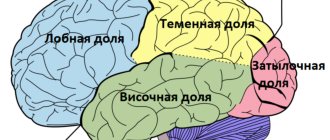
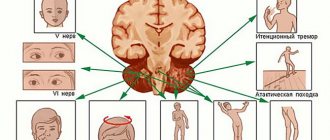
The frontal lobes are located at the front of the brain. When talking about them, we must also mean the premotor area, the section of the anterior central gyrus and the pole. The functional purpose of the frontal lobe is to analyze the activity of motor functions. If these parts of the brain are affected by a malignant tumor, then the motor parameters of synthesis and analysis will be significantly distorted. However, this depends primarily on which areas of the frontotemporal lobes the cancerous tumor is localized in - upper, basal, anterior or posterior.
Types of symptoms for frontal tumors
There are 3 fundamentally different types of symptoms characteristic of tumor lesions:
- Local – depend on the location of the pathological focus.
- General at the level of the brain - explained by increased intracranial pressure, disruption of the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (the fluid that nourishes the brain).
- Long-term symptoms indicate involvement of other parts of the nervous system in the process.
- Changes in the composition of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Displacement or dislocation of brain matter.
- General signs at the level of the whole organism indicate the presence of cancer intoxication.
What is a tumor of the frontal part of the head?
A tumor is a new growth that occurs as a result of uncontrolled cell division. The disease can affect people of any age and in some cases be congenital. Tumors can develop in the tissues of the brain and its membranes, in blood vessels, and lymphatic tissue. Based on their location, they are divided into intracerebral and extracerebral (tumors of the meninges and blood vessels).
Tumor damage to the frontal lobes, where the centers responsible for human social skills, speech, writing and tone recognition are located, often leads to disruption of these functions and often provokes frontal lobe epilepsy. The causes of tumors are traumatic brain injuries, infections, heredity, and hormonal imbalances. Treatment is preferably surgical for radical correction of the condition.
All brain structures are located in a limited space, so the appearance of any tumor causes tissue compression and increased intracranial pressure. Even benign neoplasms, when they reach a certain size, can become malignant and lead to death.
Epileptic seizures may continue after the brain tumor is removed.
This is due to impaired blood supply and lack of oxygen at the site of the postoperative scar, as well as the presence of secondary foci formed during the tumor process.The earlier a tumor is detected and eliminated, the lower the risk of developing epilepsy.
Neurologist, reflexologist, hirudotherapist
Kislitsyna Ekaterina Nikolaevna
10 years of experience
Tumors are primary, arising in brain tissue, and secondary, developing as a result of metastases from other organs. Secondary formations occur 5-10 times more often than primary ones.
Local symptoms
Specific local symptoms are characterized by the occurrence of the following phenomena:
- memory impairment;
- false memories;
- lack of attention;
- fatigue;
- worsening mood;
- sudden changes in emotional reactions;
- fussiness;
- speech disorders;
- impaired sense of smell;
- lack of criticism;
- autonomic disorders;
- frontal disorders of motor coordination and balance;
- obsessive grasping movements;
- convulsive seizures.
Memory impairment
Considering that memory is the basis for obtaining new information, patients stop in their development and become unteachable. Impaired motor memory is manifested by the fact that a person periodically forgets for a few seconds how to do a familiar action, and then remembers. In advanced cases, the work started is not completed, because the patient cannot put together and complete the entire chain of necessary actions in a certain sequence.
Distorted Memories
The presence of false memories and the emergence of distorted information in memory are especially characteristic of the presence of a tumor in the dominant frontal lobe (for right-handers - on the left, in left-handers - on the right) or in both frontal lobes.
Attention disorder
At the first stages of the disease, attention impairment is manifested by the inability to focus on a specific action for a long time. Constantly being distracted, a person is bound to forget something. He doesn't remember what needs to be done or why he went somewhere.
Fatigue
Increased fatigue and drowsiness, which patients usually associate with stress, hypovitaminosis, and physical overexertion, while these symptoms are an integral part of the depressive syndrome, which is characteristic specifically of organic damage to the frontal lobe.
Worsening mood
Important! For differential diagnosis, it is necessary to take into account that a reduced mood background can be of 3 types, depending on the location:
- when the hypothalamus or pituitary gland is affected, the mood decreases gradually, over the course of several years the person becomes more and more depressed.
- the localization of the tumor in the temple determines the presence of a low background mood, alternating with unmotivated outbursts of gaiety, while maintaining the basic personality traits;
- when the frontal lobe is damaged, deterioration in mood is accompanied by poverty of spirit, gross changes in mental reactions, and destruction of personality.
Sudden changes in emotional reactions
There are sudden mood swings from unreasonably happy to negative. This serves as a manifestation of the syndrome of inappropriate emotional reaction.
A person’s stable feelings about loved ones disappear, and a positive attitude towards loved ones changes sharply to the opposite, negative. Interest in everything except sex life decreases, gluttony, sloppiness, and rude, tactless jokes appear. This situation is typical for a tumor located on the lower surface of the frontal lobe of the brain (the dominant left hemisphere for right-handed people).
With right-sided localization, similar indifference is accompanied by laughter, foolishness, and talkativeness. There are still no worries about loved ones.
Fussiness
When located on the inner surface of any hemisphere, the tumor causes fussiness. There is increased activity, the desire to accomplish as much as possible. But a person quickly becomes exhausted, apathy and indifference to surrounding people and events set in. Periods of apathy alternate with outbursts of negative reactions towards family members and friends. From time to time, there is a spontaneous surge in business activity, which just as abruptly fades away.
Speech disorders
With a tumor of the frontal lobe of the brain, speech disorders develop, which are characterized by slow speech and difficulty combining individual syllables into words.
First, the patient’s speech is deprived of certain parts of speech, reminiscent of a distorted telegraph text that is understandable to others. Subsequently, the pronunciation of words suffers to such an extent that the patient can only hum and his speech is completely devoid of semantic meaning. In this case, the patient assesses the existing speech defect adequately and becomes depressed about the disorder and becomes tearful.
Such patients pronounce words into a chant perfectly, therefore, in order to convey information to others, some of them begin to chant the words. Reading and writing are not impaired. The second option that a patient can use to communicate with loved ones is by writing notes with different contents. The patient forgets how to count very quickly.
Often, against the background of a sharp violation of the pronunciation of even simple words, patients remain able to pronounce certain obscene phrases. They are in the nature of verbal emboli that involuntarily jump out of the mouth.
Speech disorders occur when the dominant hemisphere is damaged. The progression of the tumor process is accompanied by weakness of the facial muscles, which also affects the ability to pronounce articulate sounds.
Impaired sense of smell
The olfactory pathways run along the base of the brain in the region of the anterior cranial fossa under the frontal lobe. When they are compressed between the hard bones of the skull and the tumor, the sense of smell begins to suffer.
Lack of criticism
The patient suffers from a critical attitude towards himself and his existing defects. If criticism persists, reactive depression or psychosis develops. Antisocial behavior is typical; patients can become dangerous to others.
Autonomic disorders
With frontal lesions, vascular disorders are observed in the skin of the hands, face, and legs. This is due to damage to the autonomic centers of the frontal brain.
Frontal coordination and balance disorders
Impaired coordination of movements due to a tumor in the frontal lobe differs from cerebellar disorders. The patient cannot sit and stand without swaying from side to side, forward and backward. In advanced cases, when the core of the personality is destroyed, due to coordination disorders, it is possible to walk only on 4 limbs and pronounce individual sounds instead of words. A person becomes like our four-legged friends.
Obsessive grasping movements
When you touch the patient’s palm, he experiences an uncontrolled, very strong clenching of his hand into a fist. He cannot unclench his fist on his own. But when there is no irritation of the palmar surface of the hand, the patient calmly squeezes and unclenches his fingers. With a tumor of the frontal lobe of the brain, grasping movements develop not only when touching the palm, but also when an object approaches it. The person begins to uncontrollably chase the object and try to grab it. At the same time, from the outside it seems that he is making a movement with his hands, as if he wants to hug the object.
Seizures
If the tumor is located close to the cortical parts of the frontal lobe, convulsive seizures develop, which at first can be focal. As the process progresses, epileptic seizures become generalized, with loss of consciousness, involuntary urination, and defecation.
Frontal lobe tumor of the brain: symptoms, treatment and prognosis
Brain tumors account for 4-5% of all brain pathologies. However, the prevalence of the disease among adults and children is increasing every year. The localization of pathological processes can be different. But most often neoplasms are detected in the frontal part of the brain.
Reasons for appearance
With an integrated approach to the treatment of such tumors, it is possible to achieve a positive result: slow down the growth of the tumor, prevent the spread of pathological processes to healthy brain tissue. But the prognosis depends on the type of tumor and at what stage it was detected.
If the disease is in the early stages of development and the tumor is not aggressive, the five-year survival rate is 80%. In case of malignant pathologies, this figure decreases.
It is not known exactly why a tumor appears in the frontal lobe of the brain. Possible reasons for its occurrence include:
- the presence of an actively growing malignant tumor in other organs;
- genetic predisposition;
- defects in gene structure;
- severe traumatic brain injury;
- abnormalities in the development of blood vessels and nerves;
- history of brain infections;
- hormonal disorders.
A tumor in the frontal part of the brain can occur for various reasons.
But there are certain factors that contribute to the development of pathology:
- electromagnetic, ionizing radiation;
- presence of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18;
- consumption of foods containing large amounts of GMOs;
- long-term exposure to chemicals (carcinogens interact with DNA, causing deterioration in protein synthesis and the occurrence of mutations);
- alcohol abuse;
- vinyl chloride poisoning (a gas used to create plastic products);
- frequent stress, severe emotional shocks;
- smoking.
As the tumor grows, brain tissue is compressed and intracranial pressure increases.
Even a benign neoplasm that reaches a large size can have a malignant course and cause death. Therefore, it is important to be able to recognize the first signs of cancer and consult a doctor in time.
Clinical picture
Manifestations of a tumor of the frontal lobe of the brain can be different: symptoms depend on the size of the tumor, its type and location. It also matters whether a person has a primary or secondary tumor.
Main symptoms
The first signs of pathology may be:
- memory loss;
- the appearance of false memories;
- epileptic seizures;
- fast fatiguability;
- loss of smell (unilateral or bilateral);
- sudden mood changes, depression;
- speech disorders: slowness and incoherence of speech;
- inability to concentrate on one thing;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- unsteadiness of gait;
- autonomic disorders: dizziness, excessive sweating, feeling hot or cold;
- involuntary grasping movements.
An increase in intracranial pressure with tumor growth leads to the development of meningeal syndrome in patients. You can suspect the presence of a pathology in the brain based on the following symptoms:
- tension in the muscles of the back of the head (it becomes difficult for patients to lift their head from the pillow);
- dull, aching or throbbing headache;
- visual and auditory hallucinations;
- decreased reflexes.
The growth of a tumor can also cause a displacement of the healthy hemisphere towards the temples or the back of the head. The development of dislocation syndrome in tumors of the frontal lobe of the brain occurs slowly. It is characterized by the gradual manifestation of the following symptoms:
- constant drowsiness: the patient sleeps for a long time (sometimes more than a day), it is difficult or impossible to wake him up;
- decrease, and then complete absence of pupillary reaction to light;
- involuntary movement of the eyeballs;
- bilateral neurological disorders (eg, limb paresis);
- change in muscle tone: from increased to decreased.
When part of the brain is displaced towards the back of the head, there is a high probability of infringement of the centers of the brain stem responsible for the functioning of the respiratory and circulatory systems. If pathology is not detected in time, death is inevitable.
Signs of a secondary tumor
With primary intracranial neoplasms, neurological symptoms appear first. If a tumor in the frontal part of the brain is the result of the development of metastases, symptoms of the pathology of the organ in which the primary cancer cells are located first appear. In severe cases, when the process is generalized, patients develop intoxication syndrome. Its main features:
- decreased appetite;
- drowsiness during the day and wakefulness at night;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- bowel dysfunction (constipation);
- constant low-grade body temperature;
- low hemoglobin, increased ESR (detected in a blood test).
If dysfunction of internal organs, frequent headaches, or memory impairment occurs, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor: the sooner the cause of the ailment is identified, the less likely it is to develop complications and the better the prognosis.
Diagnostics
The clinical manifestation of a brain tumor resembles the symptoms of meningitis, encephalitis, diseases of the endocrine system, psychiatric and vascular disorders. Therefore, the doctor is obliged to conduct a differential diagnosis. For this, patients are recommended to undergo a comprehensive examination. It includes:
- Examination by a neurologist.
- Ophthalmological examination: assessment of visual acuity and field of vision, ophthalmoscopy.
- X-ray of the lungs, mammography, ultrasound of the kidneys - are carried out to detect cancer in other organs (prescribed if a secondary brain tumor is suspected).
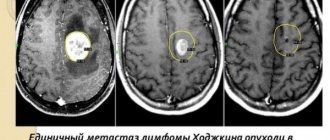
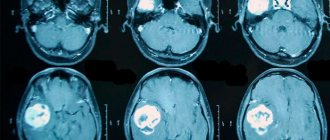
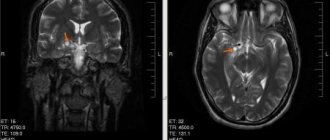
- Computer (magnetic resonance) tomography allows you to visualize a neoplasm, distinguish it from edema of cerebral tissue, determine the size and stage of its development, and assess the extent of the spread of pathological processes in the brain.
- Sampling and examination of tumor tissues.
If necessary, additional examination is prescribed:
- PET scan of the brain and MRI of its vessels.
- MR thermography.
- Examination by an endocrinologist, psychotherapist and angiosurgeon.
Therapeutic measures
The doctor decides how to treat the tumor based on the diagnostic results. The following methods are used:
- Surgery is the main method of treating brain tumors. It is used when there are clear boundaries between the tumor and healthy tissues of the organ. If a benign or malignant formation is located in a hard-to-reach place, is large in size, or has grown into the meninges, other treatment methods are recommended. Sometimes, to reduce intracranial pressure, partial removal of the tumor is performed. During the operation the following can be used: scalpel;
- laser;
- ultrasound;
- radio knife
In the first case, pathological cells are destroyed by implanting a special capsule directly into the brain tumor, in the second - through irradiation. But regardless of the method of treating the tumor, the following side effects may occur after radiation therapy:
- hair loss;
dryness and soreness of the skin at the site of irradiation;
- systemic – medications are prescribed intravenously or orally;
intrathecal – the drug is injected into the cerebrospinal fluid;
An integral part of the treatment of frontal lobe tumors is drug therapy. Before surgery, diuretics or hormonal drugs (Mannitol or Prednisolone) must be prescribed to reduce cerebral edema. If seizures are present, anticonvulsants (Valproate) are prescribed.
A neoplasm in the frontal part of the brain is a diagnosis that can scare everyone. But when a tumor is detected, it is important to immediately begin treatment measures. After all, only timely treatment can prolong life and make the symptoms of the disease less severe.
Source: https://oinsulte.ru/opuxol/lobnoj-doli.html
General cerebral symptoms
An increase in the volume of the frontal lobe tumor leads to the appearance of brain symptoms, indicating an increase in intracranial pressure. The cranial cavity is closed, and any increase in its contents leads to compression of normal brain tissue and disruption of the flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
Meningeal syndrome develops, which is characterized by the following manifestations:
- Headache, which may be accompanied by vomiting. Unlike diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, vomiting in this situation does not bring relief.
- Tension of the neck muscles, manifested by the inability to tear the pillow away from the head.
- Blackouts of consciousness, periodically accompanied by auditory or visual hallucinations. Periodically, depression of consciousness is interrupted by episodes of psychomotor agitation.
- Decreased reflexes.
Treatment of frontal meningioma
Treatment of the tumor depends on the location of the tumor (left or right frontal region), size, accompanying symptoms and general condition of the patient. Therapy consists of watchful waiting, surgery, radiosurgery and radiation therapy.
The use of medications is aimed at relieving symptoms; they have no effect on the formation itself. In relieving the symptoms, the use of diuretics, analgesics, glucocorticosteroids, and anticonvulsants for convulsive paroxysms is effective.
Symptoms at a distance
Long-term symptoms develop when a tumor from the frontal lobe grows into nearby parts of the brain.
The clinical picture of neurological disorders depends on the location of the tumor and the direction of its growth:
- If the process spreads to the anterior and posterior central gyri, then motor and sensory disorders develop.
- Damage to the temporal lobe leads to hearing impairment, vision impairment, epileptic seizures, and speech impairment due to a defect in understanding words. The patient cannot write or read, forgets the name of an object, but is able to describe its functions in detail.
- The tumor cannot grow to the occipital lobe and cerebellum from the frontal lobe. This is a situation incompatible with life. But when the pathways that go from the frontal lobe to the pons and cerebellum are damaged, a cerebellar disorder of motor coordination develops, which differs from the frontal one.
- Oculomotor disorders. The movements of the eyeballs and upper eyelid, the width of the pupils are ensured by the normal functioning of the cranial nerves. When a tumor grows into the nuclei of these nerves or due to compression by a space-occupying formation, the innervation of the muscles of the eyeball is disrupted. Divergent or convergent strabismus, narrowing or widening of the palpebral fissure, changes in the size of the pupils, etc. appear. The attending physician will help interpret such manifestations.
- If tumor growth is directed towards the third ventricle, then, due to irritation of powerful periventricular zones, episodes of indomitable sexual arousal develop with the transition to a convulsive syndrome, epistatus, and death.
- When the right frontal lobe is affected, symptoms occur on the opposite side. Often, all symptoms develop on the side of the tumor. This occurs because the tumor on the right, soft in consistency, grows, displacing the healthy left frontal lobe, pressing it against the hard bones of the skull. That’s why symptoms that seem uncharacteristic at first glance predominate.
Advantages of treatment in Israel
- Highly qualified, internationally recognized neurosurgeons.
- Equipping clinics with the latest diagnostic and treatment equipment.
- Prompt accurate diagnosis.
- Comfortable conditions for treatment.
- Reasonable prices.
Successful treatment of brain cancer is possible in the early stages of the disease. Therefore, do not waste time, contact the clinic of your choice and start restoring your health under the guidance of qualified specialists.
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(1 vote, average: 5 out of 5)
Changes in the composition of cerebrospinal fluid
With the advent of modern diagnostic methods, such as computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, PET, angiography and others, the relevance of studying cerebrospinal fluid - cerebrospinal fluid - has disappeared. But you need to know that the cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity is under pressure. This is due to the increase in contents in a confined space. The circulation of cerebrospinal fluid slows down. There is more and more protein in it, it becomes more viscous. This further complicates the circulation of liquor and nutrition of the brain.
How is pathology diagnosed?
A comprehensive examination of the patient is necessary to determine the nature of the neoplasm, its size and location, and the stage of development of the pathological process. In Israeli clinics, a comprehensive diagnostic examination takes, on average, no more than three days.
- The first day
- Second day
- Day three
On the first day of stay in the clinic, the patient is sent for a consultation with a leading neurosurgeon.
At the appointment, the doctor examines the medical history, clarifies the patient’s painful symptoms, conducts a neurological and physical examination, and prescribes the necessary examinations. Completing prescribed examinations, including:
- visual research methods (CT, MRI, PET-CT) - are carried out for a detailed study of the structure of the brain, its structure, identifying a tumor, determining its size, precise localization;
- biopsy - taking samples of tumor tissue using a special needle, followed by laboratory histological analysis of the resulting material;
- angiography of cerebral vessels - makes it possible to assess the degree of blood supply to tumor formation;
- general and biochemical blood tests.
A medical council, which includes the attending neurosurgeon and a number of highly specialized specialists, reviews the results of the examinations, makes a final diagnosis and develops a treatment regimen.
Displacement or dislocation of brain matter
As the tumor of the frontal lobe of the brain increases in volume, symptoms of damage to the occipital lobe, brainstem, and cerebellar disorders develop.
A tumor of the frontal lobe of the brain can cause a displacement towards the opposite hemisphere or towards the back of the head. Posterior displacement pushes the brain stem toward the foramen magnum. It indicates infringement. The brain stem contains vital centers responsible for breathing and blood circulation. Their defeat leads to death.
Clinical picture of dislocation syndrome
Unlike injuries, dislocation syndrome with tumors develops gradually. The person manages to adapt, and the clinical picture of brain displacement becomes obvious even in advanced cases.
The following symptoms gradually increase:
- Impaired consciousness to the point of stupor or coma, which is manifested by constant drowsiness. It is impossible to wake a person.
- The reaction of the pupils to light decreases and then disappears completely.
- Trembling movements of the eyeballs appear.
- If the patient had neurological symptoms on one side, then it becomes bilateral. For example, if one arm and leg were paralyzed, then with the development of dislocation, paresis progresses to all four limbs.
- Pathological symptoms increase.
- Muscle tone first increases and then decreases.
- Respiratory and cardiovascular disorders lead to death.
Types of tumor
The tumor itself and its parts must be classified according to its location. And the clinical course of the disease will be different:
- basal tumor;
- convexital neoplasms, which can also be divided into polar tumors and cancer of the posterior region of the frontal lobes;
- bilateral tumors of the corpus callosum frontalis;
- parasagittal cancer;
- tumor of the interhemispheric fissure.
Symptoms that are observed with frontal lobe cancer are conventionally divided into three main categories:
- By type of cerebral signs
- By type of focal signs
- Signs of relative importance. In this case, the severity of the symptoms will depend on the type of tumor, its location, the degree of pressure on the brain stem, medulla and vascular system. And also on the intensity of the release of toxic products of tumor decay and the direct response of the brain itself to the presence of mutated cells.
Intoxication syndrome
As a rule, patients with primary brain tumors do not wait for the development of intoxication syndrome, since neurological symptoms come to the fore. Impaired memory, attention, speech and other problems lead the patient to the doctor. This allows you to provide timely assistance without waiting for the development of cancer intoxication.
In the case where there is metastasis in the frontal region, the damage to the organ in which the primary focus is located comes to the fore. Intoxication syndrome develops in severe advanced cases, indicating the generalization of the process.
The most common symptoms that develop are:
- poor appetite;
- sleep inversion: a person is awake at night and wants to sleep during the day;
- nausea, vomiting, alternating with constipation;
- constantly elevated body temperature no more than 37.1 - 37.3 0 C, accelerated ESR, anemia in blood tests;
- tendency to thrombus formation in blood vessels, etc.
Treatment
In most cases, surgical treatment is indicated. In addition, depending on the type of tumor, its size, stage and location, the following treatment methods may be prescribed:
- radiosurgery - the operation is performed using a special gamma knife, which has a targeted effect on those areas of the brain where the tumor is located, without affecting healthy tissue; the absence of bleeding and incision significantly reduces the risk of developing postoperative complications, which is extremely important when performing brain surgery ;
- chemotherapy - can be prescribed both as part of complex therapy and as an independent method of treatment;
- immunotherapy;
- radiation therapy;
- gene therapy is an innovative treatment method that is successfully used in modern medicine to treat certain types of brain tumors.
Good health to you!
Types of neoplasms
Brain tumors, including frontal tumors, based on their histological structure, are divided into 2 types - vascular and glial.
The most common are:
- Glial astrocytoma, which has 4 degrees of malignancy. Even the most malignant brain tumors do not metastasize to other organs.
- Tumors that develop as a result of embryogenesis disorders are dysontogenetic.
- Neoplasms of the meningovascular series, which originate from connective tissue and blood vessels. Meningiomas are always associated with the dura mater, i.e. they have a superficial location. More often, the disease begins with a convulsive syndrome due to irritation by a tumor of the cerebral cortex. More often, benign tumors take decades to grow. But they can become malignant and degenerate into meningosarcoma.
- Metastases to the brain from the lungs, mammary glands, intestines, kidneys, melanoma.
Causes
The reasons for the transformation of healthy cells into cancer cells are not yet fully understood. However, factors that can provoke carcinogenesis have been identified:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- viral infections;
- hereditary predisposition;
- hormonal imbalances;
- prolonged exposure to ionizing radiation, heavy metals, chemical reagents;
- drug abuse ;
- bad habits.
In children, congenital tumors can be caused by pathologies of intrauterine development. Modern research has already proven that in many cases the disease develops as a result of mutations in genes that regulate cell division.
Differential diagnosis
All of the above symptoms are often found in a wide variety of diseases, even not always related to the brain. Some of these diseases:
- psychiatric illnesses;
- endocrine pathology;
- neurotic syndromes;
- vascular disorders;
- abscess;
- parasitic diseases;
- infectious diseases, for example, meningitis, encephalitis.
Each of the above symptoms smoothly flows into the other. They are interconnected to such an extent that sometimes it is difficult to see that fine line that indicates the appearance and growth of signs of a terrible pathology. The slightest suspicion of a problem should lead you to see a doctor. Timely medical assistance has saved the lives of millions of patients with brain tumors.
Consequences and complications
Even if the diagnosis and treatment of the tumor were carried out in a timely manner, some symptoms may persist in the patient throughout his life, since the damaged brain structures are not restored. However, such phenomena are observed quite rarely.
Main complications of the disease:
- irreversible changes ;
- postoperative bleeding;
- malignant degeneration of a benign formation;
- relapse of the disease.