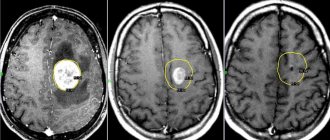
Indications for MRI of the brain in children
An examination is prescribed if a child has the following problems:
- deterioration of hearing and vision;
- unexplained changes in behavior;
- dizziness and headaches;
- convulsions and periodic fainting;
- head injury with concussion;
- speech development delay.
Frequent headaches or dizziness as usual
The cause of pain may be disturbances in the blood supply to the brain and inner ear. For correct diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a modern, highly informative study.
Fainting occurs periodically without visible external influences
Fainting in children that occurs repeatedly may indicate serious illness. If such signs occur, an MRI of the head and brain with contrast is prescribed; a special substance is injected into a vein for better visualization.
Convulsive syndrome occurs periodically
This is a nonspecific reaction of the body to irritants, which manifests itself in involuntary muscle contractions. To determine the causes of seizures, specialists are consulted and an MRI of the child’s head is performed.
Markedly progressive decrease in vision and/or hearing
The study provides an image of the structures located inside the skull. The presence of layer-by-layer images is an opportunity to conduct an accurate diagnosis.
What does MRI determine?
An MRI of a child’s head can be performed not only in the presence of pathologies, but also as a preventive method. This procedure has a fairly wide spectrum of action, based on which it will determine any brain pathology. MRI of the brain and spinal cord is recommended in the presence of the following conditions:
- frequent dizziness, headaches;
- fainting states;
- impairment of vision, hearing;
- seizures;
- inhibited mental development;
- emotional instability;
- various head injuries.
Contrast agent for MRI of the brain
The listed symptoms are a reason to do an MRI of the brain. Many parents are interested in what this study diagnoses. With its help you can see the presence of the following diseases:
- epilepsy;
- cerebral hemorrhages;
- vascular pathologies;
- sclerosis;
- pituitary diseases;
- spine pathologies;
- oxygen starvation.
In addition, MRI shows cystic and tumor neoplasms in the initial stage of development quite well, which is important for their further treatment.
Features of the procedure in children
Parents are interested in how MRIs of the brain are done for children. The main problem is the difficulty of getting the child to remain still while the tomograph takes pictures. You are required to remain motionless for 15-20 minutes. The device is noisy and can frighten the baby. However, patient immobility is a mandatory requirement, so tomography in some cases is performed under anesthesia. Indications for the use of anesthesia are age under 5 years, fear of confined spaces, panic fear of examinations, hyperactivity, and the presence of mental illness. To conduct examinations in infants, special incubators are used, which are used in conjunction with a magnetic tomograph. Anesthetic agents are propofol-based drugs, which are characterized by:
- short action;
- low level of toxicity;
- minimizing side effects;
- falling asleep quickly;
- minimal impact on the central nervous system;
- no effect on the respiratory centers;
- rapid elimination from the body.
When using anesthesia that does not affect the central nervous system, the baby's infancy is not a contraindication. Doctors at specialized diagnostic centers have extensive experience in conducting examinations of children of different ages. Parents ask what an MRI of the child’s brain shows. The study allows you to visually analyze the state of the brain and identify pathological changes that appear due to difficult pregnancy and childbirth. Using the method, problems in brain development caused by intrauterine development disorders, previous diseases, bruises and injuries are identified.
How MRI works
Magnetic resonance imaging is a hardware diagnostic method that allows you to see the state of a person’s internal structures by influencing the body with a magnetic field. In the absence of contraindications, magnetic radiation is absolutely safe and harmless for patients of all ages.
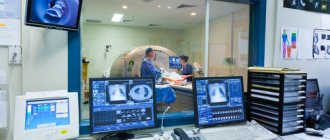
MRI in our center
Power 1.5 Tesla
High image quality
Study for patients up to 250 kg
Burn to disc for free
How is the research performed?
Doctors create the most comfortable atmosphere for the child so as not to frighten him. It is necessary to ensure the patient's immobility; if this is not possible, anesthesia is used for children. Older children undergo the test in the presence of their parents, who can help reassure them. The child is placed on a special table, which slides into the apparatus. The use of an open type tomograph allows the baby to see his parents and feel comfortable. The equipment is equipped with a feedback system for communication, listening to fairy tales and music. You can watch a video of how an MRI of the brain is done for children
.
Reviews
Below are reviews from women whose babies had head MRI scans as children.
Ulyana from Novo-Lenino: I had to give my daughter an MRI of her head at 3 months under anesthesia. Everything went well. The baby then slept for almost half a day, and after waking up she behaved as if nothing had happened.
Tatyana from Irkutsk: We examined our son at 1 month. Anesthesia was given intravenously, and during the examination they were not allowed into the equipment room. After the procedure, we observed the child for 4 hours, then sent him home. I fed her half an hour after diagnosis. The child was completely gone in the evening. There were no consequences after anesthesia.
Olga from Moscow: We did an MRI of the brain of a 1-year-old child. Anesthesia was not administered by injection, but rather a mask was given to breathe. The daughter moved away quickly and did not cry at all.
Contraindications for the procedure for children
The study is not carried out if the child has: foreign metal objects (staples, stents, prosthetic heart valves);
- electronic devices (pacemaker, insulin pump);
- hematopoietic anemia (in case of administration of a contrast agent).
If a teenager has a tattoo on his body, the doctor determines whether the procedure can be performed.
The solution depends on the dye used (paints should not be metal-based). Examination under anesthesia is not carried out if there is a history of:
- rickets;
- developmental delay;
- lack of body weight;
- feverish conditions;
- bronchial asthma during exacerbation;
- mental disorders;
- bacterial and viral infections;
- acute neurological diseases.
What is the preparation of a child?
No prior preparation is required for magnetic resonance imaging. The exception is small children, who will be put into medicated sleep before the procedure. In this case, a preliminary visit to an anesthesiologist is necessary, who will give recommendations on preparing for the procedure.
You should not feed your baby before an MRI.
The study is carried out in the morning, before which the child cannot be fed or given water. In addition, it is advisable to avoid eating from 19:00 the previous day. These requirements are necessary if the child will undergo anesthesia. If the procedure is carried out without anesthesia, then you can eat food in the evening, but it is better to refuse it in the morning to avoid vomiting.
There are cases when the study is carried out in the afternoon, then you can eat 6 hours before the procedure. If an MRI of the brain is performed on a newborn, then feeding is done within a couple of hours. One-year-old children can be fed within 4 hours.
Before placing a child in a tube, all earrings, chains, crosses, belts and hairpins must be removed.
In addition to dietary restrictions, liquid intake should be limited 12 hours before the procedure. And before the procedure itself, the child must be taken to the toilet to empty the bladder and, if necessary, bowel movements.
Before the examination, the child must be taken to the toilet
Anesthesia: is it necessary or not?
MRI of the brain of children is done under anesthesia if the parents are sure that he will not be able to lie quietly throughout the entire procedure. In addition, there are a number of contraindications in which a child should not be given anesthesia.
That is why it is very important to consult with an anesthesiologist. Taking into account the individual characteristics of the baby’s body, previous diseases and current condition, the doctor will choose the appropriate type of anesthesia:
- parenteral - is an intravenous administration of the drug, which provides the child with medicated sleep;
- inhalation - the child is put on an oxygen mask through which anesthesia is delivered.
During the procedure, the anesthesiologist will monitor cardiac activity and control the child's breathing. After the examination, the anesthesiologist will monitor the baby's condition until he fully returns to consciousness. You need to be prepared for the fact that some children experience side effects from anesthesia. This may be an allergic reaction, or in rare cases, anaphylactic shock due to intolerance to the administered drug.
Indications for the study
Magnetic resonance imaging helps to visualize all brain structures and simulate a three-dimensional image. In addition, the entire diagnostic process is recorded on a digital medium, which allows the attending physician to re-examine a separate structure or system in the brain.
For parents, recording a diagnosis is sometimes essential. If there are doubts about the competence of the attending physician, namely, he deciphers the results on the basis of which a treatment plan is drawn up, then you can seek advice from a “second person”.
For a child, MRI is an important diagnostic procedure, since based on complaints from parents, the neurologist has the right to prescribe a procedure for preventive purposes. This is what makes it possible to identify many pathologies at the inception stage and prevent central nervous system dysfunction.
Frequent complaints with pathologies in the brain:
- Dizziness, tinnitus;
- Fatigue, decreased performance at school (or regression of learning skills in preschool);
- Decreased vision;
- Changes in behavior (irritability or apathy);
- Hearing impairment;
- Delayed psychophysical development;
- Headache;
- Excessive regurgitation in infants and obvious developmental deviations.
MRI of the brain allows you to examine in detail each cell or all tissues layer by layer. This has greatly facilitated the diagnosis of brain pathologies in pediatric neurology, since previously only X-ray irradiation was performed, but in the most emergency cases.
Radiation affects the developing central nervous system and quite often this results in negative consequences. After a year, it was extremely difficult to diagnose the brain, since the large fontanel closes and it is not possible to visualize the tissue using ultrasound.
Indications for MRI include a fairly extensive list - the patient’s subjective complaints and already identified pathologies that must be periodically monitored to monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
Indications:
- Traumatic brain injuries, including birth injuries;
- Suspicion of hemorrhage;
- Epileptic seizures or convulsive syndrome;
- Preventive examination after radical tumor removal;
- Assessment of brain perfusion;
- Suspicion of intracranial formation;
- Inflammation of the meninges.
The attending physician usually decides where to get an MRI of the child’s brain. Currently, there are diagnostic rooms in clinics or hospitals where the procedure is carried out upon the direction of a specialist. But parents have the right to refuse diagnosis at a government institution and undergo examination at any private clinic.