© Author: A. Olesya Valerievna, candidate of medical sciences, practicing physician, teacher at a medical university, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
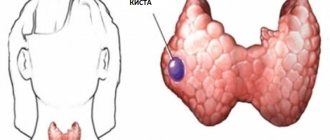
A cerebrospinal fluid cyst is a cavity formed by elements of the arachnoid membrane of the brain and filled with something like cerebrospinal fluid. It can be congenital or formed as a result of various acquired pathological processes - inflammation, collagenosis, neurosurgical operations.
A cerebrospinal fluid cyst is called an arachnoid cyst because its walls are the cellular elements of the arachnoid (arachnoid) membrane of the brain, as well as collagen fibers formed there as a result of scar changes. Arachnoid cysts are adjacent to the outer surface of the brain on the inside, and to the arachnoid membrane on the outside.
The arachnoid membrane of the brain lies between the hard and soft membranes and consists of collagen fibers, fibroblasts, and neuroglial cells that cover it outside and inside. The thin network of the arachnoid membrane limits the space filled with cerebrospinal fluid, and due to the villi protruding into the sinuses of the dura mater, it ensures the exchange of cerebrospinal fluid.
Normally, there are no focal cavities in the substance of the brain or between the layers of its membranes. However, disturbances in the structure, cicatricial adhesions, and malformations of the arachnoid membrane contribute to the local formation of cavities filled with fluid - cysts. Cysts can communicate with other cerebrospinal fluid spaces or be isolated from them.
Liqueur cysts are diagnosed several times more often in males. Liqueur arachnoid cysts are often found outside the temporal regions of the brain, at the base of the skull in the middle cranial fossa. In these places, the arachnoid membrane is extensive and entwines the so-called liquor tanks. Cystic cavities lead to expansion of the cisterns, disruption of the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, and mechanically affect the nervous tissue.
A large or growing cerebrospinal fluid cyst of the brain puts pressure on the surrounding nervous tissue, causing general cerebral and focal neurological symptoms, contributing to increased intracranial pressure and the development of hydrocephalus. The patient's vision, hearing, speech, etc. may be impaired.
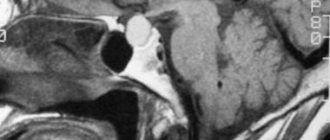
In the picture on the right there is a large cyst compressing the brain.
Causes
The formations can be congenital, that is, they arise during intrauterine development due to failures in tissue formation, as well as secondary. The latter appear under the influence of various diseases.
CSF cysts in the brain can appear as a result of:
- Postponed meningitis. This disease is characterized by an inflammatory process in the arachnoid membrane. With it, small adhesions of connective tissue are formed that disrupt the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid;
- Surgery on the brain. At the same time, adhesions from connective tissue are also formed;
- Marfan syndrome. The pathology is hereditary. When it occurs, the synthesis of collagen fibers is disrupted, which is why the connective tissue becomes more elastic and can develop in different parts of the brain, accompanied by the formation of cysts.
What it is
In addition to the brain, the skull contains tissues of hard, arachnoid and soft membranes. Between the arachnoid and soft layers there is a space filled from the inside with cerebrospinal fluid - cerebrospinal fluid. The function of this substance is to maintain normal brain activity and protect the brain from traumatic damage. It is in this part of the brain that a benign cerebrospinal fluid cyst is localized. The small size of the formation does not cause harm to the vital organ. However, with an impressive diameter of the tumor, the nearby membranes of the space are affected, disrupting the normal functioning of the brain. Treatment in such cases must be prompt in order to prevent life-threatening consequences.
Classification
Depending on the location of the formation, the following may occur:
- Arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cyst. It is located in the subarachnoid space.
- Cerebral formation. Characterized by damage to brain tissue.
- Lacunar affects the frontal lobes of the brain.
- The pineal extends to the superior medullary appendage.
- Retrocerebellar is diagnosed near or behind the cerebellum.
There are a large number of cysts, but the properties of all of them are the same: as they grow, they compress healthy tissue and cause displacement, this is accompanied by disruption of the functions of any organ or system.
Types of arachnoid cysts
Primary (congenital) cerebral cysts include abnormalities of brain development. They can be isolated or combined with other deviations in the formation of brain structures and internal organs (tetralogy of Fallot, underdevelopment or absence of the corpus callosum, arteriovenous malformations). Secondary ones appear after birth against the background of inflammation, stroke, or injury.
Along the way, an arachnoid cyst can be frozen and stable . It can have a hidden course and does not pose a health hazard. With progressive symptoms, the cavity of the formation increases, which leads to the appearance of new signs, some of which are life-threatening.
Depending on the location, several clinical types of arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cysts of the brain have been identified.
Retrocerebellar
Such cysts are found behind the cerebellum. When it is compressed, gait is disrupted, movements become difficult to coordinate, they become sweeping and appear involuntary. Characterized by paroxysmal occurrence of dizziness, nausea, and tinnitus. Eyes move from side to side (shifty gaze).
Temporal region
In patients with large cysts, learning and the ability to remember information, music, and faces of familiar people are impaired. Reading and perception of the spatial arrangement of objects may suffer. Possible decreased vision and hearing, convulsive syndrome, periodic weakness in the limbs.
Posterior cranial fossa
Compression of the stem structures of the medulla oblongata leads to breathing disorders and regulation of heart contractions, disturbances in gait and coordination of movements. This location of the arachnoid cyst is dangerous with a progressive course, since large sizes lead to coma with a fatal outcome.
Parietal region
Compression of brain tissue is accompanied by loss of joint-muscular sensation. Patients may not be aware of their limbs, written and oral speech, and attention to visual stimuli are impaired. Increased sensitivity to pain.
Left and right frontal region
These zones are responsible for motor functions. When the structures of the brain are compressed, the ability to make purposeful movements is lost, transient paralysis or paresis (muscle weakness), and falling on the back when walking are possible.
Large cysts or those that grow over a long period of time change the thinking and behavior of patients. Impulsivity appears, increased irritability, interest in others is lost, mental activity decreases, and slurred speech occurs.
Why is it dangerous?
In most cases, a cerebrospinal fluid cyst is not accompanied by any symptoms and does not threaten human health or life. The diagnosis is usually made incidentally during a magnetic resonance imaging scan.
But in some cases, a cyst develops and grows. This process is typical for secondary disorders. Formations resulting from head trauma and infectious and inflammatory diseases grow rapidly.
Gradually, the size of the formation increases, which is accompanied by painful sensations caused by compression of the brain. Tissues and blood vessels are compressed, which leads to poor circulation and necrosis of soft tissues. Gradually, serious neurological disorders begin to appear in the form of seizures or partial paralysis.
The greatest danger is rupture of the cyst under the pressure of accumulated fluid. In this case, the contents of the formation pour into the skull, causing severe poisoning and death of the patient.
If the cerebrospinal fluid cyst is located in the area of the transparent septum, then even its slight growth can lead to the development of headaches and neuralgia.
WE RECOMMEND SEEING: Brain lymphoma - is treatment possible?
Do they take you into the army with a cyst?
The Medical Commission uses the provisions of Article 23 of the Schedule of Diseases. Paragraph “d” describes in detail the examination of conscripts with congenital brain abnormalities. A congenital pathology that does not manifest itself in any way, does not cause pain and does not impair functions, allows the commission to consider the guy fit for service in the “B-4” category. He will repay his debt to his homeland in a certain branch of the military.
Severe damage to the nervous system gives the right to receive a fitness category of “D” or “B”. The conscript receives release, the army does not shine for him.
The secondary nature of the neoplasm is considered under Article 25 of the Schedule of Diseases, on the basis of which the following fitness categories are assigned:
- "D": not fit for service.
- “B”: limited eligibility, receiving a military ID without serving, not conscripted in peacetime. Obtaining this category is possible only if the person is registered, carries out the necessary medical procedures and the treatment does not help.
With or without a cyst, life goes on. A person’s well-being depends only on a responsible attitude towards it. What prevents you from undergoing a medical examination on time, a couple of times a year? The consequences of negligence can be costly. Time is one of the main factors in detecting tumors.
Typical symptoms
The development of the cystic process can have different manifestations depending on the location and size of the tumor. If the pathology is congenital, then for decades it may not reveal itself in any way. In other cases, the development of nonspecific symptoms is observed, which manifests itself:
- general cerebral symptoms in the form of diffuse or targeted headaches and dizziness. Periodically disturbing nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief;
- neurological symptoms. At the same time, muscle strength decreases, sensitivity is impaired, numbness and tingling occur in the limbs;
- dysfunctions of the sensory organs. Vision and hearing decrease, spots appear in the eyes, noise in the ears;
- mental disorders. This occurs if a cerebrospinal fluid cyst forms in the subarachnoid spaces. It is accompanied by the development of visual and auditory hallucinations, increased aggressiveness of the patient, and destabilization of the emotional sphere.
If the slightest manifestations of the presence of formations in the brain appear, it is necessary to visit a neurologist and undergo a series of diagnostic tests.
In the right temporal region
The clinical picture of a cyst in the right temporal region is similar to that of the left side, but speech impairment develops.
This symptom is often mistaken for an indolent stroke.
There are no pronounced differences between left- and right-sided arachnoid cysts. They proceed the same way.
Symptoms appear only when the tumor grows and begins to affect other parts of the brain. The only difference is the location of the pathology.
The prognosis of an arachnoid cyst in the early stages of development and proper treatment is favorable. The danger of the disease lies in the enlargement of the tumor, increased pressure on other parts of the brain and the likelihood of rupture of the cerebrospinal fluid bubble.
Establishing diagnosis
Diagnosing a cerebrospinal fluid cyst is a rather difficult task. Previously, it was almost impossible to detect a formation until it grew to a large size. But thanks to the advent of such techniques as magnetic resonance and computed tomography, it has become possible to trace the process of liquor dynamics of brain tissue and identify the presence of formations.
The diagnosis process begins with taking the patient's medical history. You may also need to consult such highly specialized specialists as an ophthalmologist, psychotherapist and others.
Before prescribing a treatment method, it is necessary to find the cause of the development of the pathological process. For this purpose they prescribe:
- Dopplerography of cerebral vessels.
- Electrocardiography.
- Research for autoimmune and infectious diseases.
- Blood test for sugar and cholesterol.
Only after receiving all the results can a suitable treatment method be prescribed.
Diagnostics
Detection of cysts is carried out using MRI and CT. These diagnostic methods allow not only to detect a formation, but also to estimate its size and clarify its location. The image is obtained in several planes - frontal, sagittal, axial.
Additionally, differential diagnosis is required, during which the cyst is distinguished from a cancerous tumor. For this purpose, a special substance is found, the accumulation of which occurs only in tumor tissues.
Due to the multiplicity of reasons leading to the formation of a cyst, additional tests are also carried out for the presence of viruses, infections, and parasites. Holter monitoring of heart rate and blood pressure is carried out, in which the indicators are recorded continuously throughout the day.
General Treatment Approaches
If no dynamics in development are observed, then the patient is simply monitored. The patient should regularly undergo magnetic resonance imaging, and if it is noticeable that the cyst is growing, then therapy will be selected:
- Drug treatment.
- Surgical techniques.
To improve metabolism and blood circulation, special medications are prescribed. Typically, treatment is carried out with drugs to resolve adhesions, normalize blood pressure, lower cholesterol levels, stabilize the coagulation system, and improve the supply of oxygen and nutrients. To eliminate inflammatory processes, appropriate medications are prescribed.
WE RECOMMEND SEEING: Causes of cerebral hemangioma
Removal of a cerebrospinal fluid cyst may be considered in the following cases:
- if a hematoma develops in nearby areas of the brain;
- the size of the tumor increases rapidly;
- hydrocephalus develops;
- I began to experience seizures regularly.
Surgical treatment for such a pathological process can be prescribed the following types:
- Shunting. In this case, the cyst cavity is emptied using drainage.
- Endoscopy. The pathological formation is removed through a small puncture in the skull.
- Trepanation of the skull. A piece of the skull bone is removed and the cyst is cut out through it.
Thanks to the use of modern technologies, severe complications can be avoided after surgical treatment. Most patients and doctors note that surgery can effectively get rid of the problem. But there are also cases of relapses.
With the help of folk remedies you can only get rid of headaches and ease the course of the pathological process. This result can be achieved with the help of hemlock, Caucasian discoreem, and herbal preparations. They reduce intracranial pressure and prevent the proliferation of cystic cavities.
Forecast
The prognosis for such a disease depends on the size and location of the cyst. If the formation rapidly increases in size, and this problem is noticed and treated on time, then the prognosis will be favorable. If severe neurological disorders develop, brain function cannot be restored. Of particular danger is the rupture of the cyst, which leads to the death of the patient.
In the absence of timely treatment and the growth of cystic cavities, serious disorders will occur, which will lead to loss of hearing and vision, impaired motor function, mental disorders and other problems.
Clinical signs of an arachnoid cyst
In most cases, the cyst is discovered during examination of a newborn or in adulthood in connection with the diagnosis of other brain diseases. Congenital pathologies may first appear only after 30–50 years of age against the background of infection, trauma, cerebrovascular accident due to atherosclerosis or hypertensive crisis.
If the cyst increases in size, intensive accumulation of fluid occurs inside it, then general cerebral and focal symptoms arise:
- persistent headaches;
- attacks of dizziness;
- noise in the head, heaviness, pulsation;
- gait disturbance (unsteadiness);
- instability when changing body position.
Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels
Intensive growth is characterized by increased headaches. It is accompanied by nausea, retching, a feeling of fullness, pressure on the eyes. Clinical manifestations of large lesions include:
- decreased hearing and vision;
- the appearance of double objects, flashing dots and spots before the eyes;
- tingling and numbness of the limbs, muscle weakness on one side of the body;
- convulsive syndrome;
- fainting conditions;
- speech disorder;
- auditory and visual hallucinations;
- mental retardation in children.
With further increase, signs of compression of brain structures increase. When they exist for a long time, neurons are destroyed. The neurological defect becomes irreversible, leading patients to disability. If fluid quickly enters the cavity of the arachnoid cyst, its walls may rupture. This condition is extremely life-threatening.
Watch the video about the symptoms and development of arachnoid cysts: