If your temples systematically swell and your overall health deteriorates, you should seek help from a doctor, since such a phenomenon may indicate that a serious illness is developing. In this case, self-medication will provoke a deterioration in the patient’s general health. Only after a thorough medical diagnosis, based on the results of the study, will the doctor prescribe an individual treatment regimen.
Features of temporal arteritis
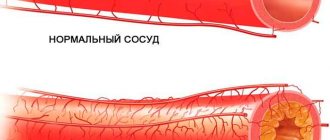
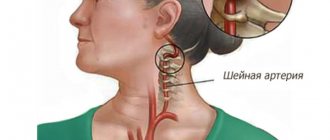
With temporal arteritis, an inflammatory process develops that affects the arteries of the arms, neck, torso and head. Under such conditions, the temporal arteries are negatively affected. But they provide a complete blood supply to the eyes, optic nerves and head. There are several factors that can cause temples to swell:
- viral;
- genetic;
- ecological.
It is almost impossible to find out the exact cause of the pathology, but most often temporal arteritis is diagnosed in women after 50 years of age. Due to inflammation of the temporal artery, swelling of its wall may occur. Under such conditions, the delivery of oxygen and necessary elements through the bloodstream to the vessels of the head becomes difficult. If a blood clot forms, the person is at high risk of developing a stroke.
Norm
The veins in the temples may be visible or protruding in older people (from 60 to 65 years old). If a person is not bothered by a headache, then this can be considered normal.
The vascular pattern becomes convex and noticeable due to age-related changes in the skin. The older a person is, the faster his epidermis loses collagen. This leads to a decrease in the elasticity of the skin.
Such natural processes are associated with the appearance of wrinkles and bulging of blood vessels under the skin.
Sometimes you can notice how the veins on the temples protrude in young and middle-aged people. The reason for this may be the impact of the following unfavorable factors:
- physical stress;
- stress;
- overheating of the body (while visiting a sauna or bath);
- blood pressure surges;
- lifting heavy objects;
- muscle tension during sports.
In these cases, the swelling of the veins is temporary, is not accompanied by pain and goes away quickly. This is also not a sign of pathology.
Deviations
If a person has a visible vein in his temple, then it is very important to pay attention to the accompanying pathological manifestations. It is necessary to consult a doctor if bloating of blood vessels is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- painful sensations in the temples;
- headaches;
- visual impairment;
- pain when pressing on the temporal region;
- nausea;
- increased blood pressure;
- sensation of pulsation in the temples.
Such signs most often indicate the presence of pathology. If bulging of blood vessels is noted as an isolated symptom, then most likely it is caused by age-related changes or random causes.
Possible diseases
Often, older people experience severe pain and swelling of the veins in the temples. Why is this happening? Such symptoms may indicate temporal arteritis. This is an inflammatory vascular disease that occurs predominantly in women over 60 years of age.
If a person has a swollen vein in his temple, and at the same time he complains of headache and nausea, then this may be a sign of blockage of blood vessels with blood clots. This condition is very dangerous as it can lead to cerebral ischemia and stroke.
If swelling of the veins is observed only on the left temple and is accompanied by pain, then this may indicate damage to the nerves of the brain and spinal cord.
The top of my head hurts and presses
Next we will look at these pathologies in more detail.
Temporal arteritis
Temporal arteritis occurs more often in older people. Its cause may be autoimmune processes or past infectious diseases. Inflammation occurs in the walls of blood vessels, accompanied by the formation of pathological large cells. Therefore, doctors call this disease giant cell temporal arteritis.
The patient exhibits the following signs of illness:
- swelling of the veins in the temples;
- severe pain in the temple, radiating to the neck, shoulder, forehead and cheeks;
- increased pain when chewing;
- drooping eyelids;
- double vision;
- decreased visual acuity;
- swelling and redness of the temporal region.
The disease must be treated immediately at the diagnostic stage. Without treatment, this pathology can lead to vision loss and stroke.
Vein thrombosis
The veins in the temples may swell due to blockage or compression of the vessels. The cause of this pathology is heart and lung diseases, as well as tumors. In this case, the outflow of blood in the veins is disrupted, which leads to their swelling.
Thrombosis is always accompanied by headache. As the pathology develops, the patient experiences nausea, dizziness, and impaired movements of the arms and legs. Such manifestations indicate cerebral ischemia. Without treatment, this pathology can lead to hemorrhage in the brain tissue.
Damage to the nerves of the spinal cord and brain
Protruding veins can be associated not only with vascular, but also with neurological pathologies. In this case, the lesion is usually noted on the left side. Bloating of blood vessels is accompanied by pain. The unpleasant sensations are shooting in nature. Patients compare the pain in the left temple with an electric shock.
Nerves in the spinal cord and brain can be damaged due to injury or compression. Damage to the nerve endings in the temple area is always accompanied by swelling and bloating of blood vessels.
Pulsation in temples
A pulsating vein in the temple is not always a sign of illness. This symptom can occur due to fatigue and stress. However, this may also be a manifestation of pathologies:
- neurocirculatory dystonia;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- arterial hypertension;
- vascular spasms;
- atherosclerosis.
The pulsation is accompanied by headache and dizziness. In these cases, you should immediately consult a doctor. Only a specialist can determine the exact cause of pulsation in the temples.
Diagnostics
Vascular diseases accompanied by bloating of the veins are treated by a surgeon or phlebologist. Patients often require consultation with a neurologist or rheumatologist. To clarify the diagnosis, the following examinations are prescribed:
- blood test for C-reactive protein and ESR;
- echoencephalogram;
- REG of brain vessels;
- MRI and CT of the brain;
- Dopplerography of the veins of the neck and head;
- biopsy of affected vessels.
If a patient complains of pulsation in the temples, then it is necessary to measure his blood pressure and take a blood test for lipids.
Treatment
Swelling of the veins in the temples is not a separate disease. This may be just one of the symptoms of various pathologies. Therefore, treatment will depend on the cause of this manifestation.
For temporal arteritis, corticosteroids (Prednisolone) and cytostatics (Azathioprine, Methotrexate) are prescribed. This treatment is aimed at stopping the autoimmune process. At the same time, it is recommended to take blood thinners (“Aspirin”).
Treatment of vein thrombosis is carried out using Heparin injections. This remedy prevents the formation of clots in blood vessels. Venoprotectors are also prescribed: “Hepatrombin”, “Ascorutin” and vasodilating drugs: “Dibazol”, “Agapurin”.
If pain and throbbing in the temples is associated with hypertension, then antihypertensive drugs are prescribed: Enap, Enalapril. For atherosclerosis, antilipid drugs are prescribed: Lovastatin, Rosuvastatin. It is recommended to follow a diet with limited fat.
When veins are swollen due to spasms and neurological pathologies, the prescription of antispasmodics and anti-inflammatory drugs is indicated: “Spazgana”, “Ketanova”, “Pentalgina”.
If there is no effect from conservative treatment, surgical intervention must be resorted to. Vascular surgery is performed - angioprosthetics or bypass surgery. This treatment is indicated in the presence of complications or severe thrombosis. Surgery is also necessary when a vessel is compressed by a tumor. In this case, the tumor must be removed.
Prevention
People over 55 - 60 years old need to undergo regular examination of the blood vessels of the head. It is at this age that problems with the veins and arteries in the temples most often arise. It is also necessary to promptly cure infectious pathologies, which often cause temporal arteritis.
It is also important to monitor your blood pressure levels. Hypertension quite often causes swelling of the veins and a feeling of pulsation in the temples. People prone to arterial hypertension need to limit their fat intake. Atherosclerosis of blood vessels often leads to problems with veins, blockage of blood vessels and cerebral ischemia.
What to do if you have a severe headache, your blood pressure is normal
Symptoms of the disease
Among the main symptoms of this pathological condition are:
- swollen temples;
- painful sensations when pressing on the affected area;
- severe migraine;
- vision problems;
- weakness.
If your temples are swollen and another symptom of the disease appears, it is important to consult a doctor immediately, since the disease can progress and develop into more complex forms.
Swollen veins in the temples
This condition, when the veins in the temples pulsate, does not always indicate the presence of a disease or pathological condition of the vascular system. More often, this phenomenon occurs as a consequence of psycho-emotional or physical stress. Swollen veins are also typical for older people, which is a natural reaction of the body to age-related changes.
Modifications of blood vessels in the temple area often indicate nervous or physical stress in the body.
Main reasons
Quite often, the veins in the temples swell and protrude in people over 60 years of age. This phenomenon is not considered a pathology if it does not cause a headache. With age, the amount of collagen in the skin decreases, which makes the skin elastic and strong.
Due to its loss, wrinkles form and natural aging processes occur. Therefore, older people experience swelling of blood vessels that protrude under the skin.
Such processes are considered irreversible and can only be eliminated with the help of modern hardware and surgical interventions.
The following external and internal factors can provoke dilation of blood vessels and their swelling under the skin and pulsation:
The expansion of blood vessels near the temple occurs due to excessive stress on the body and psyche, taking pills, fluctuations in blood pressure, high temperature, and inflammatory processes.
- stressful situations;
- physical exercise;
- lifting weights;
- temperature changes (sauna, bathhouse);
- muscle tension;
- viral and inflammatory diseases;
- vascular spasms;
- changes in blood pressure;
- atherosclerosis.
Therapy process
Treatment should only be prescribed by a specialist. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor completely examines the patient. The patient must undergo a complete clinical blood test to determine the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein. Based on the identified symptoms of the disease, symptomatic treatment is prescribed, which will help improve the patient’s overall well-being.
If your temples are swollen, your doctor will prescribe medications. The effectiveness of treatment depends on timely contact with a specialist. At the initial stage of disease development, therapy is carried out much faster and more effectively with the help of medications. During the treatment process, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs - glucocorticoids. Such drugs must be taken strictly according to the prescribed regimen. At certain intervals it is necessary to increase the dosage of medications. After a few days of therapy, the patient’s general well-being will significantly improve, but in order to get a lasting result, drug treatment must be carried out for one and a half to two years. All this time, it is advisable to be under the strict supervision of the attending physician - this will help prevent the development of health problems.
Why temples swell (in women): what to do
Temples swell when chewed
Swelling of the sides of the head as a result of diseases
Diagnosing and establishing the causes of swelling in the temple area is not always easy. The examination of the patient is approached in a comprehensive manner with visits to doctors:
- ophthalmologist;
- neurologist;
- otolaryngologist;
- allergist;
- vertobroneurologist;
- a dermatologist if there are skin problems: rashes, discoloration;
- Additionally, a parasitic source of inflammation is excluded by visiting an infectious disease specialist and undergoing tests.
Why several areas of examination of the body are required can be understood after establishing signs of inflammation:
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- heaviness around the affected area, spreading to the eyebrow, ear, neck;
- loose skin;
- swollen temple veins;
- pain in the temple area when pressed, which does not appear in all cases.
Sources of swelling of the side of the head
Swelling in the temple area is caused by the following reasons:
- chronic tonsillitis, accompanied by severe enlargement of the tonsils;
- persistent sore throat;
- inflammation of the adenoids;
- allergic reactions;
- an increase in blood pressure, which can occur due to nervous situations, resulting in swollen veins in the temples;
- inflammatory processes in the area of the parotid gland, causes of mumps can be hypothermia, infection, trauma;
The causes of swelling in the temple area may be the development of many diseases of the masticatory muscles and temporal bone. Allergic reactions can occur as a result of applying low-quality cosmetics, an insect bite or infection.
Vascular problems can be the cause of swelling in temporal artery disease.
This disease is also called arteritis Horton's disease. Similar consequences include Kawasaki and Takayasu disease, as well as periarteritis nodosa. The sources of such ailments, in turn, are hepatitis and herpes viruses.
In addition to causing swollen areas, Horton's disease can lead to partial or complete loss of vision, so this condition must be treated.
Diagnostics
The reason for undergoing diagnosis should be the presence of the following symptoms:
- persistent discharge from the eyes;
- cyclically recurring pain in the face and head;
- blurred vision of surrounding objects;
- lethargy of the eyelid, its drooping is observed.
In search of the main reason why the temple swells, the following types of examinations can be used in different areas of the body:
- heart electrocardiogram;
- tests for allergic reactions and infections;
- reencephalopathy of cerebral vessels;
- computer diagnostics;
- in case of disease of the temporal artery, ultrasound diagnostics of the head and biopsy of the vessels of the head are performed;
- examination of the eye vessels by an ophthalmologist;
- laboratory blood tests, detection of increased levels of leukocytes;
The ophthalmologist checks the patient's fundus pressure and vision. If a disease of the ENT organs is suspected, he is referred to an otolaryngologist. If swelling of the temporal region of the face appears, you should contact any of the listed specialists. You can start by visiting a therapist, who will analyze the existing symptoms, conduct initial tests and, if necessary, refer to the next specialist.
Prevention and treatment of swelling
Health measures are selected based on the complete picture of the disease and the establishment of the cause that caused it. It may be necessary to relieve facial swelling very quickly, due to its rapid development. In this case, powerful drugs that have an effective anti-inflammatory effect are prescribed. Among these are glucocorticoids.
At the initial stage, even before receiving the results of laboratory tests, large doses of medication are prescribed. Subsequently, the number of drugs is gradually reduced. Severe conditions are rarely eliminated promptly, because the vessels of the temple are very small. These operations are expensive and belong to the section of microsurgery.
To reduce swelling, follow an appropriate diet, which recommends reducing salt intake and fluid volume. All nutrition rules apply here for any swelling.
Diet for swelling
In addition to medical therapy prescribed by the doctor, proper nutrition will help reduce swelling in the temple area. It is recommended to limit the consumption of the following products:
- exclude mineral water, carbonated drinks, coffee, alcohol for the duration of prevention;
- Tomatoes, celery, beets, and beans contain a large amount of salts;
- Semi-finished products, smoked foods, fried foods, and canned foods contribute to water retention in the body;
- fast foods, disrupted eating patterns, aggravating factors;
- working too hard upsets all systems of the body, restless sleep and nervousness contribute to the development of swelling of the temple and other more dangerous diseases;
- spicy dishes and pickled vegetables;
- reduce the number of servings per meal;
- remove yeast, sweets, and flour products from the diet.
There are a large number of diets that effectively help in reducing temple swelling:
- watermelon;
- herbal, tea;
- apple;
- vegetable;
- lactic acid;
- taking various juices.
Choosing a diet on your own when your temples are swollen is extremely dangerous. You can use the appropriate type of diet only after examination and receiving recommendations from a doctor. Each person has their own chronic diseases that need to be taken into account when choosing products. In some cases, a transitional preparatory period will be required to establish the functioning of all body systems.
Measures to reduce swelling
Drink clean water, without additives. Water alone can reduce swelling by half in a short time. Boiled and mineral liquids are not suitable. The speed of operation of almost all vital systems of the body depends on molecules unrelated to other substances.
Unbound water promotes the rapid removal of fluid and waste from the area of temple swelling. Among the products it is advisable to choose:
- lemon, fresh cabbage and cucumbers;
- drinks: berry juice, cranberry, green tea, lingonberry, pumpkin juices;
- herbal decoctions: birch buds, burdock, pine buds, parsnips;
- melon, strawberries, apples, currants, bananas, citrus fruits and brown rice.
Proper nutrition will help not only remove swelling from the temple, but also lose extra pounds. However, some of the listed products remove the important trace element potassium from the body. Such diets are contraindicated for people with heart disease and vascular problems. Light sports, walks in the fresh air and a positive attitude will be a supporting factor on the path to recovery.
Causes of pain
Pain in the temple area can be caused by certain diseases. For example, migraine or increased intracranial pressure often cause an unpleasant symptom. Why do temples swell? If discomfort occurs in an elderly person, then it is necessary to exclude arterial hypertension and serious pathological changes in the brain. When the body is intoxicated, the patient often feels a feeling of heaviness in the back of the head. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor, since self-medication can only cause harm. Most often, pain in the temples occurs when:
- atherosclerosis;
- flu;
- alcohol intoxication;
- infectious sore throat;
- stroke;
- arterial hypertension;
- temporal arteritis;
- migraine and cluster pain;
- neuralgia;
- inflammation of the trigeminal nerve;
- osteochondrosis;
- osteoarthritis;
- hormonal disorders;
- during pregnancy or menopause;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
After mental or emotional stress, pain in the temples may occur. Stress, regular lack of sleep, and taking certain medications provoke a deterioration in overall health. To prevent the development of an unpleasant symptom, it is recommended to regularly visit a doctor and not eat smoked foods, fast food and excessively salty foods.
The problem of fluid accumulation in the temples
There is a lot of information on the Internet describing swelling of the face or head.
But few can find comprehensive articles on the topic of tumors in the temple area. It itself is formed from bone, which cannot accumulate fluid; only subcutaneous neoplasm occurs. Swelling extending down to the cheek is often observed. Rarely does fluid accumulation occur on both sides, so why does swelling occur, for example, in the left temple?
Swelling of the sides of the head as a result of diseases
Diagnosing and establishing the causes of swelling in the temple area is not always easy. The examination of the patient is approached in a comprehensive manner with visits to doctors:
- ophthalmologist;
- neurologist;
- otolaryngologist;
- allergist;
- vertobroneurologist;
- a dermatologist if there are skin problems: rashes, discoloration;
- Additionally, a parasitic source of inflammation is excluded by visiting an infectious disease specialist and undergoing tests.
Why several areas of examination of the body are required can be understood after establishing signs of inflammation:
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- heaviness around the affected area, spreading to the eyebrow, ear, neck;
- loose skin;
- swollen temple veins;
- pain in the temple area when pressed, which does not appear in all cases.
Sources of swelling of the side of the head
Swelling in the temple area is caused by the following reasons:
- chronic tonsillitis, accompanied by severe enlargement of the tonsils;
- persistent sore throat;
- inflammation of the adenoids;
- allergic reactions;
- an increase in blood pressure, which can occur due to nervous situations, resulting in swollen veins in the temples;
- inflammatory processes in the area of the parotid gland, causes of mumps can be hypothermia, infection, trauma;
The causes of swelling in the temple area may be the development of many diseases of the masticatory muscles and temporal bone. Allergic reactions can occur as a result of applying low-quality cosmetics, an insect bite or infection.
Vascular problems can be the cause of swelling in temporal artery disease.
This disease is also called arteritis Horton's disease. Similar consequences include Kawasaki and Takayasu disease, as well as periarteritis nodosa. The sources of such ailments, in turn, are hepatitis and herpes viruses.
In addition to causing swollen areas, Horton's disease can lead to partial or complete loss of vision, so this condition must be treated.
Diagnostics
The reason for undergoing diagnosis should be the presence of the following symptoms:
- persistent discharge from the eyes;
- cyclically recurring pain in the face and head;
- blurred vision of surrounding objects;
- lethargy of the eyelid, its drooping is observed.
In search of the main reason why the temple swells, the following types of examinations can be used in different areas of the body:
- heart electrocardiogram;
- tests for allergic reactions and infections;
- reencephalopathy of cerebral vessels;
- computer diagnostics;
- in case of disease of the temporal artery, ultrasound diagnostics of the head and biopsy of the vessels of the head are performed;
- examination of the eye vessels by an ophthalmologist;
- laboratory blood tests, detection of increased levels of leukocytes;
The ophthalmologist checks the patient's fundus pressure and vision. If a disease of the ENT organs is suspected, he is referred to an otolaryngologist. If swelling of the temporal region of the face appears, you should contact any of the listed specialists. You can start by visiting a therapist, who will analyze the existing symptoms, conduct initial tests and, if necessary, refer to the next specialist.
Prevention and treatment of swelling
Health measures are selected based on the complete picture of the disease and the establishment of the cause that caused it. It may be necessary to relieve facial swelling very quickly, due to its rapid development. In this case, powerful drugs that have an effective anti-inflammatory effect are prescribed. Among these are glucocorticoids.
At the initial stage, even before receiving the results of laboratory tests, large doses of medication are prescribed. Subsequently, the number of drugs is gradually reduced. Severe conditions are rarely eliminated promptly, because the vessels of the temple are very small. These operations are expensive and belong to the section of microsurgery.
To reduce swelling, follow an appropriate diet, which recommends reducing salt intake and fluid volume. All nutrition rules apply here for any swelling.
Diet for swelling
In addition to medical therapy prescribed by the doctor, proper nutrition will help reduce swelling in the temple area. It is recommended to limit the consumption of the following products:
- exclude mineral water, carbonated drinks, coffee, alcohol for the duration of prevention;
- Tomatoes, celery, beets, and beans contain a large amount of salts;
- Semi-finished products, smoked foods, fried foods, and canned foods contribute to water retention in the body;
- fast foods, disrupted eating patterns, aggravating factors;
- working too hard upsets all systems of the body, restless sleep and nervousness contribute to the development of swelling of the temple and other more dangerous diseases;
- spicy dishes and pickled vegetables;
- reduce the number of servings per meal;
- remove yeast, sweets, and flour products from the diet.
There are a large number of diets that effectively help in reducing temple swelling:
- watermelon;
- herbal, tea;
- apple;
- vegetable;
- lactic acid;
- taking various juices.
Choosing a diet on your own when your temples are swollen is extremely dangerous. You can use the appropriate type of diet only after examination and receiving recommendations from a doctor. Each person has their own chronic diseases that need to be taken into account when choosing products. In some cases, a transitional preparatory period will be required to establish the functioning of all body systems.
Measures to reduce swelling
Drink clean water, without additives. Water alone can reduce swelling by half in a short time. Boiled and mineral liquids are not suitable. The speed of operation of almost all vital systems of the body depends on molecules unrelated to other substances.
Unbound water promotes the rapid removal of fluid and waste from the area of temple swelling. Among the products it is advisable to choose:
- lemon, fresh cabbage and cucumbers;
- drinks: berry juice, cranberry, green tea, lingonberry, pumpkin juices;
- herbal decoctions: birch buds, burdock, pine buds, parsnips;
- melon, strawberries, apples, currants, bananas, citrus fruits and brown rice.
Proper nutrition will help not only remove swelling from the temple, but also lose extra pounds. However, some of the listed products remove the important trace element potassium from the body. Such diets are contraindicated for people with heart disease and vascular problems. Light sports, walks in the fresh air and a positive attitude will be a supporting factor on the path to recovery.
What to do if your temples are swollen and painful?
To improve your overall well-being, you need to seek help from a neurologist. The following activities can help speed up the healing process:
- taking medications;
- performing acupressure;
- use of folk remedies;
- complete rest;
- regulation of diet.
If such recommendations do not help get rid of the unpleasant symptom, then you need to take a medication that will help temporarily eliminate pain in the temples.
What will help?
If the temple and eye are swollen, treatment must be started immediately. The medicine should only be prescribed by a doctor. Tablets can cause the development of health problems if they are not taken as recommended by a doctor.
Thanks to the anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic and analgesic effect, you can eliminate:
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- weakness;
- drowsiness.
Liposarcoma - diagnosis
Patients with different types of tumors under the skin often wonder how to recognize liposarcoma? To make a diagnosis, just one examination is not enough, since the tumor is very similar to a harmless lipoma. Therefore, first of all, in order to distinguish the quality of the tumor, the dermatologist prescribes magnetic resonance imaging.
Magnetic resonance imaging
This study allows, among other things, to suspect liposarcoma, however, the diagnosis requires clarification using a histopathological examination that reveals cancer cells. First of all, histopathology allows us to accurately determine whether the change described in the studies is liposarcoma or lipoma. In addition, microscopic tests allow you to diagnose a specific type of tumor, identifying, for example, liposarcoma, myxoids.
Knowing the type of change is important to determine the patient's prognosis for cure. Material for histopathological examination is obtained by biopsy.
The most effective means
If the temples are swollen on both sides, it is recommended to use the following medications:
- Analgin contains metamizole sodium. The drug effectively eliminates the inflammatory process and relieves pain, helps relieve a migraine attack. Among the main advantages of the drug are its affordable price and effectiveness. There are also disadvantages - the drug has a detrimental effect on the liver.
- "Citramon" is one of the most effective blood-thinning and analgesic drugs. The medicine contains caffeine and acetylsalicylic acid. The medication is effective and versatile, but has a number of contraindications for use.
- Ibuprofen effectively eliminates the inflammatory process, relieves pain and relieves fever. Often, specialists prescribe medicine in the treatment of osteochondrosis or vascular inflammation. Among the main advantages of the medicine are its effectiveness and affordable price. Disadvantage: It is bad for the kidneys.
- "Imet" is one of the best non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Effectively relieves pain, dilates blood vessels and eliminates spasms. Ibuprofen is the main active ingredient. This is a universal drug that will help improve the patient’s well-being in the shortest possible time.
It is not recommended to systematically take medicinal painkillers to improve well-being, since the disease must be cured, and not just masked. Any medications can aggravate the course of the disease if the doctor’s instructions are not followed.
The veins in the temples are swollen: causes and consequences
Throughout life, a person inevitably faces various painful manifestations. This is due to the fact that the body constantly experiences not always favorable influences of both external and internal factors. Any unfamiliar symptom is cause for concern. Many people are faced with a situation where the veins in their temples are swollen. The reasons may vary. Let's take a closer look.
Violation of venous outflow
One of the most dangerous reasons why swollen veins appear on the temple is a violation of venous outflow. The fact is that with the normal functioning of blood vessels, blood must not only be delivered to all cells of the body in a timely manner, but also flow back in a timely manner. If this process is disrupted, the reasons may be as follows:
- a tumor appeared in the head region;
- the person severely injured the skull;
- suffered a stroke;
- frequent jumps in blood pressure;
- addiction to smoking and alcohol-containing drinks;
- the presence of pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- excessive motor and mental stress;
- prolonged crying in children;
- an unnaturally long absence of breathing, for example, when diving.
Note to the patient
It is difficult to answer the question of what swollen temples of the head indicate and how to cure this pathological condition. As noted earlier, there are many diseases that can trigger the appearance of an unpleasant symptom. Only after a thorough medical diagnosis of the patient can a specialist make a diagnosis and prescribe an effective treatment regimen. Based on the laboratory tests obtained, the doctor will prescribe effective medications. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. This is a truly serious problem that requires a competent approach and comprehensive treatment.
The duration of treatment and dosage of drugs is determined by the doctor depending on the severity of the unpleasant symptoms and the severity of the disease. If your temples become swollen when chewing, you should visit a doctor immediately. This symptom often occurs with hypertension. Only after making a diagnosis will a specialist prescribe suitable medications. Self-medication in some cases can lead to serious health problems.
Lump on the head - what could it be?
Insect bites and neoplasms in fatty or bone tissue may be responsible for the appearance of lumps, bumps, and swelling.
The right or left temple may be affected by a bruise, most often occurring when exposed to a blunt blow with a large area. With this problem, reversible destruction of neuronal membranes can occur. This functional state with immediate onset has no morphological background and is accompanied by vasomotor and autonomic symptoms. Soreness in the eye appears, pain in the temple, and swelling occurs. Headaches and nausea are also common.
Allergy
An allergy is an exaggerated, inappropriate response of the body's immune system to substances that a person commonly encounters in the environment. These substances - allergens - include mites, pollen, animal hair, and food ingredients.
- swelling of the nasal mucosa (allergic rhinitis);
- various types of eczema, rashes;
- redness, itching, swelling of the eyes (allergic conjunctivitis);
- narrowing of the trachea, bronchitis, shortness of breath, sometimes an asthmatic attack.
If your temples are swollen on both sides, accompanied by these symptoms, consult an allergist.
On the topic: Vastus medialis attachment
Lipoma
A fatty tumor or lipoma is actually a tumor, but a benign one. Lipomas grow very slowly, consist of fat cells, and look like a ball under the skin. Wen can occur anywhere in the body where there is fat, for example, near internal organs, and can be multiple.
Most often, fat deposits come from the layer of subcutaneous adipose tissue, therefore, they can form on the temples in the form of a lump. Lipomas are soft, elastic, mostly non-painful. The wen hurts when you press on a nerve or if you have an angiolipoma (a lipoma richly supplied with blood vessels).
Osteoma
This is a benign tumor growing from bone tissue. The neoplasm is usually diagnosed in children and adolescents, accounts for about 10% of all bone tumors, and can occur without clinical manifestations or appear as a lump, including on the temples. Only in certain localizations does osteoma cause serious disorders.
Atheroma
This is a skin cyst that occurs due to blocked sebaceous glands and overproduction of sebum.
Atheroma is an enlarged sebaceous gland. Its content has a whitish color (it may differ during infection or other processes). On the side facing the surface of the skin, there is often a small filled hole - in most cases, the cause of atheroma. Depending on the size of the atheroma, the skin deforms and becomes thinner in different ways. Atheroma in the form of a lump on the temples is one of the most noticeable.
Important! On the cheek, gumboil looks like atheroma, but it is painful.
Furuncle
A furuncle is an abscessed purulent inflammation of a hair follicle or skin glands, causing epithelial necrosis that spreads to the surrounding area.
The area of the boil is red, painful, hot, and swollen. As it develops, pus forms in the middle, forming a mucous crust that usually bursts.
Hemangioma
This is a benign tumor formed from blood vessels. Approximately 2% of hemangiomas are congenital; they have a high probability of disappearing over time. 10% of hemangiomas appear within 1–2 years of life. Some hemangiomas appear in adulthood, others are characteristic of old age. If a neoplasm has formed and does not disappear, it tends to grow, change color, and multiply.
If it occurs on the surface of the skin (superficial hemangioma), it does not pose any health risk, it is only an aesthetic problem. Deep or mixed hemangioma can be life-threatening, putting a person at risk of extensive bleeding. Fortunately, these complications are quite rare.
Fibroma
This is a benign tumor formed on the body from connective tissue. It is harmless and is mainly a cosmetic defect.
Fibroma appears on the skin and is characterized by a spherical lesion, harder than the surrounding tissue (sometimes, on the contrary, it is soft). The tumor can occur anywhere on the body - on the left or right temple, in the cheek area and other places.
Lymphadenitis
This is an inflammatory infectious disease that affects the lymph nodes, which become swollen and painful. At the temple, lymphadenitis appears both from the right area and from the left.
Based on the origin of the infection, there are several types of inflammation, according to which the course of the disease can be determined.
Sialadenitis
Inflammation of the salivary glands - sialadenitis - according to the cause, is divided into:
Sometimes the disease occurs under the picture of acute inflammation, sometimes it becomes chronic. Acute inflammation lasts several days and is manifested by redness, swelling, pain at the site of inflammation and slightly higher (up to the temple), the skin over the affected gland may be warmer. With chronic inflammation, these symptoms are alleviated; the person may feel mild pain or observe swelling of the salivary gland.
Mastoiditis
A very unpleasant inflammatory disease that requires hospitalization. Mastoiditis rarely occurs as a primary disease; it often occurs as a complication of otitis media.
With inflammation, there is fever and ear pain. Deterioration of hearing and swelling of the temples may occur.
Mastoiditis can occur within 3 weeks of otitis media.
Insect bites
A common reaction to insect bites is severe pain at the site of the bite, spreading to surrounding tissues, and swelling. When bitten, a small itchy bump appears in the temple area. The intensity of pain changes over time. Redness and swelling occurs within 10 minutes after the bite. Within a week (in the absence of allergies to insect bites), the skin condition returns to normal.
Important! If you have previously had swollen surface tissues after being bitten, consult a specialist; you may have an allergy.
Bump on a child's head
In children, bumps on the temples and on the head in general occur mainly due to bruises or certain disorders. But there may be growing pains accompanied by swelling. This condition is most often reported in children 3–12 years old, but the exact age cannot be specified. Therefore, if your child has swollen temples and complains of pain, take him to the pediatrician - growing pains can affect all children in the process of development.
Growing pains are not associated with other symptoms. If the pain is accompanied by fever, tremors, or redness, consult a doctor immediately. It is necessary to exclude other ailments (bone inflammation, orthopedic defects, metabolic, muscle, joint diseases, blood diseases, cancer).