The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
Brain cancer is a dangerous disease that is difficult to treat and can lead to the death of the patient. The greatest threat lies in its asymptomatic course - the fourth stage of brain cancer, in which the patient has severe symptoms of the disease, is difficult to treat and the prognosis for such patients is disappointing.
At the same time, the symptoms with which a patient may consult a doctor can easily be confused with manifestations of other diseases. Thus, headaches, vomiting and dizziness in combination with visual impairment are characteristic of migraine and hypertensive crisis. Head pain can also be caused by osteochondrosis. Therefore, in the treatment of brain cancer, much depends on the qualifications of the doctor who is consulted for diagnosis - whether he will be able to detect dangerous signs in time and conduct the necessary examination, which will help identify the oncological process.
Tumors are classified according to the tissues in which they begin to grow. Thus, tumors developing from the membrane of the brain are called menangiomas. Tumors that arise in brain tissue are gangliomas or astrocytomas, the common name is neuroepithelial tumors. Neuroma is a malignant neoplasm affecting the sheath of the cranial nerves.
Gliomas make up 80% of malignant brain tumors; meningiomas are also common tumors, occurring in 35% of cases of primary brain cancer.
- Surgery
- Gamma Knife - targeted radiosurgery
Causes of brain cancer
The causes of brain tumors have not been sufficiently studied - in 5-10% of cancers are caused by hereditary gene pathologies, secondary tumors arise when metastases spread from cancer of other organs.
The following causes of brain cancer can be identified:
- Genetic diseases such as Gorlin syndrome, Bourneville disease, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, tuberculous sclerosis and APC gene disorders can cause the development of brain cancer.
- A weakened state of immunity, which can be observed after organ transplantation, increases the likelihood of cancer in the brain and other organs in patients with AIDS.
- Brain cancer is more common in women than in men. The exception is meningiomas - neoplasms of the arachnoid membrane of the brain. Race also plays an important role - white people are more likely to suffer from the disease than representatives of other races.
- Exposure to radiation and carcinogenic substances also carries an oncogenic hazard and is a risk factor for the development of brain cancer. The risk group includes people involved in hazardous industries, for example, in the industrial production of plastics.
- Brain cancer is more common in adults; with age, the risk of malignant neoplasms increases, and the disease is more difficult to treat. Children are also at risk of developing cancer, but the typical sites of tumors differ: for example, in adults, cancer often affects the lining of the brain, while in younger patients the cerebellum or brain stem is affected. In 10% of adult brain cancers, the tumor involves the pineal gland and pituitary gland.
Secondary tumors are a consequence of other oncological processes in the body - metastases enter the skull through the circulatory system and give rise to a malignant neoplasm in the brain. Such tumors are often found in breast cancer and other cancers.
The first signs of brain cancer
With brain tumors, symptoms are of two types: focal and cerebral. General cerebral are characteristic of all cases of brain cancer, while focal ones depend on the location of the tumor.
Focal symptoms can be very diverse, their type and severity depend on the area of the brain that is affected by the disease and the functions for which it is responsible - memory, oral and written speech, counting, etc.
Focal symptoms of brain cancer include:
- Partial or complete impairment of the mobility of certain parts of the body, impaired sensitivity of the limbs, distorted perception of temperature and other external factors;
- Changes associated with personality - the patient’s character changes, a person may become hot-tempered and irritable, or, on the contrary, too calm and indifferent to everything that previously worried him. Lethargy, apathy, frivolity in making important decisions that affect life, impulsive actions - all this can be a sign of mental disorders that occur with brain cancer.
- Loss of bladder control, difficulty urinating.
All brain tumors are characterized by common symptoms associated with increased intracranial pressure, as well as the mechanical effect of the tumor on various centers of the brain:
- Dizziness, loss of balance, a feeling that the ground is disappearing from under your feet - occur spontaneously and are an important symptom that requires diagnostic testing;
- Pain in the head is often dull and bursting, but can have a different character; usually occur in the morning before the first meal, as well as in the evenings or after psycho-emotional stress, and intensify with physical activity;
- Vomiting - appears in the morning or occurs uncontrollably with a sudden change in head position. May appear without nausea and is not associated with meals. With intense vomiting, there is a risk of dehydration, which is why the patient is forced to take drugs that block the stimulation of the corresponding receptors.
Other symptoms of brain cancer
Symptoms of brain cancer that appear in later stages:
- Partial or complete loss of vision, “floaters” before the eyes are a symptom provoked by the pressure of the tumor on the optic nerve, which in the absence of timely treatment can lead to its death. In this case, it will be impossible to restore vision.
- Compression of the auditory nerve by the tumor causes hearing impairment in the patient.
- Epileptic seizures that occur suddenly in young people are a dangerous sign that should promptly consult a doctor. Characteristic of the second and later stages of brain cancer.
- Hormonal disorders are often observed with adenomatous neoplasms of glandular tissue that are capable of producing hormones. Symptoms can be very diverse, as with other diseases associated with hormonal imbalance.
- Lesions of the brain stem are characterized by dysfunction of breathing and swallowing, distortion of smell, taste, and vision. Despite the seriousness of the symptoms, which can significantly reduce the quality of life and make a person incapacitated and dependent, brain damage can be minor and benign. But even small tumors in this area can lead to serious consequences, displacement of brain structures, which creates the need for surgical intervention.
- Tumors in the temporal zone of the brain manifest themselves as visual and auditory hallucinations, while tumors in the occipital region are characterized by disturbances in color perception.
Diagnosis of brain cancer
Types of diagnosis of brain cancer include:
- Personal examination by a doctor. During the initial examination, the doctor asks the patient to perform a number of tasks that help identify violations of coordination, tactile and motor functions: touch your nose with your fingers with your eyes closed, take a few steps straight after spinning around yourself. A neurologist checks the tendon reflex.
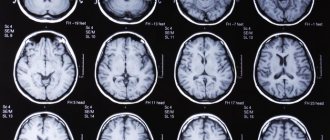
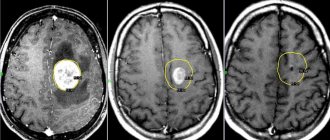
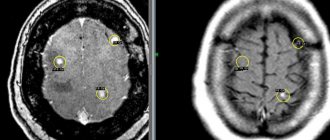
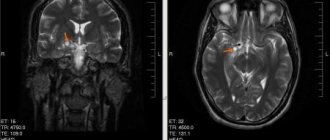
- MRI with contrast is prescribed in the presence of abnormalities, which makes it possible to detect brain cancer at an early stage, determine the location of the tumor and develop an optimal treatment plan.
- Puncture of brain tissue allows you to determine the presence of abnormal cells, the degree of tissue changes, and determine the stage of the oncological process. However, tissue biopsy is not always possible due to the difficult-to-reach location of the tumor, so such an analysis is most often performed when a malignant neoplasm is removed.
- X-ray – allows you to determine the presence and location of a tumor by the blood vessels shown in the image, for which the patient is first injected with a contrast agent. Craniography allows you to determine changes in the bone structure of the skull, abnormal calcium deposits caused by the oncological process.
After a diagnostic examination, the doctor draws up an individual treatment plan.
Indications and contraindications
Complete safety, high information content and low cost of the procedure make MRI very popular in diagnosing various diseases. Using this method, you can diagnose various ailments and deal with strange symptoms:
- pathologies of cerebral vessels;
- brain injuries that can lead to cerebral hemorrhage;
- damage to hearing, speech, etc.;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- pituitary adenoma;
- epilepsy;
- brain tumors;
- pathologies of the base of the skull and more.
As for contraindications, they are conditionally divided into two groups - relative and absolute.
In the first case, special preparation is required, but diagnostics using this method is not prohibited. As for the second option, if there are absolute contraindications, the procedure is strictly prohibited.
Relative contraindications:
- pregnancy up to 12 weeks;
- mild to severe claustrophobia;
- tattoos with metal connections;
- drug or alcohol intoxication;
- heart problems;
- heart valve prostheses, insulin pumps, etc.
Absolute contraindications:
- hematopoietic anemia (if it comes to MRI with contrast);
- presence of foreign metal bodies;
- pacemakers and other electrical devices inside the body.
Stages of brain cancer
Due to the almost asymptomatic course of the disease, it is difficult to accurately determine the stage of cancer, especially since the transition from one stage to another occurs quickly and unexpectedly. This is especially true for cancers in the brain stem. The stage of the disease is accurately determined only after a post-mortem autopsy, so the slightest manifestations of pathology must be treated carefully from the first days - in the last stages, cancer is not amenable to surgical treatment and responds poorly to medications and other types of therapy.
Stage 1 brain cancer
At the first stage of cancer, a small number of cells are affected; surgical treatment is most often successful with a minimal likelihood of relapse. However, detecting cancer at this stage is very difficult - the symptoms are characteristic of a number of other diseases, so cancer can only be detected with special diagnostics. The first stage of cancer is characterized by weakness and drowsiness, periodic headaches and dizziness. People rarely consult a doctor with such symptoms, since these manifestations are attributed to weakened immunity due to climate change or to chronic diseases.
Stage 2 brain cancer
The transition of the cancer process to the second stage is accompanied by the growth of a tumor, which engulfs nearby tissues and begins to compress the brain centers. Dangerous symptoms are convulsions and epileptic seizures. In addition, the patient may experience digestive dysfunction - problems with bowel movements and periodic vomiting. At this stage, the tumor is still operable, but the chances of a complete cure are reduced.
Stage 3 brain cancer
The third stage of brain cancer is characterized by rapid growth of the tumor; malignant degeneration of cells affects healthy tissue, which makes surgical removal of the tumor almost impossible. However, surgical treatment can provide good results if the tumor is located in the temporal lobe.
Symptoms of the third stage of brain cancer - the symptoms of the second stage intensify, hearing, vision and speech impairments become more pronounced, the patient has problems with selecting, “remembering” words, it is difficult for him to concentrate, attention is scattered and memory is impaired. The limbs become numb, there is a tingling sensation in them, and the mobility of the arms and legs is impaired. In an upright position and when walking, it becomes almost impossible to maintain balance due to dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus. A characteristic symptom for the third stage is horizontal nystagmus - the patient has moving pupils, even if the head remains motionless, the patient himself does not notice this.
Stage 4 brain cancer
At the fourth stage of cancer, surgical treatment is not performed, since the tumor affects vital parts of the brain. Palliative techniques, radiation therapy, and drug treatment are used to reduce the patient's suffering with the help of strong painkillers. The prognosis is disappointing, but much depends on the state of the patient’s immune system and his emotional state. Symptoms of brain cancer at this stage are associated with the loss of basic vital functions as the malignant process spreads to the corresponding areas of the brain. With poor treatment success, the patient falls into a coma from which he never recovers.
How long do they live with brain cancer?
To predict the development of the disease and assess the health status of patients with brain cancer, the concept of “five-year survival” is used. People who have been diagnosed with the disease are assessed, regardless of the course of treatment they are undergoing. Some patients live longer than five years after successful therapy, others are forced to constantly undergo treatment procedures.
On average, the survival rate of patients with brain tumors is 35%. For malignant brain tumors, most of which are gliomas, the survival rate is about 5%.
What could be the consequences?
Common consequences include:
- Swelling or hydrocephalus. Hydrocephalus is the accumulation of fluid in the cavities of the brain. The condition is characterized by severe headaches, nausea, convulsions, and deterioration of visual acuity.
- Convulsive attacks. Antiepileptic drugs are used to prevent seizures.
- Depressive states. Caused by the emotional state of the patient. To normalize the psycho-emotional state, antidepressants are prescribed.
Treatment of brain cancer
Treatment of brain cancer requires the interaction of specialists in different fields - oncologist, therapist, neurologist, neurosurgeon, radiologist and rehabilitation specialist. Diagnosis of the disease usually begins with a visit to a general practitioner or neurologist, from where the patient is referred to other specialists for additional examination.
The further treatment plan depends on the patient’s age (therapy for cancer tumors in the younger age group 0-19 years, middle and older differs). In addition, when drawing up a course of treatment, the patient’s general health, the type of tumor and its location are taken into account.
Radiation therapy, radiation therapy, and surgery are used in the treatment of oncogenic brain tumors. The most reliable method is surgery to remove the tumor, but this is not always possible due to the inaccessible location of the tumor. Surgery is rarely performed at the third and fourth stages of cancer, as this entails great risks and does not give the desired result - at this stage of the disease, the tumor affects vital parts of the brain, penetrates deeply into healthy tissue and its complete removal is impossible.
Surgery
Surgical removal of a tumor is an effective method of treating brain cancer in the early stages, especially when it comes to benign tumors. Surgical intervention in this case differs from abdominal operations, in which the surgeon can capture part of the nearby tissue to prevent the spread of the oncological process.
When performing brain surgery, maximum precision must be observed - an extra millimeter of tissue damaged during surgical procedures can cost a person a vital function. This is why surgical treatment is ineffective in the terminal stages of cancer - it is impossible to completely remove the tumor, and the pathological process spreads further. Palliative techniques can reduce the pressure that the tumor puts on neighboring areas, and drug treatment, radiotherapy and chemotherapy slow down the growth of the tumor.
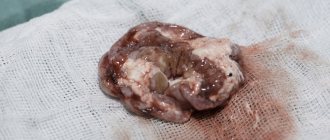
In the first and second stages of cancer, when a benign tumor is removed, the symptoms of the disease are completely eliminated. Therefore, with timely diagnosis, the prognosis for the patient is favorable. If the tumor is located in a difficult-to-reach location, surgical intervention requires additional research to accurately determine the location of the tumor. To classify the tumor and determine the stage of the cancer, the doctor does a tissue biopsy.
To reduce tissue damage that may occur during surgery, modern techniques are used - stereostatic radiosurgery. This is a surgical procedure that uses high-precision delivery of high-dose gamma rays or x-rays to destroy the tumor. In this case, healthy tissues are minimally affected or remain undamaged. The possibility of using the technique depends on the location and size of the tumor. This treatment is less traumatic for the patient, shortens the rehabilitation period and minimizes the risk of complications after surgery.
Conservative or drug therapy is carried out before surgery and includes:
- Anticonvulsants - reduce the symptoms of the second and later stages of cancer, reduces the likelihood of an epileptic seizure;
- Steroid anti-inflammatory drugs - drugs in this group relieve swelling of tumor tissue, which reduces mechanical pressure on healthy areas; a common remedy is dexamethasone;
To reduce intracranial pressure, shunt surgery may be necessary, the purpose of which is to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid, the removal of which is difficult due to compression of the cerebrospinal fluid tract by the tumor. Fluid is removed through a catheter during the process of ventriculoperitoneal shunting - the lateral ventricle is connected to the abdominal cavity through a plastic tube.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy for cancerous tumors is used in two cases: if the patient is contraindicated for health reasons, or after tumor removal to prevent relapse. Surgical removal of the tumor is ineffective in the later stages of brain cancer, then radiation therapy is used as the main method of treatment. The presence of concomitant chronic diseases and pathologies of the cardiovascular system may be a contraindication for surgical intervention. In other cases, radiation therapy may be used to destroy abnormal cells that may be causing cancer after the tumor has been surgically removed.
The specialist prescribes the dose of radiation individually; the exposure is carried out locally to minimize damage to tissues close to the tumor. When carrying out radiation therapy, it is important to take into account the type of tumor, its location and the size of the tumor. Two radiation therapy techniques are used:
- Brachytherapy – performed during inpatient treatment; A radioactive substance is injected into the tumor tissue, which destroys it from the inside. The dose of injected grain is calculated in such a way that the tumor is destroyed, but healthy tissue remains undamaged.
- External beam radiation therapy is carried out over a course of several weeks, during which the patient is exposed to high doses of radiation for several minutes. Sessions are held five days a week, you can visit the hospital only at the appointed time, then the patient goes home.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is not used as the main method of treating cancer due to the fact that its effects affect not only the tumor tissue, but also affect the body as a whole. The treatment regimen is drawn up by the doctor, including drugs of a certain group - antimetabolites, drugs of the alkylating group, synthetic antibiotics, etc. Treatment is carried out in a course of several cycles, between which it is necessary to take pauses. The drugs are taken orally or administered by injection or through a liquor shunt. After three or four cycles, they take a break to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy.
The danger of chemotherapy lies in its negative impact on the hematopoietic organs and epithelium of the digestive tract.
Endoscopic treatment
Endoscopic surgery is less traumatic than traditional neurosurgery methods, as it is performed using special equipment without wide incisions. During conventional brain surgery, access is achieved by trephination, during which the skull is opened, which further traumatizes the patient, prolonging the rehabilitation period. Endoscopic methods minimize damage to nerves and small blood vessels, which is especially important when working with brain tissue. Thus, endoscopic operations are used to treat hydrocephalus in children caused by stagnation of fluid in the ventricles of the brain; this operation is called ventruloscopy. A pituitary adenoma can also be removed using endoscopic methods, by inserting endoscopic instruments through the nose - transnasal endoscopy.
Endoscopic surgery is also used for traumatic brain injuries, removal of cysts and hematomas.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is carried out on the basis of information received about the patient’s condition:
- interview . The doctor asks the person about existing symptoms, checks memory, coordination of movements, hearing, and vision. Based on the information collected, the specialist makes a preliminary diagnosis. If cancer is suspected, a number of tests are carried out.
- Analyzes. The patient undergoes general blood and urine tests, biochemical analysis, and blood tests for tumor markers.
- MRI of the brain. Helps take pictures of tumor formation from different viewing angles. This will allow you to determine the size and location of the formation.
- CT, like MRI, allows you to determine the location of the tumor, possible swelling, and bleeding.
- PAT. Allows you to monitor brain activity, see the location of scar tissue, dead and malignant cells.
- EEG. Allows you to determine how different parts of the brain work by measuring electromagnetic impulses created by neurons.
- MR angiography. Allows you to evaluate cerebral blood flow.
- puncture . This type of procedure is intended to detect the presence of cancer cells in the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Biopsy. It can be taken both during the operation itself and before it. With this procedure, a sample (suspected cancer cells) is taken and compared with a healthy one. The study helps to identify the malignancy of the formation, as well as the type of cancer.
The latest methods of non-surgical treatment of brain cancer
Brain oncology is the most difficult to treat, since the quality of processing incoming and outgoing information from a person depends on the nerve cells of the cerebral hemispheres and the connections between them. Simply put, when trying to destroy cancer cells, it is easy to affect healthy ones, and when localized in the brain, this means a high risk of loss of memory, intelligence, and communication between various organs and muscles.
In this regard, neurosurgeons are innovating, developing new methods of microscopic intervention to reduce this risk, and in the meantime, Japanese scientists have found an alternative means of combating cancer and other diseases.
Gamma Knife – targeted radiosurgery
The creation and implementation of the gamma knife gave doctors the opportunity to remove brain tumors of various origins without trephination. This innovative technology is also used to treat formations in the soft tissues of the head and neck.
Gamma Knife has a whole range of advantages, the main ones of which are: no need to immerse the patient in general anesthesia, no rehabilitation and no lengthy preparation. Complications are kept to a minimum. The prognosis when using this method is as favorable as possible. After the procedure, in patients with benign tumors, the survival rate remains at about 95%, and in patients with malignant tumors - 89%.
The cost of therapy is high, it starts from 250,000 and can reach 350,000 rubles per procedure - this is the cost in Russia, prices abroad are much higher. Patients can apply for a quota, but it will not be provided as quickly as possible.
At the radio wave microsurgery center, up to 8,000 procedures using a gamma knife are performed annually. The use of modern equipment makes this method effective and safe, making it possible to treat patients with complex diagnoses.
Benefits of therapy:
- The doctor does not open the patient's skull. It is no secret that trepanation is associated with a high risk of developing severe complications.
- The patient does not need anesthesia. The procedure is painless; doctors limit local anesthesia to the area on which the frame is installed in order to fix the head in the desired position.
- The person is in a room, in an open space, and not in a cell. The method can be implemented even for treating children. However, they do not require sedatives.
- The effect is targeted, only cancer cells are destroyed. Healthy tissues are not affected.
- Gamma knife is a method of treating tumors located in areas that are simply impossible to reach with a scalpel.
- The process is controlled by artificial intelligence, which reduces the likelihood of error to zero.
Flaws:
- During the procedure, the patient will have to remain motionless for a long time. To do this, his head is fixed using a special frame. It puts a serious load on the skull, which is accompanied not only by discomfort, but also by pain. To minimize discomfort, local anesthesia is used.
- The method is available for implementation only if the tumor does not exceed 35 mm in diameter.
- The price of the course is high, and it is possible to obtain a quota only in a few months, and sometimes even years. Cancer patients cannot afford such a long waiting period. During this time, the tumor may increase in size, making surgery unavailable.
- Limited application of the method. It is used only to treat tumors in the brain, neck and head.
Another innovative method of treating cancer has become less widespread - the cyber knife. Its disadvantages: even higher cost and little experience in practical application.
If treatment using Gamma Knife was started at an early stage of the disease, the prognosis is favorable in 89% of cases.
Even Gamma Knife cannot be considered a panacea. This method is not suitable for every patient. Often the relief is temporary, and complete recovery is never achieved. However, with the help of a gamma knife it is possible to get rid of metastases in the brain and prolong the life of the patient.
Radiosurgery centers in Russia
The main radiosurgery centers in Russia are located in Moscow and St. Petersburg:
- Research Institute named after Burdenko;
- "Gamma Clinic";
- branch in Obninsk (nearest Moscow region);
- in St. Petersburg;
- Oncology clinic MIBS in St. Petersburg;
- Berezin Institute (St. Petersburg);
- ambulance for them. Sklifosovsky (Moscow).
In addition, similar equipment is located in Tyumen, Kazan, Khanty-Mansiysk, Saratov, Krasnoyarsk and Ufa. There are gamma knives in some private clinics.
[Video] What is Gamma Knife and how does it work:
Preparation for the procedure
Basically, no preparatory work is required before the procedure. In some cases, the patient may be asked not to drink or eat before the MRI. To diagnose a brain tumor, the patient will need to remove all metal jewelry and wear a loose hospital gown. As a last resort, you can stay in your clothes if they are spacious and there are no metal parts on them.
Women who are pregnant are required to notify the doctor about this before the procedure is performed. Medical practice confirms the fact that over the past 30 years, the MRI method has not had a negative impact on the health of the mother and fetus. But it is still too early to talk about the complete safety of carrying out such diagnostics on pregnant women. You should inform the specialist about recent operations, metal plates installed inside, as well as the presence of allergies.
Brain tumor size
If it is necessary to carry out this procedure, but the patient is very nervous or suffers from claustrophobia, then he can be given sedatives. They are not an obstacle to successful diagnosis.