What is a concussion?
A concussion is damage to the bones of the skull or soft tissues, such as brain tissue, blood vessels, nerves, and meninges. An accident can happen to a person in which he can hit his head on a hard surface, this is precisely what entails such a thing as a concussion. In this case, some disturbances in brain function occur that do not lead to irreversible consequences.
There is no exact description of the course of all stages of this pathogenic process, but most experts argue that during a concussion, dysfunctions of nerve cells occur: their nutrition deteriorates, a slight displacement of the layers of brain tissue appears, and communication between brain centers collapses. As a result, multiple microbruises, numerous minute perivascular edema and hemorrhages develop. In this case, obvious morphological changes and changes on MRI are not observed.
A severe concussion is dangerous because it can cause serious injury to certain areas of the brain or rupture of blood vessels inside the skull.
Such a traumatic brain injury can cause a person to lose consciousness for anywhere from a couple of seconds to several minutes. The severity of the concussion is determined by the time spent unconscious. The extreme form is coma.
When the victim comes to, he often does not understand where he is or what happened to him. Sometimes he doesn’t recognize those around him. The severity of the injury can also be judged by retrograde amnesia: the longer the period of time lost from memory, the more serious the damage. The appearance of these signs is due to the fact that the vital centers of the brain are affected - the regulation of breathing and cardiovascular activity.
In the first hours or days after a concussion, the victim turns pale, complains of weakness and dizziness, and tinnitus. The headache is pulsating in nature and localized in the back of the head. Nausea and vomiting may appear, breathing becomes more rapid, and the pulse may change towards faster or slower. After some time, these indicators normalize. Depending on the injury itself and the accompanying stress factors, blood pressure can either quickly return to normal or rise. Body temperature remains unchanged.
Due to dysfunction of the nerve cells of the brain after a concussion, negative phenomena in the organs of vision are observed: pain when moving the eyes, difficulty focusing the gaze, constricted or dilated pupils, pupils of different sizes, divergence of the eyeballs when reading.
There may be other symptoms: sweating, flushing, discomfort or sleep disturbances.
During the first two weeks, the general condition of the victim improves. However, it should be borne in mind that health problems can last much longer. For example, headaches in those who suffer from hypertension are particularly intense.
With a concussion, symptoms are largely subjective. They are often determined by the age factor. In infants and young children, concussion occurs without loss of consciousness. During the impact, the skin (especially the face) turns pale and the heart rate increases. A little later, drowsiness and lethargy appear. When feeding, regurgitation and vomiting occur more often than usual. Sleep disturbances and general anxiety are noted.
In preschool children, all symptoms of a concussion disappear within two to three days.
Young and middle-aged people lose consciousness at the time of injury much more often than children and the elderly. At the same time, representatives of the older generation exhibit pronounced disorientation in space and time.
Typically, for most people, the neurological symptoms of a mild concussion resolve within a few weeks. However, after any concussion, energy metabolism in the brain remains in an altered state for a long time (a year or longer).
Treatment
The main task in treating a concussion, both at home and in a hospital setting, is rest and bed rest for a period of one and a half weeks to two.
Rest should be not only physical, consisting of minimal physical activity of the victim, but also psycho-emotional (exclude nervous tension, it is not recommended to watch TV, read, listen to music).
Drug treatment for concussion is based on relief of concussion symptoms and includes the following medications:
- Sedatives, the most popular of which are valerian, motherwort, and Corvalol.
- Sleeping pills: donarmil, relaxone, phenobarbital.
- Painkillers are prescribed to relieve headache attacks. For these purposes, analgin, pentalgin, dexalgin are prescribed.
- Drugs that help eliminate dizziness (Betaserc, Vestibo).
- Medicines with a general strengthening effect (complexes of vitamins and minerals, antioxidants and tonics).
In addition to traditional medicine, traditional medicine recipes can also be used in complex home therapy. Almost all of them have a calming effect. Among them the most popular are:
A mixture of motherwort, mistletoe, mint and lemon balm . To prepare, you need to take 100 g of dry crushed motherwort, mistletoe and mint plants, add 75 g of lemon balm. Pour the mixture into half liters of boiled water, leave overnight, take 50-100 ml. 3-4 times a day.
Thyme based infusion . To prepare, you need 10 g of herb, pour 300-400 ml. water, bring almost to a boil, then turn off the heat. Let the broth cool, strain and take 100 ml. before meals. This recipe must be consumed for up to six months; it promotes stable functioning of the nervous system.
Alcohol tincture of Aralia . To prepare 10 g of the plant, add 100 ml. alcohol or vodka. Infuse for about 3 weeks, take 30 drops in the morning and at lunchtime. The tincture helps normalize brain function.
St. John's wort decoction . To prepare, pour 2 teaspoons of dry herb into a glass of boiling water, boil for 5 minutes, then cool, strain and consume a third of a glass three times a day.
Symptoms of a concussion
In order to help a person with a traumatic brain injury due to an accident, it is important to identify the symptoms that accompany a concussion. It should be noted that not all of the following symptoms may appear immediately. It all depends on the severity of the concussion; some symptoms may not appear at all.
The most common symptoms of a concussion are:
- Nausea and gag reflex in the case when it is not known what happened to the person and he is unconscious;
- It is normal to have a headache after hitting someone's head;
- The victim wants to sleep or, on the contrary, is hyperactive;
- Loss of coordination also indicates a brain injury, and the person also feels dizzy;
- One of the most important symptoms is loss of consciousness. The time of loss of consciousness can be long or, conversely, short;
- It is necessary to check the size of the pupils: with a concussion, pupils of different shapes are possible;
- Direct confirmation of concussion seizures;
- If the victim is conscious, he may experience discomfort in the presence of bright light or loud sound;
- When talking to the victim, he may experience confusion. He may not even remember what happened before the accident;
- Sometimes speech may not be coherent.
After some time, all signs of a concussion weaken and completely disappear. If symptoms persist for a long time, this may indicate more serious disturbances in the functioning of the brain. Perhaps this indicates cerebral edema, bruise or cerebral hematoma.
The difficulty of diagnosing this condition in some cases leads to underestimation of the degree of damage to the skull bones as a concomitant injury. This occurs when, during a fall in the event of an epileptic seizure or during alcohol intoxication, a person hits his head on a hard surface. The result of this is a fracture of the internal vitreous plate of the skull bones. There are no external injuries at all; only a mild concussion can be diagnosed or there are no symptoms at all.
Compression of brain tissue due to an intracranial hematoma obtained during a concussion manifests itself in severe symptoms only 10-14 days after the injury. This complication grows in stages; its treatment requires emergency surgical intervention, the result of which cannot be predicted. Appearances like these highlight the importance of accurately diagnosing concussion symptoms and getting prompt medical attention.
First aid
If a concussion does occur, you must adhere to the following algorithm of actions. What to do if you have a concussion.
The first action is to call a medical ambulance . First aid for a concussion is to lay the patient down, with the head on an elevation, and do not allow the victim to fall asleep, eat or drink. It is strictly forbidden to suddenly move or transport the patient; you should also not give medications without prior examination by a medical professional.
If the victim experiences numbness and immobility of the limbs, this indicates possible damage to the spinal cord. In this case, moving the victim is contraindicated.
It is better to unbutton the clothes on the patient’s body so that nothing restricts breathing, do not create a crowd, in order to ensure normal access of oxygen to the victim. Ensure normal patency of the upper respiratory tract. If the patient is unconscious, to ensure breathing, you should turn your head to the side and stick out your tongue.
If for some reason it is not possible to call medical help and it is necessary to transport the patient yourself , transportation is allowed in a supine position in the back seat. In order to bring the victim to consciousness, you can use a piece of cotton wool moistened with a few drops of ammonia.
Causes of concussion
A concussion can be caused by bruises, blows, or sudden movement (either acceleration or deceleration). The most common cause of concussion is road traffic accidents, work-related, sports or household injuries.
Criminal circumstances can also play a negative role.
Mechanical causes of traumatic brain injury
The axial load on the brain produced by the spinal column during an insufficiently cushioned jump or a sudden fall on the buttocks can, just like a direct impact on the bones of the skull, lead to a traumatic effect on the brain.
Having an understanding of the mechanisms of brain injury, it is possible to predict the consequences of even the most minor forms of concussion in various age categories.
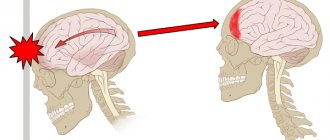
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which fills the closed space between the brain and the bones of the skull, protects the brain “floating” in it from serious physical influences. During a sudden impact, the brain continues to move in the opposite direction by inertia for some time. The pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid between the inner shell of the skull and the brain at this moment increases many times. As a result, the brain receives a mechanical or hydraulic shock.
A counter-impact on the side opposite to the area of high pressure creates an impact of the same force with a minus sign. Forced vibrations produced by the brain “floating” in the cerebrospinal fluid expose it to repeated damage. In addition, the brain receives additional trauma as a result of its rotational displacements around its axis, as a result of which it hits the protrusions of the skull. There is a directly proportional relationship - the more sudden and strong the mechanical impact, the more significant damage to the brain.
Biological causes of traumatic brain injury
The vessels of the brain do not receive significant damage during this injury, but the concussion triggers a mechanism of inadequate reactions of the vessels themselves, nerve cells of the brain and intracranial nerve pathways. Studies conducted with animals, after modeling a concussion in them, showed the following results: when examining brain tissue under a microscope, displacements of the nuclei of nerve cells, damage to their elements - membranes, mitochondria, as well as pathologically altered space between them, an increase in the size of axons (nerves) were discovered. fibers).
Such damage indicates that a traumatic brain disease is occurring.
Symptoms of traumatic disease:
- Pathological dilatation of cerebral vessels, which occurs after their initial spasm, leads to impaired cerebral circulation. It is quickly restored with a mild concussion, but this recovery occurs unevenly in different parts. Complications of this process include slowing blood flow, vascular congestion, and intracellular edema.
- Changes in the metabolism of brain structures, colloidal balance, chemical and physical properties of the brain matter, resulting from changes in intracranial pressure at the time of traumatic exposure. Studies conducted with experimental animals have documented increased vulnerability of nerve cells in rodents, disruption of extracellular and intracellular ion metabolism, and an imbalance between the energy supply from blood cells and the need for it.
- A short-term disruption of axonal conductivity, expressed in the loss of relationships between nerve cells and the centers regulating their vital functions. At the same time, the structure of the nerve tissue maintains its physical integrity.
- Impaired coordination between important functional centers of the cerebral hemispheres (breathing, thermoregulation, cardiovascular activity) due to a breakdown in connections between them and the rest of the brain due to rotational displacement.
Analysis of the mechanism of concussion makes it possible to adequately assess the symptoms of injury and first aid tactics.
A sleepless night is tantamount to a concussion
According to a study conducted by Swedish scientists, a night without sleep, regardless of the reason for it (insomnia, night shifts, entertainment), is equivalent in its consequences to a concussion. A sleepless night has a negative impact on a person’s health, performance and mood.
Their findings were confirmed by an experiment conducted at Uppsala University with 15 volunteers in excellent health. The results of blood samples taken from participants after a sleepless night were analyzed. Brain damage was indicated by 20% increased levels of calcium binding protein (S-100B) and neuron-specific enolase (NSE). This is a dangerous sign, since the indicators differ from the norm, but are close to similar indicators in patients after a concussion.
During a sleepless night, the tissues of the human body do not cleanse the tissues of the human body at the cellular level from toxins received while awake. Disruption of this physiological process leads to an increase in the concentration of markers in the biochemical parameters of the blood, similar to the same results after a concussion. The symptoms experienced by those forced to spend the night without sleep are similar to those of a concussion: headache, noise in the head, impaired memory and attention, nausea.
Toxins tend to accumulate in the body, so several sleepless nights in a row are comparable in severity to physical trauma to the brain.
How to get a concussion
Knockout in boxing
The easiest way is to call a boxer friend with a good knockout punch.
A concussion usually occurs during a swing, less often during a direct blow, and even less often during an uppercut to the chin.
However, if someone wields a knockout uppercut, such a blow will almost certainly cause a concussion, since the design of the head is not naturally designed to withstand blows from below.
When using an uppercut, you need to put on a mouthguard - otherwise you can split your teeth. But such boxers are rare; it will be easier for him to hit a direct or side blow to the cheekbone. There are good side strikes with the “teisho” plane - the base of the palm. They are more likely to cause a concussion than a fist, but few people wield them.
It is advisable to avoid blows to the temple - without gloves, a 3-4 mm thick bone can be broken even with a not very strong blow. Ask your partner to hit the cheekbone. For a good blow, he will need to stand for several seconds. It is useless to hit him in the forehead - the blow will be absorbed; the design of the head resists such blows best of all. In other parts of the head from above, in the back of the head - just as dangerous as in the temple.
Punch in the face
The safest thing is a blow to the face, but there is a risk of not only getting a concussion, but also a fracture of the upper or lower jaw.
On the other hand, a hematoma on the face will be evidence that a concussion was received.
A blow to the nose will also bring nothing but bleeding and a broken nose.
The second way is to get a concussion at home from a fall.
The problem is that a person will reflexively stop himself from falling and hitting his head on the floor.
Therefore, you will also need a partner. The sequence of actions is as follows:
- Free up space in front of you on the floor near a wall or cabinet - God forbid you get caught with some dumbbell or metal nut on the floor.
- The floor must be wooden - otherwise there is a risk of serious damage.
- You need to squat down near the wall and prepare a thick, wide scarf or belt.
- Take twenty to thirty deep breaths.
- Stand suddenly near the wall - the partner immediately takes a thick scarf and presses his neck against the wall.
- Consciousness will begin to disappear.
- Until the legs completely give way and the body slides smoothly down, the partner must jerk the body around, put on the step and forcefully throw the back of his head on the floor.
- There will be no pain when falling; consciousness, if everything is in order, should return in a minute.
In this case, the situation is safer than with a punch to the back of the head, since the blow falls over a larger area.
Dangerous ways:
- Jumping from a height onto your feet, which are spread slightly wider than your shoulders onto the asphalt, can seriously damage your knees.
- A blow with a heavy object, a stack of books, a plastic bottle with water or a piece of wood - the force of the blow is unpredictable; if hit with full force, the pain can even split the skull.
The stupidest thing you can do is to tell the military registration and enlistment office with a satisfied smile that you got a concussion on purpose so as not to serve in the army. According to the law of the Russian Federation, evasion of military duty by self-mutilation is punishable by imprisonment for up to 8 years.
Complications of concussion
The list of complications possible after a traumatic brain injury is very diverse. The most common is the so-called “post-concussion syndrome.” After some time - and this can be days, months, and sometimes even years - a person begins to experience headaches. These pains can be excruciating—a headache-like sensation, so to speak. A person is bothered by anxious thoughts, he gets irritated, and cannot concentrate on something specific. Sleep is disturbed and it becomes very difficult to do work.
In such a situation, it is necessary to begin treatment with medications. Seeing a psychotherapist does not bring relief. When prescribing narcotic painkillers, it is important to remember the negative consequences of drug addiction.
For treatment, it is very important to maintain rest and strict bed rest. There should be no bright light in the room to avoid pain. Medications used include sedatives, hypnotics and painkillers. Elderly people are treated for multiple sclerosis and accompanying diseases.
In order to avoid complications after a traumatic brain injury, it is necessary to undergo clinical observation for one year by a neurologist in a clinic at the place of residence.
In people who practice boxing, “boxer's encephalopathy” may occur as a complication. Its symptoms are as follows: imbalance, mental changes and trembling of the limbs.
How to recover at home?
The recovery process after a concussion should last at least one year.
Throughout this year, it is necessary to follow a special diet, which consists of easily digestible foods; if possible, the patient should not drink alcohol, energy drinks, coffee and similar drinks. This way, the body can focus on restoring normal brain function after the injury. also necessary to strictly follow the instructions of your doctor , visit a neurologist from time to time, do not skip medications, and give your body a little physical activity.
Important! In order for the recovery process to proceed quickly, the patient should not overload himself with physical or mental work.
So, we looked at how long and how a concussion is treated. Pathological changes that occur as a result of a concussion are reversible. It is important to consult a doctor in time to avoid all sorts of complications.
Diagnostics
An accurate diagnosis is made by a traumatologist based on the existing signs of a mild concussion and the results of the examination.
First of all, the doctor conducts an external examination, finds out the circumstances of the injury, and checks the reflexes. If a more severe injury is suspected, the patient is referred to a neurologist. To establish a diagnosis, the following diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- Radiography.
- Spinal tap.
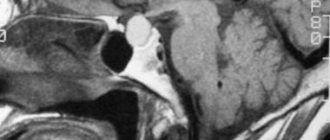
- CT and MRI.
- Electroencephalography.
- Echoencephalography.
Doctors use the Glasgow scale to determine the severity of a brain injury. The essence of diagnosis is to conduct several tests, on the basis of which each patient is given a certain number of points from 3 to 15, depending on the reaction.
A mild concussion is diagnosed in cases where the doctor establishes a score of 13 or more on the Glasgow scale. Based on all studies, examination and observation, the specialist determines whether there is a risk of complications.