What it is?
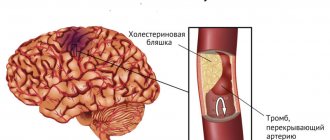
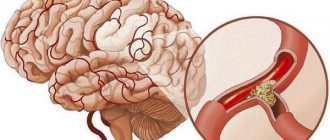
The disease is considered one of the most common among diseases affecting blood vessels. In particular, atherosclerosis affects the elastic and elastic-muscular arteries of the brain with the formation of deposits (usually cholesterol) on the inner surface of the vessels in the form of plaques with the growth of connective tissue in them over time and impregnation with calcium salts.
Reference! As the disease progresses, the lumen of the blood vessels narrows, which leads to a deterioration in the blood supply to the affected organ (in this case, the brain). Sometimes blockage of blood vessels by plaques leads to the formation of blood clots, which can lead to necrosis of organ tissue.
Methods for diagnosing cerebrovascular atherosclerosis
Modern medical practice has developed a clear sequence of actions to identify the disease:
- The doctor conducts a survey to identify external signs.
- Listens for noise at critical points.
- Palpates to identify nodes in all accessible places (iliac, femoral, popliteal arteries, etc.).
- Laboratory tests of urine and blood are carried out for the presence of cholesterol and lipid balance.
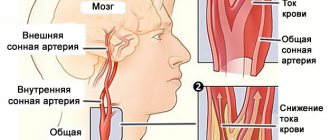
- Ultrasound examination helps to identify the localization of plaques.
- MRI is prescribed if necessary to finally clarify the picture if there is a fear of a stroke.
- The veins are examined with a contrast solution under X-ray.
The presence of a problem can be fairly reliably determined using the first five techniques. The doctor receives a detailed picture of the disease by performing the last two studies.
Causes
Unfortunately, there is still no clear answer to the question of what is the root cause of the development of cerebral atherosclerosis: is it either a natural aging process, or is it really a disease that affects the blood vessels.
But several factors can be identified that influence the process of formation of plaques on the walls of blood vessels, leading to blockage of the arteries and numerous complications. Factors influencing the development of cerebral atherosclerosis are as follows:
Physical inactivity (sedentary lifestyle).- Psycho-emotional stress, which is permanent (this condition leads to a deterioration in arterial tone over time).
- Heredity (a genetic factor can play an important role in the development of atherosclerosis (ICD 10)).
- Improper, poor-quality nutrition (prevalence in the diet of foods containing large amounts of fat and cholesterol).
- Bad habits (tobacco smoking, alcohol).
- Disorders of the body's metabolic processes.
Expert opinion
Zemlyanukhina Tatyana Vyacheslavovna
Ambulance and emergency paramedic at the Clinical Emergency Hospital #7 in Volgograd.
Ask an expert
I will not tire of saying that many problems of the cardiovascular system owe their existence to such a bad habit as smoking. To be honest, even alcohol (in acceptable quantities) does not cause as much damage as nicotine. During smoking, blood vessels contract, the accompanying substances contained in cigarettes disrupt the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels and in the future there is a high probability of damage to these walls at the most unexpected moment with the slightest mechanical impact.
Diagnostics
Since the symptoms of vascular pathology appear during the progression of the disease, it is more often diagnosed at stages when urgent treatment is already required. Diagnosis of cerebral atherosclerosis occurs in several stages:
- identification of complaints;
- inspection;
- identification of risk factors and ways to eliminate them;
- laboratory and instrumental analyses;
- determination of plaque localization.
During the collection of information, the doctor not only identifies complaints, but also establishes the possibility of a genetic predisposition to the disease, determines the psychological climate and lifestyle of the patient. During the general examination the following is carried out:
- weight and height measurement;
- determining whether you are overweight or thin;
- determination of blood pressure level;
- presence of swelling;
- condition of the lymph nodes.
The systolic murmur must also be listened to, after which the time of onset of the first symptoms, the degree of their progression and the general state of health at the time of treatment are determined. Risk factors such as smoking and alcohol consumption, diet, lifestyle, physical activity and the presence of chronic diseases are also established.
Laboratory research
After a survey and examination, laboratory tests and instrumental research methods are prescribed to establish the general picture of the disease. The need for specific tests is determined by your doctor. On the eve of the test, it is advisable to avoid heavy physical activity, alcohol, heavy, spicy or salty foods.
According to biochemical blood tests, sugar, protein, creatine and uric acid are determined. Urea plays an important role in normal protein metabolism. Protein contains a lot of nitrogen, which is converted into ammonia during metabolism. The liver converts ammonia into urea, which enters the kidneys and is excreted in urine. Total protein consists of albumin and globulin, which are present in blood serum. It is needed for normal blood clotting and healthy pH levels, as well as for immune reactions. With its help, fats and steroid hormones are transported to tissues and organs.
An immunological blood test is needed to determine:
- the ratio of the magnitude of antibodies to cytomegalovirus and chlamydia, which often provoke atherosclerosis;
- the level of C-reactive protein, a high value of which indicates inflammatory processes.
According to the lipid profile, the presence of 2 lipid groups in the blood is determined. The first includes cholesterol, low-density and very low-density lipoproteins. The second is high-density lipoproteins. After studying the lipid spectrum, the level of risk of atherosclerosis is determined.
To confirm the diagnosis, the following coefficients can also be calculated:
- atherogenicity;
- homocysteine amino acids;
- triglyceride concentrations.
Another important indicator of the chemical characteristics of blood is the degree of acidity. The reference value is used to confirm the presence of diabetes mellitus and cerebral vascular damage.
Instrumental methods
The use of instrumental diagnostic methods allows not only to confirm the presence of atherosclerosis, but also to establish the exact location and extent of damage to the vessel.
At an early stage of the disease, when cholesterol metabolism is disrupted, the use of ultrasound radiation is effective. It is used to identify areas of thickening of the walls of the arteries of the brain, the presence of plaques and the speed of blood movement. The ultrasound method is based on the use of high-frequency sound waves to obtain a transverse image of blood vessels. After converting the sound reflection, the digital image is displayed on the monitor.
Angiography for atherosclerosis
Angiography is based on contrast examination of blood vessels. The patient is connected to a cardiac monitor and a contrast agent is injected into a vein. Further examination takes place using radiographic and fluoroscopic examination methods. The method allows you to study:
- condition of blood vessels and peripheral blood flow;
- places of vasoconstriction;
- aneurysm;
- malformations;
- size of the pathology;
- development of thrombosis and atherosclerosis;
- other vascular damage, inflammatory processes, pathologies.
Before angiography, an electrocardiogram must be done to detect heart disease and fluorography to determine the condition of the lungs and bronchi. It is forbidden to eat or drink 4 hours before the procedure. Angiography is not performed if you are allergic to a contrast agent, have heart or kidney failure, have thyroid disease, or have exacerbations of infectious and inflammatory diseases.
CT angiography refers to a radiological X-ray contrast diagnostic method. It is carried out using a computer and software that displays a three-dimensional image of the vessels on the monitor.
The use of duplex scanning makes it possible to study the walls of intracranial arteries and the speed of blood flow, the presence of blood clots, cholesterol plaques, the degree of tortuosity of the vessels and the places of their thickening. With the triplex ultrasound method, the structure of the vessel and its patency, the speed of blood flow is displayed on the monitor in a color image.
Duplex scanning of cerebral vessels
The transcranial Doppler method is aimed at identifying the speed of blood movement and deviations from the norm in certain areas, and determining the diameter and condition of blood vessels. It is usually prescribed for MRI, MRA and Doppler ultrasound of the carotid arteries. MRI is performed using a tomograph to determine the exact location of the atherosclerotic plaque, as well as to assess the anatomical and functional features of blood movement through the vessels. Computed tomography is usually used for patients who have had a stroke. It allows you to determine the area of the affected vessel and choose treatment tactics.
Symptoms of the lesion
Symptoms of the disease manifest themselves depending on the severity of development. There are a number of clinical signs of the presence of the disease (they can appear either simultaneously or progressively, with the addition of more and more new symptoms):
- Exacerbation of character traits, sometimes reaching the point of absurdity.
- Various sleep disorders (nightmares, drowsiness during the day, frequent awakenings at night).
- Frequent headaches of varying intensity, tinnitus.
- Excessive excitability, anxiety.
- Fatigue, decreased performance.
- Memory impairment (in some cases, dizziness).
- Impaired coordination and speech.
- Choking while eating.
There are several stages of the disease:
- Stage I (initial manifestations of atherosclerosis). At the initial stage of the disease, a person experiences only some of the symptoms described above, and most often this occurs after overwork or a long stay in a closed, poorly ventilated room. Increased symptoms (tinnitus, headaches, decreased performance and memory impairment) occur more often in the afternoon and after rest everything goes away.
Stage II (progression). There is an intensification of the manifestation of primary symptoms and to them are added tremors of the hands, unsteadiness of gait, deterioration of speech, depressive states, etc. A person blames others for his failures, often overestimating his own capabilities.- Stage III (decompensation). At this stage, a person is practically unable to exist without outside help. Physical indicators deteriorate significantly, mental processes slow down, memory deteriorates, etc. There is a high risk of stroke or paralysis.
- Stage IV (transient ischemic attack). A short-term condition that looks like a stroke, but goes away within a day. Arms, legs, and tongue may be affected, and then it becomes difficult for the patient to move his limbs, problems appear with pronouncing words, and the tongue becomes numb.
- Stage V (ischemic/hemorrhagic stroke). An ischemic stroke occurs when the arteries of the brain are completely blocked, which in turn leads to the death of brain cells due to lack of nutrition and oxygen. A stroke manifests itself in several signs: weak movement of the limbs (its complete absence), decreased sensitivity of the limbs, speech impairment, dizziness, problems with the swallowing reflex.
Reference! Hemorrhagic stroke differs from ischemic stroke in that it does not occur due to blockage of the arteries, but due to hemorrhage into the white/gray matter of the brain. Such a stroke is difficult to detect and is treated in a different way than an ischemic one.
It is worth reporting at the Clinic of High Medical Technologies named after. N.I. Pirogov.
Diagnosis of cerebral atherosclerosis: degrees
Based on the state of reaction to the external environment, three main stages in the development of the disease can be distinguished.
1 – initial degree
In this condition, a person has virtually no symptoms. Possible:
- decreased performance;
- slow recovery during rest;
- dizziness;
- inability to undergo extreme physical and mental stress.
All these signs can easily be attributed to temporary illness or age. Therefore, during such a period, diagnosis is difficult.
How is cerebral atherosclerosis treated?
Statins
These are drugs that are inhibitors of the enzyme that is involved in the synthesis of cholesterol (HMG-coenzyme A reductase). Due to its action, the concentration of LDL and VLDL in the blood decreases, and the inflammation of the atherosclerotic plaque decreases, as a result of which its condition stabilizes. Researchers say statins thin the blood, thereby reducing the risk of blood clot formation.
In pharmacology, this group of drugs is divided into generations depending on the time of their introduction:
- I generation:
- Simvastatin.
- Lovastin.
- Pravastatin.
- II generation: Fluvastatin. It contains sodium salt, activating the production of HDL (good cholesterol), and LDL is reduced due to increased uptake of its particles.
- III generation:
- Atorvastatin.
- Cerivastatin.
- IV generation:
- Pitavastatin.
Rosuvastatin.
This is a new generation group that is considered the best cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Statins (Mertinil, Atoris, Zakor). Medicines designed to lower blood cholesterol levels and stabilize the size of atherosclerotic plaques.
Contraindications:
- during pregnancy and lactation;
- for liver/kidney diseases;
- with hereditary muscle dysfunction;
- for problems with the endocrine system (including the thyroid gland);
- children under 18 years of age.
| A drug | Indications | Contraindications |
| Zovatin (Simvastatin). Price: about 540 rubles |
| Absolute:
Relative:
|
| Leskol (Fluvastatin). Price: about 2660 rub. |
|
|
| Atoris (Atorvastatin). Price: about 180 rub. |
|
|
Fibrates
Another remedy for treating cerebral atherosclerosis is Fibrates.
Fibrates (Bezafibrate, Gembifrozil, Liprimar). Designed to reduce triglyceride levels in the blood. They are prescribed only when their levels are elevated, or when atherosclerosis is combined with gout. Contraindications:
- with cholelithiasis;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- renal failure;
- problems with the gallbladder;
- children under 18 years of age.
The principle of action of these medications is to activate lipoprotein lipase, which breaks down bad cholesterol (LDL, VLDL). At the same time, the amount of HDL increases, and fat metabolism accelerates, reducing the risk of developing an atherosclerotic process. Among other things, fibrates strengthen vascular walls, reducing plaque inflammation, and remove free radicals.
| Gemfibrozil. Price: from 1600 rub. |
|
|
| Bezafibrate. Price: about 3000 rub. |
|
|
| Fenofibrate. Price: about 500 rub. |
|
|
| A nicotinic acid. Price: about 30 rub. |
|
|
Nicotinic acid and its derivatives
This treatment is prescribed for high cholesterol levels, also as an effective means for improving blood supply to the brain and removing small blood clots. Contraindications:
- liver and lung diseases;
- heart and stomach problems.
Excellently reduces the concentration of LDL and VLDL and triglycerides in the blood, normalizing the ratio of fat fractions. In addition, it is capable of activating enzymes that enhance metabolic processes in the cell with the release of energy from fats and carbohydrates.
Nicotinic acid dilates blood vessels, improving blood circulation in organs and tissues. Vitamin PP reduces the risk of thrombosis.
Bile acid sequestrants (Cholestyramine, Colestipol, Azithromycin). Used as an adjuvant treatment during the break between treatment courses. Stimulate the excretion of bile from the body, lower the level of high-density lipoproteins. Contraindications:
- problems with the liver and biliary tract;
- frequent or chronic constipation.
The mechanism of action of these drugs is based on the binding of bile acids and cholesterol, which are produced in the liver. About 97% of bile acids are reabsorbed in the intestine and travel through the blood to the liver, where they are again excreted in bile. Thanks to this, the total amount of cholesterol decreases, as it is additionally consumed.
| Colestipol. Price: about 300 rub. |
|
|
| Cholesteramine. Price: about 1800 rub. |
|
|
Other groups of drugs
Antihypertensive drugs (Octadine, Reserpine, Captopril). Designed to lower blood pressure and are prescribed in most cases for life. These drugs can only be prescribed by the attending physician. He will also tell you individually about possible contraindications for use. If any reactions to the drug occur as a result of long-term successful treatment, it is possible to replace it with a new one. Such actions are also discussed with the doctor.
Antiplatelet agents (Heparin, Ticlopidine). They are used to reduce the likelihood of ischemic stroke: the drugs inhibit platelets, which are actively involved in the formation of cholesterol plaques. Most often prescribed by a doctor as a prophylactic agent. Contraindications:- liver/kidney pathologies;
- acute cardiac aneurysm;
- bleeding of any etiology.
- Hypolipid tablets . These tablets have the opposite effect on sclerosis and atherosclerosis of blood vessels, and also normalize lipid metabolic processes, producing a hypocholesterolemic and hypolipidemic effect.
Attention! It is worth noting that statin treatment is considered one of the most effective and, at the same time, harmful.
Therefore, if there is a slight increase in the level of fatty acids in the blood, it is preferable to use natural statins for treatment, which are harmless and at the same time pleasant to the taste. Thus, medications can be replaced with vitamin complexes (C, B3), fish oil, flaxseed oil, peanuts, dark grapes, turmeric, etc.
| Probucol |
|
|
| Omacor. Price: from 1400 rub. |
|
|
| Ezetimibe. Price: from 1200 rub. |
|
|
There are also a number of drugs and special additives created based on natural ingredients:
- Coenzyme Q10. It is a powerful antioxidant that can qualitatively protect the cardiovascular system and to some extent reduce cholesterol levels.
- Beta-sitosterol. It is used to qualitatively reduce the amount of cholesterol in the blood (by almost 45%).
- Niacin. A drug based on nicotinic acid. Helps reduce cholesterol and triglycerides, improves brain function. Contraindicated in: diabetes;
- liver diseases;
- gout;
- bleeding, etc.
Treatment
Therapy involves the use of medication (conservative) and surgical techniques.
Surgery
If an ultrasound reveals more than 70% reduction in the diameter of a cerebral artery, the question arises about the need for surgical treatment of the damaged vessel. The most commonly used method is carotid endarterectomy. During the procedure, the vessel is dissected at the site of the blood clot, which is removed, and the integrity of the vessel is restored using sutures.
Other methods are endovascular operations, stenting.
Drug treatment
It is prescribed only by a doctor, taking into account contraindications, medical history and based on the results of studies and tests.
Therapy for cerebral atherosclerosis is aimed at:
- harmonization and restoration of lipid metabolism;
- lowering cholesterol levels (find out the norm from the table);
- elimination of metabolic disorders;
- treatment of concomitant diseases.
To solve these problems, several groups of medications are prescribed:
Statins are an active group of drugs that block cholesterol synthesis in the body, reduce its amount and prevent the formation of plaques. These drugs are Lovastatin, Mevacor, Fluvastin, Mekafor, Simvastatin, Pravastatin.
Means for improving microcirculation , dilating blood vessels, relieving spasms and at the same time preventing platelets from aggregating (sticking together) into clots:
- "Actovegin", "Cavinton", "Curantil".
- “Parmidin”, “Anginin”, “Aspirin” restore blood flow in small vessels, reduce the permeability of the walls, suppress the adhesion of platelets into clots, stimulate the resorption of blood clots, and prevent the deposition of fats and cholesterol on the vascular wall.
Vasodilators:
- “Nicotinic acid”, Nikoshpan” - expand small capillaries, strengthen the cells of the arterial wall, and effectively help reduce cholesterol concentrations. From simple standard means - “Papaverine”, “Eufillin”.
- Among the more progressive medications: Isoptin, Lomir, Amlodipine, Diazem. Cinnarizine and Nimodipine are suitable for long-term use.
- Medicines containing the alkaloid of the periwinkle plant - Vinpocetine (Cavinton, Bravinton) allow you to dilate blood vessels and stimulate metabolism.
- Dietary supplements based on the Gingko Biloba plant are good at relieving vasospasm, stimulating the work of brain cells, and reducing blood viscosity. Taking Gingium, Tanakan, Ginkor Fort is not combined with medications containing aspirin (Trombass, Cardio-magnyl) due to the risk of a serious increase in blood flow and bleeding.
Nootropic drugs activate the process of energy exchange in brain cells, improve memory, mental activity, cerebral circulation and cell resistance to oxygen deficiency.
They treat problems of mental disorders, senile dementia: Piracetam, Nootropil, Bemitil, Cerebrolysin, Aminalon, Sermion (nicergoline), Meclofenoxate, Phezam, Biotredin, Vinpocetine.
Medicines that activate energy metabolism and remove lipids - Lipostabil, Omacor, Eikonol, Thioctic acid.
Medicines to prevent the formation of blood clots when blood viscosity increases and the content of prothrombin in it increases - “Trental”, “Aspirin-cardio”, “TrombASS”, “Pentoxifylline”, “Cardiomagnyl”.
Doctor's advice
There are risk factors for developing stroke and heart attack in the next 5 years that have long been studied and taken into account, called the “SCORE Scale”, in which the higher the cholesterol, the greater the risk. Accordingly, cerebral atherosclerosis increases the risk of sudden cardiovascular accidents. In the first place in the treatment regimen are statins - drugs that lower cholesterol and help reduce the volume of plaques.
Victoria Druzhikina Neurologist, Therapist
Additional tools:
Fibrates – suppress the formation of fats and total cholesterol: “Clofibrate”, “Gemfibrozil”, “Fenofibrate”, “Atromid”, “Bezafibrate”, “Atromidine”.
Fibrates currently cause much controversy in the treatment of cerebral atherosclerosis. When used uncontrolled, fibrates are dangerous, so the dosage regimen and therapy regimen are agreed upon with a cardiologist.
“Nicotinic acid” and “Enduracin” are recommended in cases where atherosclerosis is associated with an increased amount of high-density cholesterol. They dilate blood vessels, but cause a rush of blood to the skin, so their use should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Hypocholesterolemic drugs - Neomycin, Guarem, Colestipol, Probucol, Lipostabil, Eikonol, Benzaflavin - reduce cholesterol, stabilize metabolism, and suppress the formation of blood clots.
In addition to the main treatment medications, it is advisable to take:
- Antioxidants that suppress oxidation processes: Mexidol, vitamins A, E, Aevit, P (strengthen the walls and increase the density and elasticity of blood vessels), microelements - potassium, silicon, selenium, vitamin C, which prevents the formation of fat deposits on the walls of arteries , group B improves the functioning of nerve cells. The use of Ascorutin (vitamin C plus rutin) requires monitoring the level of blood viscosity.
- For neurological manifestations and depression, antidepressants are used: Paxil, Azafen, Amitriptyline.
- When phobias, panic attacks, or severe anxiety appear, tranquilizers are prescribed: Alprazolam, Diazepam, Atarax, Phenazepam.
- If sleep is disturbed, sleeping pills and antidepressants (Donormil, Nitrazepam) are prescribed.
- For headaches and myalgia, the use of drugs that relieve pain and spasms is indicated: “Spazgan”, “Spazmalgon”, “Pentalgin”.
Among the more progressive medications: Isoptin, Lomir, Amlodipine, Diazem. Cinnarizine and Nimodipine are suitable for long-term use. Nootropics are prescribed with caution for dementia, as well as in older people - they activate the nervous system, and thus, as a side effect, can cause hyperexcitability, irritability, and aggression.
Physiotherapy for cerebral atherosclerosis
Aimed at activating blood circulation in the brain and processes in nerve cells, increasing arterial tone, and improving adaptive capabilities. This:
- Electrophoresis with medications.
- Hydrotherapy using carbon dioxide, oxygen, iodine-bromine, sodium, radon baths.
- Electrosleep procedures to strengthen and restore the nervous system.
- Special therapeutic exercises to improve and stimulate proper motor skills, motor functions, and relieve muscle spasms.
Diet therapy
The main provisions of the diet for cerebral atherosclerosis:
- Salt per day up to 3 g.
- Meals are frequent, in small portions.
- The amount of fat is no more than 65 g per day, of which 72% is vegetable.
- The amount of protein is not limited. Animal protein prevents fatty liver and cholesterol deposits in blood vessels.
What you can do:
- lean veal, pork, beef, turkey, fish;
- eggs in the amount of 1 pc. per day: in the form of steamed, baked, soft-boiled omelettes; milk, low-fat cottage cheese, kefir, peas, beans, buckwheat, wheat, oatmeal;
- once a week a little caviar and tongue are allowed. 10-20 g per week of butter is allowed;
- sunflower, rapeseed, corn, cottonseed, olive seeds promote intestinal motility and remove excess cholesterol;
- seafood is very healthy (up to 6 times a week): fish, squid, shrimp, mussels, seaweed, kelp;
- vinaigrettes, salads from cucumbers, zucchini, cabbage, tomatoes, potatoes, pumpkin, soybeans, eggplant, pumpkin, dill;
- You can have low-fat sausage, ham, mild cheeses, dry cookies, marmalade, dried fruit candies, muesli.
What not to do:
- animal fats, offal products saturated with cholesterol, including liver, brains, kidneys are excluded;
- limit sweet dishes, fresh white bread, pure sugar, jam, honey, jams, cakes, buttery sweet cookies;
- Rich meat and mushroom soups, cream, ice cream, butter and custard creams, mayonnaise and sauces based on it, dark chocolate, strong coffee, tea, and alcohol are not recommended.
Folk remedies
In complex therapy of atherosclerosis, traditional methods are used with caution and after consultation with a doctor. They must be combined with medications
Among them:
- Collection for spasms of cerebral vessels, nervous tension. A collection is prepared from valerian root, cudweed, and St. John's wort in equal parts. Drink as an infusion.
- Honey and lemon juice are mixed equally with vegetable oil and taken a teaspoon in the morning (dangerous for allergies and gastritis).
- Drink 100 g of freshly squeezed potato juice for frequent headaches (harmful for stomach diseases).
- An alcohol tincture with garlic and lemon along with zest is known (extremely dangerous for gastritis, peptic ulcers, inflammation of the pancreas).
- Dill seeds (teaspoon), brewed in a glass of boiling water. Drink as tea for headaches.
Despite the fact that atherosclerosis occupies only the walls of blood vessels, the consequences for the brain, the entire body, psyche and intellect are devastating. A person gradually loses his personal qualities and turns into a thoughtless organism that requires constant care and regular feeding.
To prevent such an existence, you should pay attention to the very first signs of the disease, do all the necessary examinations and take timely the whole range of measures aimed at recovery.
How to recognize and how to treat cerebral atherosclerosis, watch the video:
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. https://www.angiolsurgery.org/recommendations/2013/recommendations_brachiocephalic.pdf
Rate how helpful this article was
4.9 7 people voted, average rating 4.9
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Pharmacological groups of drugs
Depending on the purpose of therapy, various medications belonging to different pharmacological groups can be used.
Cholesterol control
These include the following groups of medicines:
- Statins.
- Fibrates.
- A nicotinic acid.
- Hypolipid drugs.
- Bile acid sequestrants (BAS).
Stabilization of fat metabolism
The following medications are used for cerebral atherosclerosis:
- Statins.
- Fibrates.
- SCV.
- Hypolipid drugs.
Ischemic syndrome
To treat such atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, the following drugs are used:
- Antiplatelet agents.
- A nicotinic acid.
- Statins.
Vitamins for atherosclerosis
Treatment and prevention of the disease involves adjusting the diet and prescribing a vitamin complex to improve the condition of blood vessels and cerebrovascular activity. Vitamins for atherosclerosis are prescribed comprehensively and depending on additional chronic diseases, blood tests and the patient’s condition.
One of the main vitamin complexes is Omega-3. This is a mixture of essential fatty acids designed to restore the deficiency of beneficial components. It is advisable to take B vitamins simultaneously with Omega-3: the effectiveness of these drugs together increases several times. However, taking it is possible only under the supervision of a general practitioner - folic acid sometimes masks a lack of B12, which leads to hypotension, chronic fatigue, weakness, and deterioration of brain function. Vitamin B6 is necessary for the conversion of homocysteine into harmless cystathionine. Without this vitamin, homocysteine grows into the walls of blood vessels and provokes the deposition of cholesterol.
Taking vitamin E daily reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Calcium is necessary for atherosclerosis for several reasons:
- it affects blood cholesterol levels;
- increases the susceptibility to platelet aggregation.
An overdose of calcium is as harmful as a deficiency: the risk of blood clots in the lumen of the vessel increases. The daily dose for an adult should not exceed 1500 mg. Along with calcium, you need to take both magnesium and chromium. Chromium is needed to normalize fats in the blood, i.e. to increase HDL and reduce LDL. Magnesium is the main mineral for the cardiovascular system, ensuring the normal functioning of blood vessels, heart, blood, and brain.
Another important mineral for atherosclerosis is selenium. It is involved in the synthesis of natural glutathione peroxidase, an enzyme that rids the body of free radicals. Selenium deficiency leads to tissue damage, rapid development of cholesterol plaques and poor blood flow.
Medicine for cerebral atherosclerosis must be prescribed by a doctor after a full examination, and taken exactly in the prescribed dosage. Self-medication and self-prescription are unacceptable: an incorrectly selected drug can significantly worsen the condition and provoke the development of side effects. For atherosclerosis, medications of several groups are usually prescribed, aimed at reducing the level of LDL and cholesterol in the blood, as well as restoring blood flow and improving brain activity. It is important in the treatment process to take vitamins to meet the body's needs for essential nutrients.
Medicinal use of aspirin for cerebral vessels
The drug has a pronounced antithrombotic effect, as it is an antagonist of vitamin K: the production of the main blood clotting factor is inhibited.
With prolonged use, aspirin can suppress the activity of cyclooxygenase in the vascular walls, which produce prostacyclin, which is responsible for blood clotting. Aspirin is often used for atherosclerosis, because. a narrowing of the lumen of the vessel occurs, which is why in patients with high blood viscosity, platelets begin to be retained with the formation of a blood clot. This threatens complete closure of the lumen and the onset of adverse consequences - stroke, heart attack, etc.
If a specialist detects atherosclerosis of the cerebral, coronary or lower extremity vessels, then it is clear that aspirin must be taken - for life.
Indications for use:
- stroke prevention;
- heart attack;
- thromboembolic complications.
Contraindications:
- Erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Increased tendency to bleed: decreased platelet levels.
- Recent hemorrhagic stroke.
- Aspirin-induced bronchial asthma.
What medications have side effects?
If you are wondering what medications cause side effects, then side effects can be observed when using any medications, regardless of their pharmacological group. To avoid negative consequences, it is recommended to strictly adhere to the dosage prescribed by a specialist and not resort to self-treatment
With the development of atherosclerotic plaques, doctors strongly do not recommend taking coagulants (Vikasol) or other drugs that can in any way increase blood viscosity (aminocaproic acid, Contrical). They provoke the formation of a blood clot and can cause the lumen of the vessel to close, which can lead to complications, including death.
When using glucocorticosteroids, hyperlipidemia and obesity develop. Some psychostimulants (Caffeine), catecholamines (Adrenaline) cause lipid metabolism disorders. For this reason, the use of these groups of medications should be discussed with your doctor.
Non-drug effects
With atherosclerosis, it is necessary to limit the consumption of foods containing large amounts of animal fats and cholesterol. It is important to increase the consumption of foods containing fiber, seafood, etc. Products not recommended for atherosclerosis:
- Chocolate.
- Cocoa.
- Fatty meats/poultry.
- Eggs.
- Dairy products with a high percentage of fat content.
- Butter.
Here are the foods that have a beneficial effect on the body:
Garlic.- Onion.
- Sea kale.
- Vegetable oils (corn, flaxseed, olive).
- Lean poultry meat.
- Seafood.
- Dried fruits.
- Any types of vegetables and fruits.
But a balanced and proper diet alone will not be enough to maintain normal cholesterol. It is important to provide the body's vascular cells with sufficient oxygen. To do this, you need to include regular walks in the fresh air and drink oxygen cocktails into the rhythm of your life.
It is also important to include regular moderate physical activity in your daily routine: running, walking, swimming, yoga, fitness, etc. Don’t forget about psycho-emotional health: stress and negative emotions do not have the best effect on the human body. Therefore, you should limit their number by changing your attitude towards the world around you.
Disease prevention
To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to follow the simple but at the same time effective rules described above. Take regular walks in the fresh air and forget about stress . If the situation is too serious and stress cannot be avoided, you should take sedatives.
Create a clear diet (diet) and include only healthy, nutritious foods that will not negatively affect blood cholesterol levels. Lead an active lifestyle by including regular physical activity in your life, but do not overload your body.
Important! Do not forget to regularly visit your cardiologist and periodically check the condition of the blood vessels in the brain, and indeed the blood vessels in general.
Remember that prevention is much better than treating cerebral atherosclerosis later. All you have to do is take care of your physical and emotional health. Love yourself and be healthy!
Causes
Atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels do not have clear causes. In most cases, cholesterol deposition is polyetiological, that is, it occurs when several provoking factors are combined:
- Causing destruction of the vascular wall and the appearance of damage on them - smoking, alcoholism, use of certain medications or poisoning with chemicals. This includes a lack of vitamins and minerals, as well as hypertension, metabolic disorders and diabetes.
- Causes of excessive accumulation of cholesterol in the blood are the consumption of large amounts of fat, liver disease, in which excess cholesterol synthesis occurs, as well as lipid metabolism disorders.
- Causing problems with the functioning of the heart and blood vessels - stress, lack of physical activity.
Older people are at increased risk of developing cerebral artery atherosclerosis. Due to the natural wear and tear of the body or many years of bad habits, they experience various vascular pathologies.
According to statistics, men are more likely to suffer from cerebral vascular atherosclerosis (65 cases out of 100). The age of most patients is 50 years or more.