The anatomical structure of the brain in detail is formed individually for many. Some deviations are normal, others are classified as diseases. There are situations when patients develop lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain. What is it and how is it treated? Below is detailed information about this.
Causes
The lateral ventricles enlarge due to problems with the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. Let's consider the main reasons: intense secretion of cerebrospinal fluid, problems with the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the lymphatic system, slow outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
Changes in cerebrospinal fluid dynamics due to increased production and too slow absorption are often caused by infections in the brain. The movement of cerebrospinal fluid is often hampered after the cerebrospinal fluid ducts are blocked by neoplasms.
Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain occurs for the following reasons:
- Infectious processes that a person has suffered from, encephalitis, meningitis, etc.
- Complex and serious traumatic brain injuries.
- Neoplasms and ulcers in the brain.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Bruising in the head.
- Hemorrhagic stroke.
- The blood vessels of the brain become blocked with blood clots.
- The blood vessels of the brain become clogged with blood clots.
- Abnormal formation of the ventricular system during the embryonic period.
The course of fetal ventriculomegaly in pregnant women after 35 years
Ventriculomegaly in the fetus most often develops if the child’s mother is over 35 years old. This happens for the following reasons:
- The risk of genetic disorders (for example, Down syndrome) increases;
- Intrauterine infections occur more often;
- A pregnant woman over 35 years of age is susceptible to complications while bearing a child.
Thus, if the mother is under 35 years old, ventriculomegaly in the child occurs only in exceptional cases.
How does the disorder develop?
If there is a slight expansion of the ventricles of the brain, this does not affect the patient’s condition. The disease is indicated by pronounced changes or expansion. The patient feels all the signs of the primary disease, leading to dilatation of the ventricles.
Some patients complain of problems with sensitivity and motor function, memory loss and absent-mindedness. When the ventricles of the brain are enlarged, intracranial pressure increases.
This condition is accompanied, firstly, by a headache, more often in the morning. When a person lies down for a long time, ICP increases. Migraines may not occur, but there is a feeling of squeezing. Nausea, vomiting. It doesn't get any easier after vomiting. This symptom occurs even with proper nutrition. Often a person feels sick with high blood pressure. My head is spinning. Anxiety, apathy, and fatigue appear.
This indicates that the disease is developing. The brain shrinks due to problems with the removal of cerebrospinal fluid into the lymphatic system. The result of such a process may be that schoolchildren may also develop such a disorder. Enlargement of the ventricles of the brain is observed due to congenital problems with the development of the organ , infections or genetic abnormalities.
Children experience such problems as movement of the eyeballs becomes difficult, the bones of the skull diverge, after tapping on the skull a specific sound is heard, and development is inhibited.
When minor events occur, the mood quickly changes. Impaired physical activity. Problems with excess weight. Attachment to parents and other close people noticeably deteriorates. In adolescents, asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain occurs after injuries or infections. At the same time, they have severe headaches, nausea, and mental disorders.
What is lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain?
20.03.2019
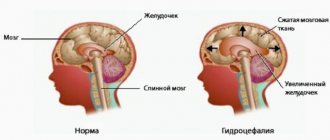
The lateral ventricles are cavity formations in the brain in which cerebrospinal fluid circulates. These are the largest ventricles among others. Between the ventricles there is a transparent plate that separates both ventricles from each other. Normally, the ventricular cavity increases with age.
What it is
Lateroventriculoasymmetry is a change in the volume of one or two lateral ventricles due to an increase or decrease in their size. Lateroventriculoasymmetry is not necessarily a pathology.
Ventricular dimensions are of little clinical significance. So, if confirmed asymmetry forms symptoms, lateroventriculoasymmetry is considered a pathology, if there are no symptoms, this is considered an individual feature of the structure of the ventricular system of the brain.
Link to mental disorders
The publication of the American Journal of Psychiatry contains an article with a meta-analysis.
The article states that thanks to the massive magnetic resonance imaging of patients with schizophrenia and healthy people, differences were found in the structure of the ventricular system.
Thus, in the conclusion it is stated that in patients with schizophrenia, in addition to a decrease in the volume of the frontal and temporal cortex, a difference was found - an expansion of the volume of the lateral ventricles.
A 2008 meta-analysis described a nonspecific change in patients with bipolar affective disorder. Thus, the article indicates that in such patients, unlike healthy people, the lateral ventricles are dilated.
Symptoms
The severity of symptoms depends on the expansion. Thus, a slight change in the volume of the cavity may not appear. Lateroventriculoasymmetry causes a nonspecific clinical picture (general cerebral symptoms):
- Periodic aching headache of a bursting nature. May worsen with sudden head movements.
- Dizziness.
- Nausea and vomiting not associated with food intake.
- Sleep disturbance, irritability, emotional lability.
- Noise in the ears, decreased visual acuity, pain in the eyes.
- Decreased performance.
There are no specific clinical signs that would suggest lateroventriculoasymmetry. To detail and clarify the nature of the symptoms, it is necessary to conduct instrumental diagnostics.
The clinical picture in children usually appears after birth, as indicated by objective signs: pulsation and divergence of the sutures between the cranial bones, delayed psychomotor development, gait disturbance, frequent tearfulness, disordered sleep-wake ratio. The clinical picture in adolescents and the elderly is the same as in adult patients.
Treatment
If lateroventriculoasymmetry does not reduce a person’s quality of life and does not cause him discomfort, treatment is not applied. If there is an objective clinical picture, a set of drugs is prescribed that reduce the volume of circulating cerebrospinal fluid and improve cerebral circulation:
- Diuretics: Spirolactone, Hydrochlorothiazide.
- Nootropics: Glycine, Piracetam. However, nootropics have an extremely weak evidence base.
Other drugs are prescribed symptomatically, depending on the dominant syndrome. For example, if a child is very agitated, he is prescribed sedatives.
People with lateroventriculoasymmetry should be constantly monitored by a neurologist. The operation is almost never performed. Surgery is indicated in rare cases, for example, in cases of dislocation of brain structures and cerebral edema. In this case, drainage of the lateral ventricles is performed, during which cerebrospinal fluid is removed. This lowers intracranial pressure and makes the patient's condition easier.
Didn't find a suitable answer? Find a doctor and ask him a question!
Source: https://sortmozg.com/zabolevaniya/lateroventrikuloasimmetriya
Classification
Lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain is divided into the following subcategories:
- Symptomatic . The disease develops for a specific reason.
- Idiopathic . It is difficult to determine the provoking factor.
Dilation of the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles is divided into:
- Mild asymmetry, for which there is no need for therapy, since there are no significant deviations.
- Moderate degree. It is characterized by minor disturbances in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Severe form - maximum dilatation of a ventricle is detected, a noticeable problem with the removal of cerebrospinal fluid into the lymphatic system.
With increased severity, other symptoms, abnormalities, diseases of the brain and central nervous system are added to the disorder.
Types of lateroventriculoasymmetry:
- Isolated view. Only the ventricles located on the sides expand.
- Extensive. There is an expansion of different groups, for example, when the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles are expanded.
- Bad heredity.
The prognosis of the disease is made after analyzing all types and forms of ventricular transformation.
In newborns
Ventriculomegaly refers to the dilatation of the lateral ventricles in infants who have recently been born. The first signs of the disease can be detected at 17 weeks of pregnancy. More often the disease develops in premature infants. If the cause of the deviation does not appear clearly, it means that after some time the size of the ventricles will return to normal.
Why does this disease develop in newborns:
- Infectious processes in the mother's body during pregnancy.
- Asphyxia as a result of the umbilical cord entangling the neck.
- Injuries received during childbirth.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Hemorrhages.
- Lack of oxygen.
- Bad heredity.
- Mothers over 35 years of age are more likely to develop the disease.
Asymmetry is formed in children taking into account their age category. A baby with an illness is constantly capricious, reacts inhibited, often refuses breastfeeding, and his gaze is directed downwards.
If the baby has an isolated disease and does not have any abnormalities or genetic abnormalities, the prognosis is often favorable. This is only possible in a situation where the newborn has been treated for a month using the correct therapeutic technique.
Forecast
The prognosis is relatively favorable. Statistics show that in 65% of cases a complete cure occurs, in 29% of cases minor residual effects are observed. The mortality rate as a result of poor blood flow from the head is about 23%. The prognosis is unfavorable in cases where the pathology is aggravated by hemorrhagic infarctions, sepsis, epileptic seizures that are difficult to control, and pulmonary embolism. Therapy is perceived more difficult by patients in early childhood and old age. Dysgemia at the third stage threatens the health and life of the patient. At the first signs of pathology, it is better to undergo a diagnostic examination and, if necessary, a course of therapy.
928
Symptoms of ventricular dilatation
The principle of the development of the disease has general features, without taking into account the characteristic causes. Fluid collects in the ventricles, they enlarge and begin to put pressure on the brain tissue. The pressure in these cavities increases.
Patients experience: headaches, nausea, vomiting, a feeling as if the eyes are being squeezed out, problems with hearing and vision, apathy, fatigue, dizziness, memory deterioration, fainting, coma, disorientation, problems with coordination of movements, enuresis. , depressive state. All these are symptoms of dilatation of the lateral ventricles.
Diagnostics
Enlarged ventricles of the brain are detected using the following procedures: ultrasound of the brain - the most informative procedure, visual examination of the fundus, detection of disc swelling on the nerves, spasms, bruises, neurosonography, MRI and CT scan of the brain.
When these methods show conflicting data, you need to do a lumbar puncture and take the cerebrospinal fluid for analysis.
Treatment options
When, based on research results, it is possible to determine that the patient has dilated ventricles, many begin to worry about the possible danger. Often, when the disease is detected, symptoms do not appear .
Therapeutic procedures are carried out to eliminate the disease, as a result of which the ventricles in the brain have enlarged. After this, the next stage of the procedure is performed. Medicines are prescribed to relieve intracranial pressure and preventive measures are taken.
If the use of medications does not produce results, surgical measures must be used. A spinal tap is performed. If the ventricles are dilated due to a brain tumor, the tumor is removed. Ventricular bypass surgery is often performed. The device is inserted into the head and drains cerebrospinal fluid into the abdominal cavity or directly into the bladder.
In most examples, the bypass procedure has not been shown to be effective. The likelihood of inflammation around the shunt, blockage, and infectious process increases. The device has to be changed. During the treatment process, there are quite positive results in children compared to adults.
Medicines: diuretics, nootropics, sedative tablets, antiviral drugs and antibiotics are used in the presence of infections. The operation is performed after the formation of tumors, head trauma, hematomas, etc.
Signs of lateroventriculoasymmetry in the brain
: 5 617
Lateroventriculoasymmetry is an abnormal enlargement of the ventricles of the brain.
The ventricles of the human brain, when they increase in size, begin to put pressure on the brain centers, which leads to poor functioning of neurons or their complete elimination.
Lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain, what is it - this is a very serious disease that must be treated after the first symptoms appear.
Causes
Many people will ask what lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain is. The ventricles of the brain are small containers that are located in the middle of the brain components.
They are connected by the spinal cord canal and the subarachnoid space. The cells that line the interior of the ventricles form cerebrospinal fluid.
The main purpose of the ventricles of the brain is to nourish the nerve cells of the brain and spinal cord, as well as to protect their fibers.
CSF circulation
The normal amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the cerebral ventricles is 150 milliliters. Three times a day it renews its composition. When the amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain increases, the size of the ventricles of the brain begins to increase. The contents of the cerebrospinal fluid changes due to poor outflow or absorption.
In children
Lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain in children can be either congenital or a consequence of pathology. This anomaly can be more often found in newborns. Enlargement of the cerebral ventricles in infants is called hydrocephalus. such disorders appear due to congenital anomalies and only in some cases due to birth injuries or as a result of meningitis.
Several factors can cause such terrible changes in a child’s brain. The main cause of lateroventriculoasymmetry in the brain is viral infections caused by maternal illnesses during pregnancy. namely syphilis, toxoplasmosis, rubella and mumps.
in adults
in adults, an increased amount of cerebrospinal fluid can be caused as a consequence of the following diseases:
- after illness with neuroinfections. such as meningitis and meningoencephalitis. It is these diseases that provoke greater appearance of cerebrospinal fluid.
- for fractures and injuries of the skull.
- various types of neoplasms - tumors, brain cysts, bruises. they can compress the outflow and thereby cause stagnation of the cerebrospinal fluid, with a subsequent increase in its quantity and, accordingly, with a disproportionate increase in the cerebral ventricles.
- vein thrombosis
symptoms of the disease
If lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain is present, pronounced symptoms are observed. They begin to appear as soon as violations appear.
These changes and symptoms of lateroventriculoasymmetry are quite dramatic, that is, it is simply impossible not to notice them. This is complete powerlessness, loss of consciousness, lack of sensitivity, loss of control over the motor system, memory, and thinking.
Manifestations of increased intracranial pressure also appear here.
The patient is worried about symptoms such as:
- Headache. It is especially worrying in the morning, after a long stay in a horizontal position, the indicator of intracranial pressure begins to rise. The pain can manifest itself as strong spiraling or, conversely, swelling in the head or simply squeezing in the temples.
- Vomiting and nausea appear.
- My head begins to feel very dizzy.
- Severe anxiety.
- Apathy towards everything.
- Drowsiness occurs even when the disease is slightly advanced.
Severe headaches
Additional signs of lateroventriculoasymmetry of the human brain:
- Consciousness is completely impaired, a coma is possible.
- There are disturbances in eye movement.
- The work of the heart changes and breathing is accordingly impaired.
- Vision deteriorates as pressure on the optic fibers increases.
- There is no sleep mode. That is, complete insomnia at night, and drowsiness during the day.
- Complete indifference to everything around.
- Inability to walk.
- Urinary incontinence and complete lack of control over bowel movements.
In children, the manifestations are slightly different from in adults. Children with such disorders have an inhibited reaction, are very whiny and capricious. Their eyes are wide open and their gaze is directed downward. The main sign of brain disease is an increase in the size of the skull, since the child’s bones are more flexible.
- Limited eye movement.
- Intercranial sutures may come apart.
- Memory impairment.
- Complete developmental delay.
- Thinking disorder.
- Children don't move much and are therefore overweight
In adolescents, this disease can be caused by head injuries and infectious diseases. Symptoms of lateroventriculoasymmetry in the brain always appear immediately: nausea, vomiting, convulsions, headaches, and sharply manifested neuroses are also possible.
Increase in size of the skull
Treatment methods
When the results of tests reveal that a person has enlarged ventricles of the brain, many are interested and concerned about the question of whether this is dangerous. After all, when the disease was detected, there were no specific symptoms at all.
First of all, therapy is prescribed to eliminate the disease, which resulted in enlargement of the ventricles. Then follows the second stage of treatment. During it, medications are prescribed to reduce intracranial pressure and prevent its increase.
If drug treatment is ineffective, doctors recommend surgery. During this procedure, a punctate is taken from the cerebrospinal fluid. An increase in the number of stomachs in the brain is associated with the appearance of a brain tumor, then it is removed.
In modern medicine, a widely known operation is bypass surgery of the ventricles in the brain. It involves inserting a shunt through which cerebrospinal fluid flows from the ventricles of the brain into the abdominal cavity or bladder.
It should be noted that ventricular bypass in the brain is in many cases not at all effective. Inflammation around the shunt, its blockage, and infection may occur. In such cases, replacement of the shunt is required. With treatment, there are more positive recovery results in children and newborns than in adults.
Source: https://SostavKrovi.ru/sosudy/mozga/priznaki-lateroventrikuloasimmetrii-v-golovnom-mozge.html