvulsants are used. Their task is to reduce the frequency and intensity of “focal discharges”, which are the cause of pain impulses.
In the photo, the drug “Lyrica” is an anticonvulsant; some neurologists prescribe this particular drug for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
The next exception, when taking classical painkillers is also ineffective, is postherpetic neuralgia, which develops after suffering herpes zoster, which arose, for example, along the intercostal nerve. A sign of this neuralgia will be persistent, excruciating, boring and burning pain, which literally exhausts the patient and can deprive him of sleep for many years.
In addition, the urgent use of antiviral drugs in the first hours and days, which can “in the bud” slow down the development of the disease, plays a decisive role in the prognosis of the development of this type of neuralgia.
Important: they should be used with caution in patients with bronchial asthma and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
The drugs are centrally acting muscle relaxants. They have an analgesic effect due to the relief of spasm of skeletal muscles, the elimination of stagnation, as well as the resulting weakening of pressure on the nerve roots, and, as a result, a decrease in swelling in them. In clinical practice, drugs such as Mydocalm (tolperisone) and Sirdalud (tizanidine) are successfully used. Mydocalm
The mechanism of their action is associated with the regulation of special neurons that are responsible for the “resting tone” of skeletal muscle, somewhat reducing it. This leads to an increase in volumetric blood flow due to the expansion of the capillary vascular network inside the muscle, the elimination or reduction of stagnation, as well as a decrease in the intensity of pain.
It should be noted that the side effects of these drugs (especially sirdalud) may include general muscle weakness and insufficient clarity of reaction, therefore, during treatment, working with machines and mechanisms, as well as driving a car, is contraindicated. Additionally, these medications are recommended to be taken at night as they may cause some drowsiness.
In fact, the listed groups limit the pronounced analgesic effect, which develops within 24 hours after taking the drug or administering it as an injection.
As a one-time administration, you can use drugs based on metamizole sodium, such as Baralgin, Trigan, Spazgan. These are combination drugs based on analgin. Their long-term use is not recommended due to the possible development of agranulocytosis and other effects on the blood, however, a single injection allows you to get relief in the first hours.
Painkiller "Spazgan"
It should be noted that in order to relieve recurrent pain, which has a burning and unpleasant component, as well as in case of specific changes in electroneuromyography, drugs for the treatment of neuropathic pain should be added from the first day, which enhance the analgesic effect.
In addition, more powerful pain relief can be obtained by combining drugs with antidepressants of various groups - from amitriptyline to paroxetine and other SSRI inhibitors. Without actually affecting the intensity, antidepressants change the emotional perception and coloring of pain, making it unimportant, insignificant, and not affecting events.
Traditional therapy with B vitamins, including combined ones, such as Milgamma - they have a therapeutic effect in combination, usually by the end of the first week with daily intramuscular injections, so they cannot be classified as “quick response” painkillers.
In the photo - The drug "Milgamma" - combination therapy with B vitamins
Intercostal neuralgia is characterized by intense pain (thoracalgia), which occurs due to compression or inflammation of nerve fibers. This condition develops against the background of many pathologies. Therefore, in the treatment of intercostal neuralgia, a complex of drugs is used, the action of which is aimed at suppressing pain and eliminating the provoking factor. Failure to comply with this rule will result in severe consequences.
Intercostal neuralgia is not a disease, but a symptom characteristic of various pathologies. The causes of the development of pain syndrome are due to compression (compression) of the nerve roots, which occurs under the influence of the following factors:
- osteochondrosis of the thoracic region and other diseases of the spine;
- injuries, fractures of the chest and spine;
- the course of inflammatory pathologies affecting the nervous system;
- infectious infection of the body (mainly signs of intercostal neuralgia occur with herpes zoster);
- toxic damage to the body;
- vitamin B deficiency;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- cardiovascular pathologies.
It is also possible to develop intercostal neuralgia against the background of compression of the structural elements of the spine caused by hormonal disorders, tumor processes and hernia.
Exposure to provoking factors leads to intense pain that occurs in the chest or back. Moreover, the zone of localization of clinical signs indicates the cause that caused thoracalgia. The appearance of symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the right indicates:
- inflammation of the muscle fibers of the back;
- osteochondrosis;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
The pain with neuralgia is severe, burning, and constant. The intensity of the syndrome changes when the patient makes movements or inhales deeply.
For left intercostal neuralgia, it is important to exclude heart pathology before starting treatment.
Both conditions are characterized by intense pain that is localized in the chest area. Pinched nerves and heart disease are especially pronounced in older people. In this case, an ECG and EchoCG are prescribed.
The development of negative consequences with intercostal neuralgia directly depends on the characteristics of the causes that caused it. Exacerbation of herpes zoster, characterized by thoracalgia, does not pose a danger to human health and life. The disease resolves within 2-3 weeks, in rare cases causing complications.
How to treat?
Regardless of the reasons that caused the spasm and the characteristics of the accompanying pathologies, drug treatment is used for intercostal neuralgia. Drugs are prescribed to relieve general symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
In addition to treating intercostal neuralgia with medications, other methods are used, including massage, physical therapy and surgery. The choice of tactics depends on the disease that led to the syndrome. Therefore, before starting treatment, diagnostics are carried out using CT, MRI and other methods.
Therapy for intercostal neuralgia is often carried out at home. Treatment in a hospital is prescribed in the presence of severe complications. To relieve pain, ointments, tablets or injections of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used for intercostal neuralgia. For muscle tension, taking muscle relaxants is indicated.
When selecting medications, it is important to take into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the nature of the concomitant pathology. If pain is associated with the gastrointestinal tract, it is not recommended to take medications in tablet form. Such medications irritate the gastric mucosa, thereby increasing the intensity of general symptoms.
In the acute period, when the pain syndrome manifests itself most intensely, bed rest is recommended. Dry heat (heated sand in a cloth bag) must be applied to the sore spot. It is important not to overheat the problem area. Otherwise, as the skin cools, the intensity of the syndrome will increase.
How to treat intercostal neuralgia should be determined by a doctor. Uncontrolled use of medications can worsen the patient's condition and accelerate the development of the pathological process.
Pain relief for intercostal neuralgia is carried out using:
- tablets;
- solutions;
- ointments or gels.
Taking these tablets for intercostal neuralgia promotes a relatively rapid recovery for the patient. However, analgesics are not always effective, in addition, the effect of drugs in this group gives only temporary results.
Analgesics are recommended to combat intercostal neuralgia when coughing.
The doctor must determine exactly which medications are recommended for the treatment of neurological disorders in children and adults. This is especially true in cases where intervention is required for unbearable pain caused by compression of the nerve roots. In this case, subcutaneous injections of anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
- tiaprofenic acid;
- menovazin;
- promedol;
- naproxen;
- ketoprofen;
- ketorolac.
- analgesics (painkillers) are sedalgin, analgin, and also spasgan. This group of drugs removes the main symptom of the disease – pain. Such tablets are taken in a dosage 3-4 times a day. You should not take them more often - this will not give results, on the contrary, side effects may appear;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory tablets - voltaren and diclofenac, indomethacin, piroxicam, and ibuprofen. They remove inflammation and can relieve painful spasms a little. These medications are taken 1-2 times a day. Increasing the dosage may lead to an increased risk of gastrointestinal pathology. Without a doctor's prescription, medications in this group are allowed to be taken for a maximum of 5-7 days;
- muscle relaxants are effective tablets for neuralgia. They are designed to remove muscle spasms, which are one of the factors in the appearance of intercostal neuralgia. This group of drugs includes clonazepam, baclofen, and sirdalud. The doctor selects the duration of taking the pills individually.
- Diclofenac;
- Ketanov;
- Ibuprofen.
Medicines with bee and snake venom
Eliminate intercostal neuralgia with medications based on snake and bee venom. The effectiveness of ointments and gels with these poisons is quite high. They warm up the skin, accelerate blood circulation, remove metabolic products, and saturate tissues with bioactive substances. The drugs regenerate damaged nerve tissue.
The product with poison is used externally, it is rubbed into the lesions with soft massaging movements, bypassing the heart area. For treatment use:
- Apisatron. Ointment with bee venom suppresses pain and inflammation, restores blood flow.
- Viprosal. Ointment with viper venom eliminates pain and improves blood circulation. Camphor and fir, which the drug contains, have an analgesic effect.
These ointments are used as prescribed by a doctor. They are not always used for treatment of:
- lactation;
- pregnancy;
- allergies;
- heart diseases.
Contraindications and side effects
You should not start taking medications on your own if:
- You have previously had allergies to medications;
- You are about to take a drug that you have not used before;
- You are not sure that the symptoms that appear are related to neuralgia (in this case, taking medications can only worsen the situation);
- You have serious underlying medical conditions;
- The child fell ill;
- You currently have an exacerbation of kidney or liver failure.
In these cases, immediately when symptoms of neuralgia appear, you should call an ambulance and act strictly as directed by a specialist.
Ointments and gels
Remedies for neuralgia in the form of ointments and gels quickly relieve pain. They instantly penetrate through the skin pores into the deep tissues, to the lesion, reduce the severity of the pain syndrome and eliminate swelling.
External agents stimulate blood circulation, distract from pain, and relieve nervous tension. Thanks to them, blood supply to the sore spot improves, nutrition of damaged tissues, and pain goes away.
To treat intercostal neuralgia use:
- Fastum-gel. The product relieves pain, stimulates blood flow, and eliminates swelling.
- Capsicam. The ointment, due to its effective warming effect, accelerates the supply of blood to tissues. It restores tissue trophism and helps replenish nutrients.
- Finalgon. The ointment warms up. Thanks to it, blood vessels dilate. Blood flow increases. Oxygen and nutrients enter the tissues.
- Indomethacin, Ortofen, Naklofen, Ibuprofen. Ointments fight inflammation, swelling and pain.
- Menovazin. The ointment has a pronounced analgesic effect.
- Chondroxyl. The chondroprotector restores mobility to the spine.
Preference is given to ointments. Their rate of penetration into tissue is higher than that of gels. In the early stages and for severe pain, ointments are used that can relieve muscle spasms and relax muscles.
For patients suffering from severe pain, try not to prescribe ointments with a burning effect. By increasing stimulation at the site of the lesion, it is possible to provoke the development of an ischemic crisis or heart attack due to excessive outflow of blood from the coronary vessels.
Anesthetic liniments help activate the regenerative properties of tissues. This type of medication is used only simultaneously with other analgesic drugs in the form of tablets, as well as injections or suppositories.
As an independent pain reliever for neuralgia, ointments have reduced effectiveness. But their long-term systematic use has a persistent anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effect.
Also, such drugs help to activate the regenerative properties of tissues, so they are used both at the stage of pain relief and in the process of restoring disorders in the disease.
The following medications are considered the most effective ointments and gels that can eliminate pain from neuralgia:
- "Ketoprofen".
- "Nimesulide".
- "Ketonal".
- "Viprosan."
- "Apizartron."
- "Finalgon"
- "Myoton."
As a rule, these medications contain bee or snake venom. Based on this, before starting therapy with an ointment or gel that eliminates the inflammatory process and pain due to neuralgia, it is necessary to consult with a medical specialist and exclude all restrictions.
If the patient’s body is hypersensitive to most analgesic liniment substances, he is most often prescribed “Myoton”, the structure of which includes plant components. But its effectiveness is somewhat less than that of other drugs in this group.
Concomitant medications
Depending on the causes of intercostal neuralgia, the patient is prescribed medications whose action is aimed at the source of the problem. These can be antiviral drugs for herpes, antibiotics for various infectious pathogens. Chondroprotectors, antispasmodics and NSAIDs for osteochondrosis and other spinal lesions. If the patient's condition is due to chronic stress, he is prescribed a course of sedatives, tranquilizers or antidepressants.
Additionally, most patients with intercostal neuralgia are prescribed medications that normalize blood flow in the problem area and stimulate metabolic processes. These can be either tablets or topical patches. The latter are used more and more often, as they provide a lasting therapeutic effect, but do not have such a pronounced negative effect on the body as NSAIDs. To consolidate the therapeutic result and prevent relapses, the patient must take a course of immunostimulants.
Treatment with ointments
Doctors often prescribe ointments, gels, and creams for therapy for intercostal neuralgia at home. Their local use promotes rapid penetration of active components into the blood, which provides quick relief. Most of these remedies have a combined effect, so they not only relieve pain, but also eliminate the very causes of its occurrence.
Finalgon can warm a sore spot.
The following have increased effectiveness for intercostal neuralgia:
- “Finalgon” – provides a warming effect, quickly relieving pain, stimulating blood flow;
- “Fastum” – fights pain, relieves swelling of tissues;
- “Menovazin” – has a pronounced analgesic effect, helps within a few minutes;
- "Capsicam" - relieves the condition, starts blood flow, restores tissue trophism.
Carrying out massage, using applicators, and physical therapy increase the effectiveness of local treatment. Despite the availability of all these approaches, even such an impact on the problem area must first be agreed with a doctor. As a last resort, you should carefully read the instructions for the chosen drug. Some products are better suited for combating the symptoms of the acute period; with others it is better to wait 3-5 days. In particular, in case of sharp and burning pain, it is better not to use aggressive ointments that greatly increase the temperature of the treated area.
Capsicam can relieve the condition.
Suppositories
One of the fastest options for neutralizing pain in various types of peripheral nerve damage is the use of special rectal suppositories. The most effective of them are:
- "Okie."
- "Voltaren."
In addition to the fact that these suppositories quickly provide analgesia, they also effectively eliminate the inflammatory process and reduce high fever.
But, despite the speed of the body’s reaction to rectal suppositories, they are extremely rarely used in the treatment of neuralgia. The reason for this is considered to be the inconvenience of their use, which includes mandatory prolonged bed rest.
In general, in the process of treating neuralgia, types of medications can be combined to provide a quick positive effect. But a prerequisite for safe and effective treatment is strict doctor control.
Other treatments
In addition to drug therapy, the following methods are used in the treatment of neuralgia:
- Traditional medicine methods: compresses with alcohol, iodine and glycerol, herbs, rubbing, etc.;
- Therapeutic, warming baths;
- Using the Applicator to improve blood circulation and relieve spasms;
- Massage: acupressure and physical therapy (especially effective for back muscle spasms);
- Surgical interventions when it is impossible to relieve pain attacks with medications.
Antispasmodics
With neuralgia, the muscle tissue surrounding the damaged nerve fibers spasms, their tone is excessively high. Without eliminating muscle spasms, you cannot get rid of pain. Increased tone is relieved with antispasmodics:
- Besalol;
- Halidor;
- No-spy;
- Papazol.
To eliminate spasms, they take pills and give injections.
Intercostal neuralgia requires complex therapeutic treatment. Thanks to it, pain is quickly relieved, the patient’s well-being is improved, and the inflammatory processes that cause the disease are blocked. Prescription of treatment by a doctor is a prerequisite. The prescribed medications will give the maximum therapeutic effect and will not allow complications to develop.
Painkillers
Direct analgesic tablets for intercostal neuralgia are not prescribed so often. Usually, combined drugs are used that have several types of positive effects on the body. Their selection, use and possible combination should be handled by a doctor.
The selection of medications should be done by a specialist.
For neuralgia, two types of painkillers are used:
- analgesics with antispasmodic properties - “Baralgin”, “Spazmalgon”, “Sedalgin” - quickly bring relief, but have a short-term effect. They relieve pain, but only act on the cause of the problem if the nerve is compressed as a result of muscle spasm;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Meloxicam - not only relieve pain, but also stop the inflammatory process. This ensures a longer lasting effect and lasting positive dynamics.
For pain caused by spasm of the intercostal muscles, the use of muscle relaxants has a good effect. “Mydocalm”, “Tizanidine”, “Sirdalud” relax muscles, relieving pressure from nerve endings.
Ibuprofen will help cope with inflammation.