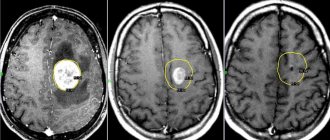
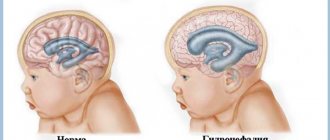
Senile degeneration of the brain is also known as senile insanity or dementia. The first prerequisites for the development of brain dystrophy can occur in a person after 60 years of age, although the weakening of memory over time is not a normal phenomenon.
The concept of degeneration means the weakening or loss of special functions of an organ. Dementia (dementia) is a chronic mental disorder in which behavioral disorders and loss of basic self-care skills are possible.
Thus, there is a violation of higher cortical functions. Senile (senile) brain degeneration is most often diagnosed in people over 65 years of age.
Types and stages of violation
In medical practice, there are three degrees of degenerative disorders in the brain:
- Mild degree . It is characterized by a loss of professional skills and apathy to what is happening around. The patient is not interested in subjects that were previously considered his hobby. In this degree of illness, orientation and consciousness are preserved.
- Average degree . The patient copes with personal hygiene skills, but may forget the rules for using household appliances. Such people often need help; leaving them unattended is dangerous.
- Severe degree . Patients lose orientation in space and are unable to serve their own needs.
Degenerative diseases of the brain can be expressed in a total or lacunar form.
- The total form of the disorder is characterized by poor emotionality and apathy. Personality degradation occurs.
- The lacunar (partial) form is characterized by impairment in short-term memory. But the “core of personality” remains.
The course of the disease occurs in stages:
- Predementia is a stage of the disease characterized by memory loss, absent-mindedness and apathy. The ability to think abstractly decreases. Thus, disturbances affect fresh layers of memory.
- Early degeneration (the second stage of the disease) is characterized by more pronounced disorders. The progressive disease is expressed in impaired motor activity and incoherent speech. The patient cannot always express his thoughts, his movements are absurd, but at the same time remnants of memory and sanity are preserved.
- Moderate dementia (third stage) manifests itself in the fact that a person begins to confuse words, does not recognize his loved ones, and partially loses reading and writing skills. There may be elements of delusion. An elderly person is able to leave home, but it is not possible for him to return back due to impaired consciousness. In addition to these symptoms, patients cease to control the natural needs of the body.
- After these stages, severe dementia . The person practically does not speak, does not get out of bed and loses the ability to perform the most basic movements. In this case, exhaustion of the body occurs. Death occurs as a result of pneumonia or bedsores that arise in such conditions.
Brain degradation. What to do?
The percentage of people complaining of difficulties with brain activity is increasing almost daily. As a rule, they experience increased absent-mindedness, namely difficulty concentrating, inability to fully concentrate on specific goals, etc. In addition, there are problems with memorizing information, as well as physical nervousness that occurs when reading large texts. There can be no question of “immersion” in books at all.
People with such disorders turn to specialists with a request to prescribe them drugs that improve brain activity and improve memory. Moreover, such disorders are observed not only in elderly people who are forced to face weakening of the brain, but also in representatives of the middle and young age categories. The peculiarity is that many people are absolutely indifferent to their condition. They don’t even try to find the reason for such changes, attributing everything to fatigue, poor environmental conditions, lack of sleep, and even age. But we note that this is not the reason for encountering problems with brain activity.
You may be surprised, but there are people 70 years of age who do not complain of poor memory, deterioration of brain activity, etc. What caused the appearance of such disorders in modern people of different ages?
Everything is very simple
The fact is that many do not want to hear any arguments and recommendations, tightly “clinging” to “information connectivity”. In other words, the rapid appearance of violations is caused by the fact that you always want to be “in touch.” And it doesn’t matter at all for what reasons you behave this way: work obligations, languishing in boredom, fear of being different from others, or something else.
According to statistics, in 2008, a large number of World Wide Web users read about 20% of the text on a resource page, while avoiding large paragraphs. In addition, studies have confirmed that people who are constantly online try to avoid reading texts, but scan them like machines, “snatching” certain pieces of information. Many people evaluate text content from the perspective of “like” or “share”, and quickly figure out whether this “cry from the heart” can be forwarded to friends/acquaintances. But they do this not in order to discuss the material, but only to get a dose of attention from the outside in the form of short remarks, comments and exclamations.
During the testing process, it was found that text pages were viewed somehow. Initially, the user pays attention to the first lines of the material, after which he immediately moves to the middle part of the text, “snatching” 2-3 lines, and lowers his eyes down to get acquainted with the end of the “story”.
In this regard, the most effective method of presenting information to a standard network user was identified - displaying any text information in the “inverted pyramid” format. That is, narrowing the text closer to the bottom, with the need to highlight significant words and phrases, showing what is important in the material and what can be excluded from attention. Moreover, in such “pyramids” one thought must be “packed” into a paragraph. Only this approach makes it possible to hold the attention of a page visitor.
If you do not adhere to the rule of “narrowing information to the bottom,” or even worse, an enlarged text appears, then only a few will focus their attention on such material.
The World Wide Web is a powerful drug, and as you know, such a substance does not provide any benefit.
Without it, people can live fully, and if someone decides to try this “poison”, then they can be called lost. The same can be said about the Internet. Having tried it once, the user becomes addicted for life, and if the drug addiction is not treated, then every “Internet addict” is quite capable of getting out of this whirlpool.
Causes and clinic of dystrophic processes
The causes of weakening of brain functions in old age may be:
- In the case of vascular dementia , a history of hypertension, atherosclerosis, and stroke is noted. Thus, the cause of this pathology is impaired blood supply to parts of the brain. For this reason, massive death of neurons occurs. In this case, the pathology is considered incurable. Cells have a low ability to regenerate in old age.
- In the atrophic type of dementia, a history of Pick's disease, Alzheimer's, and Parkinson's disease should be noted. There is cerebrovascular insufficiency here. Alzheimer's disease more often affects older women. Prerequisites for its occurrence are genetic predisposition, alcohol and smoking, severe stress, thyroid pathologies or traumatic brain injuries.
- The mixed type is characterized by a combination of vascular pathologies with atrophic changes.
Among the causes of the disease are also brain tumors, chronic alcoholism, and severe viral infections.
Vascular etiology of dystrophy
Vascular dementia accounts for 25% of cases. It develops with chronic oxygen starvation of brain cells due to vascular disorders in the organ. The cause may be congenital vascular defects, diabetic angiopathy and stroke.
At risk are people who lead a sedentary lifestyle, have an unhealthy diet and are addicted to alcohol. Patients with obesity, diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis are susceptible to vascular degeneration.
With this pathology, the patient’s thinking process is disrupted and he is unable to identify the logical connection of events. A person loses his things that are in plain sight. The appearance loses its neatness. In this state, tearfulness, apathy, and unpredictable mood swings are often observed. Due to decreased physical activity, a person sleeps a lot.
Alzheimer's type dementia
Despite the fact that this type of disease is the most common, it is very difficult to distinguish it from vascular dementia.
Often the correct diagnosis is determined after the death of the patient. At risk are women over 70 years of age, patients with atherosclerosis and diseases of the endocrine system, and people with unfavorable heredity.
At the beginning of the development of Alzheimer's brain degradation, there is a decrease and partial loss of short-term memory, and later long-term memory.
In patients, an aggressive state may predominate. They behave rudely and lack the attention of loved ones.
Progressive pathology further causes delusions of persecution, delusions of grandeur and other similar deviations.
The tendency to wander is manifested by frequent leaving home. The patient's appearance is sloppy.
Alcohol-type brain dystrophy
This condition develops in people with alcohol dependence over 10-20 years. It is characterized by aggressive behavior, impaired intellectual qualities and apathy.
But in rare cases, when you give up a harmful addiction, the pathological process regresses.
Senility
Elderly people become absent-minded, grumpy, and intractable. Forgetfulness and behavior changes occur due to aging and death of brain cells.
Patients may suffer from insomnia at night and tend to sleep during the day. Mental disorders, touchiness and tearfulness are typical for them. Apathy and even hallucinations may occur.
The cause of these disorders may be surges in blood pressure and hyperglycemia.
Epileptic dementia
This is a secondary disease secondary to epilepsy. It is also called functional dementia.
This condition is caused by oxygen deprivation and the consequences of traumatic brain injury and brain tumors. There is a decrease in memory and impaired thinking abilities, accompanied by an indifferent attitude to what is happening.
Patients become rude, selfish and vindictive. A characteristic feature is the use of most words from a poor vocabulary in a diminutive form. With this form of the disease, therapy is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause.
Signs of degradation
In this case, a person becomes infantile in his life, he does not strive to develop in life, he does not want to earn money and live better. This happens to people who inherited a weak IQ from their parents, that is, reduced intelligence. But it also happens that this manifests itself due to various mental disorders or diseases associated with cerebral circulation disorders.
In the following case, the level of reduced intelligence is characterized by certain facial features. This may include a relaxed jaw and an open mouth. Communicating with such people, you can understand that this is a weak-minded person. Typically, these signs are characteristic of alcoholics. Bad habits belong to people who are addicted to something. A person does not control himself and plunges more and more into “everything bad.” He lacks the willpower to respect his body. Gradually his personality degrades in all areas of life.
Irresponsibility characterizes people who tend to degrade. They do not see the need to be held accountable for the actions they have committed or the words they have spoken.
A person does not expand knowledge in new areas. He is not at all interested in learning about the changing climate of the planet or watching the latest news on TV.
What modern medicine has to offer
Treatment of brain dystrophy of any origin and maintaining a stable state of health of the patient consists of two main methods:
- drug therapy;
- care.
Senile brain degeneration is treated taking into account concomitant diseases, of which the patient may have many by this age. These include hypertension, pneumonia, heart attacks and strokes and many others. Patients are treated with herbal and synthetic drugs.
The first group of drugs includes psychostimulants. Their action is aimed at increasing the ability of the nervous system to adapt to stress. The second group of drugs are nootropics, the action of which is aimed at restoring memory and improving cognitive functions. This group is able to reduce the brain's need for oxygen.
Treatment of senile dementia involves the use of medications that can restore nutrition to the nervous tissue of the brain. Their effect is somewhat weakened by combinatorial treatment with drugs that improve blood supply to the organ. But the results of treatment still have positive dynamics.
Feelings of unreasonable fear, anxiety, and insomnia are treated with the use of tranquilizers. Patients may need psychotherapeutic methods of influence that can return a person to normal behavior.
Features of care
Drug therapy will not give the expected effect without proper care. The patient’s relatives should know that it is almost impossible to create the necessary conditions at home.
This is explained by the fact that at home there are a large number of objects dangerous to the patient (cutting, piercing, electrical and fire hazardous). In addition, due to the patient's possible aggression, it is very difficult to remain calm in the house. The diet of patients should be monotonous.
Their cognitive abilities are impaired, and the variety of dishes can cause unpredictable confusion. Older people need help going to the toilet. You may need to use special hygiene items (diapers).
From all this it follows that the best option is to place the patient in a specialized medical facility or care for a professional nurse.
The patient should be treated with respect. His behavior is a manifestation of a serious illness, not a character trait. With a positive attitude, good, patient care, there is a significant improvement in the condition.
Stages
The clinical picture of senile dementia is determined by the degree of brain damage. In the initial stage of the disease, the patient’s intelligence and ability to work decrease, and the skills of generating ideas and time planning are lost. Patients have difficulty making decisions. They develop distrust of others, paranoia, and difficulties in doing everyday work.
In the second stage of senile dementia, the patient's intellectual abilities disappear. A person loses basic skills in using surrounding objects. He may unintentionally cause harm to himself and his home. At this stage of dementia, the sick person should not be left alone. However, he retains his self-care skills.
At the third stage of senile dementia, a person needs constant supervision. He loses personal hygiene skills and becomes unable to take care of himself.