The main organ of the central nervous system, which is involved in controlling the activities of all other organs and systems, is the brain. Its structure includes functional cells and neurons. In some cases, when exposed to negative factors, the formation of a tumor-like neoplasm in this area may occur. According to statistics, brain cancer accounts for 10% of the total number of oncological pathologies. If there is a brain tumor, how long can a person live with it? Read more about this and other issues in the article.
Features of the development of brain tumors
The disease was assigned a code according to the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10 code) – C71.
The frequency of diagnosing a brain tumor is 10-15 cases per 100 thousand people. Cancer can appear in both women and men in equal percentages and at any age.
The manifestation of tumors in the brain can be primary or secondary. The primary type of disease occurs directly in the brain tissue, and in the second - as a consequence of the spread of malignant cells (metastasis) from another pathological focus. It is the secondary tumor that is diagnosed several times more often than primary tumors.
A child is susceptible to pathology in the same way as an adult
A feature of neoplasms in this area is that their location can only occur in a limited intracranial space. That is why any large tumor can cause compression of brain tissue and increase intracranial pressure.
Even a benign type of tumor, when enlarged to a voluminous size, can become a malignant type and thereby cause irreversible consequences, including death. For this reason, it is important to identify the beginning symptoms of the pathology in order to begin appropriate therapy in a timely manner.
Classification of tumors
This type of cancer includes both benign and malignant neoplasms, which differ from each other in the cause of development, their distribution, symptoms and prognosis.
To date, there is no unified classification of brain tumors. This can be explained by their diversity and difficulty in diagnosis. The most accurate classification is considered to be one in which oncological tumors are distinguished by histological structure and degree of maturity.
Based on the degree of maturity, there are 2 types of neoplasms:
- malignant (glioblastoma, etc.);
- benign (gliomas, etc.).
Considering the area of the brain in which the tumor developed, neoplasms are distinguished:
- inside the brain;
- inside the ventricle;
- outside the brain;
- in the intermediate zone: embryonic, teratomas;
- according to the type of metastatic nodes, cysts (in the frontal and other lobes).
Taking into account histogenesis, experts distinguish the following types of neoplasms:
- neuroepithelial, which are formed from the medulla;
- meningovascular, which are formed from the membranes of the brain;
- pituitary adenomas;
- neoplasms, derivatives of mesenchyme;
- neoplasms from the nerves of the skull;
- teratomas that form as a result of impaired embryogenesis;
- metastatic neoplasms (the so-called tumors that develop from malignant cells spread from another primary focus).
The most common benign tumor is meningioma, which is formed from cerebral vessels. If such a neoplasm is diagnosed at the initial stage of its development, one can hope for a favorable prognosis. The only exception is the localization of meningioma in the trunk. Even with a small tumor size, compression of nerve tissue can occur and serious disorders can develop.
Common malignant neoplasms are glioblastoma and medulloblastoma. Medulloblastoma has a high level of malignancy, as it is formed from the least immature cells - medulloblasts. The main source of formation is the development of dysgenetic changes.
Glyblastomas in most cases form in people after 40 years of age. The tumor is characterized by rapid progression, has no clear boundaries, and is prone to secondary changes (even with timely treatment) - necrosis, hemorrhages, cysts.
Metastatic tumors can be classified as a separate group of brain tumors. Pathogenic cells most often spread to the brain from a neoplasm located in the mammary gland, lung or kidneys.
Types of cancer stage 4
There are four types of stage 4 tumors:
- relatively benign tumor;
- malignant formation with minor signs;
- malignant neoplasm;
- neoplasms are rapidly developing, which in most cases cause the death of the patient.
An accurate diagnosis is made based on studies of cancer cells. If new cells on the surface of the vessels of the lymphatic and circulatory system are formed and grow at high speed, and dead cells are found in the tumor tissues, stage 4 of the tumor is determined.
The neoplasm does not have to go through all stages. Sometimes it happens that stage 2 of the disease or stage 4 is discovered. It cannot be that the tumor was benign in nature, and after some time turned into a malignant formation.
Causes of brain tumors
The main sources of tumor formation include:
- Genetic predisposition. If any close relative in a person’s family has such a pathology, the risk of its formation also increases in him.
- Living in an unfavorable environmental environment. It is impossible to say exactly what the relationship between ecology and the formation of malignant cells is. First of all, the negative impact is caused by: nutrition, strong electromagnetic and other fields of unnatural origin, carcinogens. One can only ascertain the formation of a tumor and begin to carry out appropriate therapeutic measures.
- Professional factor. If a person is engaged in professional activities that involve exposure of the body to radiation or other harmful substances (radiation), this increases the risk of tumors.
Frequently talking on a mobile phone increases the chances of developing a tumor
Carrying out chemotherapy and radiation therapy in the past, organ transplantation, the development of infections in the body - all these factors can affect the formation of tumors in the brain by suppressing the functions of the immune system. Other risk factors include age (after 55 years) and race (white people are more susceptible to the disease).
Is there any hope for recovery?
Looking back, we can say with confidence that we are lucky to live in the age of high technology. Today, domestic medicine has all the capabilities to provide high-tech treatment. Firstly, this is an accurate diagnosis, thanks to which it is possible to differentiate active tumor tissue from healthy brain tissue, assess the actual extent of spread and monitor the dynamics of treatment. Secondly, the use of the latest drugs to control the disease. And, of course, the development of surgery and radiation therapy. Modern radiation therapy is developing towards the most precise irradiation of the tumor with minimal involvement of surrounding healthy tissue. Radiosurgery is at the forefront of high-precision radiation techniques.
The use of this technology makes it possible to cure many benign brain tumors and intracerebral metastases without trephination, pain and a long recovery period.
Despite the fact that “brain cancer” has not lost its threatening significance, you definitely shouldn’t be afraid of it - primary malignant brain tumors are statistically quite rare. The incidence rate of the most “evil” tumor, glioblastoma, is about 3 cases per 100 thousand population.
The main thing to remember is that the earlier the disease is detected, the greater the chances of a favorable outcome. This applies equally to malignant and benign tumors. “Folk methods” should be avoided, as there is no reliable evidence of their effectiveness. Self-medication can be fatal, while modern technologies improve treatment outcomes for millions of patients year after year. The best means of prevention is a healthy lifestyle and careful attention to your own health.
How symptoms occur in pathology
The clinical picture of tumors in the brain is divided into 2 groups:
- Focal clinical manifestations.
- General cerebral clinical manifestations.
Focal symptoms depend on the area of tumor localization, the level of compression of nerve endings and the degree of tissue destruction. General cerebral symptoms appear against the background of progression of pathology and involvement of other brain structures in the process.
Focal symptoms
The first sign of brain development is an increase in the sensitivity of the skin. As the tumor grows, the skin begins to become too sensitive to touch, heat or cold.
Recognition reflexes are impaired. The patient's hearing function decreases (to the point of complete hearing loss) due to involvement of the auditory nerve in the lesion. Visual function is also impaired, both partially and completely. Due to compression of the part of the brain responsible for the perception of images by the tumor, a person becomes unable to read and recognize surrounding objects.
Coordination of movements is impaired due to the formation of a formation in the cerebellar area. You can notice how the patient's gait gradually changes. Partial or complete paralysis of certain areas of the body also occurs, which can be explained by a disruption in the flow of impulses from the brain to the spinal cord and muscles.
At the early stage of tumor formation, the patient’s speech is slurred, and his handwriting also changes. Over time, as the tumor progresses, such disorders only increase in intensity and it is almost impossible to understand what a person is talking about.
There is a decrease in memory, mental activity, and concentration. In addition, irritability increases, the patient quickly gets tired, even with light physical exertion. He is unable to remember the names of objects, names, or remember recent actions.
Hormonal levels are disrupted. The reason for this is the formation of a formation in the part of the brain that is responsible for the production of hormones. Vegetative-vascular dystonia can also be observed, the symptoms of which are dizziness, increased heart rate, general malaise, and pressure changes.
General cerebral symptoms
A person with a brain tumor may experience constant headaches. The intensity of the pain increases in the morning after waking up, as soon as the person makes the first movements. Medicines are ineffective and cannot cope with this symptom. The severity of headaches is similar to attacks of intracranial hypertension. A common symptom of a brain tumor is dizziness. The symptom is caused by compression of the cerebellar tissue.
The tumor-like formation causes increased pressure inside the skull and compression of the structures responsible for the gag reflex. As a rule, even vomiting does not help relieve attacks of nausea, because it is of high intensity. At the same time, a person quickly gets tired due to impaired blood flow and insufficient oxygen exchange in the brain.
Survival of patients with brain cancer
Survival rates for patients with brain tumors depend on the type of tumor, the patient's age, and a number of other factors. For some types of tumors, such as ependymoma and oligodendroglioma, the 5-year survival rate of patients is more than 80-85%. The most malignant tumor is glioblastoma multiforme: only 13% of patients with this tumor live more than 5 years.
Review of breast cancer treatment in Israel
In September 2015, I felt a lump in my left breast. I'm not an alarmist, but I knew what this could mean. I had an appointment in a month with my OB/GYN, so at first I thought I'd wait and talk to my doctor about it.
I had a mammogram just six months ago. But after studying information on the Internet, I realized that to be safe, I need to meet with a doctor earlier.
Read more…
Review of pancreatic cancer treatment in Israel
Five years before I was diagnosed, I was working out four times a week and was in great shape. Friends noticed that I had lost a lot of weight , but I just thought it was due to my active lifestyle. During this time I constantly had stomach problems. My doctors recommended over-the-counter medications.
I also had constant diarrhea for a month. My doctors didn't find anything wrong.
Read more…
Feedback on treatment of cervical cancer in Israel
At the beginning of 2021, I took my doctor's advice and had a colonoscopy. I've never done this before. My doctor showed my husband and me a picture of my colon. Two polyps were visible on the image. The doctor pointed to the first spot on my colon, reassuring us there was nothing to worry about. He then pointed to another area and told us that he thought it was cancerous. During the procedure, he took a biopsy and the tissue was analyzed.
Read more…
Review of prostate cancer treatment in Israel
In 2011 I started having acid reflux. It was uncomfortable and worrying, so I went to our family doctor for a check-up. During the visit, he asked me when was the last time I had my canine antigen tested, a routine test that many men do to check for possible signs of prostate cancer. It had been about three years since I had this test done, so he added it to my appointment that day.
Read more…
Review of brain cancer treatment in Israel
My story begins with numbness. One day in 2012, three fingers on my left hand suddenly lost feeling. I immediately made an appointment with the doctor. By the time the doctor was able to see me, everything had already passed, but my wife convinced me to go for a consultation. I had an x-ray to see if there was any evidence of damage to my spine, possibly from driving the truck. When some...
Read more…
Review of ovarian cancer treatment in Israel
In the winter of 2010, when I was 30 years old, I felt a sudden pain in my right side. The pain was sharp and began without warning. I immediately went to the nearest hospital.
The doctor received the results of my blood test and he saw that my white blood cell count was extremely elevated . The doctor and others who saw these results were alarmed and asked the on-call gynecologist to come see me right away.
Read more…
Review of lung cancer treatment in Israel
I struggled with an intermittent cough for about three years . It appeared in winter and disappeared by spring, and then I forgot about it. But in the fall of 2014 this happened earlier. In October, my wife called a local pulmonologist. We were scheduled for our first meeting in three months.
... At the Ichilov Cancer Center we met with a thoracic surgeon. We decided to completely remove the nodule. Read more…
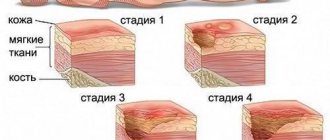
Stages of the pathological process
In medicine, there are 4 stages of brain cancer. Modern diagnostic methods and tests make it possible to accurately determine the degree of organ damage and prescribe effective treatment in a timely manner. If a brain tumor is diagnosed, how long you live with it depends on the stage at which it was detected.
Stage 1
A mild degree of pathology occurring in the brain is characterized by headache, dizziness, and increased fatigue for no apparent reason. A person attributes the first symptoms to banal overwork, without attaching any importance to it.
In this phase of tumor development, it is impossible to identify a malignant process only by the symptoms that arise, because they have many similarities with other pathologies. Often a tumor is diagnosed by chance, during the analysis of a completely different disease, for example, according to the results of a computed tomography scan.
When the disease is detected at this stage, there is a 100% survival rate.
Stage 2
Compression of areas adjacent to the tumor causes damage to the blood vessels. Clinical symptoms at stage 2 are still nonspecific: headache, dizziness, impaired coordination of movements. Over time, there is a loss of weight, nausea, blurred vision (“floaters” in front of the eyes, flickering, etc.).
Stage 3
The tumor grows and spreads its metastases to the deep medulla, to the auditory and visual centers, and to the departments responsible for sensory and motor functions. Specific symptoms of the disease at stage 3 are severe headache, which is present on a constant basis, nausea and vomiting syndrome, unsteadiness of gait, increased general temperature, and rapid fatigue.
It is impossible to relieve vomiting and headaches with medications. It is difficult for the patient to move without assistance. The lesion involves the lymph nodes, as well as other internal organs, which can be explained by the spread of metastatic cells.
Stage 4
Stage 4 brain cancer is characterized by constant headaches, vomiting, paralysis and paresis, blurred vision, seizures, and fainting. The intensity of all clinical manifestations is higher than in previous stages.
Also, stage 4 brain cancer occurs with intoxication syndrome. This is a sharp weight loss, uncontrollable nausea and vomiting syndrome, loss of appetite, exhaustion. It is difficult for a person to move and even stand.
Brain tumor symptoms
The tumor can develop inside the brain or get along with metastases from other organs through the bloodstream.
Brain
Depending on the location of the tumor, symptoms characteristic of this type are distinguished:
- headache, one of the first and very important signs of the onset of an illness; bursting pains that appear in one place, often at night, closer to the morning, and occur with the slightest movements;
- dizziness;
- nausea, feeling of heaviness in the stomach, vomiting;
- mental abnormalities in behavior, mood swings, sudden tearfulness, touchiness, irritability; decreased attention;
- loss of appetite, weight loss; fatigue;
- difficulty speaking, forgetfulness, finding the right words; slow pace of speech;
- difficulty in recognizing objects;
- impaired consciousness and perception of others;
- disorder in coordination of movements, unsteady gait;
- paralysis of any part of the body;
- hallucinations;
- auditory and visual impairments;
- disorders in the hormonal system;
- coma.
Diagnostics
The presence of a tumor requires confirmation of the diagnosis in order to prescribe treatment. This will determine how long the sick person will live after surgical treatment.
In addition to the usual examinations during MRI, CT, ultrasound, X-ray, a visual examination of the fundus of the eye and the condition of the blood vessels passing through this organ are carried out. If any disturbances appear, there is a loss of visual acuity and hearing.
CT scan of the brain
The vestibular system also suffers, so the doctor collects a complete history to clarify the diagnosis.
Diagnostics
The first stage of diagnosing the disease is a consultation with a neurologist. The doctor examines the motor function of the eyes, hearing, tendon reflexes, the level of sensitivity of the skin and sense of smell, coordination of movements, muscle tone, balance. If there is a suspicion of the presence of a neoplasm, instrumental diagnostic measures are prescribed.
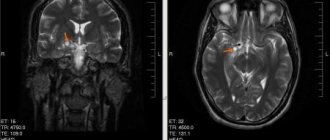
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging is the most reliable method for detecting brain tumors. The appearance of the neoplasm in the image is presented in the form of a three-dimensional image and in the thinnest section. At the initial stage of development of the disease, the formation in the picture appears in the form of edema.
The diagnostic measure is capable of identifying even a small neoplasm, as well as a formation whose location is near the bone or brain stem.
CT scan
Computed tomography is a less informative method. Using CT, you can determine the exact location of the tumor, as well as accompanying symptoms, such as hematoma and swelling.
Computed tomography is one of the main studies necessary to detect a brain tumor
Positron emission tomography (PET)
Radioactive labeled sugar is delivered to the brain area, which makes it possible to determine the state and activity of the brain: the absorption of glucose by pathological cells occurs faster than normal cells. Using PET, cancer cells are detected at any stage of pathological development.
Laboratory diagnostics
One of the most effective diagnostic measures carried out in the laboratory is a blood test for tumor markers. There are specific tumor markers, the presence of which can accurately determine the type of tumor.
A biopsy is also performed - the collection of biological material from the neoplasm, which is then subjected to microscopic examination. This allows you to determine the malignancy or benignity of the pathology. The study also provides answers about the type of tumor and its structure.
The most common symptoms include:
- intense headache, poorly relieved by analgesics. Sometimes - with nausea and vomiting
- seizures
- visual disturbances (rapid decrease in vision, limited visual fields, double vision, flashes before the eyes)
- movement disorders (impaired limb strength) in half of the body
- problems with coordination, dizziness
- sensory disturbances in half the body
- hearing impairment (ringing or tinnitus, hearing loss)
- problems with speech, memory or thinking
Many of the symptoms that occur with brain tumors can also occur as a result of other diseases, so a neurologist will help you understand the cause of your complaints. A neurological examination allows one to suspect a brain tumor and promptly refer the patient for examination.
For diagnosis, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with intravenous contrast is performed - this simple and safe method allows you to clearly visualize the structures of the brain and identify any deviations from the norm.
Treatment of tumors
It is possible to slow down the growth of the tumor and subsequently cure it using chemotherapy. But this remedy does not always help, and in some cases it turns out to be ineffective. This can be explained by the fact that the cerebral lobes are “separated” from the main bloodstream by the brain barrier, and many medicinal substances do not penetrate through it. And the effect of a large number of synthetic drugs on all organs is sharply negative.
Surgical treatment also does not always help, especially if there is an inoperable type of tumor that has formed in a hard-to-reach area. Removal of a tumor can cause dangerous consequences in the form of involvement of brain tissue in the pathological process and further disruption of the functioning of the central nervous system.
As a rule, pathology can be cured only with the help of radiotherapy (radiation therapy). The tumor formation is exposed to radioactive radiation in the required dosage. In this case, it is possible to achieve maximum survival and stop the uncontrolled growth of pathological cells.
Sometimes a three-stage treatment is carried out: surgical removal of the tumor - taking special medications - radiation exposure. Traditional medicine for brain tumors is ineffective and is applicable only at the first stage of the appearance of the tumor.
Benefits of treatment in Belgium
Malignant tumors of the central nervous system (CNS) are always associated with a fairly serious prognosis. Ensuring good survival with such a diagnosis largely depends on the quality of the surgical treatment performed and on the correct application of modern methods of cancer therapy.
All available means must be used in full. It is their complexity that ensures their effectiveness.
Thus, the following treatment methods are currently available in Belgium:
- antiangiogenic agents;
- tyrosine kinase inhibitors;
- cancer vaccines;
- stereotactic radiosurgery.
Most of these opportunities can be used in other countries with developed medicine - Germany, Switzerland, Israel - but the cost of treatment in Belgium will be more comfortable.
In clinics in Belgium, operations to remove tumors of the central nervous system are carried out using modern neurosurgical robots. Robotic surgery guarantees greater completeness of tumor removal with less damage to healthy brain structures.
In addition, clinics in Belgium have their own technologies for the treatment of central nervous system cancer, which have not yet been introduced in other European countries. For example, the method of introducing an immunodrug directly into the brain, developed by doctors at the University Hospital of Brussels, makes it possible to prolong the life of patients with complex forms of aggressive oncology of the central nervous system.
Prevention and prognosis
Experts divide the prevention of brain tumors into primary and secondary. Primary prevention is the elimination of provoking factors, namely:
- a ban on the consumption of processed meat products (sausages, smoked meats, hams, etc.);
- a ban on the consumption of fried and nitro-containing foods that contain carcinogens;
- limiting smoking and drinking alcohol, including energy drinks;
- restriction of cell phone use.
Secondary prevention is the implementation of measures aimed at excluding other diseases accompanied by the spread of pathological cells to the brain area.
How long can the life of a patient suffering from this disease last? Its duration depends on many factors. That is why it is impossible to accurately answer such a question.
If a benign neoplasm is detected in a timely manner and appropriate therapy is started, one can hope for a favorable prognosis. Life expectancy is high: not one year or two. The “former” patient lives for a long time, forgetting about his diagnosis.
How long do people live with stage 4 brain cancer? Unfortunately, the prognosis is not encouraging. In 70% there is death. Average survival rate is up to 5 years.