Glioblastoma multiforme (malignant glioma) is one of the most common malignant neoplasms in adults. 20% of all primary brain tumors are glioblastoma multiforme.
Get an MRI of the brain in St. Petersburg
The life prognosis for glioblastoma is extremely unfavorable due to the high degree of malignancy. Mortality associated with MFG exceeds 90% within 5 years with an average survival of 12.6 months.
Glioblastoma: symptoms detected by MRI. Axial T1 image after gadolinium contrast shows widespread right frontal lobe tumor. Image courtesy of Dr. George Jallo.
MRI of the same patient. The T2-weighted image demonstrates the same lesion as in the previous image with marked edema and displacement of the midline structures. These findings are consistent with the high grade of the tumor.
Causes of glioblastoma
Cancer is an unpredictable phenomenon. It is difficult for doctors to determine the causes of the development of the disease and the occurrence of tumors. However, among the most likely are:
- genetic predisposition (presence of the disease in close relatives);
- the effect of ionizing radiation on body tissues;
- as a concomitant pathology of neurofibromatosis, astrocytoma (grades 1 and 2), etc.;
- when interacting with chemical reagents (for example, regular inhalation of vapors of harmful substances);
- congenital pathology in children that appears during the formation and development of the child (embryo).
The risk group includes:
- men from 40 to 60 years old;
- those who have close relatives with this disease (or with low-quality formations in general);
- people working in the production of harmful substances (PVC, chlorine compounds, etc.);
- patients who previously had cancer (including glioblastoma).
Statistics
Glioblastoma has an ICD-10 code - C71. It includes several varieties with certain differences.
On this topic
- Neuro-oncology
How does a headache hurt with brain cancer?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 3, 2021
According to statistics, pathology is detected in 20% of cases of diagnosis of neoplasms affecting the brain.
Glioblastoma of the brain is diagnosed predominantly in male patients over the age of 40 years. In rare cases, it is detected in children and adolescents.
Symptoms of the disease
Detecting cancer is difficult. Pathology is not diagnosed without tests and studies. And the initial course of the disease is usually asymptomatic.
Unfortunately, it is possible to detect a blastoma either by chance during an adjacent examination, or at a late stage. As the tumor develops, filling the space of the skull with new tissue, it gives a number of symptoms that patients treat. Symptoms of the disease include:
- Loss of appetite.
- Headache. Feelings of fullness from inside the skull (cerebral edema).
- Nausea, vomiting, general weakness and malaise.
- Violation of the vestibular apparatus - dizziness, changes in gait.
- Problems with the heart and lungs.
- From the side of the central nervous system - memory, sleep, and speech deteriorate.
- Vision deteriorates, intraocular pressure appears.
- Changes in the sensitivity of the limbs.
- Coma.
Classification of tumors
Based on cell type, there are three types:
- giant cell glioblastoma (large cells containing two or more nuclei);
- multiform (different tissues, many hemorrhages and blood vessels);
- gliosarcoma (the tumor affects only glia).
Based on localization in the brain, malignant tumors are divided into 5 types:
- stem;
- isomorphic cell glioblastoma;
- multiform;
- polymorphocellular;
- Grade 4 glioblastoma.
The first type is not curable. Operations in this case are impossible. Malignant cells are located in the trunk connecting the spinal cord and brain.
Surgical intervention in such a delicate area is dangerous and leads to disruption of the musculoskeletal system. For this reason, in most cases, stem glioblastoma is inoperable. They are usually detected by the presence of problems with heart rate and breathing.
The isomorphic cellular form is less common than the others. The tumor consists of cells of one type - round or oval. It is characterized by unclear contours and numerous centers of neoplasms.
Multiforme is characterized by a variety of atypical cells that arise from glia (the connective tissue of the network of neurons). As a result of exposure to unfavorable factors, healthy cells transform into malignant ones.
It is possible for head cancer to descend down the trunk, engulfing the spinal cord and further spreading to other neural systems. A third of brain glioblastoma tumors are of the multiforme type.
The most common type is polymorphocellular. Cells, as a rule, are large, single-celled and of different shapes. Histological examination does not clearly reveal the cytoplasm of the cells due to its low content, so this species is not easy to detect.
Based on the number of malignant cells, tumors are divided into 4 grades. The first stage is transitional. Some benign ones turn into cancerous ones. This type is the easiest to treat.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to diagnose glioblastoma at this stage. This is due to the complete absence of symptoms. Only a random examination reveals this degree of brain cancer.
At the second stage, slow growth of cells occurs, among which atypical ones are increasingly found. The third is characterized by a large number of malignant tumors. Growth occurs much faster. Photos of the patients' brains before and after treatment are shown below.
The most dangerous grade 4 glioblastoma (Grade 4) is the most common. Simply because the last stage is easier to diagnose. Usually at this stage, pronounced syndromes appear, with which the patient consults a doctor. Once diagnosed, people die within months.
The more malignant tumors there are, the less chance of recovery. Of course, this also depends on the location of the tumor in different lobes of the brain and on many other factors.
Pathogenesis
Gliomas are any malignant brain tumors that form glial cells . When malignant transformation occurs, glial cells, namely astrocytes , become less differentiated, losing the characteristics of functional mature cells. In addition, their connection with neighboring cells is lost, and division becomes uncontrolled.
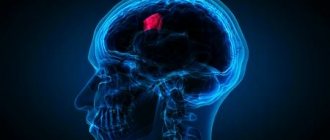
Thus, glioblastoma consists of poorly differentiated astrocytes, it has foci of necrosis and areas of vascular proliferation. A characteristic feature of this formation is a random arrangement of cells, polymorphism of cell nuclei and extensive perifocal edema. The tumor grows rapidly and invades the brain tissue. It is impossible to trace clear boundaries of the affected area. The neoplasm does not metastasize beyond the nervous system.
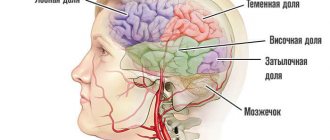
It is most often found in the frontal and temporal lobes. Very rarely, a tumor forms in the brain stem, spinal cord, or cerebellum.
In some cases, glioblastoma develops from anaplastic and low-grade astrocytomas, but most often this lesion is primary.
The tumor spreads to neuroglial cells, whose functions are related to the nutrition and protection of neurons. These cells do not reproduce in adulthood, but there are precursors of glial cells in the brain. If disturbances occur in their development, glioblastoma may develop.
A characteristic feature of glioblastoma, which determines its aggressive course, is its heterogeneity. The nature of the neoplasm differs in different patients. Moreover, even in one patient, the tumor can contain different cells that are not genetically similar, with different mutations. During the treatment process, cells mutate, actively evolve and develop new methods of survival.
Characteristic signs of glioblastoma
During the research, scientists noted that a significantly lower risk of developing glioma – by 40% – is observed in people suffering from various types of allergies . Experts explain this by the fact that in such people the immune system is in an activated state and prevents tumor growth.
Diagnostics
Modern diagnostic methods include:
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- CT (computed tomography);
- MRS (magnetic resonance spectroscopy);
- histological examination;
- PET (positron emission tomography).
These methods are used to identify the disease. The latter is considered the most accurate and modern.
To determine the malignancy of tumors and their size, it is better to use a comprehensive diagnosis. Otherwise, there is a risk of detecting a lower stage of the tumor and sizes that do not correspond to reality.
Prevention
The most effective method of prevention is regular attendance at preventive examinations, which make it possible to identify problems at an early stage. It is especially important to undergo annual examinations for people over 45 years of age, because with age the likelihood of this dangerous disease increases.
To reduce the risk of developing this disease, you must follow the recommendations regarding a healthy lifestyle:
- Get a full night's rest - healthy sleep and its sufficient duration are important.
- Spend time outdoors – you need to walk as much as possible every day.
- Avoid stress and emotional turmoil.
- Give up bad habits - do not smoke, do not consume excessive amounts of alcohol.
- Do not abuse spending time with various gadgets.
- Eat right - lots of vegetables, fruits and grains, be sure to have legumes, high-quality proteins, and unsaturated fats. Harmful foods - fast food, smoked meats, soda, confectionery, etc. - must be excluded.
Treatment methods for glioblastoma
Glioblastoma does not metastasize. For this reason, removal of malignant tumors is often prescribed. Unfortunately, cases of relapse are not uncommon, since it is not possible to completely remove cancer cells.
Treatment directly depends on the location and size of the tumor. In most advanced cases, it is simply not operable. After excision, radiation therapy and chemotherapy are sometimes prescribed in order to be sure to get rid of the recurrence of the disease. Among other things, they recommend following a certain diet, including increased intake of calcium, sodium, etc.
A new method is considered to be laser removal of glioblastomas. The targeting of the device helps to carry out targeted and selective interventions, which makes it possible to preserve more healthy cells.
Radiosurgery is also used along with the above treatment methods. But it is more of a prevention against relapse than an independent method.
In some cases, cryosurgery is used. If surgical removal is not possible, resort to this method. Malignant tissues are locally frozen. Of course, healthy people also suffer partially.
To relieve symptoms, painkillers, anti-swelling, and sedatives are prescribed. While not a treatment, they help at least somehow get through the last months.
All methods of alternative medicine and folk remedies are also ineffective.
How long do they live with her after surgery?
According to statistics, patients are given a maximum of 5-6 years for the entire course of the disease. There is little chance of recovery. But do not forget that statistics are a very relative thing. For this reason, you should not despair and accept these numbers as final.
In cases of depression, the course of the disease is unlikely to slow down; most likely, the opposite is true. While following treatment, diet and other doctor’s recommendations, a healthy lifestyle and an optimistic attitude will help prolong the time.
Complications
The disease is accompanied by severe pain that cannot be relieved with painkillers. Lack of treatment leads to brain swelling, and mental disorders also occur with glioblastoma.
When the tumor begins to disintegrate and the disease becomes grade 4, treatment is no longer carried out. In this case, patients most often completely lose self-care skills. Memory loss, impaired concentration, and partial or complete loss of vision are observed. Personality disorder also occurs.
But even after treatment, relapse is observed in more than half of the cases. The recurrence of glioblastoma is caused by cancer cells remaining after surgery. Sometimes it is not possible to completely remove them.
The most severe consequence is death, which occurs 30-40 weeks after the transition to the last stage.
Consequences and prognosis
Glioblastoma is a disappointing diagnosis, almost a death sentence. Some doctors present the fact of the presence of a tumor this way. The life prognosis may vary depending on the stage of neglect.
Those who become ill are given a life span of no more than 5 years, and sometimes less. It is necessary to detect cancer as early as possible - at a stage when it is still curable.
Even with a successful operation, the probability of getting sick again is about 75%. Cancer comes back again and again. Given the delicacy of the tumor location, the likelihood that living tissue will not be affected is very small.
The functioning of various systems may be disrupted during the removal operation, in particular the central nervous system and the musculoskeletal system. Not to mention brain activity in general.
As malignant tissues develop and grow, they have a compressive effect on vital neural networks in the cerebral cortex. As a result, malfunctions appear in the body.
Certain diets aimed at a healthy balanced diet for glioblastoma, acceptable physical activity, psychological health - all these factors affect life expectancy, but to a lesser extent.
Depends largely on:
- type of glioblastoma;
- stage of cancer;
- tumor size;
- localization (frontal, parietal, right and left temporal lobes, etc.);
- genetic inheritance;
- health of the body as a whole;
- age (older people suffer the disease the worst) and gender;
- lifestyle, bad habits;
- environment.
There is no cure for stage 4 glioblastoma. Photos of patients in the last stage of cancer are presented below. We are talking about recovery only when the disease is detected at stages 1-2, and then in rare cases.
The main problem is the lack of a clear tumor boundary. Therefore, even when removed, part of it remains, and cell division continues. As a result, after 2-3 months the tumor grows again, so it cannot be cured, nor can one live with it for a long time. There are chances at stage 2 - 60% of patients continue to live. Cases of cure occur at the 1st stage, less often at the 2nd stage.
Forecast
With standard treatment for the disease, the average survival rate for adults with glioblastoma is about two years. For patients with more aggressive disease treated with teramolamide and radiation therapy, the average survival is about 14-15 months, and the two-year survival rate does not exceed 30%. However, studies from 2009 reported that nearly 10% of patients with glioblastoma could survive five years or more.
Children with tumors (stages 3 and 4) have a higher chance of survival than adults; The five-year survival rate for children is about 25%.
Additionally, glioblastoma patients in whom the MGMT gene has been disabled by a process called methylation also have long survival rates. The MGMT gene is considered an important predictor of response.
However, not all glioblastomas have the same biological abnormalities. This may be the reason why different patients respond differently to the same treatment and why different patients with the same tumor have different results.
Researchers continue to study the common features of brain tumor patients who have had high survival rates; and how personalized and targeted treatments can be optimally used to treat brain tumors.
Many cases of complete recovery of people who have suffered this terrible disease have been documented around the world, so life expectancy with glioblastoma can be the same as that of healthy people. Statistics should not deprive people of hope for recovery.