The gap between our ideas about the world and external circumstances often leads to depression. It is better to fight it by changing priorities, but you also have to resort to medications. Let's figure out what helps more in this case - antidepressants or tranquilizers, what are their differences and their effect on the body.
antidepressant vs tranquilizer
What are antidepressants?
Antidepressants are psychotropic drugs that stimulate the nervous system.
The main signs of depression are:
- loss of active interest in life;
- Bad mood;
- chronic fatigue;
- low performance;
- passivity in decision making.
Antidepressants help regain vital activity by directly acting on the brain and stimulating the nervous system. The very first such remedies were herbs, in particular St. John's wort. And until now, the safest antidepressants are natural herbal preparations that are sold in pharmacies without a prescription.
Helpful: Antidepressants without a prescription
Emotional disturbances and antidepressant treatment
If for schizophrenic disorders the psychiatrist’s main weapon is antipsychotics, then for emotional disorders the entire treatment is not so monotonous. This is due to the fact that affective disorders constitute an extremely diverse group and vary greatly in:
- symptoms;
- degree of severity;
- etiology;
- leakage.
Let's consider a group of unipolar and bipolar disorders. The first is characterized by the fact that light periods are replaced by attacks of depression, and in the second group there is an alternation of depressive, light and euphoric phases. And in both groups, paroxysmal episodes began and passed abruptly, even without the use of antidepressants. Here, the main role of these drugs is to reduce the time the patient spends in a depressive episode. However, the disease itself cannot be cured; even after several years, a depressive attack may recur.
This leads to the requirement to take antidepressants for six months after the last depressive attack.
If a person’s attacks of depression occur with sufficient regularity, then today a multi-year program for lithium maintenance therapy has been developed. If the patient individually does not tolerate lithium, then, as a rule, Tegretol (carbamazepine) is used.
Long-term use of antidepressants is also possible in the prevention of depressive attacks of secondary origin, for example, after a trauma (victims of rape, loss of a loved one), which served as a trigger for the first attack.
Antidepressant groups
Currently, a huge number of anti-depression drugs have appeared, which are divided by professionals into several groups and classes, depending on the methods of influence. For an ordinary person, it is important what effect is obtained from their action:
- sedative;
- stimulating;
- anti-anxiety;
- relieving fears;
- vegetative stabilizing.
The sedative group of antidepressants helps cope with insomnia. Stimulating, on the contrary, increases activity and improves mood. Two more groups relieve fears, phobias and anxieties. And the latter reduces the external manifestations of depression: rapid heartbeat, sweating, problems with the intestines and digestion.
But depression often manifests itself in several ways, so it is difficult to choose the right drug to combat it without side effects.
The correct choice of an antidepressant can only be made by a psychotherapist, neurologist or psychiatrist. Don't self-medicate!
Antidepressants
The main area of application of antidepressants is the treatment of depression.
However, these drugs are also used for some other pathological conditions. The first medications that began to be used in the treatment of depression appeared in the 50s of the last century. The ancestor of antidepressants was iproniazid, which was used in the treatment of tuberculosis and caused euphoria in patients.
CM. SEE ALSO: Tranquilizers: list of drugs
The term “thymoanaleptics” is also used in the medical literature.
The main area of application of drugs in this group is the treatment of depression, however, the drugs are effectively used in the treatment of other pathological conditions:
- Depression of various etiologies.
- Affective insanity.
- Phobias (fears).
- Schizophrenia.
- For alcoholism, drug addiction, substance abuse.
- Anorexia, bulimia.
- Functional enuresis.
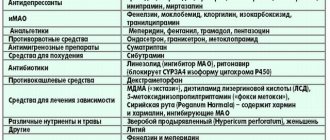
There are several classifications of antidepressants. According to their mechanism of action, they are divided into the following groups:
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAO).
- Irreversible MAO inhibitors (pirlindole, incasan, etc.).
- Reversible MAO inhibitors (aurorix, feprosidnine).
- Inhibitors of neuronal reuptake of transmitter monoamines.
- Non-selective inhibitors of neuronal reuptake of neurotransmitters (insidone, amitriptyline).
- Selective inhibitors of neuronal reuptake of serotonin, norepinephrine (doxepin, fluoxetine).
- Antidepressants of different groups (mirzaten, coaxil).
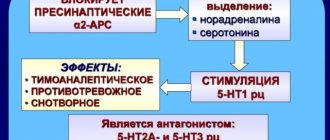
The effect of antidepressants is associated with the influence on mediators (biologically active substances in the central nervous system), which have a stimulating effect on the functioning of brain structures. Some drugs block the release of monoamine oxidase, others increase the release of norepinephrine and adrenaline, and promote the accumulation of serotonin.
In the clinical picture, this can manifest itself in the form of the following effects:
- The sedative effect manifests itself in the form of calm, reduction of tension, and motor restlessness.
- The stimulating effect is manifested by activation of mental activity and a decrease in general inhibition.
It is worth noting that different drugs from this group have different degrees of severity of the main effects described above.
Unlike tranquilizers, the effect of antidepressants appears several days or weeks after starting to take the drugs.
The most common side effects encountered when taking it are:
- Confusion, anxiety, disorientation in space.
- Cardiac dysfunction (arrhythmias, sudden cardiac arrest, conduction disturbances).
- Reduced blood pressure.
- Violation of attention, memory, cognitive activity.
- Weight loss or gain, loss of appetite.
- Drowsiness during the daytime.
- Nausea, vomiting.
What are tranquilizers?
Tranquilizers also help fight depression, but in a different way: they depress the nervous system, suppressing the manifestations of anxiety and fear, reducing the level of emotionality.
The main effects of tranquilizers are similar to the effects of antidepressants:
- anti-anxiety (reducing anxiety, eliminating obsessive thoughts and suspiciousness);
- sedative (reduced excitability, accelerated sleep);
- sleeping pills (improving the quality and duration of sleep);
- muscle relaxant (muscle relaxation);
- anticonvulsant (relief of seizures).
Tranquilizers can also increase the pain threshold.
There are broad-spectrum tranquilizers, daytime, selective and non-selective. And, of course, most drugs have contraindications and side effects, and some of them can be addictive, which is especially dangerous.
Tranquilizers, like antidepressants, should not be used without consulting a doctor.
Tranquilizers
Tranquilizers are indicated where a depressant effect on the nervous system is needed: for various phobias, tics, convulsive syndrome, and so on.
The term "tranquilizers" comes from the Latin word tranquillo, which means calm, serenity. The era of tranquilizers began in 1952, when the first drug, meprobomate, was synthesized.
They are used in the treatment of the following conditions:
- Neurotic reactions to stress, fears (phobias), emotional stress.
- Neurosis-like reactions (tics, anorexia, stuttering).
- Sleep disturbance.
- Premedication (auxiliary therapy before anesthesia).
- Hyperkinesis.
- Convulsive states.
Also in the medical literature, the terms “anxiolytics” or “anti-anxiety drugs” are used to designate this group of drugs, but the designation “tranquilizers” remains the most common.
The molecular structure of drugs varies greatly; they may belong to different groups of chemical compounds, but most drugs have (to varying degrees) all of the effects listed below.
There are five main mechanisms of action of drugs in this group:
- Anxiolytic effect (anti-anxiety, antiphobic) is manifested by a decrease in symptoms of anxiety and fear.
- Hypnotic effect. The drugs facilitate the onset of sleep, which in its indicators is close to physiological.
- The sedative effect is expressed in the appearance of lethargy, drowsiness in a person during the daytime, and decreased concentration. Medicines help reduce the rate of reactions and enhance the inhibitory effect of alcohol on the central nervous system.
- The muscle relaxant effect is associated with an effect on the central nervous system, which leads to a decrease in tension.
- Anticonvulsant action.
The mechanism of action is associated with the influence of tranquilizers on subcortical structures (hypothalamus, limbic system, reticular formation, etc.), which are responsible for human emotional behavior.
It is worth noting that when taking tranquilizers, symptoms of anxiety and fear of neurotic origin are relieved quite quickly, but they do not have much effect on hallucinations or delusional states.
The classification of tranquilizers is based on their ability to act on different types of receptors in the central nervous system.
- Benzodiazepine receptor agonists (sibazone, phenazepam, etc.).
They bind to GABA receptors in the central nervous system, enhancing the inhibitory effect of GABA on subcortical structures.
Benzodiazepines are represented by a large number of drugs that differ in duration of action and effect.
For example, drugs that have a long-term effect on the body include diazepam, phenazepam; lorazepam has a medium duration of action, and midazolam has a short duration. The hypnotic effect is more pronounced in phenazepam and diazepam, the anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant effect is more pronounced in sibazone and phenazepam.
- Serotonin receptor agonists (buspirone).
Binds to serotonin receptors, reducing the synthesis and release of serotonin from cells. Buspirone has a pronounced anxiolytic effect, but does not have muscle relaxant, hypnotic or anticonvulsant effects.
- Drugs with a different mechanism of action (amizil).
Despite their good tolerance, tranquilizers are prescribed by a doctor strictly according to indications. Uncontrolled use in most cases leads to the development of side effects.
- Mental and physical dependence develops, so drugs should not be prescribed for more than 2 months.
- Frequent development of drowsiness, unsteady gait, slowness of motor reactions. These parameters limit the use of medications in people whose profession requires accurate and quick reactions (driver, crane operator, etc.).
- The menstrual cycle is disrupted and libido decreases.
- Paradoxical excitation reactions develop.
- There is a decrease in memory and attention.
What are the differences between antipsychotics?
There is another important group of psychotropic drugs - antipsychotics. Not so long ago they were classified as “heavy tranquilizers,” but are now considered separately.
Neuroleptics block receptors of the nervous system and are used in psychiatry in difficult cases, in the treatment of:
- severe psychosis and schizophrenia;
- alcoholism;
- dementia and Parkinson's disease;
- triangular neuralgia, etc.
Neuroleptics can very effectively relieve manifestations of mental disorders, but also significantly affect the state of a person’s personality. They differ from tranquilizers in that they do not cause feelings of euphoria or addiction at all.
anti-depression pills
What does practice show?
Of course, we are all used to hearing that many problems can be solved on a psychologist’s couch. We also know that many people with borderline and severe disorders also visit psychotherapists, but within an inpatient setting. However, psychotherapy does not always give the desired result in painful conditions, and it is simply impossible to work with a patient who is in the world of delusional experiences.
That is why, during treatment in a hospital or a “seasonal” visit to a psychiatrist, drug therapy is usually prescribed. Sometimes it acts as an accompaniment to psychotherapy, sometimes as an independent practice, and sometimes the psychotherapist plays only a secondary role.
In any case, none of these treatment approaches excludes the other, and sometimes requires support. For example, a large number of people with borderline disorders, as a rule, are not in hospitals, but on an ongoing basis they use certain recommended medications, undergoing examination from time to time.
What is the difference between antidepressants and tranquilizers?
The difference between antidepressants and antipsychotics with tranquilizers lies in the mechanism of action:
- antidepressants stimulate;
- tranquilizers suppress the nervous system.
It is difficult to compare one and another group of drugs, although sometimes the treatment results are very similar. The doctor’s qualification level allows you to choose from a wide range of medications the combination that will most effectively and individually lead to the desired result. Moreover, it is necessary to take into account the interaction of medications taken.
Therefore, for self-medication for depression, you can only use antidepressants or tranquilizers that are sold without a prescription, and then not systematically, but only for one-time relief of individual depressive conditions.
Features of antidepressants
Antidepressants are prescribed to treat depression. Each of the drugs in this group has its own spectrum of effects: there are stimulating, sedative, anti-anxiety antidepressants, with a strong hypnotic effect, and completely devoid of hypnotic effect. These medications normalize pathologically altered depressive mood, improve the thinking process, increase inhibited motor activity, and increase concentration. The duration of treatment with antidepressants is six months or more, so a significant number of these drugs do not cause dependence. Some antidepressants, which have significantly pronounced stimulating properties, can cause exacerbation of mental disorders, transform depression into a manic phase, and cause convulsive seizures, so drugs in this group should be prescribed by a doctor.
A one-time use of antidepressants is useless; a long course of treatment is necessary. Taking into account the peculiarities of the action of these drugs, treatment begins with small amounts of the drug, gradually increasing it to a therapeutic dose. Therapy is completed by gradually reducing the daily amount. With this dosage regimen, some side effects are eliminated. Both tranquilizers and antidepressants should be prescribed by a doctor. Uncontrolled use of these drugs can harm the body.
List of strong antidepressants
Strong antidepressants include:
- Amitriptyline;
- Clomipramine;
- Imipramine;
- Maprotiline;
- Paroxetine;
- Fluoxetine;
- Rolipram.
They have the most pronounced effect on symptoms of depression.
Less strong ones include:
- Trazodone;
- Eprobemid;
- Nomifensine;
- Toloxatone;
- Alprazolam;
- Azafen;
- Indopan;
- Minaprine;
- Femoxetine;
- Cefedrine;
- Sidnofev.
Schizophrenia and neuroleptic therapy
In the acute stage of the disease, psychotherapy is simply meaningless and sometimes even dangerous. That is why “acute” patients, in addition to hospitalization, are prescribed a course of antipsychotic drugs, under the influence of which most patients find peace. Sometimes the effect of antipsychotics turns a recent psychotic into a person who becomes susceptible to the environment, social influence, and, consequently, to psychotherapy. Neuroleptics help patients get rid of deep-seated fears, reduce the influence of delusional ideas and regain at least weak criticism of their experiences.
At the same time, subsequent psychotherapy does not mean that the patient stops taking antipsychotics. Under the strict supervision of a psychiatrist and staff, the hospitalized patient continues to take medications. In this way, a reduction in the patient’s excessive emotionality is achieved, the general background of mood is stabilized, which facilitates further relationships with the treating specialist.