Types of stroke
There are two main types of stroke:
- ischemic (occurs in 80% of cases);
- hemorrhagic.
Ischemic occurs due to blockage or narrowing of the arteries through which essential nutrients and oxygen reach the brain. It is sometimes called a cerebral infarction. It most often occurs after 50-60 years, but at the same time, closer to old age, the risk of getting sick decreases. Depending on the reasons, there are:
- Lacunar stroke. The diagnosis is made if damage to the small vessels of the brain occurs.
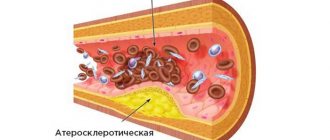
- Atherosclerotic (or atherothrombotic). As a result of this type of disease, large vessels of the brain are affected.
- Cardioembolic. It is provoked by a thrombus of the heart and blood vessels (or aorta), which is carried by the bloodstream to the brain and causes a blockage.
- Cryptogenic (or rare). Such strokes occur due to individual health problems. This may be increased blood clotting, diabetes mellitus, thinness of the walls of blood vessels, trauma, tumor, etc.
If, as a result of increased blood pressure, blood vessels rupture and hemorrhage in the brain, a hemorrhagic stroke is diagnosed. After an attack, there is a low survival rate.
Depending on where this rupture occurred and where the hematoma formed, the following subtypes are distinguished:
- Intracerebral (the rupture occurred directly in the medulla). Occurs in patients over 45 years of age. Those at risk are those with blood problems and high blood pressure.
- Intragastric (rupture in the ventricle of the brain). It occurs due to a bulging of the arterial wall (aneurysm), causing it to become thinner and burst.
- Subarachnoid (bleeding occurs in the membrane between the brain and the skull). Occurs less than in 5% of cases. Diagnosed in patients over 30 years of age. The cause may be smoking, drinking alcohol, or obesity.
A microstroke should be highlighted. Most people don’t even realize that it happened, because the discomfort lasts no more than 5-7 minutes.
A micro-stroke is a signal from the body that you urgently need to take care of your health, and if left unattended, the consequences can be disastrous. Most often, it is not the elderly who suffer, but the young.
Forecasts
Cerebral hemorrhage and its outcomes are always individual for each person, as is treatment. But most often, a stroke has 10 consequences, and how the patient will be treated depends on them:
- The body can be paralyzed either partially or completely.
- Parts of the body, in particular limbs, become numb and cease to be felt.
- The patient cannot walk or navigate in space.
- Speech is difficult or completely absent.
- There is no swallowing function.
- Loss of hearing function, either partial or complete.
- Mental disorder.
- There is no control of urination and bowel movements.
- The patient needs constant monitoring and care.
- Death.
It is impossible to say what consequences a particular patient will have after a stroke. There are elderly people who lived happily after it, and there are those for whom the prognosis was unfavorable. Treatment and prognosis can be adjusted by assessing the presence of the following signs:
- If the cause is extensive hemorrhage occurring in the center of the brain, then the prognosis is death.
- Survival among those previously diagnosed with hypertension or atherosclerosis is usually minimal or with the most severe consequences.
- The prognosis is no less bad if the patient falls into a coma caused by swelling in the brain.
- Relapse is 100% fatal.
Treatment and rehabilitation can be effective if the following factors are observed in the patient:
- laboratory tests confirmed that the hematoma is small;
- there was no loss of consciousness;
- diseases of the cardiac system, atherosclerotic plaques of blood vessels in the neck and head have not been diagnosed;
- blood pressure is within standard values.
How positive the prognosis will be depends on the timely provision of qualified medical care. If this is done in the first six hours after the onset of the attack, then you should not prepare for the worst manifestation of the post-stroke condition.
WE RECOMMEND SEEING: What kind of surgery is done for a stroke?
It is the skillful and prompt actions of doctors that guarantee life and a positive prognosis for an elderly patient. Ischemic stroke always begins with transistor attacks, and if they are recognized in time, the development of pathology of cerebral circulation can be avoided, which often causes death or coma.
Signs of stroke in older people
Stroke in older people does not occur suddenly. There are always warning signs. Headache, blurred vision, dizziness, tinnitus, difficulty speaking, memory problems, partial short-term numbness of the limbs and facial muscles may occur, and symptoms are more pronounced after 50 years.
Signs of a stroke in women over 60 years of age may be atypical: loss of the ability to adequately assess the situation, fainting, attacks of fear, hiccups, chest pain, double vision, vomiting, fever.
There are also cases when none of the above symptoms are noted and the patient does not complain about his health. But in this case, a stroke in the elderly can be identified by worsening reactions, slowness of movements and leakage of liquid food from the mouth due to impaired swallowing.
If these symptoms of stroke are observed in elderly women, emergency medical attention is needed.
The consequences of stroke in old age are severe. Complications can include complete or partial paralysis, as well as death.
Which older women are at risk?
Most women, approaching the age of 50, have various diseases that can trigger a stroke. Most often it is caused by atherosclerosis. Therefore, older people mainly face the ischemic type.
Although this type of stroke is less dangerous, medical prognosis for elderly patients is not very encouraging. This is caused by the age of patients and changes occurring in the body:
- Brain tissue is affected at a high rate, increasing the likelihood of death. Statistics show the death of 90% of patients who experience a stroke after 65 years of age.
- The recovery of older people is much more difficult, which affects their rehabilitation after an attack. In addition, most elderly patients refuse to receive full treatment.
- People under 60 years of age are more likely to experience the most severe type of the disease - the hemorrhagic type.
- Stroke in elderly women 80 years of age and older is fatal in 95% of cases. No more than 5% of patients survive the attack, but their full recovery is no longer possible.
- Women are more likely to suffer major strokes in old age than men.
Read the material on the topic: How to prevent a stroke
The first symptoms of an impending attack can be noticed several days before it. We are talking about micro-strokes, which are usually left unattended. If the first symptoms are not recognized in time, or a late visit to the doctor will lead to a major attack. The causes of stroke in older women can be different. The risk group is represented by patients suffering from:
- rheumatic diseases;
- vasculitis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- cerebral aneurysm;
- hematological diseases;
- arterial hypertension;
- atherosclerosis;
- hypertension;
- endocrine diseases;
- kidney pathologies;
- heart disease;
- acute infections.
In addition, a sedentary lifestyle, nervous shock and anxiety contribute to the development of stroke. Most older people are characterized by increased emotionality caused by hormonal changes and age-related characteristics. Any little thing that would previously have gone unnoticed can contribute to imbalance. Statistics indicate more frequent cases of stroke resulting from emotional stress in lonely old people and in people living separately from children and feeling lonely.
Occurrence of stroke
A stroke can develop within 3 to 24 hours. If you take measures in time, you will be able to stop the death of cells; if not, then you will have to treat the consequences. The later you see a doctor, the more severe the complications will be. The onset of an attack is indicated by a sharp headache on one side, accompanied by dizziness or short-term loss of consciousness.
Most patients at this moment take heart drops or tablets, a sedative, but these drugs only relieve the main symptoms, while the development of the disease continues.
This can be understood by the patient’s attacks of fear, strong heartbeat, and decreased attention. People even stop recognizing their loved ones and don’t understand where they are.
Such attacks can pass without medical intervention, but each time they will become more and more prolonged, and the consequences will be irreversible.
Features and symptoms
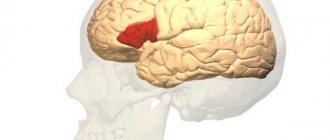
A stroke can affect different hemispheres of the brain. Depending on which side the violation occurred, right-sided and left-sided brain strokes are distinguished.
Attention! In this disease, if the right hemisphere is damaged, paralysis of the left side of the body occurs, and if the left is damaged, paralysis of the right side occurs, that is, there is a violation of symmetry.
Each hemisphere is responsible for different functions of the human body. Therefore, damage to the left hemisphere of the brain is different from damage to the right. Stroke on the left side of the brain is more common and easier to recognize. It has general and its own special characteristics.
Common symptoms include:
- Severe headache;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Change in breathing;
- Loss of coordination;
- Increased sweating.
Specific symptoms include:
- Speech impairment or loss of ability to speak;
- Incoherent expression of thoughts;
- Hearing impairment;
- Lethargy;
- Distortion of the right side of the face;
- Impaired functioning of the facial muscles on the right side. There is drooping of the corners of the mouth and eyes;
- Numbness on the right side of the face;
- Paralysis of one right eye;
- The right side of the body is paralyzed either completely or partially;
- Possible disruption of the right-sided organs;
- Impaired perception of colors, letters and numbers;
- Aggressive and inappropriate behavior, depression.
Symptoms can vary and vary depending on the severity of the condition. If the above signs of a stroke appear, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance.
Age specificity of the disease
According to statistics, 1-1.5% of the total population suffers from a stroke per year, but only half seek medical help. This disease becomes a cause of disability, and occupies a leading position, and in terms of mortality is in third place among all diseases.
Women are more susceptible to the disease after 60 years of age; in men, the risk of developing a stroke occurs after 40. At the same time, women experience the disease more severely. This is facilitated by taking hormonal drugs, a tendency to form blood clots, smoking, alcohol and other causes of stroke.
After this, only a small percentage of patients are able to return to their usual lifestyle, and only if medical care was provided in a timely manner. In other cases, recovery occurs only partially if death was avoided.
Prevention is better than cure, so everyone needs to know how to avoid a stroke. To do this, you should lead a healthy lifestyle, control your blood sugar levels and monitor your blood pressure, quit smoking and alcohol, get enough sleep and eat more fresh vegetables and fruits, regularly undergo a full medical examination and do not ignore the signals that the body sends.
Danger of left-sided stroke
The most dangerous is a left-sided hemorrhagic stroke of the brain. Its mortality rate exceeds 50%. If you wait until the symptoms disappear and do not call an ambulance in a timely manner, your chances of survival are slim.
Survivors may experience severe complications and residual effects. Relapses occur frequently.
The importance of timely diagnosis
Patients should be treated after a preliminary diagnosis has been made. It is important to establish the type of stroke (hemorrhagic or ischemic). Treatment tactics and choice of medications depend on this. The diagnosis should be made within the first hours after the onset of symptoms. Late diagnosis worsens the prognosis for life and makes treatment ineffective.
If an acute cerebrovascular accident is suspected, the following is carried out:
Survey. Complaints, the time of their occurrence, and risk factors are determined.
- Physical examination. Includes percussion, palpation and auscultation.
- Measuring blood pressure, counting pulse and breathing rate.
- Visual inspection.
- Neurological examination (detection of pathological reflexes, assessment of sensitivity, determination of muscle tone and range of motion, examination of the fundus).
- Special tests for stroke.
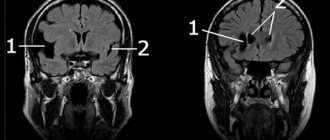
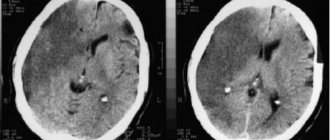
- CT and MRI (computer and magnetic resonance imaging). The most informative research methods to identify areas of cerebral vascular damage. Signs of hemorrhage are swelling and the presence of a hematoma.
- Electromyography.
- Electroencephalography.
- ECG. It is carried out to assess cardiac function and exclude myocardial infarction.
- Ultrasound of the heart.
- Angiography (x-ray examination of the arteries of the brain).
- Duplex scanning.
- Rheoencephalography. Allows you to evaluate the filling of blood vessels and the speed of blood flow.
- Coagulogram.
- Clinical and biochemical tests.
- Lumbar puncture.
- Cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
Symptoms of a stroke
You can independently determine that the situation is critical in the following ways:
- smile widely (with a stroke, part of the face will remain motionless);
- quickly repeat any phrase;
- raise your arms (you won’t be able to do this if you have a stroke).
This method is called SLM (smile, talk, lift). This abbreviation is easy to remember, and in an emergency it will remind you what needs to be done.
You can ask the patient to stick out his tongue (during an attack, the tip will deviate towards the lesion).
If the test fails, you must urgently call a doctor, describing the patient’s condition as accurately as possible, and during this time:
- position the patient so that the head is 30° above body level;
- help him breathe freely (untie his belt, unbutton his clothes, open the windows);
- when vomiting, do not lift, so as not to increase the pressure, but turn your head to the side;
- regularly measure blood pressure and pulse and record readings;
- behave calmly so as not to irritate the victim even more.
The first signs of a stroke and how to identify the warning signs
Signs of stroke in women are more pronounced, although in men they are observed at an earlier age (after 40 years). Many people who want to receive medical help face the consequences of impaired cerebral blood supply.
What are the warning signs of stroke or early markers of a transient attack?
Precursors of stroke appear in the initial stages of the disease. They are caused by a transient ischemic attack (acute disruption of blood supply to the vessels of the brain). Precursors persist for 3 hours and then regress or turn directly into a stroke. If qualified medical care is provided during this interval, serious complications of the pathology can be excluded.
The first signs of a stroke:
- Severe weakness;
- Speech and swallowing disorders;
- Increased heart rate;
- Headaches and dizziness;
- Failure to perceive the speech of surrounding people;
- Loss of consciousness.
In women, the precursors quickly develop into a pronounced clinical form, and in men they can regress. As a result, during an electroencephalological study, doctors often diagnose representatives of the stronger half of humanity as having suffered a micro-stroke.
The first signs of stroke in women depend on its type: ischemic or hemorrhagic.
The ischemic type of disease is accompanied by impaired blood supply due to blockage of a cerebral artery by a thrombus or atherosclerotic plaque.
When a vessel is blocked by a blood clot, a cerebral infarction is formed, and cell death occurs at the site of damage (cerebral infarction). This causes symptoms to form. They depend on the volume of the lesion and the localization of the pathological focus in the brain tissue.
What are the signs of a stroke or manifestations of cerebral blood supply disorders?
The first signs of stroke in women develop acutely, so it is not difficult for a specialist to diagnose the pathology. After examining the patient, neurologists can even determine the level of damage to the brain stem.
Early symptoms of cerebral microcirculation disorders:
- Rare pulse;
- Speech disorders;
- Facial redness;
- Numbness in the legs.
These manifestations are more typical for men. Women experience severe weakness, dizziness and loss of consciousness due to the psychophysiological characteristics of the body.
It is difficult to make a clear gradation of symptoms of the disease between opposite sexes. The disease progresses rapidly, and within 3 hours after its onset, the symptoms depend on the location of the lesion in the brain tissue.
How to identify warning signs of brain circulatory disorders at home
To determine the first symptoms of the disease at home yourself, we offer the following list of diagnostic measures:
- Ask the victim to smile. His smile will be crooked during a stroke, since one corner of the mouth is not innervated (on the side opposite to the tissue damage);
- Let the person say his name. With brain pathology, he will stammer and speak incoherently, like an alcoholic;
- The hand on the affected side, when raising your arms up, will be lower than the opposite one;
- The tongue will be asymmetrical and crooked when a person sticks it out. He will fall to the side.
After the warning signs, the following symptoms of the disease are observed:
- Impaired hearing or consciousness;
- Changes in the rhythm and frequency of blood supply and breathing;
- Involuntary defecation and urination;
- Facial asymmetry;
- Paralysis and cramps of the limbs.
The first signs of a stroke in men or why the stronger sex dies
The first signs of ischemic brain disorders in men are detected late, as the stronger sex neglects their health. This approach is confirmed by statistics: in men, cerebral blood supply disorders are observed after 40 years, and in women - after 60 years. However, mortality from pathology is higher among the fair sex.
What stroke symptoms should men pay attention to:
- Unsteady gait and poor coordination of movements;
- Clouding of consciousness;
- Difficulty in perceiving the surrounding world and pronouncing sounds;
- Severe weakness;
- Visual impairment.
It should be understood that with a microstroke, the above symptoms may be less pronounced. But it is necessary to pay attention to such signs of a stroke in a man, since without treatment after some time they will lead to serious consequences.
The second blow for the stronger sex can be fatal. A sharp increase in temperature during illness looks especially threatening. It is not relieved by analgesics and leads to secondary pathology of other organs.
To determine on which side the pathological focus is formed in the brain, it is necessary to determine the side on which disturbances in muscle innervation can be seen. Consequently, the damage to the brain tissue will be from the opposite part.
Left-sided stroke is manifested by right-sided pathological changes. Right-sided stroke – paresis and paralysis on the left side.
The problem for men is bad habits: smoking and alcohol. They increase the permeability of blood vessels, increasing their fragility, which can lead to impaired blood supply to the brain.
However, women also have provoking factors for the disease - long-term use of hormonal contraceptives, increased weight, frequent stress and nervous experiences.
It is stressful situations that often provoke hemorrhagic stroke in the fair half. It can be fatal.
The danger of pathology increases if stress develops against the background of high blood pressure. If a large vessel does not rupture, men experience hematoparesis (unilateral impairment of muscle sensitivity) and paralysis.
In conclusion, here are some tips on how to prevent the disease:
- If your blood pressure is high, constantly monitor its level and take medications in a timely manner if it increases;
- Quit smoking, reduce the amount of alcohol and fatty foods;
- Adjust your daily physical activity;
- Do exercises for your mind - solve crosswords, write poetry.
If you notice the first signs of a stroke, consult a doctor immediately!
Prognosis for older people
Stroke has the most severe consequences for older people. With the most favorable prognosis, one can count on only a partial restoration of those functions that depend on the lesion. There are movement disorders and maladjustment in society.
Almost half of the victims suffer post-stroke coma, which leads to either death or paralysis (complete or partial).
Probability of disability
Disability in older people after a stroke occurs in 100% of cases, and the third group, in which mild impairment of motor functions and difficulties in self-care are noted, is rare, and more often the consequences are more severe.
Problems arise not only with the musculoskeletal system, but also with vision, hearing, and speech. Patients who can move independently should not be ignored. They may get lost or begin to behave inappropriately in society.
In most cases, after illness, older people must be provided with permanent, lifelong care.
Possible complications
It is impossible to predict how an attack will affect the human body. Most often there are:
- paresis and paralysis;
- anemia;
- strabismus and other vision problems;
- violation of the swallowing reflex;
- speech defects;
- hearing impairment;
- disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract;
- fecal and urinary incontinence;
- cardiac ischemia;
- Parkinson's disease, etc.
How long do they live: forecasts for life after a stroke
The prognosis depends on many factors. This includes the general state of health, the type of stroke, the timeliness of care, the experience of doctors, and subsequent care.
Mortality is increased with hemorrhagic stroke. No more than 35% of patients survive. Survivors of ischemic stroke survive in 75% of cases.
According to statistics, more than 65% of patients die within a year after the disease, and in the first month this figure is 35%.
We recognize a brain stroke by speech
Signs of speech impairment in a woman following a stroke depend on the extent of damage to the area of the brain responsible for speaking and writing. The patient either loses the ability to speak or speaks incoherently. A sick woman sometimes understands the meaning of speech, but is not able to give an adequate answer.
With a stroke, there is often a speech disorder when a person cannot express himself, sometimes he does not even understand the conversation
In some cases, an elderly patient during apoplexy does not understand the conversation. She is unable to construct a sentence and rearranges syllables in words. The patient does not remember how to hold a pencil or write numbers. With a stroke, life skills that a person acquired from childhood are lost.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation of a patient who has suffered a stroke is of great importance. Poor blood circulation in the brain causes many pathologies, and only full compliance with the rules protects against relapse and improves the patient’s condition.
The emphasis should be placed not only on physical, but also on psychological recovery. The patient must feel supported so that complexes due to inferiority do not develop even more.
Particular attention should be paid to the diet. It should consist only of healthy foods and contain the maximum amount of vegetables and fruits.
It is advisable to purchase an orthopedic mattress, even if motor functions are relatively normal. If they are violated, you need to ensure that the patient’s position changes regularly so as not to provoke the appearance of bedsores.
Doctors often prescribe diuretics to help cope with leg swelling, a problem that often plagues patients after a stroke. If there are signs of aggression or, conversely, apathy, it is necessary to involve a psychologist. His help will be needed not only by the patient, but also by those who care for him.
Treatment
In the hospital, the patient must be connected to a ventilator and all life support functions must be monitored.
Then it is necessary to eliminate all the causes that contributed to the development of stroke , namely: elimination of hemorrhage depending on the type of stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic), dissolution of blood clots and their systems.
In some cases, surgery is necessary (for example, to remove a blood clot).
Doctors will treat hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes of the left hemisphere differently, since the causes of stroke are different in both cases. In hemorrhagic, there is a strong flow of blood into the brain; in ischemic, on the contrary, there is insufficient blood supply to the brain.
Drug treatment
Includes:
- For hemorrhagic stroke: drugs that strengthen blood vessels, prevent recurrence of hemorrhage (Gordox, Contrical), drugs to prevent vasospasm (verapamil), angioprotectors (Ascorutin), neuroprotectors (Actovegin), etc.
- For ischemic stroke: taking thrombolytics immediately after the onset of stroke (heparin, thrombo ass, aspirin, cardiomagnyl), anticoagulants (nadroparin, dalteparin), vasoactive drugs (Cavinton), anticonvulsants (Depaksin), etc.
- Common medications for both types of stroke: sedatives and hypnotics (phenosipam, tenoten, negrustin, novopassit), venotonics (troxevasin), diuretics and decongestants (indopamite, furasemide, diacarp), headache medications (arlevert), drugs to combat bedsores (Bepanten, Actovegin, Levomekol), etc.
Attention! Most often, hemorrhagic stroke of the left hemisphere of the brain requires surgical intervention.
Physiotherapeutic methods
Physiotherapy is used to improve cerebral circulation and eliminate residual symptoms after a stroke. Most often, for a stroke of the left hemisphere of the brain, the following is used:
- Magnetic therapy is one of the most gentle methods of physiotherapy. Promotes anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effect, has neurotropic and vasoactive treatment;
- Vibroacoustic therapy - vibration therapy, which dilates blood vessels, reduces swelling, and lowers blood pressure;
- Acupressure - treatment of a disease through a certain point on the body, helps to thin the blood, as well as improve movement;
- Acupuncture is the use of thin needles on certain active points on the human body. Thanks to it, blood flow through the capillaries increases, the nervous state improves, and sensitivity is restored.
Important! Most often, physical therapy is used when the patient is already less weakened.
Physiotherapy
To restore the functioning of parts of the body on the right side, physical therapy is often prescribed.
It is necessary to develop movement and sensitivity of the arms and legs of patients after a left-sided stroke.
Some useful exercises:
- Clench and unclench your hand in a fist.
- Gently raise your hand in front of you, then up, slowly lower it back and repeat this several times.
- Lying on your back, lift one leg up.
- You can also do an exercise for your eyes: alternately open and close.
Breathing exercises
To restore and strengthen the lungs after a stroke, it is necessary to do breathing exercises. A couple of simple exercises will help restore breathing and normalize the functioning of the heart and blood vessels. For example, you can inflate a regular rubber ball; blow air through a tube or pen without a rod; inhale, hold your breath and exhale.
Next we will talk about recovery and possible consequences of a left-sided stroke.
Health care
Treatment of stroke is divided into 3 stages:
- Acute phase. To reduce cerebral ischemia and reduce intracranial pressure, antihypertensive drugs (ACE inhibitors, diuretics), calcium antagonists (Isoptin, Diazem) and antispasmodics (Drotaverine, Atropine) are used. The patient is provided with rest and external stimuli (loud sounds, bright light) are eliminated. Taking sedatives (Phenazepam, Relium) is also indicated.
- Subacute phase. After cerebral circulation has been restored, the patient is transferred to the general ward. The woman is given vascular therapy and symptomatic treatment is prescribed. To restore motor activity, they give massage, exercise therapy and physiotherapy.
- Late recovery period. The patient is undergoing courses of maintenance drug therapy and is engaged in exercise therapy. Full recovery takes several years.
For large hematomas (outflow of more than 30 ml of blood), before conservative therapy, the accumulated clot is promptly removed to eliminate compression of the brain tissue.
The first signs of pre-stroke in women
Representatives of the fair sex more often experience harbingers of an impending stroke. Pre-stroke is manifested by the following symptoms:
- causeless anxiety;
- sweating;
- feeling of weakness;
- chilliness of the limbs;
- blood pressure surges;
- tachycardia (120 or more per minute);
- dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation);
- facial hyperemia;
- dry cough.
The symptoms of pre-stroke that occur do not always seem dangerous. The woman ignores the signs of an approaching illness, believing that after rest her health will improve.