Maltseva Marina Arnoldovna
Neurologist, specialist in the field of extrapyramidal pathologies, doctor of the highest category
Shabunina Ekaterina Mikhailovna
Neurologist, category 2
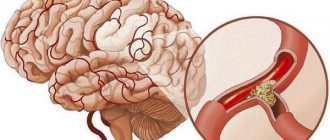
Aching, headache... How often do we have to talk about this. And sometimes a person does not attach importance to the onset of a migraine, attributing his poor health to a sharp change in temperature, pressure changes, age, or simply to his own fatigue or lack of sleep. Most people take headaches for granted and do not consider it a problem. But, in fact, such a harmless symptom may hide processes that are dangerous to the body. For example, discirculatory encephalopathy. Simply put, it is a narrowing of blood vessels in the brain. Due to the narrowing, blood does not flow to the brain in sufficient quantities. And if a large area of the brain is damaged by this process, a “harmless” headache or dizziness can lead to ischemia.
Development mechanism
The formation of the pathological process is based on a group of primary deviations. Stenosis of cerebral vessels does not occur on its own. This is not a spontaneous phenomenon. There are two reasons.
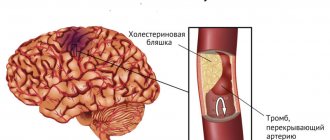
Atherosclerosis. It is accompanied by a narrowing or deposition of cholesterol plaques on the inner lining of the arteries.
Both options are equally difficult. They affect hemodynamics (blood flow), the general health and well-being of a person.
The immediate causes of this process are smoking. Poor nutrition. Organic pathologies, genetic aspects, hereditarily determined metabolism.
The second direct cause involved in the development is arterial hypertension. An increase in pressure in the bloodstream is formed as a special compensatory mechanism, usually against the background of atherosclerosis.
The blood flow is disrupted because there is an obstacle in the vessel in the form of a plaque or area of narrowing. As the risk of artery rupture increases, the body is forced to increase the tone of the walls of the structure and thicken them.
In the medium term, this leads to a decrease in the elasticity of blood vessels, therefore the quality of trophism (nutrition) of brain structures drops even more.
In the system, both causes end with cerebral ischemia, poor cerebral nutrition and the development of neurological deficits.
At first it manifests itself with general symptoms. Headaches, nausea, vomiting, and fainting occur.
Then things get worse. Higher nervous functions are lost, such as intellectual functions, memory, the ability to speak, read, write, and perform arithmetic operations correctly.
Unlike a classic stroke, when any department is affected, or at most several, if there is extensive damage, here the process affects the entire brain at once.
A diffuse (spread) disorder develops. Therefore, there is no need to talk about focal symptoms (manifestations of damage to a separate lobe - frontal, parietal, etc.).
If we continue the comparison with acute cerebrovascular accident, narrowed blood vessels lead to gradual, minimal destruction of the nerve tissue of the brain.
Individual cells become necrotic. Because of this, a critical condition is not observed.
The progression is gradual, over many years. Deviations can only be detected by comparing the basic functions before the onset of the disease and at the time of detection of problems.
Causes
The factors for the development of narrowing of the blood vessels of the head are diverse. As already mentioned, there are two main points.
Arterial hypertension
Increase in pressure. It develops as a result of cardiovascular diseases or kidney pathologies, hormonal instability, the onset of menopausal changes, and natural aging of the body.
The list goes on. Hypertension, symptomatic or primary, as a disease, is found in almost 15% of the world's population.
Sooner or later, the compensatory mechanism fails. Therefore, in approximately 60% of patients with hypertension, there is a violation of vascular tone in the head and neurological symptoms.
Atherosclerosis
The actual narrowing of the arteries or the deposition of cholesterol plaques on their walls.
Basically, the factor in the development of the disorder is not associated with obesity or poor nutrition; this is a misconception.
The main points are related to genetic predisposition, metabolic characteristics caused by hereditary factors.
Another possible option is acquired hormonal disorders: pituitary insufficiency, deficiency of thyroid substances, adrenal cortex. Also diabetes.
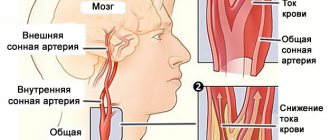
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
It provokes stenosis of the basilar arteries, a malnutrition of the occipital lobe of the brain. There may be a reflex narrowing of other blood supply structures along the chain. Which is associated with further progression of the pathological process.
Diet therapy and cessation of bad habits
Giving up bad habits - and the blood vessels in the brain will not be narrowed
Changing habits involves giving up alcohol and smoking, and switching to an active lifestyle. Try to spend more time outside, watch your weight, get good sleep and control your blood pressure, preventing it from unexpected jumps.
By giving up bad habits, a person not only gets rid of vascular problems that can lead to deterioration of health, but also improves his well-being. Try to avoid using transport as much as possible. By walking, you will speed up blood flow, thereby preventing the arteries of the cervical region from narrowing. Hardening procedures are also very useful.
Diet therapy also brings tangible benefits. You need to drink more water and increase the amount of vegetable dishes in your diet. They contain a lot of slowly digesting fiber, which has a beneficial effect on blood vessels, as well as other organs. Drink juices and fruit drinks constantly. Fatty foods clog arteries, while water, on the contrary, cleanses them, washing away all excess deposits.
After waking up, it is useful to drink some water at room temperature. The lumen in the vessels under the influence of water significantly expands, as a result of which blood circulation is normalized.
Avoid salty, fried foods, cakes with rich cream, and carbonated drinks. What else should people suffering from vascular pathologies not eat? They should not eat pickled vegetables, meat broths, or chocolate products. You should also minimize your salt intake.
All food should be cooked in vegetable oil, which contains polyunsaturated acids. It is also beneficial to eat seafood. Their regular use will help normalize the functioning of not only blood vessels, but also the thyroid gland.
Risk factors
They cause the development of atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, and musculoskeletal disorders.
These include smoking, alcohol abuse, drug addiction, systematic and uncontrolled use of medications (oral contraceptives, antibiotics, glucocorticoids, antipsychotics, antidepressants, psychotropic medications).
Other options are senile changes in the body due to menopause (menopause or andropause in men), other pathologies, cardiovascular, renal and hepatic.
The causes of cerebral vasoconstriction are used to identify the origin of the process, develop treatment tactics, and early diagnosis. This is the basis for high-quality supervision and complete relief from the disease.
Forms and symptoms of cerebral vasoconstriction
Acute form
Constriction of cerebral vessels in adults and children occurs differently: it can occur suddenly, or it can be chronic. The acute form is extremely dangerous for human life, as it causes a stroke or cerebral hemorrhage, which often leads to premature death.
The first symptoms of a stroke, which in no case should be ignored and urgently call an ambulance, are headache, numbness of the tongue, limbs, impaired thinking and a general serious condition. If these signs occur, the first thing to do is call an ambulance: if the patient is not provided with immediate medical care, the acute form of the disease can be fatal.
A cerebral hemorrhage is characterized by a blood clot blocking a blood vessel. This leads to the fact that, under the influence of strong blood flow, the walls of the arteries break through, blood enters the brain and damages its structures. This usually happens suddenly, due to physical or emotional stress. Cerebral hemorrhage is characterized by the following symptoms:
- flushed face;
- severe headache;
- vomiting, rapid breathing;
- slowing or speeding up heart rate;
- disturbance of consciousness.
How dangerous this condition is depends not so much on the size of the hemorrhage, but on the location where it occurred. In any case, if such symptoms appear, if timely assistance is not provided to the patient, the patient may fall into a coma and die.
Chronic form
The chronic form has mild symptoms for a long time. At the initial stage, a person periodically feels a mild headache, fatigue, nervousness, and drowsiness. After some time, he becomes distracted and his memory begins to deteriorate.
At the second stage of development of the disease, the symptoms become more obvious. Symptoms of an approaching exacerbation are a significant deterioration in well-being, migraines intensify and become more frequent, the gait becomes shuffling and unsteady, and problems arise with the urinary system. The disease also affects the functioning of the nervous system: performance decreases, and frequent mood swings often lead to conflict with others.
Many people do not pay attention to the symptoms of the first two stages, relieving headaches with painkillers. Therefore, the disease continues to progress and enters the third stage. At this time, severe problems are observed in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system: the patient often stumbles, loses balance, and may completely lose the ability to move. Sometimes speech is impaired and vision loss occurs.
Involuntary urination often occurs, and dysfunction of the pelvic organs is observed. Memory continues to deteriorate, the first signs of dementia appear when a person loses the ability to speak, walk, control his actions, and orient himself in space. After some time, a stroke or cerebral hemorrhage may occur.
Symptoms
In total, there are three stages of the pathological process. A group of authors speaks of four, calling a separate zero, which is determined by the previous state. But in this case there are still no signs of disorder.
First phase
The clinical picture is pronounced, but, paradoxically, patients rarely take health problems seriously, although everything is obvious.
Among the points:
- A headache of low or moderate intensity is a characteristic symptom of cerebral vasoconstriction.
It is highly resistant to analgesics. Therefore, it is poorly relieved with standard available drugs or does not stop at all.
Localization is unclear, the patient is unable to show one place. Diffuse, wandering discomfort usually has a stabbing, shooting character.
The duration of each painful episode ranges from 30 minutes to several hours. Then it goes away, just as abruptly as it started.
- Dizziness. Another name for the symptom is vertigo. It develops spontaneously and is accompanied by poor coordination and unsteady gait. The person cannot walk in a straight line and falls or stumbles.
The world literally spins before your eyes, and pronounced disturbances in orientation in space occur. The lying position allows you to partially weaken the symptom, but not completely eliminate it.
At an early stage, the intensity of the manifestation is insignificant, and you do not yet have to take a forced position.
- Ringing in the ears, darkening of the eyes. Both of these are a typical sign of vasoconstriction in the brain and provoke focal moments from the occipital, temporal lobes, and extrapyramidal system.
- Nausea and vomiting. They don't always occur. Lasts for a minimum period of time. Up to an hour maximum, sometimes less often. The act of emptying the stomach does not bring any relief; it is a reflex phenomenon. The body's false defense mechanism against poisoning, to evacuate toxic substances.
- Weakness, drowsiness. General asthenia and weakness. A person cannot work or perform household duties as before. Apathy occurs, which is of organic origin. Even with a strong desire, the patient is unable to act.
- Mental disorders such as emotional lability and changeability. Hot temper, depressive mood (dysthymia), irritability. There are also frequent and rapid transformations of the background mood: at one moment - euphoria, and a couple of minutes later - a deeply opposite state.
- Insomnia. Accompanied by the inability to rest, a long period of transition into unconsciousness, or frequent awakenings. The symptom is especially painful for patients.
Second stage
Accompanied by gradual disability of a person. Catastrophic symptoms of stenosis occur.
- Intellectual impairments. There is no ability to solve logical problems or think sensibly. And if at the very beginning of this phase we are talking about a decrease in speed while maintaining productivity, then total dysfunction occurs. The phenomena of dementia and vascular dementia are increasing. This is not yet obvious.
- Memory impairment. It manifests itself as a decrease in the speed of memorization and reproduction of already acquired information.
- Deviation of analytical abilities. Also refers to the cognitive, mnestic spheres.
- Fainting. Loss of consciousness develops spontaneously, suddenly. It is not difficult to remove the patient, but this is a formidable prognostic sign.
Attention:
As soon as a similar symptom is discovered with narrowed blood vessels in the brain, you should wait for a stroke within 6-24 months. There is no time to think anymore. It is necessary to start treatment urgently.
- Behavioral disorders. Emotional reactions become inadequate and clearly do not correspond to the strength and nature of the stimulus. To put it exaggeratedly, a person can be inappropriately cheerful, humorous, silly at a funeral, sad and whiny at a wedding.
Hypochondriacal phenomena and increased suspiciousness are almost always detected. Personal qualities become coarser, become stereotypical and erased.
A classic sign of incipient vascular dementia.
- Discoordination. There is no way to control your own limbs. The person walks awkwardly, shuffles, and makes a lot of unnecessary movements.
- Tremor. Trembling of fingers, chin.
- Convulsive syndrome. Corresponds to tonic-clonic seizures within an epileptic seizure. Such manifestations are not always found.
- Imperative postures to empty the bladder or bowels. They occur against the background of impaired innervation of the excretory system. A threatening sign.
Cerebrovascular disease in the second phase does not always manifest itself with the full range of described aspects; everything is purely individual.
Third stage
Corresponds to the final condition, profound disability, vascular dementia. Despite the overall severity of the pathological process, there is a chance for correction and recovery, albeit not complete.
This does not happen, for example, with Alzheimer's disease, with which it is necessary to differentiate between narrowing of blood vessels in the brain. Looking at the patient, it is difficult to imagine that there is a chance of help.
Detected:
- Apathy. Complete lack of intellectual and any physical activity. The person constantly lies down and does not show any emotions. Interest in the outside world is minimal or non-existent.
- Lack of control over physiological functions. Accordingly, the third stage of the condition is accompanied by spontaneous urination and defecation. This complicates the care of a bedridden patient.
- Memory loss. Total amnesia.
In some cases, speech and interest in the world are preserved. There is no adequacy, no logic in attempts at interaction. Because there are delusional ideas and global thinking disorder.
Attention:
The longer the patient remains in this state, the more difficult it is to influence the dysfunction.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk remedies for narrowed blood vessels in the brain
Folk treatment for pronounced or initial cerebral atherosclerosis is drinking medicinal decoctions and tinctures and other traditionally used methods.
When treating arterial pathology with folk remedies, they often drink homemade preparations made from plant materials:
- A decoction prepared from pine shoots. If you drink a spoonful of this decoction once a day, your blood pressure will normalize, vitamins will enter your body, and your arteries will dilate.
- St. John's wort infusion (a spoonful of St. John's wort in a quarter liter of boiling water) helps to dilate blood vessels.
- There is a popular belief that hawthorn decoction is a good remedy for vasoconstriction. It provides nutrients to the heart muscle, relieves spasms, and ensures vasodilation. This decoction is also useful for strengthening the immune system.
- Clover tincture also copes well with the first signs of atherosclerosis. To prepare it, you should take any glass container and fill it to the top with the flowers of this plant, then fill them with vodka and close tightly. Keep in a dark place for two weeks.
Of course, such decoctions can only complement the main drug treatment prescribed by the doctor.
Diagnostics
It is carried out in the early stages. In developed forms everything is obvious; the process needs to be staged. The profile specialist is a neurologist.
Activity:
- Oral questioning of the patient and collection of anamnesis. The simplest primary actions. Aimed at identifying the possible origin of the disorder and determining the clinical picture.
- Measurement of blood pressure, heart rate. Both levels are usually changed. At the first stage, growth is detected, then decline.
- If necessary, 24-hour Holter monitoring is performed. Such a need arises infrequently.
- EEG. To assess the intensity of brain activity and identify areas of reduced activity. Based on the topography of the altered signal, we can tentatively talk about the location of the pathological process. That is, areas where blood flow is impaired to a greater extent.
- MRI of the brain.
- X-ray of the cervical spine.
- Duplex scanning, Doppler ultrasound of neck vessels.
- ECG, ECHO-KG.
- A general and biochemical blood test with a detailed picture of cholesterol and lipid structures is required.
If necessary, other studies are prescribed: ultrasound of the kidneys and abdominal organs.
Diagnosing vasoconstriction in itself is not difficult. But you need to take a responsible approach to developing tactics.
Treatment
Treatment of cerebral vasoconstriction is mainly conservative. It involves the use of drugs from several pharmaceutical groups.
- Antiplatelet agents. To restore blood fluidity. Aspirin-Cardio, less often Heparin. You cannot take them constantly.
- Statins. To remove excess cholesterol, dissolve soft plaques (Atoris and others).
- Antihypertensive. ACE inhibitors, short-course diuretics, calcium channel blockers and others. According to indications. The names are selected strictly by the doctor. If the recommendation is not followed, there is a risk of death from kidney or heart failure.
- Cerebrovascular agents. Restore normal blood flow in the brain. Piracetam, Actovegin.
- Nootropics. Glycine and others. Metabolic processes are stabilized.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes. Must be used.
These medications solve three important problems at once: eliminate the root cause (not always), relieve symptoms, and prevent emergency conditions.
At the same time, the result is not achievable in a conservative way in all cases. According to indications, surgery is performed.
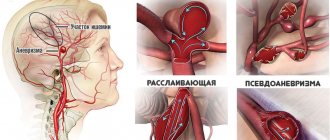
Among the reasons for surgical intervention are vascular diseases of the brain - malformations, aneurysms, advanced atherosclerosis with calcification of plaques, kidney tumors (can provoke malignant hypertension).
It is mandatory to adhere to the regime for the rest of your life: avoidance of smoking, alcohol, drugs, refusal to self-administer medications of any kind, diet correction (treatment table No. 10 is suitable).
Providing adequate sleep (at least 7 hours per night), physical activity at an accessible level (walking in the fresh air, walking or cycling at a slow pace).
Prevention of cerebral vasoconstriction
To protect yourself from brain spasms, you must:
- Play sports: swimming, fitness, cycling.
- Temper the body with a contrast shower.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Maintain proper drinking regime.
- Eat right: eat more raw and minimally processed foods, avoid foods with flavor enhancers, preservatives, etc.
If you have a hereditary predisposition to atherosclerosis, hypertension and other diseases of the cardiovascular system, you should be regularly monitored by a doctor.
Complications
The main consequence is vascular dementia. Further, a major stroke is possible. The logical outcome is the death of the patient or severe disability.
Narrowing of the blood vessels in the head is not a diagnosis. This is a factor in the development of cerebrovascular insufficiency or, more simply, a disturbance in the nutrition of nerve tissue.
Treatment is carried out urgently; the longer the pathological process lasts, the more difficult it is to cope with the disorder. It is not recommended to hesitate. At the first symptoms you need to contact a neurologist.