A very common reason for visiting a neurologist are complaints such as: headaches of varying localization and intensity, swelling of the eyelids, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, pressure changes, dizziness. These symptoms can appear suddenly, or they can increase gradually over time, reducing social adaptation, professional skills, self-care skills, etc. Older and middle-aged people fear that this condition may further progress into dementia (dementia). Unfortunately, in some cases these fears are unfounded. However, these symptoms rarely lead to dementia. The most common cause of this condition is external replacement hydrocephalus of the brain. In common parlance, this disease is also called dropsy. There is congenital and acquired hydrocephalus. The first is in the scope of the pediatric service and is a topic for a separate discussion. Hydrocephalus of the brain in adults is always acquired.
Features of the disease
Due to the fact that the symptoms of dropsy in children of the 1st year of life are more pronounced, it is accompanied by:
- clearly visible changes in the shape of the head;
- protrusion of the fontanel;
- developmental delay.
For a long time, the prevailing opinion in medicine was that only infants suffer from hydrocephalus. In fact, people of all ages are susceptible to this disease, but its causes, symptoms and consequences are different in adults and children.
External replacement hydrocephalus in adults, depending on the etiology of the disease and the place where excess fluid collects and the degree of brain damage, can:
- proceed easily, making itself felt only by headaches;
- cause serious consequences, sometimes leading to severe disability or death;
- have a chronic, subacute or acute form, differing in symptoms and treatment methods.
Causes
Hydrocephalus in any form can develop as an “independent” pathology (primary) or as a consequence (secondary) of certain diseases. In both cases, the main cause of dropsy is a violation of the outflow of fluid and its accumulation in the ventricles of the brain.
Experts name a number of conditions under which the development of moderate external hydrocephalus is possible:
- Suffered a stroke.
- Atherosclerosis.
- The presence of malignant or benign formations that interfere with the normal outflow of fluid.
- High blood pressure.
- Current or past infectious diseases (encephalitis or meningitis).
- Hernia in the cervical spine or osteochondrosis.
A disease such as minor external hydrocephalus can also appear as a consequence of head injury, concussion, alcohol poisoning, or alcoholism.
In children, the occurrence of the disease is facilitated by factors such as:
- The birth of a baby ahead of schedule.
- Intrauterine infection.
- The influence of unfavorable external conditions on the development of the fetus during the perinatal period.
Causes and mechanism of development
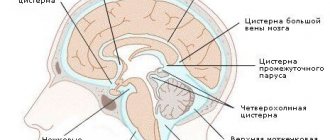
The human brain, enclosed in the cranium, is located in the cerebrospinal fluid (livcor), which performs 4 important functions:
- Protecting the brain from mechanical damage.
- Stabilization of intracranial pressure, compensation for its changes that occur when moving the head, talking, laughing - any actions performed by a person.
- Providing nutrition to brain cells.
- Removing their waste products.
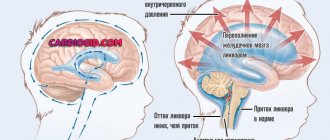
Normally, livcor is produced in the 4 ventricles of the brain, then through the interventricular canal and cerebral duct it enters the space between the arachnoid and pia mater of the brain. It is removed by being absorbed through the capillaries that penetrate the arachnoid membrane into the venous blood.
The total amount of cerebral fluid remains unchanged; for an adult, its volume should range from 140 to 270 ml.
If the process of circulation (outflow) of livcor is slowed down, and the ventricles continue to produce it in the same volume, then excess fluid will accumulate, creating excessive pressure on certain brain structures and causing disturbances in their functioning.
Hydrocephalus will develop, the main causes of which are considered to be:
- head injuries;
- age-related changes in cerebral vessels;
- strokes, cerebral hemorrhages;
- neoplasms, brain tumor
- unfavorable heredity;
- hypertension;
- infections and inflammatory diseases affecting the brain, in particular: meningitis and encephalitis;
- cardiovascular diseases in severe form.
In some cases, the cause of the disease cannot be identified.
External replacement hydrocephalus in adults has its own developmental characteristics. It is associated with the appearance of cavities in the membranes of the brain, which are a consequence of the destruction (atrophy) of their tissues. If there are voids, cerebral fluid from the subarchnidal space enters them, replacing the destroyed tissue. At the same time, the volume of the brain decreases.
The causes of brain tissue atrophy can be:
- atherosclerosis and other diseases of the vascular system;
- encephalopathy (chronic deficiency of nutrition of brain tissue);
- regular poisoning of the body with alcohol, nicotine, drugs;
- traumatic brain injuries (in the absence of adequate treatment);
- age-related diseases associated with degenerative changes in the brain: Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, Huntington's, Pick's disease;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- infectious diseases affecting the brain;
- exposure to radiation.
The following factors increase the risk of tissue atrophy and the development of atrophic hydrocephalus:
- frequent stress;
- insomnia;
- unhealthy diet;
- water imbalance due to dehydration or excessive fluid intake;
- working with potentially hazardous substances that can cause poisoning: heavy metals, toxic gases, pesticides, paints, solvents.
In adults and children, there are 3 stages of development of atrophic (external replacement hydrocephalus):
| Stage | Description |
| Initial | Atrophy is insignificant, there are no symptoms, the patient feels well, there are no complaints or the person does not pay attention to them. It could be:
|
| Moderate | There are noticeable symptoms:
|
| Expressed | Its symptoms are as follows:
|
Existing types
In medicine, there are a number of terms, such as:
- Mixed replacement hydrocephalus.
- External replacement hydrocephalus.
- Internal replacement hydrocephalus.
Of course, these diseases are very dangerous and can lead to severe disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system.
Description of mixed replacement hydrocephalus
The basis for its occurrence are various pathological conditions that cause brain atrophy, for example:
- Age-related aging processes.
- Encephalopathy. This term refers to changes in brain tissue caused by a lack of nutrition. It, in turn, is provoked by the consequences of various head injuries, cholesterol deposits in blood vessels, high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, intoxication with alcohol and other poisons.
- A number of genetic diseases.
Since this type of hydrocephalus is the most common, its main danger is that for a long time it occurs without symptoms, without showing itself in any way. The first clinical signs and complaints indicate that the disease is already progressing intensively. With this pathology, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) accumulates in the internal cavities of the brain and directly under its membranes. In this type, neurologists also distinguish moderately expressed external replacement hydrocephalus, when the dropsy does not progress, but remains in a latent form for a long time.
Internal replacement hydrocephalus.
With this type of hydrocephalus, fluid accumulates in the internal cavities of the brain without damaging the cerebral cortex (gray matter). The cause is a violation of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the internal cavities, brain tumors (tumors, cysts). This condition is malignant. In the absence of restoration of normal fluid pressure, it will certainly lead to death, since the effect goes directly to the respiratory and vascular centers. The disease manifests itself quite clearly: convulsive conditions, respiratory and heart rhythm disturbances. This pathology requires timely surgical treatment - conservative treatment will not bring results.
Classification
The classification of hydrocephalus is complex because it takes into account several criteria at once.
Depending on the time of occurrence, it can be:
- Congenital. It is formed in the womb under the influence of diseases she suffered during pregnancy: toxoplasmosis, syphilis, cytomegaly.
- Acquired. Appears after birth under the influence of certain factors: infections, inflammation, injuries.
According to the location of excess fluid, it can be:
- Internal. In this case, livcor accumulates in the ventricles, which at the same time increase in size, squeezing nearby tissues. Its cause may be a blockage of the channels connecting the ventricles with the space between the membranes of the brain.
- External. An accumulation of CSF is observed in the subarchnoid space: the membranes, supersaturated with fluid, expand and create excessive pressure on the brain from the outside. The cause of this hydrocephalus is usually a violation of the absorptive capacity of the brain vessels.
- Mixed. This case combines internal and external forms.
According to the development mechanism it can be:
- Open when the connection between the ventricles and the cavity between the membranes of the brain is maintained. The cause may be increased secretion of cerebral fluid.
- Closed. With it, this connection is broken (blocking the outflow channels).
Based on the reasons for their appearance, the following types are distinguished:
- Post-traumatic, which appeared after a traumatic brain injury.
- Post-infectious, which is a consequence of previous neuroinfectious diseases.
- Posthemorrhagic, developing as a result of a violation of the integrity of blood vessels and hemorrhage into the ventricles of the brain. Mainly diagnosed in newborns.
- Tumor, in which the tumor can block the outflow pathways of livkor or stimulate its production.
The following forms differ according to the nature of the course and rate of development:
- Progressive (acute), in which no more than 3 days pass from the onset of the first symptoms of the disease to the development of persistent disorders of brain function.
- Subacute, which takes a month to develop.
- Compensated (chronic), characterized by a slow but steady deterioration of the patient’s condition over six months.
The effect on intracranial pressure indicators may be
- Hypertensive, leading to its increase.
- Normotensive, does not change blood pressure.
- Hypotensive, reducing it.
External replacement hydrocephalus in adults is a type of external hydrocephalus in which excess fluid fills damaged, atrophied areas of the brain. With this form of dropsy, no increase in intracranial pressure is observed.
The disease can be congenital or acquired. As a rule, it is chronic and develops in old age. Its acute form is less common, resulting from head injuries and previous neuroinfections.
Diagnostic methods
A doctor cannot make an accurate diagnosis of this disease based only on the patient’s complaints and symptoms. Although the first suspicion of the presence of pathology arises on the basis of characteristic manifestations.
The doctor conducts a full examination:
- tests coordination of movements;
- studies the degree of sensitivity of the limbs;
- reaction of body parts to skin irritants;
- test results: cholesterol level, hormonal balance, blood clotting, etc.;
- establishes a history of illnesses;
- Finds out information about past injuries.
Even if a concussion occurred more than a year ago, it can become an impetus for the development of external replacement hydrocephalus.
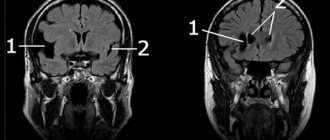
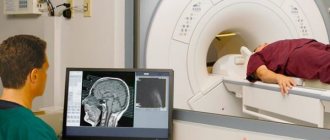
To have a complete understanding of the extent of the disease, the specialist prescribes magnetic resonance imaging. The MRI image is the most important for making a diagnosis. It makes it possible to determine the condition of the ventricles of the brain, determine the presence and severity of tissue damage, and an increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid.
The doctor may also send the patient for a number of other studies, such as:
- Computed tomography helps diagnose the brain, determines the state of the gray matter, indicates the contours of the cortex, and changes in the size of cavities with cerebrospinal fluid.
- An examination by an ophthalmologist is necessary to exclude fundus pathologies.
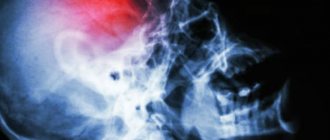
- An X-ray of the head shows the volume of dropsy and the nuances of the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Angiography is an X-ray of the vascular system of the head, which can detect deterioration of blood circulation in the brain and vascular pathology.
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the brain - neurosonography - is performed on infants whose fontanel has not yet closed. With its help, it is possible to determine the type of dropsy and its size.
If an infectious etiology is suspected, the blood is tested using PCR for the presence of antibodies to rubella, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, and herpes virus.
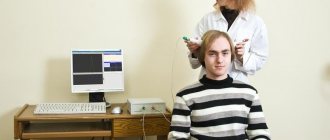
When a patient suffers from epileptic seizures, frequent convulsions, it is necessary to undergo echoencephalography. It shows negative changes in the brain, the presence of foci of increased activity.
Symptoms
Symptoms of hydrocele largely depend on age.
In children of the 1st year of life they are brighter:
- increase in skull volume;
- thinning of the bone and separation of the cranial sutures;
- the appearance of a clearly visible venous pattern on the scalp;
- strabismus;
- developmental delay.
In adults, the symptoms are less pronounced, many of them can be explained by other diseases.
This:
- frequent and severe headaches that do not disappear even after taking painkillers;
- disorders of the vestibular apparatus;
- nausea, vomiting;
- deterioration of vision: double vision, blurring, narrowing of visual fields;
- decreased motor ability of the limbs, sometimes complete paralysis;
- decrease in tactile abilities;
- loss of sensitivity of the skin.
With atrophic hydrocephalus, the disease is asymptomatic for a long time or its manifestations are so weak that they are mistaken for fatigue and overwork. Later, the symptoms intensify and become more pronounced, but are often mistakenly considered to be a consequence of various mental disorders, which leads to incorrect diagnosis and incorrect treatment.
It can be:
- memory losses;
- decreased mental abilities;
- difficulties in pronouncing words;
- gait disturbances;
- bed-wetting;
- irritability, aggressiveness, inappropriate behavior.
Diagnostics
Similar symptoms to external replacement hydrocephalus can be caused by other types of dropsy, as well as diseases not associated with cerebral edema.
The main goals of diagnostic studies are:
- Clarification of the diagnosis and detection of indisputable signs of brain atrophy.
- Determination of the factor that led to changes in brain tissue: infections, head injuries, tumors, heredity, lifestyle.
- Choosing the optimal treatment method.
To solve these problems, the following procedures are performed:
| Procedure | Description |
| MRI | The method involves exposing the desired areas of the brain to electromagnetic waves and obtaining a series of images that provide comprehensive information about the structure of the brain. Particularly informative are studies done at different times, which allow us to see the dynamics of change. |
| CT | Computed tomography is similar to MRI, but instead of electromagnetic waves, it uses x-rays. |
| Ultrasound | Ultrasound examinations will show whether there are diseases that can cause atrophy of brain tissue. |
| Doppler diagnostics | Study of the characteristics of blood flow in the membranes of the brain and determination of disturbances in the absorption of cerebral fluid. |
| Lumbar puncture | It allows you to examine the cerebrospinal fluid. |
| Laboratory blood tests | They are necessary to determine its biochemical parameters: coagulation, cholesterol levels, and the presence of hormones. |
In addition, as part of the diagnosis, the patient may be asked to undergo additional examinations from a number of specialists:
- endocrinologist;
- ophthalmologist;
- Laura.
Their goal is to exclude other causes of the identified symptoms and determine whether there are contraindications to certain treatment methods.
Survey
The algorithm is based on a competent analysis of the patient’s complaints by a neurologist and MRI results. In laboratory studies, it is necessary to determine the level of cholesterol fractions in the blood, blood clotting and a number of other biochemical indicators, including the hormonal profile. You may need to consult an endocrinologist, ophthalmologist, as well as study the vessels of the neck and brain using ultrasound scanning and Doppler diagnostics. It is necessary to determine whether hydrocephalic syndrome is caused by excessive production of cerebrospinal fluid or whether the atrophy of the brain matter comes first. This is important because different causes require different treatment approaches.
NDH differs from other types in that it does not pose a clear threat to life. Infections, injuries, tumor processes, hormonal disorders, lack of B vitamins and psychogenic factors have only an indirect effect on its development. The determining factors in the occurrence of the disease are the individual characteristics of the body: heredity, lifestyle. It is they that lead to true hydrocephalus, causing the corresponding symptoms, and require a radically different approach to diagnosis and treatment. The opportunity to treat and correct NDH still exists, including at the stage of primary medical care.
It happens that no obvious cause can be found. Then the therapy algorithm is aimed at correcting risk factors: work and rest schedule, diet, eliminating habitual intoxications (alcoholism, smoking, occupational hazards), eliminating stress factors, and, if possible, normalizing relationships in the family and society.
Why is it dangerous?
The main danger of open replacement hydrocephalus is that it develops practically asymptomatically over a long period of time.
When the symptoms begin to disturb the patient and he consults a doctor, the disease reaches intractable stages, and the volume of the brain due to atrophy of brain tissue is reduced so much that the changes become irreversible.
What is external replacement hydrocephalus of the brain?
Brain tissues do not come into contact with bone tissues, since they are in the cerebrospinal fluid. This is cerebrospinal fluid that protects the brain from mechanical injury. It provides a stable temperature and supplies nutrition to the cells. The standard volume of cerebrospinal fluid is 150 ml. Several times a day, the composition of the liquid is completely renewed.
The fluid is absorbed by the ventricles, which begin to put pressure on the brain.
If this process is disrupted, cerebrospinal fluid is poorly absorbed and accumulates between the membranes, causing dropsy. Sometimes the fluid is absorbed by the ventricles, which will put pressure on the brain. As a result of the development of microadenoma, brain activity is disrupted and alarming symptoms arise.
Drug treatment
The goal of conservative treatment is to eliminate the cause of the disease and relieve symptoms.
At the initial and moderate stages, drugs are used to combat swelling and stabilize the patient’s condition:
- promoting the removal of excess fluid from the body;
- antibiotics (for post-infectious hydrocephalus);
- normalizing blood supply to the brain;
- lowering the level of glutamate, a substance that promotes the destruction of neurons;
- antioxidants that normalize the functioning of nerve cells.
The course of drug treatment is prescribed by a doctor. Most of the drugs used for hydrocephalus have many side effects, so if used incorrectly, they can cause serious damage to health. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable.
In addition to drug therapy, the patient may be recommended as restorative measures:
- a set of exercise therapy exercises developed by a specialist taking into account the causes of the disease and the patient’s condition;
- restriction in fluid intake;
- diet;
- medicinal baths based on pine extract;
- electrotherapy;
- massages.
With timely treatment, patients experience:
- gradual weakening of symptoms;
- strengthening cerebral blood vessels;
- normalization of their ability to absorb liquid.
Treatment prognosis and disease prevention
How long do people live with a diagnosis of hydrocephalus? The earlier the disease is detected, the more optimistic the prognosis for recovery. The fight against pathology can be completed successfully with the correct diagnosis, the appointment of comprehensive treatment, and timely measures taken to eliminate the causes that cause it.
If the patient seeks help at a late stage, when significant neuralgic disorders occur, there is a possibility that some functions will not be restored and he will remain disabled. The negative processes in the brain inherent in dropsy are irreversible. In case of acute outflow disturbance and large accumulation of fluid, death is possible if surgery is not performed.
It is easier to prevent any disease than to cure it. In order to detect pathology in a timely manner, you need to pay attention to deteriorating health conditions, treat infectious diseases in a timely manner, give up bad habits, and prevent increases in intracranial and blood pressure. If symptoms appear, do not start self-medication, guided by someone’s advice or information from the Internet, but go for a consultation with a specialist.
Surgery
If conservative methods are ineffective, surgical treatment is used. In the arsenal of modern neurosurgery there are several minimally invasive methods for normalizing the amount of cerebral fluid, which consists of creating an additional outflow pathway for the cerebrospinal fluid.
Typically, endoscopic surgery is performed through the nasal passages, leaving no open scars.
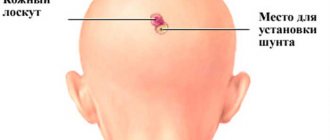
Bypass surgery
If endoscopic surgery is impossible or ineffective, a shunt method is used to normalize the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. It consists of installing a shunt under the scalp - a thin hollow silicone tube equipped with a valve that prevents the reverse movement of fluid.
There are different types of shunting:
- verticulo-peritoneal - when excess livcor is directed into the abdominal cavity;
- verticuloatrial - the other end of the shunt is sewn into the circulatory system.
The most common indications for shunting are types of hydrocephalus that develop as a consequence of a stroke or traumatic brain injury.
Treatment exclusively with shunting is also possible in the presence of a pathology concomitant with hydrocephalus, known as normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH), which usually develops in elderly patients (over 65 years of age).
The operation is performed after a thorough examination, which is prescribed by a neurosurgeon to confirm the diagnosis and select the optimal type of bypass.
Contraindications for this procedure may include:
- infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- skin infections;
- unsatisfactory condition of the oral cavity.
The limitations are due to the fact that the shunt, being a foreign body, can provoke increased inflammatory processes in the body.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia and lasts approximately 1 hour. To install the shunt, the neurosurgeon makes incisions in the head and neck (abdomen) area. The duration of the postoperative period is no more than 5 days, during which the patient remains under medical supervision. Painkillers are used to relieve pain in the incision area.
Depending on the severity of the disease and the characteristics of the patient’s body, an improvement in his condition can be observed immediately after the operation or a month later. The shunt remains for life, periodically, due to wear and tear and the occurrence of various defects, it requires correction.
Surgery
Surgical interventions for this pathology are most often inappropriate. They are carried out only in the presence of decompensated dropsy - a clear violation of the outflow of fluid from the cranial cavity and increased intracranial pressure. Modern neurosurgical care is based on endoscopic minimally invasive methods, i.e. with minimal risk of injury to the patient, usually through the nasal passages. Bypass routes are established to evacuate excess fluid from the skull into the vascular bed and bloodstream. In this case, intracranial pressure normalizes and the quality of life stabilizes.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine can provide only symptomatic treatment.
After consulting a specialist, some of its techniques can be applied:
- to alleviate the patient's condition;
- to increase the effectiveness of medications;
- as part of rehabilitation therapy in the postoperative period.
External replacement hydrocephalus in adults in treatment can be supplemented with the following folk recipes:
- Grind the garlic and radish in equal parts into a paste, squeeze out the resulting juice and take ½ tsp. 3 times a day for 3 weeks.
- Finely chop the black elderberry root and add alcohol (1 part chopped root to 10 parts alcohol). Infuse for 7 days, then take 25 drops three times a day.
- Dry and chop buckthorn bark or berries. Take the resulting powder (½ g, 3 times a day), use as a decoction (1 tbsp. 3 times a day). You can replace the powder with buckthorn extract purchased at the pharmacy, drinking 30 drops daily in 3 doses.
- Pumpkin juice will remove excess fluid from the body, cleanse the body, and normalize sleep. To prepare it, you need to pass the pumpkin pulp through a juicer. For treatment, only fresh juice is used, which can be stored for no longer than 2 days, drinking half a glass every day.
pumpkin juice - Infusion of birch buds and leaves: grind dry birch leaves or swollen buds, add vodka (1:1), leave for 3 weeks. Strain, drink, diluting ½ tsp. infusion in 1 tbsp. l. water, 3 r. in a day.
- Melissa can relieve migraines accompanying hydrocephalus. 15 g of herb pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, leave for 2 weeks, drink 15 drops after each meal.
- Cornflower has the ability to remove fluid from the body and fight bacterial infection. To prepare the decoction, you need to pour 1 liter of boiling water over 50 g of dried flower, take 50 g of the decoction after meals.
Rehabilitation and prognosis
With drug and surgical treatment of hydrocephalus, the cause of the disease is eliminated and the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is normalized. To restore full brain function, motor activity, speech, vision and other functions lost during the disease, a long rehabilitation period is required.
The patient may be offered:
- Physiotherapy . Exercises are prescribed by a doctor; when performing them, you must strictly follow the specialist’s recommendations, without trying to force things by increasing the intensity or duration of exercise. Neglecting this rule can worsen the patient's condition.
- Massage. It will strengthen the muscles and increase their tone.
- Classes with a speech therapist, neuropsychiatrist. This will allow you to quickly cope with the manifestations of aphasia and remove the irritability, aggressiveness, and depression associated with these difficulties that accompany this condition.
- A set of measures aimed at eliminating cognitive disorders: restoring memory, the ability to concentrate, and the ability to think logically.
There is no universal method for the rehabilitation of patients with hydrocele.
The choice of specific techniques depends on several factors:
- age;
- degree of brain damage;
- specifics of previous treatment;
- presence of concomitant diseases.
Provided that external replacement hydrocephalus was identified in the early stages of development, proper treatment and compliance with rehabilitation requirements, the disease is completely curable, changes in the structure of the gray matter are reversible. As a rule, the patient can lead a normal life after the end of the recovery period.
At stages 2 and 3, it is possible to partially relieve the symptoms and alleviate the patient’s condition, sometimes to stop the development of the disease, but it is no longer possible to reverse the process of brain destruction. A number of restrictions are imposed on a person, the purpose of which is to prevent a relapse and increase in the symptoms of hydrocephalus.
Without treatment, the disease progresses and brain volume gradually decreases, leading to:
- further decline in intellectual abilities;
- loss of motor functions;
- loss of vision.
Ultimately, the person becomes deeply disabled, and in some cases death cannot be ruled out.
It is difficult to detect external replacement hydrocephalus in the early stages, its treatment requires a long time and does not provide a 100% guarantee of recovery, and the consequences of the disease can be unpleasant.
However, you can try:
- avoid head injury;
- follow a schedule of vaccinations that will protect against neuroinfections;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- undergo regular MRI examinations;
- At the first signs of illness, consult a doctor.
These simple steps will minimize the risk of becoming closely acquainted with external replacement hydrocephalus in adults and maintain brain health.
Treatment methods
Most often, patients are prescribed conservative therapy for external replacement hydrocephalus of the brain. The choice of drugs and treatment methods is made by the doctor after studying test data and the person’s health. Treatment is carried out with the aim of: relieving intracranial pressure, normalizing cerebral circulation, strengthening the body.
Medication and therapeutic methods
To treat the pathology, the patient is prescribed:
- taking nootropic drugs;
- diuretic medications, they remove excess fluid from the body;
- massage;
- various types of baths;
- physical exercise;
- special diet.
Surgical
Surgical treatment of replacement hydrocephalus is rarely performed - in extreme cases. There are 2 types of operations performed for dropsy: bypass surgery, endoscopic surgery.
Surgeons perform bypass surgery. It allows you to remove excess liquid. Various tubes and valves are inserted into the patient, through which cerebrospinal fluid flows into the peritoneum. Endoscopic surgery is performed to provide additional pathways for the drainage of cerebrospinal fluid into the cisterns of the brain, in which it is absorbed naturally. Blood clots and hematomas are removed from a person, and veins are treated.
The second type of surgical intervention is used more often, as it is less traumatic for the patient. In mild cases of the disease, surgery can completely restore the patient’s health. In advanced situations – to alleviate the patient’s condition.