Hemihypesthesia is considered one of the most common symptoms in neurology. It is observed in almost every patient who has had a stroke.
The term "hemihypesthesia" means decreased sensitivity on one side of the body - left or right.
All sensations that a person experiences are associated with the work of the central nervous system. The sensitivity function is necessary in order to perceive information from the environment and respond to various influences.
Functions and anatomy of receptor sections
Receptor sections are located throughout the surface of the body, as well as in the internal organs.
They are divided into several types:
- exteroreceptors perceive superficial irritations, they are responsible for pain, tactile and temperature sensitivity;
- interoceptors are located in internal organs;
- proprioceptors are necessary for spatial sensations - tension of skeletal muscles, changes in body position.
The reflex arcs of superficial and deep sensitivity differ from each other. When an impulse is received indicating pain or temperature stimulation, the signal is sent to the spinal cord. There is also the 2nd neuron of the reflex arc.
Next, the nerve fiber passes through the segments of the spinal cord and crosses. Rising upward, the impulse enters the 3rd neuron located in the visual thalamus. From there, the signal enters the cortical region - the posterior central gyrus and the parietal region.
The first neuron of deep sensitivity, like the superficial one, is located in the spinal cord. From there, the impulse is sent to the medulla oblongata. The second link of the reflex arc is located in the nuclei of the posterior columns. At this point, a medial loop is formed - the intersection of nerve fibers. The third neuron is located in the nucleus of the visual thalamus. Next, the fibers are subdivided: some of them go to the central gyrus, some to the cerebellum and parietal region.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Hemihypesthesia develops when one of the links of the reflex arc is damaged. With damage to the upper parts of the nervous system (cerebral cortex, medulla oblongata), a decrease in sensitivity occurs on the opposite side due to the intersection of the pathways. So, if a person was struck by a left-sided stroke, then hemihypesthesia will be right-sided.
If the disturbances occurred at the level of the spinal cord, then loss of sensitivity covers the side that was affected.
Reasons for decreased sensitivity include:
- stroke;
- head and spinal column injuries;
- neuroinfections and inflammatory lesions;
- ischemia of a portion of the brain or spinal cord;
- compression of fibers by neoplasms or spinal hernia;
- degenerative processes in the central nervous system and brain.
Damage to nerve structures due to sensory disorders
Most often, hemihypesthesia develops after an acute disruption of blood supply to the brain. Moreover, in the case of a stroke in the right sections, sensitivity is lost on the left side of the body, and vice versa. Superficial sensations are reduced on the affected side in spinal cord injuries.
Deep sensitivity is lost on the side of the same name if the violation occurs below the level of the medial lemniscus - to the chiasm.
Hemihypesthesia - what is it?
What is hemihypesthesia?
Image source: en.ppt-online.org Hemihypesthesia is a decrease in any type of sensitivity, up to partial or complete loss (anesthesia) on one side of the body (hemianesthesia), usually the opposite side of the brain (BM).
In the case of a stroke, it manifests itself in the form of an acute disruption of the blood supply to the area of the brain responsible for sensitivity or nerve pathways
Hemihypesthesia, as a syndrome, in medicine and neurology, in particular, has other synonyms. It is also called a decrease in sensitivity according to the hemitype (left or right).
Types of sensory disorders
There are several types of sensitivity disorders:
- Hyperpathy (hyperesthesia) . Characterized by a decrease in the pain threshold. Any touch causes a pronounced reaction.
- Hypostesthesia – decreased sensitivity.
- Paresthesia . Characterized by a tingling sensation, goosebumps.
- Anesthesia is a complete loss of the ability to feel. There may be a loss of certain types of sensations (temperature, tactile).
- Allocheiria . When a certain area of the body is irritated, unpleasant sensations are projected onto the opposite side.
- Dysesthesia is a distortion of perception.
- Analgesia is loss of pain sensitivity.
Characteristic symptoms
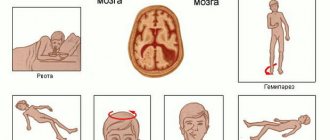
The loss of the ability to perceive sensations on one side of the body can manifest itself in different ways. This depends on the level at which the lesion has developed. The following symptoms may be observed:
- Decreased sensation in the transverse areas of the torso , arms and legs, loss of circular areas of sensitivity on the face and genital area. These signs characterize the segmental type of disorder.
- Inability to feel your body move . It develops according to the conductor type during pathological processes in the cords of the spinal cord.
- Loss of sensation below the affected area.
Patients may also be concerned about symptoms of intoxication in inflammatory and infectious diseases, movement disorders, changes in speech, strabismus, distortion of facial features, etc.
Causes
Decreased sensitivity in the left half of the body (hemitype).
- The main and most common cause is ischemic stroke (IS), which occurs in the branches of the internal carotid artery (ICA). It is known that its branches participate in the blood supply to the cortex of the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes, the white matter of the subcortex, and the internal capsule. Hemihypesthesia (HH) occurs when the intracranial part of the ICA is blocked, combined with contralateral hemiparesis (changes in the motor sphere on the opposite side of the body).
- HHZ up to hemianesthesia (GAZ) occurs with infarctions in the branches of the middle cerebral artery (MCA), which is responsible for the blood supply to the cortex of the temporal and parietal lobes, subcortical nodes and internal capsule (IC). If the trunk of the MCA is affected in the area before the branches of the deep type depart from it, total IS appears, which, in addition to GAZ, is characterized by severe hemiplegia and hemianopsia (blindness of half the visual field on both sides). After the branches depart, similar manifestations form, but to a lesser extent.
- With strokes in the vertebrobasilar region , when the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) is blocked, Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome develops, characterized on the affected side by pain and temperature hemihypesthesia of the face, cerebellar ataxia, Horner's syndrome (presence of ptosis, miosis, enophthalmos), pharyngeal paralysis, dysphagia , dysphonia, dysarthria, and on the opposite side – pain and temperature hemihypesthesia in the trunk and limbs, as well as dizziness, nausea and vomiting. This syndrome is one of the varieties of alternating syndrome that occurs with brainstem stroke. Hemihypesthesia (HH) in this case may be a thalamic type of sensitivity disorder, that is, it occurs with damage to the thalamus, or visual thalamus (a paired structure in the form of accumulations of gray matter, the main function of which is the transmission of information from sensory organs, except for the olfactory, to the corresponding areas of the cortex hemispheres), accounting for approximately 25% of all cases of vertebrobasilar strokes.
- If the small arterial branches of the brain are affected, a lacunar stroke (LI) develops, leading to pain and temperature-type HHS, which is called a “pure sensory microstroke.” Also, such manifestations can be combined with motor disorders when the posterior leg of the AC, the anterior leg or knee of the AC and the thalamus are affected (the so-called “sensorimotor microstroke”).
- In hemorrhagic stroke (HI) with hemorrhages in the basal ganglia (BG) and VC, GAS also appears in combination with a decrease or loss of muscle strength in half of the body - hemiplegia, hemianopia, paresis of the facial muscles and signs of changes in the dominant (aphasia) and subdominant (changes in the body diagram, autopathognosia and anosognosia) hemispheres. GAZ occurs with hemorrhages in the thalamic region, combined with hemiataxia, hemianopsia, amnesia, drowsiness and apathy.
What to do if there is a decrease in muscle strength in half of the body - hemiparesis, read here
Types of decreased sensitivity by hemitype
Characteristic is a decrease in sensitivity in the extremities of the half of the body opposite the lesion in the brain with a predominance of a decrease in its deep types (spatial sense of position of the body and limbs - muscular-articular; two-dimensional-spatial - determination of pressure and own body weight; vibration - the ability to perceive the action of vibrations ; and skin-kinesthetic – determining the direction of shifting of one’s own skin fold).
Moreover, such disorders usually arise against the background of hyperpathy (distortion of the threshold of perception, including pain: the patient cannot distinguish a cold object from a hot one, or a weak pain impulse causes severe pain).
Thalamic pain is burning, periodically intensifies and is generally difficult to treat
In case of damage to the sensory pathways of the posterior leg of the VC, contralateral HGZ or GAZ occurs.
In case of damage to the cerebral cortex of the brain, paresthesia occurs - feelings of tingling, crawling and numbness on one side of the upper lip, tongue, face, arm or leg, and they can occur in the form of focal sensory paroxysms.
If the trunk of the brain is affected, a disorder of surface sensitivity (pain, temperature and partially tactile) develops in an alternating type in the form of GAZ (for example, with stroke in the VBB - indicated above).
Diagnosis and treatment methods
The diagnosis is made during a neurological examination. This syndrome is not considered an independent pathology, but occurs against the background of some disease. Treatment methods include:
- etiotropic therapy – vascular drugs, nootropics;
- B vitamins to improve metabolism in nervous tissue;
- muscle development - training the usual movements of the arms and legs;
- massage of the non-sensitive area.
To prevent this syndrome from developing, it is necessary to avoid traumatic factors and promptly consult a doctor for diseases of the osteoarticular system.
With an increased risk of stroke (acute cerebrovascular accident), it is important to monitor blood pressure, take antiplatelet drugs, normalize body weight and give up bad habits.
Hypesthesia: how this disorder manifests itself and is treated – Suppressed
Loss of sensitivity or hypoesthesia - causes and treatment of the disease
- If this happened once, for example, as a result of an uncomfortable position in a dream, then there is nothing wrong with it.
- But if loss of sensitivity occurs quite often and lasts a long time, then this is an alarming symptom that requires immediate medical intervention.
- Hypoesthesia is a dulling of sensations, a weakening of sensitivity in certain parts of the body, as a result of which a person loses the ability to adequately perceive the action of external stimuli, as well as respond to changes occurring in his body.
This is due to a disruption in the functioning of human nerve endings. Often the disease can appear during pregnancy, and after childbirth it disappears on its own.
The disease manifests itself as follows:
- a person does not feel anything when he touches objects;
- he feels the pain dulled, even if it is quite strong;
- cannot determine temperature differences;
- If the vagus nerve is damaged, hearing may be impaired.
Often the disease makes itself felt when metabolic processes are disrupted, resulting in fluid accumulation in the fingers and hands.
— causes and symptoms, treatment methods, prognosis and prevention of the disease.
How does brain astrocytoma, whose life prognosis is extremely unfavorable, stand out from other brain tumors? Is there a chance of salvation?
Hypoesthesia usually occurs due to pathological changes in the central and peripheral nervous system, provoked by such factors:
- Brain injury.
- A malignant formation, which, by limiting the volume of the skull, leads to numbness of the head. Moreover, as the tumor grows, the damage intensifies, vision is impaired, and headaches occur.
- Migraine.
- Circulatory disorders.
- Pinched nerve.
- Multiple sclerosis, as a result of which certain areas of nervous tissue are replaced by connective tissue cells. In this case, coordination of movements may be impaired.
- Diabetes mellitus, which contributes to nerve damage.
- Transient ischemic attacks, accompanied by damage to the arms and legs.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Deficiency of vitamins and microelements in the body, for example, lack of vitamin B. Associated symptoms may include excessive irritability, dizziness, fatigue and problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Rheumatoid arthritis, which affects the nerve and leads to joint deformation. Usually in the morning there is pain and stiffness at the site of the lesion.
- Genetic predisposition.
Depending on which group of analyzers is affected, the following types of hypoesthesia are distinguished:
- Facial hypoesthesia – occurs due to vascular or neurological pathologies. If sensation is lost in one half of the face, we can talk about trigeminal neuralgia, and in the case of redness or rash in the affected area, the development of herpes zoster may be involved.
- Hypoesthesia of the hands - with loss of sensitivity for two or more minutes, we can talk about the presence of diseases of the nervous or vascular system. This condition can also be caused by multiple sclerosis, a tumor, or a cerebrovascular accident.
- Hypoesthesia of the lower extremities – occurs when blood circulation in the lower extremities is impaired and nerves are damaged. In the presence of severe pain, vascular disease can also be diagnosed - obliterating endarteritis, venous insufficiency, atherosclerosis. If you experience shooting pain in the leg or lower back, this may indicate sciatica.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Hypoesthesia can be recognized by the following signs:
- high frequency of disease attacks;
- insensitivity to temperature changes;
- numbness in the head, neck, back, as well as paralysis;
- weakness and speech disorders;
- loss of smell;
- short-term loss of consciousness, difficulty breathing;
- dizziness and gait disturbance;
- burning, itching, tingling sensation and rash;
- numbness of the limbs while walking;
- pain in the lumbar region, muscle spasms;
- with facial hypoesthesia, vision and hearing may deteriorate, and the temperature may rise;
- Involuntary bowel movements or emptying of the bladder may occur.
If hypoesthesia occurs frequently and lasts more than 2–3 minutes, you should immediately contact a neurologist for examination. It includes the following procedures:
- initial examination, identification of complaints, symptoms, clarification of the patient’s lifestyle and adherence to his bad habits;
- a general blood test to detect iron deficiency or pernicious anemia;
- a blood test for cholesterol and lipoprotein, which makes it possible to identify a tendency to form atherosclerotic plaques;
- computed tomography (CT) and x-ray - these studies will help determine the presence of bone fractures that have caused damage to nerve fibers, and will also help diagnose osteochondrosis, arthritis and other pathologies;
- electroneuromyography, which will make it possible to find the place where the nerve is damaged;
- Doppler ultrasound examination, which makes it possible to detect vascular pathologies such as varicose veins, atherosclerosis, thrombosis and others.
- The selection of medications is carried out depending on what exactly caused the disease.
- For example, if there is hand hypoesthesia associated with metabolic disorders, the doctor may prescribe a course of vitamin and mineral complexes.
- Also, to treat numbness, a course of corticosteroids is sometimes used to relieve the exacerbation of the disease.
- If the sensitivity of the legs is impaired, a warm shower and evening walks are usually used.
- Additional treatment methods include:
- phonophoresis;
- electrophoresis;
- ultrasonic waves;
- darsonval;
- paraffin and ozokerite wraps;
- radon baths and mud;
- massage;
- yoga classes;
- acupuncture.
There is also the opportunity to use traditional medicine. You just have to keep in mind that self-medication is fraught with consequences, so you should always consult with your doctor.
Here are a few popular recipes for hypoesthesia:
- If your fingers are affected, you can take half a glass of sugar and vegetable fat and mix. Apply in circular motions to affected areas. After this, add 2 tablespoons of salt to a liter of warm water and dip your fingers in it for 45 minutes.
- If your legs are numb, honey wraps will be helpful. Sore legs should be lubricated with honey and wrapped in natural fabric. The course of treatment is 3–4 procedures.
- You can also take half a liter of vodka and 50 g of bush lilac flowers, leave for a couple of weeks, and then apply compresses to numb legs. Repeat for two weeks.
- Before the treatment has its effect on the patient, he should exercise maximum caution so as not to accidentally harm himself.
- So, if attacks are provoked by external factors, such as ambient temperature, time of day or physical condition, then they should be avoided if possible.
- If you often experience numbness in your face, you need to be careful when eating, as you may accidentally bite your tongue or cheek.
- If you have hypoesthesia, which manifests itself in the form of insensitivity to temperatures, you need to be extremely careful near heat sources, since during an attack you can involuntarily get burned.
- The consequences of the development of the disease greatly depend on the causes that caused it.
- If pathologies leading to loss of sensitivity are not treated, this can lead to disability and even death.
- Therefore, you should not neglect your health and keep it in good condition on time.
Disease prevention
In order to prevent further development of the disease, it is necessary to start leading a healthy lifestyle:
- rejection of bad habits;
- healthy, full sleep;
- a balanced diet including vegetables and fruits;
- light exercises to ensure limb mobility;
- walks in the open air;
- alternation of work and rest;
- timely treatment of chronic diseases that can cause hypoesthesia.
- So, we found out that hypoesthesia is a rather serious disruption of the body’s functioning, which should not be left to chance, expecting that it will go away on its own.
- Because sometimes this disease can lead to the most tragic consequences.
- Therefore, if you often feel signs of numbness in any part of the body, you should consult with an experienced doctor, and, if possible, get rid of bad habits that contribute to the development of hypoesthesia.
: perceptual disorder
Basic properties of perception and the problem of experiencing reality. Changes in the intensity of perception: hypoesthesia, hyperesthesia and paresthesia.
Reasons for violations
Sensitivity disturbances occur when nerve tissue is pinched and damaged. Main causes of violations:
- Inflammatory processes in surrounding tissues;
- soft tissue or musculoskeletal injuries;
- hemorrhages in the spinal cord or brain;
- tumors, including those caused by the inflammatory process, benign and malignant formations.
Diagnosis and treatment of sensitivity disorders
If sensitivity disturbances are detected, contact a neurologist. At the initial consultation, the doctor will listen to complaints and conduct sensitivity tests. To determine tactile sensitivity, the doctor touches the skin with a light object, such as a cotton swab. For pain sensitivity, needles are usually used. For thermal sensitivity - containers with hot and cold water.
If necessary, the doctor will refer you for additional examinations: electrophysiological studies, computer or magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and spinal cord.
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the root cause of the disease. To alleviate the symptoms of disorders, the patient, in addition to drug therapy, is usually prescribed a balanced diet, massage, therapeutic exercises, swimming or cycling.
- Let's find out the reason for the decrease in sensitivity
- Let's eliminate the cause of diseases
- Let's prevent the development of complications
- neurologist Viktor Vladimirovich Musinsky work experience – 8 years
- Make an appointment
Source: https://glpni.ru/deppecciya/gipesteziya-kak-proyavlyaetsya-i-lechitsya-eto-rasstrojstvo.html