Brain oligodendroglioma is a pathological formation that originates from glial cells - oligodendrocytes. Their function is to form special lipid membranes to protect nerve cells. Tumors of this type are characterized by slow development, so the first clinical manifestations take a long time to form, the manifestations are scanty, and sick people do not immediately notice the severity of the disease. Treatment of oligodendroglioma is always complex: the main choice is surgery to remove dangerous nodes. The life prognosis is relatively favorable, much depends on the degree of malignancy and the results of radical removal of neoplasia.
What is oligodendroglioma
The disease is a severe pathology, since the pathological process affects the membranes of the brain.
The tumor begins to form from fat cells that are part of the membrane of nerve cells. In medicine, such formations are classified as primary glial.
Depending on the degree of malignancy, they are divided into several types. Each of them has its own characteristic flow characteristics.
In some cases, oligodendroglioma is characterized by a slow course, but can grow rapidly.
After treatment, patients live for a certain number of years, but after a while death occurs. Thus, oligodendroglioma is considered a dangerous disease, which, even with treatment after a certain time has elapsed after the onset of symptoms, is fatal.
Types of tumor
Oligodendroglioma occurs:
- highly differentiated - a neoplasm characterized by slow growth and a certain shape;
- anaplastic - a neoplasm that is characterized by rapid growth, unclear forms, and is a rare tumor.
Oligodendroglioma also comes in several degrees of malignancy, with the last degree gradually developing into glioblastoma and localized in the frontal and parietal lobes of the brain.
Classification
Oligodendroglioma in medicine is divided into several subtypes, depending on the nature of the course and other features. Among them:
- Anaplastic oligodendroglioma. The neoplasm is characterized by rapid growth, the symptoms appear quite acutely.
- Well-differentiated oligodendroglioma. The pathology is characterized by a partially favorable course. The disease can occur for a long time without showing signs.
- Mixed type. It is the most severe form, as it most often mutates into glioblastoma. In this case, the tumor is difficult to treat and often causes death.
On this topic
- Neuro-oncology
How does a headache hurt with brain cancer?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 3, 2021
The type of oligodendroglioma is determined based on the results of instrumental diagnostic methods.
The disease occurs in several stages, each of which has its own specific characteristics. At the initial stages, the pathology manifests itself in the form of headaches and dizziness. As the tumor grows, clinical manifestations become more pronounced.
Causes
Experts have not been able to establish the reasons for the development of brain tumors. It is assumed that various factors can provoke tumor formation.
Age
According to statistics, most often such a neoplasm is diagnosed in patients over the age of 40 years.
Experts explain this by saying that immunity decreases with age, and external factors begin to have an even greater impact.
Gender
Oncological pathologies in which the structures and membranes of the brain are damaged are observed more often in men.
Women are less susceptible to developing the disease.
Heredity
Scientists determined that most patients with established oligodendroglioma had close relatives who suffered from cancer.
It is believed that genetic predisposition plays a large role in the development of many cancers.
Radiation therapy
Based on the data, it was found that radiation therapy previously carried out for the treatment of other diseases is also of great importance and can cause the occurrence of a pathological process.
Inflammatory diseases
According to experts, the development of a brain tumor can be triggered by diseases accompanied by inflammatory processes affecting the meninges.
Such pathologies include meningitis. In the absence of therapy or improper treatment, a tumor may develop.
Short description
Oligodendroglioma (ODG) is a highly differentiated (WHO-2), diffusely infiltrative intracerebral tumor of predominantly adult age, consisting of cells of oligodendroglial origin. Among oligodendrogliomas, there is also a malignant variant of the tumor - anaplastic ODH (WHO-3) and the so-called “mixed tumors” - oligoastrocytoma and anaplastic oligoastrocytoma.
Code according to the international classification of diseases ICD-10:
- C71 Malignant neoplasm of the brain
- D33 Benign neoplasm of the brain and other parts of the central nervous system
Histopathology. Characterized by moderate cellular density and the presence of cells with typical round nuclei and light cytoplasm (the so-called “honeycomb”, “fried egg”). Anaplastic ODH (WHO-3) differs from ODH (WHO-2) by the presence of significant mitotic activity, expressed by proliferation of the vascular endothelium. In addition, there may be necrosis in anaplastic ODH. Epidemiology. Oligodendroglial tumors account for 4–5% of all primary brain tumors, corresponding to an incidence of 0.3 cases per 100,000 population per year. The male/female ratio among patients is 3/2. The average age of operated patients is 43 years.
Localization. ODCs are usually localized in the cerebral hemispheres cortically - subcortically (in 50-60% of cases the frontal lobes are affected).
Symptoms
The clinical picture of the disease is varied. First of all, patients are diagnosed with increased intracranial pressure. A similar symptom occurs as a result of the growth of a tumor.
There is also vomiting, which does not bring relief. Nausea and dizziness occur for no apparent reason. Signs are diagnosed in 9% of cases.
Patients complain of decreased quality of vision, irritability and frequent mood swings. When diagnosed, personality changes, speech disorders and movement coordination are noted.
On this topic
- Neuro-oncology
Who needs to be tested for tumor markers for brain cancer?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- May 27, 2021
Symptoms also include hearing loss and epileptic seizures accompanied by contraction of muscle tissue. The muscles of the limbs weaken, and over time there is a complete loss of motor activity.
As the tumor develops, memory impairment occurs. Headaches are observed in 20% of cases of oligodendroglioma. The attacks are frequent and prolonged.
In some cases, paralysis of one side of the body may occur.
Diagnostics
First of all, if a brain tumor is suspected, a neurological examination is performed. It allows you to determine hearing and eye reflexes.
Testing may be performed on facial muscles, balance, coordination, gag reflex, head mobility, mental status, memory, and thinking.
Other diagnostic methods are also necessary.
CT
Computed tomography is used to obtain layer-by-layer images of the affected part of the brain and determine the extent of the pathological process.
CT is one of the most informative diagnostic methods and has virtually no contraindications.
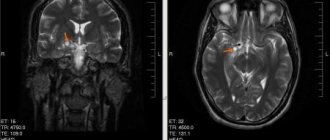
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging is used in cases where CT is not possible.
Using a tomograph, it is possible to visualize the structures of the brain and determine the extent of damage.
Audiography
The study helps determine the degree of hearing impairment that develops as a result of tumor formation.
The technique is quite informative and allows you to accurately identify all violations.
Electroencephalogram
The study is prescribed to identify brain activity and determine the activity of the nervous system.
Based on the results of the study, the degree of development of the pathology is determined. As additional diagnostic methods, a biopsy, examination of cerebrospinal fluid and other methods may be prescribed.
Treatment
Brain oligodendroglioma is treated with chemotherapy, radiological or surgical treatment. When prescribing a therapy method, the specialist takes into account the degree of development and growth rate.
Using only one treatment method will not lead to a cure. Several steps will be required.
First stage
Surgical treatment is performed using osteoplastic craniotomy. Using the method, according to anatomical accessibility, it is possible to remove the tumor.
Depending on the size of the tumor, complete or partial removal is performed. After surgical treatment, samples of biological material are sent for cytological examination. This allows you to determine the presence of cancer cells and the degree of malignancy.
Based on the results of the molecular genetic study, further treatment tactics are determined.
Second phase
Among all tumor types, the most sensitive to chemotherapy is anaplastic oligodendroglioma.
On this topic
- Neuro-oncology
What are the consequences of brain radiosurgery?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- May 27, 2021
Radiotherapy after surgery is performed in cases where other types of tumors are diagnosed. Cumulative drugs are used. The active substances of drugs accumulate in cancer cells, leading to their death.
The frequency of chemotherapy or radiotherapy courses is determined individually based on the results of diagnostic measures.
Complex of surgical and conservative techniques
As mentioned earlier, the patient undergoes surgery. It is imperative to remove the tumor and try to preserve the volume of healthy brain tissue as much as possible. Then complex therapy is carried out to maintain the patient’s normal condition and achieve long-term remission.
Surgical intervention is carried out using modern systems. MRI results help to accurately determine the location of the tumor, and CT results provide an opportunity to map out the path to achieving the tumor. As a result, the operation becomes safe and effective.
The patient may also be prescribed radiation therapy, which can suppress the growth of the tumor. During the procedure, ionized radiation is used, which does not have a negative effect on the body, but helps to obtain a positive result.
Oligodendroglioma is one of those types of tumors that can also be treated with a certain type of chemotherapy. It allows you to increase the effectiveness of treatment. It is recommended for use in cases of relapse of oligodendroglioma with signs of anaplasia. Modern methods of chemotherapy are highly effective and have low negative consequences.
Article on the topic: Heart failure - symptoms of acute and chronic
Treatment should be carried out comprehensively. The patient may be prescribed medications that help not only during therapy, but also as a preventive measure:
- antitumor agents : Hydrozine sulfate or Proxyfein;
- antimetabolites : Hydroxycarbamides, Methotrexate;
- alkylating agents : Dacarbazine, Carmustine, Lomustine, Fotemustine;
- antitumor antibiotics : Daunorubicin.
After the tumor has been removed, it is necessary to be observed by a physiotherapist. He helps to create an individual recovery plan, which consists of psychological and motor adaptation. The patient is also required to undergo an annual preventive examination, which helps to detect relapse of the disease.
Complications
If oligodendroglioma is left untreated, various complications arise. First of all, as the tumor develops, there is a deterioration in memory, attention, decreased vision, and hearing. This is due to the fact that the tumor begins to put pressure on the brain structures.
Also among the complications are various personality changes, patients suffer from mental disorders. In severe cases, the tumor spreads, affects neighboring structures, and metastatic lesions develop. Ultimately death occurs.
Forecast
When oligodendroglioma is diagnosed, the prognosis is considered relatively favorable. It depends on the location of the neoplasm and tumor growth. Treatment is quite effective only in the presence of the second class of pathological process.
The patient’s life expectancy depends on the timeliness of treatment, the degree and activity of tumor growth. On average, after complex therapy, life expectancy is about 5 years.
In the case where the tumor is removed through surgery, it is possible to significantly increase the patient’s life expectancy, in contrast to chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
On this topic
- Neuro-oncology
How quickly does brain cancer develop?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- May 27, 2021
Within ten years, only no more than 40% of patients with established oligodendroglioma survive. Timely diagnosis of the disease is of great importance for a favorable prognosis and longevity.
After therapy, experts recommend periodically checking the level of blood tumor markers.
Recommendations
Taking into account risk factors, you should:
- Avoid contact with formaldehyde, arsenic, mercury, rubber, derivatives in the production of plastics; if you cannot avoid it, then do not neglect protective equipment (doctors, firefighters, farmers).
- Avoid smoked meat products, boiled ham, and fried bacon; they contain nitrates/nitrites and secondary amines, which contribute to carcinogenesis in the body.
- Eat foods containing antioxidants that protect body cells from mutations:
vitamin C (currants, gooseberries, sauerkraut, cranberries, kiwi, dried rose hips, etc.);
- retinol, vitamin A (carrots, sea buckthorn, persimmon, chicken liver, spinach, etc.)
- tocopherol, vitamin E (wheat germ oil, cottonseed oil, almonds, etc.)
Knowing about hereditary predisposition, you should adhere to the following rules:
- Refuse to work in hazardous industries involving toxic substances; if forced contact occurs, wear protective clothing, gloves, and a mask.
- Remove smoked meats, boiled sausages, and ham from the diet.
- Include in your diet foods, vegetables and fruits with antioxidants, vitamins A, C, E: gooseberries, apples, kiwi, citrus fruits, cranberries, chicken liver, persimmon, sea buckthorn.
- Remember the dangers of smoking and avoid bad habits.
Full recovery depends on the stage at which treatment began. To detect the disease at an early stage, it is necessary to do a blood test for tumor markers every six months.