If a person has a cold of the trigeminal nerve , symptoms appear almost immediately. The patient feels a sharp pain that appears in the facial area. This nerve is considered one of the most important nodes found in the head.
For this reason, untimely treatment can lead to negative consequences and even loss of sensitivity in the facial area. When the first symptoms appear, there is no need to hesitate and wait until they disappear on their own.
The person is strongly advised to see a doctor to confirm the diagnosis and prescribe a treatment regimen.
What is the trigeminal nerve
The human face has many muscles and nerve endings. Not only the mucous membranes of the nose, pharynx, and conjunctiva, but also the nerve endings can become inflamed. This is most often associated with neurological disorders that change the sensitivity of the fibers that conduct impulses.
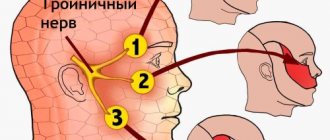
With neuropathy of the facial area, acute shooting pain occurs on the right or left. Mirror inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is extremely rare. It is located in the temporal region, near the base of the auricle. And from it there are branches along the entire half of the face:
- jaw nerve (upper and lower);
- optic nerve;
- infraorbital nerve.
The trigeminal nerve passes through the bone tissue in several places, which plays an important role in the occurrence of inflammation associated with pinching. Thus, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve can result in acute pain both in the upper and lower jaw, and in the forehead area, covering the eye sockets.
Review of effective drugs
Let's talk about how to treat a cold trigeminal nerve. In pharmacotherapy, an integrated approach using symptomatic and pathogenetic drugs is used to eliminate neuritis. The most effective in eliminating neuralgia will be:
- "Acyclovir" is an antiviral agent that helps eliminate pathogens at the site of inflammation;
- “Promedol” is an anesthetic drug that affects the functioning of the central nervous system, preventing the processing of impulses coming from affected tissues;
- "Indomethacin" is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that promotes decompression of the affected nerve bundles;
- "Dexamethasone" is a glucocorticosteroid hormone that eliminates inflammation and swelling of tissues;
- "Mydocalm" is a muscle relaxant that inhibits the reflex excitability of nerve cells.
Causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
There are several reasons leading to inflammation of the nerve ducts:
- Poor blood supply associated with physical compression of the nerve. First of all, this is swelling caused by diseases of the ENT organs. The resulting tumor can also pinch the nerves.
- Inflammation associated with dentistry. This includes gingivitis, periodontitis, caries, pulpitis, and eruption of wisdom teeth. Each of these diseases can lead to suppuration, abscesses, swelling and bacterial infections of tissues.
- Medical error by an anesthesiologist - if the injection was given unsuccessfully and the needle got into a nerve, pain cannot be avoided.
- Hypothermia causes muscles to lose their elasticity, which leads to pinching of the nerves passing between the fibers.
- Bacterial infections, in particular tetanus and polio.
- The cause of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, which is difficult to diagnose, is the psychological state of a person - frequent experiences, stress, and nervous disorders.
To determine the cause of inflammation, you need to consult a specialist.
How to treat a cold nerve?
Self-medication with medications or traditional methods is strictly contraindicated in this case.
It is also important to know that the sooner the patient seeks qualified help, the greater the likelihood of being treated with conservative means, and also of avoiding serious consequences. The doctor will recommend how to treat a cold trigeminal nerve with tablets, and what medications to take. Depending on the nature of the disease, these may be:
- antiviral drugs that can eliminate the viral pathogen that causes inflammation in the tissues and pinching of the trigeminal nerve;
- analgesics that relieve pain symptoms and thereby alleviate the course of the disease;
- antiphlogistic drugs eliminate the inflammatory process, providing decompression of the nerve roots;
- antispasmodics eliminate spontaneous muscle contraction syndrome;
- glucocorticosteroid drugs accelerate regenerative processes in tissues, while simultaneously relieving swelling;
- antiepileptic drugs (eg, Lyrica).
Lyrica is used in the treatment of neuritis and neuralgia
. If the nerve is cold, treatment at home is quite acceptable. The main thing is to follow the doctor’s recommendations and take the necessary medications according to the schedule.
When a patient at a certain age has a cold of the trigeminal nerve and does not know how to treat the disease, it is important to consult a specialist as early as possible for symptoms to manifest. The same applies to other groups of patients.
Treatment methods
Depending on what caused the inflammation, a course of treatment is prescribed. For bacterial lesions, the emphasis is on antibacterial therapy through systemic administration of drugs.
However, regardless of the reasons, the doctor prescribes painkillers to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. It could be:
- ibuprofen;
- paracetamol;
- analgin;
- ketorol;
- diclofenac.
All of the listed drugs can be prescribed either in the form of tablets for oral administration, or prescribed in the form of solutions for intramuscular administration.
When conservative methods are not possible, the help of a surgeon may be needed. This primarily concerns abscesses due to the eruption of wisdom teeth, pulpitis or other dental diseases. In this case, the abscess will be opened, pus will be removed, the wound will be treated with antiseptic, and the tooth will be removed, if necessary. If a pinched nerve occurs as a result of pathologies in the structure of the skull, the surgeon will perform an operation to correct the situation and free the nerve bundles.
As a complex therapy, massage, heating or exposure to a magnetic field and electric current can be prescribed. You cannot massage or warm the inflamed area yourself, because this can lead to complications associated with rupture of the purulent capsule, blood poisoning and paralysis of the facial nerve.
Separately, you may need to consult a neurologist who will determine the cause of the inflammation if other specialists have not found obvious foci of infection and abscesses.
Traditional methods of treatment are permissible only as an addition to the main therapy. For example, rinsing with chamomile decoction will relieve inflammation and reduce swelling. But you can resort to such procedures only with the permission of the attending physician.
Main symptoms of neuritis
What are the symptoms of a cold trigeminal nerve? Neuritis is characterized by an acute course, so when inflammatory processes occur, severe pain immediately appears, which resembles electric shocks. Depending on the type of nerve root damage, symptoms will vary slightly.
Symptoms of a cold trigeminal nerve with damage to the brain centers:
- severe attacks of pain in the facial muscles;
- discomfort and “lumbago” while chewing food;
- pain on one or the other side of the face;
- hypo- or hypersensitivity of facial skin;
- disturbances in the functioning of the eyes and ears.
In case of damage to individual branches of the facial nerve, signs of neuritis will be:
- monotonous pain in the lower or upper part of the face;
- changes in taste and auditory reactions;
- numbness of the wings of the nose, lips, chin and other parts of the face;
- hypo- or hypersecretion of fluid by the conjunctiva of the eyes.
Symptoms and treatment of a cold trigeminal nerve can certainly only be determined by a specialist. Therapy depends on the cause that provoked the development of neuritis, as well as the severity of the disease.
Possible complications
Doctors call facial paralysis the first complication that appears in the absence of adequate treatment. This means that a person who does not receive medical care in a timely manner is deprived of the opportunity to express his emotions through facial expressions on one side of his face. This condition can no longer be corrected, which will certainly affect the quality of life. Distortion of facial expressions will lead to the development of depression and constant dissatisfaction with one’s appearance. Not every patient can come to terms with irreversible changes in their appearance without deep distress.
One of the most unpleasant manifestations of paralysis is the inability to close the eyelids on the injured side of the face. In this case, the eye will have to be regularly instilled with artificial tears to prevent the cornea from drying out, since natural hydration through blinking becomes unavailable for this eye.
Symptoms
The main symptom of the disease is severe pain in the facial area. It is paroxysmal in nature and feels like small electric shocks on one side of the face.
Other signs of a cold trigeminal nerve may include:
- Increased tearing and salivation;
- Runny nose;
- Increased irritability, anxiety, sleep disturbance;
- Sensitivity disturbance in some areas of the head;
- High body temperature.
Visible signs on the face are:
- Redness and peeling of the skin;
- Twitching of facial muscles;
- Spasm of the eyelids;
- Facial asymmetry.
The first signs of a cold trigeminal nerve resemble a common cold.
Sensitivity, characterized by pain or numbness, is most pronounced in areas such as the nasolabial triangle, chin and wings of the nose. It is necessary to begin treatment at the first signs of a cold trigeminal nerve.
Prevention of inflammation
To prevent the risk of developing inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, it is recommended to follow a number of measures:
- monitor oral hygiene and consult a dentist in a timely manner;
- do not stay in the cold for a long time or protect your face from freezing with a scarf;
- do not self-medicate otitis media.
At the first manifestations of pain on the face, you should immediately consult a doctor. This will stop the development of inflammation. In addition, early diagnosis allows for conservative treatment methods.
Symptoms
As statistics show, neuritis most often manifests itself in patients of the older age group, or more precisely, over 50 years. If such a patient has caught a cold of the trigeminal nerve, treatment cannot be delayed, since the disease in this case will progress quite rapidly. For what reason the nerve was cold, what to do in this case and how to treat it, only a neurologist can determine. Self-medication in the treatment of neuritis is contraindicated.
If a patient of a different age category is admitted with suspicion of neuritis, most likely we are talking about a serious pathology in the body. Symptoms that the facial nerve is cold are manifested in the following factors:
- severe pain in the facial muscles;
- while chewing food, discomfort and painful shootings are felt - trigeminal neuralgia has appeared;
- pain appears only on one side of the face;
- the skin on the face becomes too sensitive, or vice versa – loses sensitivity. In this case, the affected part of the face may become distorted, and the corner of the mouth may go down.
Review of effective drugs
There are a lot of medications used to treat colds of the trigeminal nerve. The most popular of them are the following:
- Anticonvulsant medications. They increase muscle tone and also improve nerve patency. The pain subsides after 1-2 days of taking the drugs, and the period of time between attacks increases. Carmabazepine, Phenytoin, Clonazepam, Lamotrigine;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process in the body. Taking them also helps to get rid of pain. Ibuprofen, Nimesil;
- Painkillers and antispasmodics. Relieves pain. This is a very important group of medications, since in some cases the pain is so severe that the patient cannot lead a normal lifestyle. Baralgin, Ketonal, Baclofen, Ketorol;
- Sedatives and antidepressants. They are taken when necessary, since constantly felt pain can provoke increased anxiety and insomnia. Sodium hydroxybutyrate, Amitriptyline;
- Glucocorticosteroids. They relieve existing swelling and accelerate the process of regeneration of nerve tissue. Alclomethasone;
- B vitamins. Stimulate metabolism, reduce pain, and have a beneficial effect on the immune system. Neurobion, Neuromultivit.
Ibuprofen is prescribed to relieve inflammation in the body.
Additionally, the following may be prescribed:
- Antiviral agents. They are aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process in the body. Rimantadine, Arbidol;
- Antibiotics. Perform similar functions with antiviral agents.
The difference is that this group of medications is used in the presence of a bacterial infection. Levofloxacin, Amoxicillin.
As you can see, in order to prevent trigeminal neuralgia, it is necessary not only to monitor your health, but also not to come into contact with the flow of cold air. This can cause not only a common cold, but also more serious health problems.
Surgical intervention
Surgical elimination of the cause of neuralgia is used in case of ineffectiveness of drug therapy or when pain persists.
There are two surgical methods:
- microvascular decompression;
- radiofrequency destruction;
The first method is trepanation of the posterior part of the cranial fossa. The trigeminal nerve root, which compresses the blood vessels, is separated. A special gasket is placed between the spine and the vessels to prevent compression to prevent relapses.
The radiofrequency destruction method is not so traumatic and is carried out under local anesthesia; current discharges are directed to the affected area, they also destroy the roots of the trigeminal nerve, which are susceptible to pathological processes.
Sometimes one operation is enough, otherwise the effect is repeated several times.
Massage
Massage for trigeminal neuritis increases tone and relieves excess muscle tension in certain muscle groups. Blood supply and microcirculation in the inflamed nerve and in the affected superficial tissues improve.
The impact on the reflex zones at the exit points of the branches of the trigeminal nerve of the facial, ear and cervical areas comes first in the massage, after which they work with the muscles and skin.
The massage is performed while sitting, leaning your head back on the headrest to relax the neck muscles. Attention is focused on the sternocleidomastoid muscle, thanks to light massaging movements. Then, with stroking and rubbing movements, they move up to the parotid areas, after which they massage the healthy and affected sides of the face.
► The procedure lasts about 15 minutes, on average there are sessions per course of treatment.