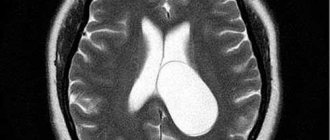
What is a cerebrospinal fluid cyst?
As mentioned above, a cerebrospinal fluid cyst is a benign tumor. It is hollow inside and filled with the same fluid that is found in the spine and protects the spinal cord (cerebrospinal fluid). It gets here through the tentorial notch (an opening in the hard shell). Hence the name.
The word “arachnoid” means that the cyst is located between the membrane of the same name and the duplication. Duplicature is the place where the shell is divided into 2 leaves. Liquid accumulates between them.
In most cases, the cyst is normally small in size. It all depends on the amount of liquid inside it. If it increases, the size of the tumor also changes. It swells and puts pressure on the brain, causing the development of unpleasant symptoms.
There is no specific localization location for the formation. However, most often it appears in the following places:
- posterior cranial fossa (PCF);
- pons-cerebellar angle;
- area above the Turkish sed;
- temporal region (pole right or left);
- Sylvian fissure.
Arachnoid changes, which are of a liquor cystic nature, usually develop in adults, and more often in men than in women. Doctors attribute this to the fact that males are more likely to experience traumatic brain injuries.
Classification of the disease
The pathology classification system is quite extensive. There are several large types of cysts and several subtypes.
Subarachnoid cyst. Is congenital. Discovered by accident. It manifests itself as a slight pulsation felt inside the skull, uncertainty in gait and convulsions. It can develop in any part of the brain, on the left, on the right, in the forehead.
Retrocerebellar. This is a cyst that is not located in the membranes, but directly in one of the parts of the brain. Appears after a stroke and with blood circulation problems. Characterized by serious consequences. Provokes tissue destruction and death.
Arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cysts. This is a consequence of the development of atherosclerotic changes. Most often it appears in older people.
Primary tumor. Formation begins in the mother's womb. Another reason for its appearance is difficult childbirth or severe asphyxia.
Secondary cyst. It happens in both children and adults. Provoking factors are brain surgery, trauma, viral infections, radiation, age-related changes.
Progressive. The arachnoid cyst of the brain increases in size, affecting the quality of life. Requires immediate local treatment, including symptomatic treatment.
Frozen. The cyst is medium in size, does not grow, and has no manifestations. Even after its detection, there is no need for specific treatment. It is enough to visit a doctor from time to time.
The structure of the neoplasm is also a parameter for dividing into types. It can be simple and complex. In the first case, the cerebrospinal fluid cyst fully lives up to its name, since it is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. In the second case, there are various tissues inside it.
Cysts are also divided into types depending on location:
- in the posterior cranial fossa;
- in the spinal canal;
- in the left or right temporal lobe;
- in the frontal region.
The type of tumor directly affects the treatment plan.
Cysts in a child
Liqueur cysts also appear in children. Most often these are boys. In most cases, the tumor is congenital and is formed as a result of disturbances in intrauterine development. Sometimes it is acquired as a result of various injuries and infectious diseases.
It is noteworthy that a child can have both a primary and a secondary cyst. The first is typical for infants, while the second develops at an older age.
Classification of pathology
Arachnoid cysts are primary and secondary. In the first case, they appear as a congenital developmental anomaly. In the second - as a result of pathological processes affecting brain tissue. The walls of the secondary neoplasm are formed by collagen and scar tissue.
In 88% of cases, single cystic formations are observed, in 12% of cases – multiple ones. The location of multiple in 5% of cases covers both hemispheres. Arachnoid changes are classified depending on the location and nature of the growth of the cystic formation. The following forms are distinguished:
- With localization in the Sylvian (lateral) fissure (34% of cases). Congenital anomaly. Symptoms depend on the diameter of the cavity and the degree of dislocation (displacement) of nearby brain tissue. More often it manifests itself as a feeling of fullness in the head area, which is accompanied by pulsation and the occurrence of tinnitus while maintaining hearing function. Seizures and visual disturbances are common.
- Suprasellar (2% of cases). Congenital form. The cavity is most often localized in the area of the chiasm formed by the optic nerves. Manifested by dizziness, visual dysfunction, and impaired motor coordination.
- Localized in the area of the lateral ventricle (2% of cases). Congenital or acquired form. The clinical picture is represented by motor and visual disturbances, hearing impairment (sensorineural hearing loss), tinnitus, dysphagia (swallowing dysfunction).
Cerebellar (localized in the cerebellum) cyst formed in the brain occurs with a frequency of 32% of cases. It manifests itself as a violation of motor coordination, changes in muscle tone (hypotonia), nystagmus (usually horizontal). The patient experiences a change in gait, which becomes unstable and shaky.
An arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cyst localized in the posterior cranial fossa is accompanied by oculomotor disorders (strabismus, loss of visual fields, paralysis of the optic nerves). A cystic formation in the area of the right or left frontal lobe is manifested by characteristic symptoms - deterioration of cognitive abilities, changes in gait, speech dysfunction (aphasia).
Causes of arachnoid changes
There are many reasons for the development of cystic arachnoiditis. They vary depending on the form of the disease.
A congenital tumor is the result of several factors:
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- smoking and drinking alcohol during pregnancy;
- intrauterine infections, in particular, toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomaglovirus, herpes;
- work in hazardous production;
- poisoning of the body with narcotic substances;
- irradiation, overheating of the body in a bath/sauna, too hot baths, prolonged exposure to the sun.
The health condition worsens if Morphan syndrome, characterized by connective tissue pathologies, is added to the listed factors.
The reasons for the appearance of an acquired cyst are:
- various traumatic brain injuries;
- brain surgery;
- neuroinfections and inflammatory diseases, for example, meningoencephalitis;
- hemorrhage, as a result of which so-called bridges and cavities remain in the membrane or tissues of the brain.
These factors either cause the formation of a new cyst or provoke the growth and development of an old one.
Symptoms
Symptoms of an arachnoid cyst formed in the brain of newborns depend on the location, the degree of isolation from the spaces where the cerebrospinal fluid is located, and the distance from the cerebrospinal fluid circulation pathways. CSF cysts are often asymptomatic and are detected in childhood or young adulthood. Usually discovered accidentally during an instrumental diagnostic study prescribed for another reason.
Neurological symptoms appear as a result of the growth of a cystic formation, when a mass effect occurs - a tangible impact on nearby intracranial structures. Symptoms appear in 20% of patients with diagnosed pathology. More often, the manifestations of the disease are associated with hydrocephalic syndrome, which provokes the appearance of cerebral symptoms:
- Pain in the head area.
- Nausea, attacks of repeated vomiting.
- Ataxia, movement disorders.
- Hemiparesis, convulsive syndrome.
- Psycho-emotional disorders.
Less common are signs of focal damage to brain tissue, which is often associated with rupture of the cyst wall. To the main symptoms in infants, specific signs are added:
- Deformation of the skull bones.
- Dehiscence of cranial sutures.
- Protrusion of the fontanel.
- Lethargy, apathy, drowsiness.
- Lack of appetite.
- Signs of damage to the pyramidal tracts (pathological reflexes, paresis, paralysis).
- Delayed psycho-motor development.
A subarachnoid cyst formed in the brain in children occurs in 4 variants of the clinical picture. Depending on the characteristics of the manifestation of symptoms, the course of an arachnoid cyst that has arisen in the brain of a child can be:
- Lightning fast (2% of cases).
- Acute (6% of cases).
- Chronic (28% of cases).
- Remitting (2% of cases).
Symptoms may appear several weeks after birth or late in childhood and adulthood. The pathology is characterized by a pseudotumorous (resembling a tumor process) course and the absence of traces of inflammation in the meninges.
Clinical manifestations
As mentioned above, subarachnoid and other types of brain cysts have practically no manifestations. They can only be detected by MRI or other diagnostic measures. Symptoms appear when the formations begin to increase in size.
Common signs include:
- cranialgia (headache in the bones of the skull);
- dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- feeling of heaviness and pulsation in the head;
- change in gait.
In some cases, hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome develops. It is a consequence of increased pressure inside the skull. Characterized by pain in the eyes, nausea, vomiting, and convulsions.
As the cyst grows, the severity of symptoms also increases. Headache, nausea and vomiting are becoming increasingly common. The patient experiences a feeling of fullness in the eyeballs. Subsequently, vision and hearing are impaired, double vision, speech problems, impaired coordination of movements, instability and partial or complete loss of sensitivity appear.
If the cyst compresses the pathways, paresis or even paralysis may develop. Muscle tone is greatly reduced, convulsions, fainting and hallucinations appear. Mental development slows down in young children.
The symptomatic picture largely depends on the location of the cyst:
- If the tumor is located in the temporal zone, the patient experiences disturbances in sensitivity and motor activity in the part of the body opposite to it. If it compresses surrounding tissues, symptoms develop like those of a stroke. The only difference is in the degree of their expression.
- A cyst located in the posterior cranial fossa manifests itself as breathing problems, disturbances in the functioning of the heart, partial or complete paralysis, and lack of coordination of movements. If the amount of cerebrospinal fluid continues to increase, the patient may fall into a coma. This greatly increases the risk of death.
- If the cyst puts pressure on the cerebellum, coordination is also impaired. The person cannot stand straight, staggers when walking, and makes involuntary movements. Dizziness, nausea, and noise in the head often appear. It's difficult to keep balance.
If at least one of the listed symptoms appears, you should immediately consult a doctor, since delay is fraught with deterioration of the condition and the development of complications.
Symptoms
If the cyst does not reach pathological sizes and does not obstruct the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, there will be no symptoms. The clinical picture appears when the neoplasm retains cerebrospinal fluid in the subarachnoid space, which leads to increased intracranial pressure. By irritating the arachnoid membrane, the cyst also causes the clinical picture of meningeal syndrome.
General cerebral signs of arachnoid changes:
- Headache of a bursting and aching nature. Worse in the morning. In response to this, vomiting occurs, bringing relief to the patient.
- Dizziness and nausea.
- Autonomic disorders: severe sweating, hand tremors, alternating diarrhea and constipation, heart pain, difficulty urinating, feeling of lack of air, feeling of a lump in the throat, aching pain in the abdomen.
- Violation of general sensitivity: numbness, chills or a crawling sensation occurs in different parts of the body.
- Diplopia is double vision. Sometimes there are episodes of visual impairment.
- Unsteadiness of walking, lack of coordination of movements and their accuracy.
Symptoms of irritation and inflammation of the arachnoid membrane include:
- Stiff neck. In patients, the muscles of the back of the head contract, causing the patient lying on his back to throw his head back. It will not be possible to bring the head to a normal position: due to a strong spasm, the torso will follow the head.
- Lockjaw. What is it - a spasm of the masticatory muscles.
- Bickel's sign - the arms are constantly bent at the elbow joints.
- Blanket symptom: The patient will involuntarily hold the blanket if he tries to pull it off.
- Photophobia, irritation to faint smells or tastes.
- Hyperesthesia is increased sensitivity to tactile contact. Touching the patient's skin causes discomfort, even pain.
With arachnoiditis, motor and sensory disorders such as mono- and hemiparesis may occur. This means that muscle strength is weakened in one limb or on one side of the body (left arm and leg together). Sensory disturbances include hallucinations. Their content and modality are determined by the proximity of the inflammatory focus to a certain area of the cortex (occipital - visual hallucinations, temporal - auditory hallucinations).
If the cyst reaches a large size and begins to compress the cortex, the patient experiences focal epileptic seizures. In severe cases, minor seizures develop into a generalized epileptic attack, aggravated by status epilepticus.
Arachnoid changes in liquorocystosis are characteristic and can imitate an intervertebral hernia. In this case, pain occurs along the spine, which radiates to the buttocks, thighs or arms. In these same places, sensitivity is weakened and paresthesia occurs.
Diagnostic methods
Due to the fact that arachnoid changes are usually asymptomatic, diagnosis is carried out only when one or more alarming signs appear.
Usually the doctor prescribes several procedures:
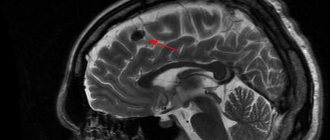
- MRI or CT. They allow you to prove the presence of a cyst, determine its size and location.
- Angiography using a contrast agent. Proves or disproves the presence of cancer cells.
- Blood test for infectious diseases.
- Cholesterol level analysis.
- Dopplerography. This is the study of the patency of blood vessels. Shows whether there are any disturbances in the blood circulation process.
- Electrocardiogram and ultrasound of the heart. Irregularities in the functioning of the heart can provoke deterioration of blood circulation in the brain.
Causes
The formations in question arise as a result of any pathological processes that can disrupt the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity. These, in particular, should include concussions and other injuries. Arachnoid changes of a liquor cystic nature can also be caused by encephalitis and meningitis. Due to disturbances in the movement of cerebrospinal fluid, the ducts filled with it expand. As a result, compression of the meninges occurs. The condition is accompanied by a persistent increase in pressure in the cranial cavity.
Treatment of arachnoid cyst
If the tumor does not bother the patient and does not increase in size, there is no need for therapeutic measures. Otherwise, it needs to be treated. Usually 2 types of therapy are prescribed:
- medicinal;
- operational.
Treatment with medications can eliminate the cause of the formation of the cyst and its manifestations.
Several types of means are used:
If the tumor is a consequence of a stroke, medications will be needed to improve blood circulation in the brain.
For infectious diseases, you need to take antibacterial and antiviral drugs. With their help, you can get rid of the infection and prevent the growth of the tumor.
Progressive arachnoid cysts are treated with medications that help relieve neurological symptoms.
In some cases, the use of such funds is indicated:
- immunomodulators and immunostimulants;
- nootropics, vasotropics, antioxidants;
- drugs to eliminate adhesions.
The dosage and duration of drug therapy is determined by the attending physician. Self-medication is dangerous. It is possible not only not to be cured, but also to worsen the condition.
If medication is ineffective or ineffective at all, surgical intervention is indicated.
Indications for surgery are several conditions:
- persistent increase in intracranial pressure (does not decrease even after taking medications);
- development of mental disorders;
- frequent fainting;
- regular cramps;
- the cerebrospinal fluid cyst has increased in size;
- hemorrhage into the tumor cavity.
Urgent surgery is required if the cyst bursts. The leaking cerebrospinal fluid puts pressure on the brain tissue, which provokes an increase in pressure.
Surgical intervention is carried out using both trepanation and minimally invasive methods. The latter are used more often than others because they are characterized by a lower level of trauma, an almost complete absence of complications and quick recovery. Trepanation must have strong indications. The doctor must carefully weigh the pros and cons of performing it and assess the possible risks.
The most popular minimally invasive operations are fenestration, bypass surgery and microsurgery. Each method has its own characteristics:
During fenestration, the surgeon uses a special cutter to make a small hole in the skull. Through it, he removes the fluid accumulated inside the cyst. After creating several additional holes, it unites it either with the ventricles or with the subarachnoid space.
During shunting, cerebrospinal fluid from the tumor cavity moves into the chest or abdominal cavity. There it is quickly absorbed by the serous membrane. It is noteworthy that this method of surgical intervention is suitable for treating both adults and children. Most often, this operation is performed in cases where, due to the increasing amount of fluid, the cyst is constantly growing.
Microsurgery involves the removal of not only the tumor, but also the surrounding tissue.
Compared to the listed methods of surgical therapy, trepanation is more effective. But at the same time it is more traumatic.
If there is a need and the doctor allows, you can use traditional medicine methods. Infusions, elixirs and poisons will help improve the general condition of the body and speed up the recovery process.
There are a lot of recipes:
1. Combine 1 tbsp. instant yeast with 3 liters of warm water. Add 40 g of elecampane there. Mix thoroughly and place in a dark place for a day. Take 100 ml 4 times a day. The course of treatment is 21 days. The drug reduces inflammation and lowers intracranial pressure.
2. To eliminate headaches, mix 100 g of hemlock seeds or stems and 500 ml of olive oil. Infuse in a place protected from sunlight for 3 weeks. Then strain and use as nasal drops. Use 2 drops three times a day.
Impact of neoplasm on health
Cysts can be divided into several types:
- Cerebellar cyst of the brain
In medical practice, the pathology is called a retrocerebellar cyst and is diagnosed in the area of mass death of gray brain cells. Inside the cyst bubble, spinal fluid and remnants of dead tissue are found. Arachnoid cysts of the presented nature are among the group of the most dangerous accumulations of cells in the brain.
- CSF cyst of the brain
It develops in another part - in the cavities between the structures of the brain, does not affect the gray matter, but can put pressure on it during growth. Pathology is formed as a result of hemorrhages and surgical interventions. Doctors prescribe symptomatic treatment; surgical intervention is rarely required.
- Congenital arachnoid cyst of the brain
Included in the category of primary pathologies, it develops at the stage of embryonic maturation. The cause of the pathology is considered to be a genetic abnormality of the skull, as well as the influence of extraneous chemical or physical factors.
- Subarachnoid leukrocystic change
It is formed during the formation of the embryo for the same reasons as the simple form. As a person grows older, it causes abnormalities in gait and strange pulsations in the skull and muscles.
Unlike an arachnoid cyst, a cerebellar cyst of the brain always forms inside the gray matter, and a simple form - only in the intermediate tissue. Ordinary arachnoid cysts do not require surgical intervention.
A retrocerebellar neoplasm destroys the central nervous system, as it always enlarges and leads to the death of surrounding cells.
Neoplasms affecting the membrane differ from each other in the place of origin: arachnoid cyst of the sella turcica, arachnoid cyst of the posterior cranial fossa, a formation in the lumbar region or the spinal canal.
Size directly affects the symptoms of the disease. The smaller the pocket of fluid, the milder the symptoms. Stable formations that do not enlarge do not require intervention. This is especially true for cysts located between the membranes.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreators
Surgical removal of the tumor is prescribed in cases where the pathological accumulation of cells constantly increases in size. Even if it is located between the shells.
A growing arachnoid cyst of the brain, the size and size of which in this case do not matter, can lead to permanent injury to surrounding tissues. This stimulates the death of cells, which, with prolonged pathological factors, begin to turn into malignant neoplasms.
Drug therapy is prescribed before surgery. But they continue it only if there is an effect of slowing growth or reversing it.
An arachnoid cyst is an ambiguous pathology that requires detailed, accurate diagnosis. Constantly monitoring the condition of the tumor will help determine the right path to treat the disease.
Preventive actions
Prevention of a primary cyst that forms in the mother’s womb includes several measures:
- The expectant mother needs to completely give up bad habits.
- Stop taking drugs that poison the body.
- Avoid taking certain groups of medications, since pregnancy is a contraindication for many of them.
- Adjust your diet by adding fresh vegetables and fruits, as well as foods that increase hemoglobin.
A pregnant woman needs to protect her baby from oxygen starvation. Regular walks in the fresh air provide invaluable assistance in this regard. It is also important to strictly follow all doctor’s prescriptions and undergo the prescribed examination on time.
Prevention of a secondary cyst looks a little different:
- Check your body regularly.
- If necessary, change your lifestyle by giving up bad habits and adding exercise.
- Monitor blood pressure levels.
- After traumatic brain injury, it is necessary to protect the body from excessive stress.
It is also important to control the amount of cholesterol in the blood, avoiding exceeding the permissible values.
Why is the disease dangerous?
A cerebrospinal fluid cyst, if not properly treated, can become a dangerous disease with serious complications and tragic consequences. It entails disability, and in isolated cases even death.
With timely assistance, the prognosis is more than favorable. The risk of worsening the condition is reduced. Otherwise, a number of conditions may develop:
- Neurological disorders. These include disturbances in motor activity, loss of sensitivity, and disruptions in the functioning of the nervous system.
- Epilepsy, frequent convulsions, involuntary movements of arms and legs, loss of consciousness.
Strict adherence to all doctor’s prescriptions will help prevent their development.
Arachnoid cysts do not pose a serious danger for the time being. They do not manifest themselves in any symptoms and are detected only during a routine examination. But sometimes, due to an increase in the amount of fluid, they begin to grow. In such situations, the person’s condition noticeably worsens and requires medical intervention.
Arachnoid changes of a liquorocystic nature. Symptoms and treatment
The brain has several membranes. One of them is called arachnoid. The space underneath (subarachnoid), containing cerebrospinal fluid, or, in other words, cerebrospinal fluid, in some cases expands, forming so-called cysts - benign formations-cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Causes and symptoms of arachnoid cysts
Arachnoid changes of a liquorocystic nature are the appearance of cavity formations in the arachnoid membrane of the brain. They can arise as a result of any pathological processes that disrupt the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity.
These include concussions, especially untreated concussions, other injuries, and meningitis and encephalitis. Due to disturbances in the movement of cerebrospinal fluid, the ducts filled with it expand and the membranes of the brain are compressed. This, as a rule, leads to a persistent increase in intracranial pressure. Therefore, arachnoid changes of a liquorocystic nature so often cause headaches that appear after physical and emotional stress. They can be very strong, causing nausea and even vomiting. However, in the case when the cyst is a consequence of a long-term illness, the manifestation of any symptoms may be absent.
An additional sign of these changes, depending on their location, is periodically appearing numbness of the limbs, a feeling of “goosebumps” on the skin and uncertainty in gait. The following symptoms may also appear: fullness or pressure in the head, a feeling of pulsation in it, noise in the ear without hearing impairment, double vision, epileptic seizures, partial paresis of the upper or lower limb, periodic blackouts.
Arachnoid changes of a liquorocystic nature. Treatment
If you find these symptoms (not necessarily all at once), then you most likely have a picture of arachnoid changes of a liquorocystic nature. And you need to urgently contact a neurologist. By the way, arachnoid cysts occur much more often in the male population and mainly in childhood or adolescence.
Please note that arachnoid changes of a liquorocystic nature are, as a rule, not a separate disease. They accompany various circulatory disorders, infections, and autoimmune diseases.
The size of the cyst is monitored using MRI or CT. Treatment is carried out
only when the cyst grows or there is a threat of the appearance of new cystic formations. But even then, attention is first paid to the underlying disease that caused the cyst. Depending on the results of the examination, the doctor prescribes treatment: medication, and, in case of emergency, surgery. Surgical interventions include bypass surgery, endoscopic surgery or craniotomy with complete removal of the cyst.
Small cystic formations generally practically do not manifest themselves. A person can live to a ripe old age without knowing that he had a cyst.
If there are no complaints, and arachnoid changes of a liquorocystic nature are only a reflection of the ratio of the size of the brain and its membranes, treatment is not required.