Hemiplegia
(
hemiplegia
; Greek hemi- semi + plege blow) - paralysis of the muscles of one half of the body as a result of disruption of the conductivity of the central neuron of the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract. Paralysis of one limb is called monoplegia. Partially expressed paralysis is called paresis; paresis of the muscles of one side of the body - hemiparesis, paresis of one limb - monoparesis; Hemiplegia that occurs when the spinal cord is damaged on the same side as the lesion is ipsilateral hemiplegia.
About the disease
Right-sided hemiparesis is a pathology that is a right-sided lesion of the muscles of the body.
It is characterized by a noticeable decrease in strength and general motor ability of muscles, and incomplete paralysis of the limbs is possible.
This condition manifests itself due to acquired or congenital pathological changes in the pyramidal tracts and the brain.
Doctors observe deviations from the norm when a lesion appears in the left hemisphere of the brain.
This disease leads to the following consequences for the patient:
- Mobility and the patient’s ability to move independently, as well as to care for themselves independently, are reduced when hemiparesis occurs on the dominant side (right-sided hemiparesis in right-handed people);
- The patient experiences inflammatory changes that are associated with prolonged skeletal muscle cramps . This consequence occurs after serious disorders - intracerebral hemorrhages and strokes;
- A problem arises when trying to follow instructions for physical therapy when the patient is undergoing motor recovery due to limited mobility. This happens when there is spastic increased muscle tone.
In children
In children, this pathology occurs as a congenital disease . The reasons for its occurrence are abnormal functionality and structure of the brain , as well as birth injuries. In medical terminology, this disorder is called cerebral palsy - cerebral palsy.
Cerebral palsy appears due to a circulatory disorder in the brain. This pathology affects the fetus while still in the womb and leads to erroneous development and damage to brain structures.
Right spastic hemiparesis
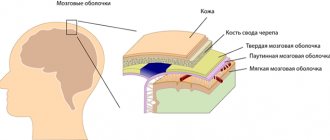
Spastic hemiparesis, often called central, occurs when there is inflammation of the brain or cervical spinal cord.
With this disease, stiffness and muscle tension are observed in the limbs of the opposite side of the body. If individual nerves of the spinal cord are subject to inflammation, then hemiparesis is combined with weakness and decreased muscle tone.
This pathology does not immediately become noticeable; it manifests itself over several months. First, muscle tone increases, which creates tension in the arm and leg, a feeling of stiffness arises, and the ability of the limbs to move decreases. Then, if no treatment is followed, muscle tone continues to increase.
Important! An increase in muscle tone indicates damage to parts of the central nervous system - the brain and spinal cord.
Disturbances in movements that are accompanied by spasticity are seen by others from the outside based on distinctive signs - people have difficulties in gait, it acquires special features. Doctors call it Wernicke-Mann gait . This indicates diseases suffered by the brain - stroke and traumatic brain injury.
Symptoms of right-sided spastic hemiparesis are varied. These include speech disorders, fever, cognitive impairment and seizures similar to epileptic seizures.
Increased muscle tone indicates that the brain and spinal cord are damaged. To reduce tone, the doctor prescribes drugs that relax the muscles. The period of admission is usually long - up to six months, but sometimes longer.
Why can your child really only get effective help at Exart?
Studying rehabilitation centers for people with cerebral palsy in Russia, people from different parts of the country come specifically to. Why?
- To treat infantile paralysis, a person’s physical capabilities are used here, rather than medications.
- Here they treat the cause, not the symptoms. We do not have template treatment plans, like most clinics. Exart always creates an individual treatment program based on functional diagnostic data. And - most importantly - they work for results: they set goals and set deadlines, work through a set of exercises and procedures to quickly achieve real results.
- Here, much attention is paid to the psychoneurological component and the emotional state of the patient. We create the most comfortable atmosphere for him, fight complexes and prejudices, and create a desire to achieve results.
The result of treatment: the child can perform all the movements necessary for his full life and continues to work independently (with his parents) to eliminate the causes of the disease according to the scheme worked out at the center. He is aimed at achieving results, at working on himself. All this significantly improves the patient’s quality of life and reduces the family’s time and expenses for treatment.
Disease by severity
Doctors determine the severity of various types of paresis on a six-point scale:
- 0 points – complete absence of movement;
- 1 point – minor muscle movements are observed, the joints are not involved;
- 2 points – movement is possible, but in a vertical position, if there is no external resistance. The joints move barely noticeably;
- 3 points – muscles cope with gravity. Joint movements are constrained;
- 4 points – the patient makes movements, while losing a little strength in the muscles;
- 5 points – the patient makes movements without losing muscle strength.
What are hemiparesis and hemiplegia? Differences
Greetings, dear readers and guests of my blog insultu-net.ru, dedicated to neurorehabilitation. Today we will talk about one of the most common and persistent consequences of injuries and diseases of the brain and spinal cord, among which stroke and its consequences are one of its most common causes. Let's talk about hemiparesis and hemiplegia - what they are and what are the reasons for their occurrence. About what needs to be done to restore lost strength and regain movement in the limbs.
Wernicke-Mann gait in hemiparesis and hemiplegia
Hemiparesis is a decrease in muscle strength in half the body , without its complete loss.
Hemiplegia is a complete lack of strength in half the body , that is, paralysis.
Causes
The reasons for the development of hemiparesis vary depending on the age at which it develops, the conditions in which the patient was before the symptoms of the pathology appeared, etc.
In children
In children, hemiparesis occurs after various anomalies of the spine or limbs , damage to the brain structure, as well as various types of injuries to the skull or spine.
Hemiparesis also appears as a consequence of pinched nerve endings in the spine , atrophy of peripheral nerves and when the functioning of the brain is impaired.
Reference! Congenital hemiparesis usually develops due to abnormalities in brain development, fetal hypoxia, or trauma that the child receives while still in the womb - cerebral palsy.
In adults
The incidence of right-sided hemiparesis in adults is higher than in children . Most often this is a consequence of injuries or diseases of the left side of the brain.
Classification
Hemiparesis is classified based on several criteria. It looks like this:
- Symptoms can be congenital or acquired.
- Both left and right limbs can be affected.
- According to the severity of muscle strength, mild hemiparesis is distinguished (strength 3.5-4 points), moderate (2-3.5 points), severe (up to 2 points). The assessment is carried out during a neurological examination of the patient.
- There are central hemiparesis, which develops as a result of impaired cerebral and spinal circulation, and peripheral hemiparesis. The latter is a consequence of dysfunction of peripheral nerve fibers (for example, with intervertebral hernias).
It is important to note that paresis can be spastic and flaccid. This sign depends on the tone of the muscles of the limbs. With increased tone, spastic paresis is exhibited, and with decreased tone, flaccid paresis is observed.
The first type is often accompanied by shortening of the limbs and is more often a consequence of damage to the central nervous system, while the second type is the result of pathologies of the peripheral nerves.
After a stroke
If after a stroke the entire right side is completely paralyzed, this indicates that a large part of the left hemisphere was affected. Such a stroke has a pronounced clinical picture.
Firstly, these are speech and language deviations. This sign is the first and strongest indicator of a stroke. The patient has slurred pronunciation of words, impaired articulation, and the patient ceases to understand the speech of other people.
Secondly, the patient experiences a loss of speech and verbal memory, he has difficulty writing and reading, and forgets the necessary words and speech patterns.
Thirdly, a clear sign is paralysis of the right side of the body: face, arms, legs.
Fourthly, the patient experiences involuntary and reflex movements of the paralyzed limbs.
Typical problems after a left-sided stroke are:
- Lack of cause-and-effect relationship, violation of logical thinking;
- Inhibited perception and analysis of current events;
- Problems with speech activity, complete loss of some words is possible;
- The patient may lose control over his body, in which case he becomes completely dependent on other people;
- The occurrence of muscle hardening and joint immobility;
- The appearance of bedsores, thrombosis, pneumonia, as the patient is immobile for a long time.
Treatment for stroke in this case is exercise therapy, physiotherapy, restorative massage, as well as surgical and medicinal intervention, classes with a speech therapist.
Features of hemiparetic gait
The gait has a “squinting” character.
The arm is bent at the elbow joint, pressed to the body. The leg does not move in a straight line, but deviates to the side and describes a semicircle. At the moment of lifting off the surface, the knee joint is extended, the foot is in a position of slight plantar flexion. The patient tilts the torso to the healthy side and raises the pelvis, the leg moves in a circular motion and is difficult to move forward. Instead of resting on the heel, the foot hits the surface. Slight spasticity and partial preservation of the functions of the muscles of the thigh and lower leg allow some patients, instead of lifting the pelvis, to compensate for an extended knee and dropping foot by increasing hip flexion. When using a cane, a person holds it with his healthy hand and transfers his weight to it with his affected leg while walking. Less commonly observed is extension in three joints (hip, knee, ankle) with typical vertical movements of the pelvis with each step.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing right-sided hemiparesis, the doctor is obliged to collect complaints, anamnesis, a full examination of the patient, as well as research using special instruments. Their nature and duration depend on the form of the pathology.
When the cause of hemiparesis is discovered, the doctor performs a computer or magnetic resonance imaging, electromyography, and Doppler ultrasound of the blood vessels of the brain on the patient.
Reference! Children are diagnosed at the age of one to one and a half years, when they develop movement skills and motor disorders become more noticeable.
Symptoms
The presence of the disease can be determined by the following accompanying symptoms:
- memory disorders;
- decreased mental performance;
- violation of purposefulness of movements;
- problems with recognizing objects and phenomena (agnosia);
- speech disorders;
- decreased sensitivity of the affected area of the body;
- persistent headache;
- epileptic seizures;
- fever;
- general deterioration of health;
- weakness and increased fatigue;
- arthralgia.
If the lesion affects the posterior part of the brain or other parts of it, then hemiparesis will primarily affect the limbs and facial muscles. The severity of all of the above symptoms will depend on the age of the patient. But for treatment, not only the intensity of clinical manifestations is important, but also the causes of the disease.
Symptoms of congenital hemiparesis
Congenital hemiparesis usually appears during the period when the child begins to learn to walk independently. Along with it, speech and intellectual disorders become more noticeable.
Early signs of hemiparesis in children are:
- asymmetric movements in the limbs;
- limitation of active movements on the affected side;
- asymmetric Moro reflex;
- flatness of the thigh muscles with slight but noticeable outward rotation;
- when taking a vertical position, the child does not lean on the affected leg, and when lying on his stomach, he stretches the affected arm worse and does not lean on it.
Children with congenital hemiparesis also experience numerous neurological disorders. In particular, stereognosis is impaired, and the so-called syndrome of ignoring the affected limb develops. This only makes an already difficult situation worse.
The development of epilepsy, unfortunately, is a common concomitant symptom of hemiparesis. It significantly aggravates the course of the disease and worsens the prognosis. It can manifest at any age, and taking into account this factor, the types of attacks also vary:
- in early childhood, generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures with secondary generalization predominate;
- at a later age, partial epileptic seizures come to the fore;
- In 80% of patients with congenital hemiparesis complicated by epilepsy, simple or complex focal epileptic seizures are identified, which can sometimes have secondary generalization.
The overwhelming majority of patients with congenital hemiparesis experience rare attacks of epilepsy. Typically their frequency is once every 3, 6 or 12 months.
Hemiparesis negatively affects the cognitive abilities of the brain, and not only. Thus, with damage to the right hemisphere of the brain (with left-sided hemiparesis), there is underdevelopment of visuospatial analysis and synthesis, as well as perceptual generalizations.
With damage to the left hemisphere of the brain, which is the cause of right-sided hemiparesis, disorders of verbal functions predominate. Children with such a deviation have a poor vocabulary, a decrease in the level of verbal generalizations and the nature of judgments.
Speech disorders are recorded in 20-40% of patients with congenital hemiparesis. This defect manifests itself especially clearly in children. Most often, such disorders are expressed by delayed speech development, dysphagia or dysarthria. They are observed in both right-sided and left-sided hemiparesis.
With the pathology in question, visual deviations may also occur. Thus, the frequency of disturbances in the functioning of the visual analyzer is 30%. Homonymous hemianopsia is diagnosed in 17-27% of patients. In 8.6% of cases, partial atrophy of the optic nerves is recorded, and in 10.5% of patients strabismus is detected.
Treatment
Treatment of hemiparesis in the first year after the onset of neurological disorders is fruitful.
In children
The complex for children with hemiparesis consists of the following components:
- Passive exercises for the affected limb. They are performed with the help of an instructor;
- Vigorous exercises performed with the help of a healthy limb and an instructor;
- Exercises that are aimed at improving coordination in the movements of the affected limbs;
- Reducing hypertonicity and movement that are intended to help;
- Walking;
- Breathing exercises;
- Development of fine motor skills;
- Relaxing massage;
- Swimming;
- Physiotherapy;
- Drug treatment.
In adults
The main thing is to approach the treatment of hemiparesis systemically. The doctor determines the severity and, depending on it, prescribes treatment. Typically it consists of the following points:
- exercise therapy;
- Swimming;
- Massage;
- Physiotherapy;
- Drug treatment.
Botulinum therapy for hemiparesis and hemiplegia
Prescribed drug therapy does not always relieve muscle spasticity (hypertonicity). This is especially true when central hemiplegia persists for more than a year from the moment of illness or injury. This usually occurs with large areas of cell death in the brain, such as a large hemispheric stroke. Often, even long-term, many-month use of muscle relaxants does not solve the problem of spasticity in such people.
Botulinum therapy - what is it?
This is an injection of a precisely calculated amount of a substance called botulinum toxin by the doctor. What it is, its mechanism of action and how it can be useful for people with high spasticity will be described further.
Botulinum toxin is a potent organic substance produced by bacteria that cause botulism. In nature it is a potent neurotoxic poison, and in small (precisely calculated) doses it relaxes skeletal muscles. This property has been learned to be used for muscle spasticity in clinical neurology.
Botulinum therapy allows you to increase the amplitude of passive movements with hemiparesis and in cases of hemiplegia. It also allows you to reduce pain, which occurs with severe spasticity and can be quite intense. The limbs on the painful side begin to move in the joints, they become more accessible for kinesiotherapy (physical therapy).
Spastic hemiplegia is one of the main consequences of a stroke, which causes limited mobility of a person in the environment.
Help the site develop - click on the social media button below and share the link. Thank you!