Home » Endocrine diseases » Pituitary tumor
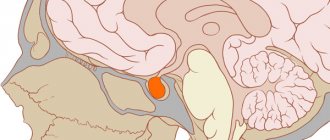
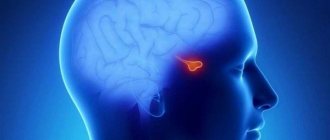
Pituitary tumors are an endocrine disease that are benign or malignant (very rare) neoplasms in the anterior or posterior lobe of the pituitary gland, an endocrine gland. Pituitary tumors occur in both men and women aged 30-40 years and account for about 15% of all intracranial neoplasms. The pituitary gland performs a regulatory function in relation to other endocrine glands and plays a great role in ensuring the constancy of homeostasis. A tumor of the pituitary gland of the brain leads to disruption of the hormonal balance of the body and, accordingly, its homeostasis, which leads to numerous pathologies.
Pituitary tumors: classification
Pituitary tumors can be malignant or benign, which are called adenomas. The most basic difference between these tumors is their functional activity. They are: - hormonally inactive (not producing hormones on their own); - hormonally active (produce one of the hormones). Among hormonally active tumors there are: 1. Somatotropin-producing adenomas. Produces growth hormone - somatotropin. 2. Prolactin-secreting adenomas (the most common - in 35% of all cases of pituitary tumors). Produces prolactin, a hormone of acidophilic cells. 3. Adrenocorticotropin-producing adenomas (occurs in 10-15%). Produces ACTH - adrenocorticotropic hormone, which stimulates the functionality of the adrenal glands. 4. Thyrotropin-producing adenomas. Produces thyroid-stimulating hormone, which activates the thyroid gland. 5. Foltropin-producing (gonadotropic) adenomas. They produce gonadotropins - hormones that stimulate the reproductive system. According to the location of pituitary tumors, they are found in the anterior part of the gland - this is the adenohypophysis (found in 75% of all cases of tumors of the gland) and its posterior part - the neurohypophysis.
Forecast of disease outcome
Timely diagnosis of pituitary pathology and its treatment provide a positive prognosis for treatment. In 93% of cases, surgical intervention helps to cope with the development of the disease. But even after it, patients may experience consequences:
- dysfunction of the reproductive system;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- adrenal dysfunction;
- vision problems;
- persistent impairment of memory, speech, attention.
Based on the results of tests and MRI, correction of the patient’s condition with medications is prescribed in order to reduce the consequences of the disease.
Recurrence of adenoma occurs in 14-16% of cases. Death from the disease occurs rarely even when the tumor is additionally accompanied by serious concomitant diseases.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=AhAJfuCf2VU
Regression of symptoms is observed in 92% of cases during surgical and drug treatment. The simultaneous combination of all types of treatment guarantees the absence of relapses during the 1st year in 82%, in the next 5 years - 68%.
Restoration of visual function usually occurs when the identified pituitary tumor was small in size and was present in the patient for less than a year. If more time has passed since the appearance of the adenoma, it is not possible to restore visual functions and hormonal balance even after surgical treatment. In these situations, the patient is assigned permanent disability.
The formation and development of adenoma in the pituitary gland is a serious disease, untimely treatment of which has serious and irreversible health consequences. And only timely consultation with a doctor will help avoid the serious consequences of the disease.
Pituitary tumor: causes
Researchers have not yet fully established the causes of these tumors. The only thing that is assumed is that they may be caused by a genetic factor. Among other things, it is customary to identify circumstances that provoke a tumor of the pituitary gland: - sinusitis of a chronic nature; - severe infectious diseases affecting the human nervous system; — traumatic brain injuries; - long-term use of hormonal drugs to normalize hormonal levels; - various harmful factors affecting the normal intrauterine development of the fetus.
Methods of treatment used
The treatment tactics for the disease are selected for the patient individually based on the manifestations of the tumor, its size, and activity. The following types of treatment are used:
- Medication.
- Ray.
- Surgical.
Drug therapy is based on the prescription of drugs that are dopamine antagonists. The method leads to shrinkage of the tumor and complete cessation of its functioning. Stage-by-stage results of therapy are monitored using test results and MRI.
Radiation therapy is prescribed when diagnosing a microadenoma with low activity. It is usually carried out in conjunction with a course of medication while monitoring MRI results. It is carried out using two methods:
- Gamma therapy.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery using a cyberknife.
During surgical treatment, 2 methods of removal are used:
- Through the nose - transsphenoidal.
- Craniotomy – transcranial.
Before starting any type of operation, the patient undergoes an ECG, X-ray, MRI, and tests to monitor hormone levels.
Transsphenoidal tumor removal is performed for micro- and macroadenomas that do not affect adjacent tissues. This type of operation is indicated if the pathology is located in the sella turcica, or extends no more than 20 mm from it. Trepanation is carried out in severe forms of adenoma by opening the skull. This method is used extremely rarely due to the risk of injury and the risk of severe complications.
Pituitary tumor: symptoms
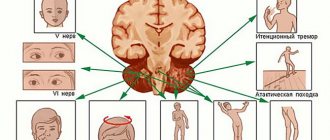
Most often (in 75%), hormonally active pituitary tumors occur, and depending on what hormone they produce, certain symptoms occur. 1. Somatotropin-producing adenomas are often the cause of acromegaly and are characterized by the following symptoms: - severe headaches; — somatics in joints and muscles; - weight gain and changes in facial features; - double vision; - increase in the size of the skull; — increase in the size of the chest and feet with palms; - impaired hair growth... 2. Prolactin-secreting tumors of the pituitary gland are characterized by the following symptoms: - enlargement of the mammary glands in men; - decreased libido; - headache; - in women, absence of menstruation... 3. Adrenocorticotropin-producing adenomas exhibit the following symptoms: - fat deposits in the face and neck; - formation of a moon-shaped face; — skin problems (thin and dry); - high blood pressure; - cardiovascular disorders; — excessive psychological “mobility” (bouts of depression alternate with euphoria). 4. Thyrotropin-producing tumors of the pituitary gland exhibit syndromes characteristic of thyroid deficiency or thyrotoxicosis. 5. Gonadotropic adenomas manifest themselves: - in men, impotence and gynecomastia; - in women, menocycle disorders and uterine bleeding. Large pituitary tumors cause a variety of nervous system dysfunctions and may be characterized by seizures, impaired consciousness, and dementia.
Treatment of headaches and seizures
Painkillers and anticonvulsants are used for therapy for a short period of time, mainly during the period of preoperative preparation. If a small prolactinoma is detected, it can be treated with medications that inhibit the formation of prolactin (Parlodel, Dostinex). Microadenomas can also be treated with gamma rays, protons, and the introduction of radiopharmaceuticals into the adenoma tissue.
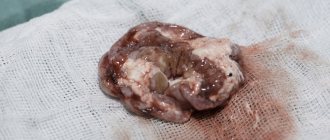
Most often, patients are recommended to remove an adenoma that does not respond to conservative techniques. A small tumor can be removed through the nasal passages, but large tumors require craniotomy and open access. The result of the operation is determined by the size of the tumor. The sooner the patient has it removed, the faster the recovery. With macroadenoma, it is possible to achieve improvement, but the risk of relapse remains.
We recommend reading the article about dysfunction of the pituitary gland. From it you will learn about the causes of dysfunction of the pituitary gland, what diseases arise from changes, symptoms in women and men, as well as methods for diagnosing and treating this pathology.
And here is more information about pituitary prolactinoma.
Compression of the growing pituitary adenoma of brain tissue causes cephalalgia and convulsive syndrome. They are often combined with visual impairment. Small tumors can manifest as pain due to disruption of the formation of pituitary hormones and changes in cerebral blood flow.
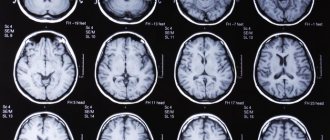
To identify a pituitary adenoma, MRI and blood tests are required; EEG and rheoencephalography help clarify the diagnosis. Treatment is usually surgical; the earlier the tumor is removed, the higher the likelihood of a favorable prognosis.
Pituitary tumor: diagnosis
If this disease is suspected, the following is necessary: - examination for hormonal levels; — neuroimaging of the tumor; - ophthalmological examinations. To identify hormonal levels, urine and blood tests are performed, which makes it possible to determine the level of certain hormones and determine the type of pituitary tumor and the degree of its activity. Neuroimaging of a pituitary tumor is done using instrumental diagnostics: - radiography; - magnetic resonance and computed tomography of the brain. Ophthalmological studies make it possible to determine the degree of involvement of the optic nerves in this pathological process. A tumor of the pituitary gland of the brain should be detected as early as possible, because... this is the key to her successful treatment.
Epilepsy with pituitary adenoma
The occurrence of convulsive syndrome is typical for large tumors, which most often grow towards the temporal lobe of the brain. The appearance of involuntary muscle contractions is caused by compression of areas of brain tissue and the development of a persistent focus of irritation in this area.
The attack may resemble epilepsy. The patient experiences severe weakness, increasing nausea and dizziness, a feeling of numbness in the lips, and a lump in the throat. After this, the patient may lose consciousness for a short time and fall. The torso and limbs are extended, and the head is thrown back. The skin becomes pale with a bluish tint, breathing is hoarse, and foam comes out of the mouth.
At the end of the attack, the muscles relax, and for some time there is no reaction to external stimuli.
Such typical signs do not always occur. Most patients note spastic contractions of the muscles of the limbs, twitching of individual muscle fibers of the face. During a seizure, as a rule, consciousness is preserved, in contrast to true epilepsy.
Pituitary tumor: treatment
There are several ways to treat these brain tumors: medication, radiation and surgery. The most radical and most effective method is removal of the pituitary tumor. As a rule, it is accompanied by radiation therapy. This method has one big drawback: when it is carried out, it “kills” the human immune system, the failures of which were the cause of the appearance of this disease. When treating a pituitary tumor, the doctor is faced with a huge problem: in parallel with the therapy, it is also necessary to raise the immune status of the patient himself, so that his body also “joins” in the fight against the disease. If this does not happen, then treatment is extremely difficult and ineffective. Moreover, it is necessary to take into account the fact that without eliminating problems with the immune system, the disease, even if it is “driven” into recession, will still return. When a pituitary tumor is removed, only a strong immune system can cope with the severe condition of the body in the postoperative period. The use of the medication method also has its drawbacks: medications cause quite unpleasant side effects, which also negatively affects the immune system. To solve these issues, the immune drug Transfer Factor is used in the complex therapy of pituitary tumors. The basis of this drug is made up of immune molecules of the same name, which, when entering the body, perform three functions: - eliminate failures of the endocrine and immune systems, and promote their further normal development and formation; - being information particles (of the same nature as DNA), transfer factors “record and store” all information about foreign agents - causative agents of various diseases that (agents) invade the body, and when they invade again, “transmit” this information to the immune system a system that neutralizes these antigens; — eliminate all side effects caused by the use of other medications while simultaneously enhancing their therapeutic effect. There is a whole line of this immunomodulator, from which Transfer Factor Advance and Transfer Factor Glucouch are used in the Endocrine System program for the prevention and complex treatment of endocrine diseases, incl. and pituitary tumors.
Treatment what you need for recovery
When a pituitary tumor is detected, treatment depends on the type of tumor. It comes in the following types:
- medicinal;
- radial;
- traditionally surgical;
- complex.
In children, adenoma is diagnosed extremely rarely, but for a young age it is a serious disease
Therefore, it is important to undergo examination in a timely manner to prevent complications that can affect the vital systems of the body. The child should be seen by a doctor at the first signs of illness.
For a favorable outcome, you must adhere to the following rules:
- regularly visit a doctor, under whose strict supervision, undergo a therapeutic course;
- do not self-medicate;
- rationally distribute time for physical activity and rest;
- avoid stressful situations and worries;
- provide the child with a rational and balanced diet;
- maintain a daily routine;
- avoid excessive mental and physical stress
If a tumor in the pituitary gland in women is treated with medication, then most often the doctor prescribes pills such as dopamine agonists, which cause shrinkage of prolactin adenomas and corticotropin. In this case, cabergoline and other medications are used to regulate the level of hormones in the body.
When surgery is not possible, radiosurgical treatment is used. It is often prescribed for elderly patients. The radiation dose depends on the size and type of tumor. But radiation therapy has a number of contraindications, for example, the tumor should not be located too close to the optic nerves. In addition, this method has side effects.
Therefore, innovative methods like cyber knife or gamma knife are often used instead. This means that the tumor is irradiated from all sides with thin pens of radiation. But the most effective treatment method remains surgery. Whether it is acceptable depends on the location of the adenoma and its size.
The tumor is removed either frontally using an optical device or by resection through the sphenoid cranial bone. In modern surgery, endonasal transsphenoidal intervention is used, that is, the tumor is removed through the nasal passage. The method is safe and does not require incisions and does not cause complications such as infection. To carry out their plans, doctors use miniature surgical instruments and an endoscopic probe.
If there is a suspicion of a pituitary tumor, treatment can be mixed. In this case, after surgical removal of the tumors, additional radiation therapy is performed and hormonal medication is prescribed. How favorable the prognosis will be depends on timely diagnosis, the size of the adenoma and its hormonal activity. In 25% of cases, prolactinomas and somatotropinomas can be cured.
But other types of tumors are successfully cured by 88%
It is important to prevent the spread of pathological processes, because it is no longer possible to restore the optic nerves at this stage
As for the treatment of children, the doctor in 89% prescribes drug therapy or hormone replacement therapy. In rare cases, if there are contraindications to the use of certain medications, then minimally invasive surgery is resorted to.
Radiotherapy is also possible. In the most extreme cases, if the formation is already too large, craniotomy is performed. Which treatment method to choose depends on the age of the child, his individual characteristics, and possible consequences.