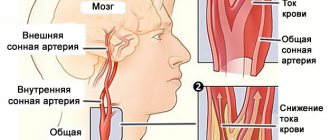
Microangiopathy is a pathology characterized by damage to small blood vessels (primarily capillaries). Most often it is a symptom of other independent diseases. One of its varieties is considered to be pathologies of the vessels of the retina and capillaries in the kidneys. The disease develops in vascular systems and organs against the background of various types of infectious or oncological diseases, diabetes mellitus, liver disease, as well as hemolysis (a pathological condition accompanied by the destruction of red blood cells and the release of hemoglobin from them).
In most cases, microangiopathy is a consequence of:
- Necrosis and death of tissues and cells of the body (necrosis);
- Thrombosis is a process that is accompanied by the formation of blood clots inside blood vessels, disrupting normal blood flow;
- Hyalinosis (or hyaline dystrophy) is a condition that is one of the types of protein dystrophy and is characterized by the deposition of hyaline in tissues;
- Fibrinoid (or fibrinoid swelling) is an irreversible condition characterized by a sharp increase in vascular permeability and manifestations of deep disorganization of connective tissue, which is based on the destruction of its main structural substance and fibers.
The clinical picture of microangiopathy completely depends on the specifics of the affected tissue, on the anatomical and morphological characteristics of the affected organs, as well as on the impact of individual external factors on the body. Its main manifestations are: damage to the integrity of the walls of small blood vessels and dysfunction of the blood coagulation system (hemostasis).
The disease is often accompanied by renal failure, purpura (subcutaneous hemorrhages - a medical symptom that is a characteristic sign of pathology of any part of hemostasis) and damage to red blood cells.
Principle of disease development
Pathogenesis is based on changes in the properties of the blood, increasing the likelihood of blood clots, as well as the structures of the walls of blood vessels in the head. This condition is caused by physiological factors or disorders that occur with a deterioration in metabolism. The brain is supplied with useful substances through the central arteries, which exit at the base from below . Then the vessels branch and penetrate the neurons. For this reason, changes in the properties of microcirculation become the cause of complex destruction of the body.
The constituent components of nervous tissue are neurons and neuroglia. These are cells with a special structure. Their processes form fibers through which nerve impulses are transported. Neuroglia are responsible for the function of the intercellular fluid, providing the proper conditions for the formation and propagation of the impulse.
Cerebral microangiopathy of the brain causes oxygen starvation, which results in the death of neurons. Neuroglia appear in their place. This process is called gliosis. In a normal state, such formed elements make up 40% of the nervous system. Neuroglia are not as good at maintaining impulses compared to neurons. For this reason, foci of gliosis impair the functioning of the central nervous system.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of cerebral microangiopathy includes measures aimed at slowing the progression of the disease, restoring blood flow and brain function, and preventing the development of acute conditions. Therapy program:
- Normalization of blood pressure indicators.
- Regulation of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism in case of their violation.
- Correction of excess weight.
- Fighting physical inactivity and bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse).
- A diet low in animal fats and salt.
Hypertensive drugs are indicated - mainly angiotensin receptor antagonists and inhibitors (substances that suppress, delay the process) of the angiotensin-converting enzyme, which have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, increase the reactivity of small vessels in the brain.
Metformin is usually used to regulate hyperglycemia, and drugs from the statin group are used to lower cholesterol levels. To prevent thrombosis, antiplatelet therapy is carried out, most often with Dipyridamole alone and in combination with acetylsalicylic acid. Simultaneously with taking pharmaceuticals, physiotherapy procedures, therapeutic exercises, and massage are prescribed.
Causes
It takes a lot of time for foci of gliosis to develop and the lumens of blood vessels to close. Therefore, the disease develops slowly.
The disease develops due to the following factors:
- Consumption of tobacco and alcohol.
- Head injuries.
- Disorders that contribute to thick blood.
- Infectious processes.
- Problems with the endocrine system, diabetes.
- Problem with the functioning of the kidneys and liver.
- Oncological disorders.
- Genetic transformations of the formation of vascular walls.
- Old age.
Destruction of small vessels occurs with tissue necrosis, lack of protein compounds, increased cell permeability, damage to the protective membranes of arteries and veins. Angiopathy of cerebral vessels manifests itself when blood clots form. The disease is divided into 3 subcategories.
Amyloid cerebral - appears when proteins are deposited on the walls of the arteries. Typical for elderly citizens. The lentiulostriate variety often occurs in children. Doctors say that this is a normal condition, but the baby needs to be under regular supervision of a specialist .
The diabetic form increases gradually. The hypertensive type is characteristic of patients who have suffered from arterial hypertension for a long time. All forms of the disease are characterized by a high concentration of glypoproteins. The walls of the capillaries then become thicker. In this case, the intensity of development of metabolic processes significantly worsens.
Microangiopathy of the brain with the presence of foci of gliosis: description of causes and treatment
This brain disease can be present in different diseases at different stages. Most often, microangiopathy is equated to a complication of diabetes mellitus, impaired blood circulation in the lower extremities, or pathology in the brain. Microangiopathy of the brain with the presence of foci of gliosis - what is it?
Microangiopathy is a disease characterized by the pathological condition of small capillaries. With microangiopathy, capillaries and parts of the walls of blood vessels are affected, which leads to the development of many other diseases (diabetes, tumors, infections, etc.). There are two types of the disease:
- renal capillaries;
- retinal vessels.
The onset of the disease occurs primarily from a lack of blood circulation in the brain and has a chronic form. Oxygen and glucose are responsible for blood circulation in the brain; with the disease, there is a noticeable shortage of these components.
This condition leads to disruptions in the performance and integrity of small vessels. As a result, everything can lead to damage to the white matter of the brain.
The pathological condition can be divided into two types:
- the first type occurs with an increase in venules (an expansion of the capillary walls can be observed);
- the second type occurs with an increase in the volume of the walls of the hyaline arteries.
Doctors attribute angiopathy to a condition in which deformation occurs in the capillaries.
Reasons for the formation of cerebral microangiopathies
The following reasons may cause deformation of the walls of blood vessels:
- Thrombosis. With thrombosis, the walls of the vessels are very small in size, and there is a lumen of the thrombus. Because of this, blood cells can only pass along one of the rows, which leads to a change in shape. It is worth remembering that any disorder and pathology in the body can lead to blood clots and adhesion of red blood cells. The result of such violations will be blockage of capillaries and arterioles.
- Necrosis. Vascular cells die due to low blood circulation to the brain or toxic effects on the body. Hyalinosis is the appearance of protein (glians) on the walls. May appear as a result of digestive and metabolic disorders in connective tissues. With this disease, the walls of blood vessels gradually decompose and become saturated with fibrins, as well as other plasma components. This is typical for hypertension, diabetes and other diseases.
- Fibrosis. The structure of fibrous tissue is replaced. It can often be found in various inflammatory reactions.
Treatment of cerebral microangiopathy
The following factors may predispose to microangiopathy with the presence of foci of gliosis:
- genetic abnormalities in the structure of vascular walls;
- consumption of toxic substances (smoking, alcohol, drugs, pesticides);
- blood clotting;
- various traumatic injuries;
- infection by infections affecting blood vessels and capillaries;
- diabetes mellitus, endocrine system disease;
- various heart diseases;
- diseases affecting blood vessels;
- effects of toxic substances on the brain and body;
- characteristics of old age.
Manifestation of the disease
During the initial stages of microangiopathy, no manifestations were detected, so this period most often goes completely unnoticed.
Minor changes in the structure of blood vessels may be observed, affecting the circulation of blood and nearby small vessels of the brain.
Therefore, it is noted that at the first stage of the development of the disease, there are no signs at all and the disease is quite difficult to recognize.
After the start of development, after a certain period of time, a large number of neurons begin to die, blood vessels are affected, which leads to low blood circulation, and pronounced symptoms appear:
- Headache. The impulses are much stronger and harder to bear. Medicines, as a rule, do not help in this case.
- Vestibular disorder. There is clouding of consciousness, dizziness, nausea. There may be a disturbance in the coordination of motor functions.
- Astheno-neurotic syndrome. Decreased emotional background. There is pronounced irritability, neurosis, depression, and a depressed state. Poor sleep at night.
- There may be insomnia at night, weakness, fatigue and a craving for sleep during the day. There is a constant state of fatigue.
The present foci stimulating microangiopathy of the brain can be varied. They manifest themselves with different symptoms depending on the location of the lesion. There may be a disturbance of sensitivity - complete or partial (pain and temperature.) There are manifestations of encephalopathy.
It can be noted that the specificity of cerebral angiopathy itself does not differ much in its manifestation. Completely other brain diseases can manifest with the same symptoms.
Foci of gliosis
Foci of gliosis are the destruction of neurons through the proliferation of glial cells. The following pathological processes and diseases can stimulate the appearance of foci of gliosis:
- sclerosis, both multiple and tuberculous;
- inflammatory processes;
- epileptic manifestations;
- hypertension.
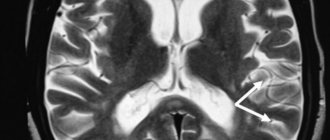
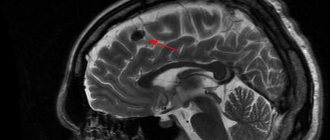
To identify the focus of gliosis, you need to do magnetic resonance imaging; from its results you can find out the size and location of the focus. In some cases, the time of gliosis formation.
This procedure allows the neurologist to determine, in a comprehensive examination, what resulted in damage to the central nervous system of a given lesion.
The focus of gliolysis may not appear clinically at all, but may be accidentally discovered during another examination. It is worth noting that the final conclusion of an MRI is not a diagnosis; it only gives a reason to undergo a full or partial examination by a neurologist. As a result of any research, it is necessary to treat the identified disease itself, and not its source.
Diagnosis of the disease
Since there are no symptoms, it can only be noticed when examining the brain. The process of applying various diagnostic methods (laboratory, hardware and others) is very important. Also, the main point is to correctly and correctly collect anamnesis of the disease. Additional diagnostic methods can be used:
- Blood plasma tests.
- EEG (encephalography).
- CT, MRI. These methods allow you to collect as much information as possible. They help determine the areas and size of the focus of gliosis, areas of ischemia, whether there are any hemorrhages in the brain, and help to combine the diagnosis with strokes (oncological, ischemic, hemorrhagic).
- Consultation with an ophthalmologist.
How to prevent a brain stroke
Treatment of the disease
Treatment is usually aimed at treating the primary pathology. This may be compensation (for example, diabetes), reducing cholesterol levels.
The following methods can also be used:
- the use of groups of nootropics that stimulate and improve metabolism;
- vitamin therapy;
- active sports, exercise therapy.
Clinical picture
The manifestation of such symptoms is due to impaired blood circulation in small vessels. For this reason, components are produced that cause damage to brain tissue. Because cerebral angiopathy syndrome occurs slowly, patients do not think about the presence of the disease. Therefore, specialists are often faced with advanced forms of the disease. Patients begin to have headaches so severe that painkillers do not help.
Soon, astheno-neurotic syndrome appears, which is characterized by: constant mood changes, insomnia, fatigue, and deterioration in performance. The disease often leads to depression. In later stages, forgetfulness and inability to concentrate appear. The location of the lesions determines the accompanying symptoms:
- Coordination of movements worsens.
- Vision decreases.
- The diameter of the pupils changes.
- Vegetative polyneuritis appears.
- Thermoregulation worsens.
- The patient does not respond well to pain.
- Aneurysm in the eyes.
- Nose bleeds constantly.
- Pain when walking.
- The skin on the feet is peeling.
- Blood in urine.
Microangiopathy of the brain is accompanied by a coagulation disorder. In the later stages, hemorrhages appear under the skin, from the nose, and in the stomach.
Symptoms
The clinical picture at the initial and even advanced stages is blurry. Because microangiopathy does not always lead to severe blood flow disturbances. This takes time.
The body also compensates for the disorder by increasing the amount of nutrition due to the formation of new capillary networks. The so-called collaterals.
They cannot replace functional structures completely, but they are enough.
You also need to take into account the number of lesions, their size, and the type of microangiopathy itself. Individual characteristics of the body. Such an array of factors makes bringing the clinic to a common denominator a difficult task.
The following symptoms occur, with varying intensity and severity and at different times:
- Headache. The strength of discomfort varies. By nature it is pressing, shooting, burning. Located in the frontal and temporal lobes. A different location is possible. The intensity increases after physical activity, stress, and smoking. Consumption of coffee, alcohol, changes in climate zone and when exposed to other negative factors.
The pain is paroxysmal. They go away on their own within a few minutes or hours. The drugs help eliminate discomfort faster.
- Dizziness. Inability to properly navigate in space. Usually low intensity.
- Due to insufficient blood flow, the patient becomes more sensitive to aggressive environmental factors. Changes in weather, vegetative-vascular crises, surges in blood pressure against the background of a new temperature regime, for example, when moving to another region or climate zone. Women have a much more difficult time with premenstrual syndrome, etc.
- Nausea. Rarely vomiting. Single episodes and not always.
- There is also an inability to control one’s own body normally. Weakness in the limbs, clumsiness, unsteadiness of gait, muscle discomfort, feeling of leaden heaviness. All these are parts of one whole.
- Asthenic phenomena. A person constantly feels tired. Weakness, fatigue, drowsiness, regardless of the time of day. All these are signs of insufficient trophism of cerebral tissues. The brain goes into an “economy” mode and does not spend energy as actively.
- Behavioral disorders. Aggressiveness, tearfulness, irritability for no apparent reason.
- Problems with thinking and cognitive sphere. Decreased speed and productivity, absent-mindedness, forgetfulness, attention deficit, inability to concentrate on a subject.
- Focal neurological signs. Disorders of the sensory organs and higher nervous activity. In severe cases, speech disorders are observed, the patient cannot perform arithmetic operations, write, read, etc.
This is not as pronounced as with a stroke, but attracts enough attention. Such signs are possible only with brain damage. What kind of plan - vascular, tumor, toxic or other - needs to be quickly clarified.
In rare cases, fainting and syncope are possible. They indicate a progressive disturbance of cerebral blood flow and indicate the severity of the process. A stroke is likely in the near future.
Symptoms are an unreliable diagnostic criterion. However, they must be taken into account.
Diabetic form of the disease
Diabetic microangiopathy is a complex manifestation of diabetes. The danger is that the disease affects the strength of tissues and the removal of toxic substances from the body. If the disease is not detected in a timely manner and the patient is not treated, the arteries and veins will become even thinner. This promotes tissue hypoxia.
This form is characterized by:
- Nephropathy. The syndrome resolves in 1/3 of patients with diabetes. It is characterized by impaired renal function and swelling.
- Diabetic angioretinopathy occurs when the blood vessels that help supply blood to the retina are damaged.
- Microangiopathy on the legs contributes to problems with blood supply and tissue nutrition deteriorates. More damage is done to the feet. Sometimes the problem spreads to the legs, knee joints, and hips.
At first, patients experience leg pain and fatigue. Initially, the pain occurs moderately, but as the disease progresses, it becomes more difficult to tolerate. Feeling burning or numbness in the legs. The dimensions of the ankle are expanding. In complex clinical disorders, ulcers form on the skin that do not heal for a long time.
Characteristic signs of microangiopathy
Clinical manifestations of the disease depend on the specifics of organs and tissues, damage to which occurred under the influence of certain external factors. Patients most often complain of pain and burning in the legs, decreased vision, bleeding from the stomach and nose, the development of intermittent claudication, dry skin of the feet, and hemoptysis.
Thus, the following signs of microangiopathy are distinguished:
- the integrity of small vessels is compromised;
- renal failure develops;
- red blood cells are damaged;
- the blood clotting process is disrupted;
- there is a high probability of subcutaneous hemorrhages.
Diagnostics
To collect anamnesis and diagnosis, the following procedures are performed: blood tests, ECG, EEG, Dopplerography to identify difficult areas and other anomalies. The patient is referred to an ophthalmologist to check the fundus for vasoconstriction and other abnormalities. The sources of microangiopathy and the complexity of the lesion are determined by the following measures: MRI, nuclear resonance.
These examination methods allow us to identify:
- Unstable areas of the vascular walls.
- Identification of areas of circulatory disturbance.
- Places of development of gliosis.
- Capillary hemorrhages.
- Increased perivascular space.
Possible complications
Consequences are relatively rare. Years pass from the development of microangiopathy to the final outcome. However, you cannot relax.
Possible problems include:
- Stroke. Acute cerebrovascular accident. Provokes the death of nerve tissue. Severe disability with neurological deficit. The death of a person is possible and even probable.
- Encephalopathy. The process is similar, but there is no destruction of cerebral structures yet.
- Vascular dementia. Dementia due to insufficient brain nutrition.
Complications develop spontaneously. Treatment is the only way to prevent them.
Healing procedures
Microangiopathy of the brain is treated with complex methods. All stages must be controlled by specialists. First of all, the degree of vascular damage is determined, after which medications are prescribed. Elderly patients require increased attention because their disease progresses more quickly.
If microangiopathy is detected, the pressure should be reduced. Hypertension in patients contributes to rapid deterioration of health. In pharmacies there is a small selection of drugs that can lower blood pressure. If the disease develops, the patient should consult a doctor and not act at his own discretion .
Additional provision of the brain with useful substances is required. Nootropic drugs are used for this. A positive effect can be achieved from drugs containing nicotinic acid. Picammilion is the most effective.
Reducing the amount of lipids is also practiced in the treatment of microagniopathy. Fibrates and statins can achieve this effect. Doctors often prescribe Simvastatin.
A decrease in the amount of oxygen in neurons will affect the intensity of the development of pathology. In order for blood composition to have a beneficial effect, you need to consume antioxidants. The treatment regimen includes blood thinning medications. Physiotherapy, regular massage and swimming in the pool have a beneficial effect on the body.
Rare situations arise when drug treatment does not restore the patency of veins and arteries or compensate for circulatory deficiency. In such situations, the patient's condition requires surgical intervention.
A positive result can be achieved if you use traditional medicine in the initial stages of the disease.
Traditional medicine:
- Herbal decoctions that stimulate metabolic processes and improve blood circulation. The list of useful plants includes: clover, hemlock, herbal preparations from the pharmacy.
- Fasting, raw food diet. Losing weight to improve your well-being.
The use of medications eliminates negative symptoms; tissues damaged by gliosis are not treated. If the causes of these formations are not dealt with, the pathology cannot be eliminated. The benefits of such traditional medicine are long-lasting, but not too noticeable . Therefore, you should not rely on self-medication; you will have to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Surgical procedures are performed in rare situations. Indications for the procedure include: difficulties in restoring vascular patency, problems with blood supply. Hirudotherapy refers to alternative methods of eliminating the disease. Non-traditional treatment methods have been used for a long time. Today it is successfully used to eliminate many ailments.
Leech has the following effects on the body: thrombolytic, regenerative, analgesic, hypotensive. This method of treatment gives a positive result, there are no contraindications, and it is safe.
The active components contained in leech saliva have a general effect on the body, stabilize blood circulation and metabolism, glucose levels decrease, and stabilize microcirculation in the capillaries. Patients with vascular pathology need to undergo herudotherapy twice a year.
Medicines
If the cause of the pathology is accurately determined, cerebral microangiopathy will be eliminated after selecting a therapeutic technique. The prognosis of the disease is determined by preventing the subsequent development of arterial damage. In the clinical picture, medications that help improve blood circulation in the head are widely used:
- Pentoxifylline in the form of tablets and injections is taken 2 times a day, starting with the minimum dose.
- Cinnarizine relaxes the artery wall, reduces the amount of calcium in the formed elements. Used 3 times a day.
- Halidor improves blood flow in the arteries of the head, consumed 3 times a day.
- Natsergoline affects receptors and vascular walls, stabilizing blood pressure.
The dosage should only be determined by a specialist; choosing the medicine yourself and drawing up a course of treatment is dangerous to health.
Possible consequences
Capillary pathology belongs to the list of serious diseases and requires the use of complex therapy. If the necessary therapy is not used, the patient's condition worsens. Results of poor quality treatment: disability, death.
Delayed contact with a specialist leads to the following results: stroke, heart attack, blindness, kidney problems.
Preliminary diagnosis of the disorder, the site of inflammation, and vascular deformation can reduce the consequences of the disease. It is impossible to completely eliminate the symptoms of the disease ; adequate treatment makes it possible to slow down the development of the disease and avoid possible complications.
Preventive actions
The following preventive measures are recommended for patients:
- Make more frequent visits to the doctor and carry out procedures.
- Follow dietary recommendations.
- Don't smoke, don't drink.
- Regularly measure your blood pressure, do a blood test, and check your glucose levels.
- Exercise. Spend time outdoors as often as possible.
Gradually worsening symptoms of the disease influence changes in the patient’s lifestyle. Destroyed brain tissue cannot be restored.