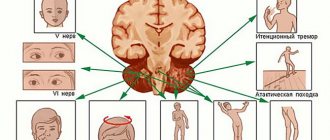
Myasthenia gravis is a disease that is characterized by a violation of neuromuscular transmission (that is, a violation of the process of muscle contraction that occurs in response to an impulse traveling along a nerve fiber). The cause of myasthenia gravis is often an autoimmune process, as a result of which the body produces antibodies to the structures of the neuromuscular synapse. According to statistics, myasthenia gravis occurs in every 5 out of 100 thousand people. It is a chronic disease with acute or gradual onset. The main manifestation is transient muscle weakness; ptosis (drooping) of the upper eyelids, impaired swallowing, and a “nasal” voice may also occur. In severe cases and as the disease progresses, weakness of the respiratory muscles may occur, including respiratory arrest.
The dangerous disease progresses rapidly, clinical manifestations may subside and worsen again. Pathological muscle fatigue is diagnosed more often in women than in men, and much less often in children. The average age of patients is from 15 to 45 years, thus, the maximum number of cases is registered in the most active part of the population.
At CELT you can get advice from a neurologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,200
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
About the reasons
Currently, the causes of myasthenia gravis are not fully understood. Sometimes it is impossible to say unambiguously why a particular patient developed a disease. It is generally accepted that the following factors play a significant role:
- Family predisposition. Very often it turns out that the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis has already been made to the patient’s close relatives.
- Frequent stress, disorders in the immune system, the harmful effects of viruses, bacteria and other microorganisms. These factors “shatter” the immune system, and the body begins to synthesize antibodies against its own tissues, in particular, against the receptor proteins of the postsynaptic membrane. This leads to a delay in the transmission of signals from nerves to muscles, even blocking impulses.
- Myasthenia gravis can be a consequence of certain diseases. For example, when the thymus gland (thymus) grows, antibodies to synapse receptors also begin to be produced.
When malignant neoplasms appear in the ovaries, respiratory organs or mammary glands, they speak of Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. Muscle weakness, sometimes mistaken for myasthenia gravis, occurs with Charcot-Marie disease, dermatomyositis (destruction of connective tissue), various forms of myopathies, ALS syndrome (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) and many other pathologies.
Soft tissue MRI
- Cost: 6,000 rub.
More details
The difficulty of diagnosis is that patients with myasthenia gravis at the onset of the disease may not have any clear complaints and symptoms. Neuroimaging (or MRI) shows no significant abnormalities in the structures of the central nervous system. Only in 30% of patients the thymus becomes enlarged or neoplasms are detected in it. When examined, the muscles are also not changed in any way; pathology can only be detected by microscopic examination.
Prevention
Myasthenia gravis is a chronic disease that is prone to progression without specialized treatment and adherence to certain lifestyle rules. The longer the patient does not receive treatment, the more serious the threat to his life, since the disease often leads to disturbances in the respiratory system. Patients with asthenic ophthalmoplegia need to balance their diet, enriching it with foods high in calcium and phosphorus, and routinely take vitamin complexes.
Features of preventive measures for paralysis of the oculomotor muscles:
- compliance with the plan of preventive examinations by an ophthalmologist, neurologist, cardiologist, rheumatologist;
- maintaining an optimal indoor microclimate - avoid overheating and hypothermia, conditions that can cause prolonged colds and inflammation;
- regularly taking medications prescribed by a doctor;
- inclusion in the daily diet of foods rich in potassium are useful: oats, beans, peas, seaweed, dried apricots, etc.
Excessive physical activity is strictly not recommended for people diagnosed with asthenic ophthalmoplegia, as they can provoke progression of the disease. Prolonged exposure to the sun is also undesirable - the effect of ultraviolet radiation is also one of the factors that provoke the development of pathology. The patient should be warned that some medications are contraindicated for him. For example, quinine derivatives and curare-like muscle relaxants.
By following a treatment plan drawn up by a doctor, a person with myasthenia gravis can significantly improve their quality of life and slow down the progression of the pathology. Useful preventive measures, sanatorium holidays, the absence of bad habits and living in an environmentally friendly region are the key to maintaining health with such a diagnosis as asthenic ophthalmoplegia.
Classification
Forms of myasthenia:
- congenital
- acquired
Congenital myasthenia gravis can be caused by genetic mutations. The fetus can also receive antibodies to the receptors of the postsynaptic membrane from the mother, in this case we are talking about neonatal myasthenia.
Acquired myasthenia gravis can develop in patients of any age. This diagnosis is given to adolescents, young adults and pensioners. The disease most often occurs in active age, from 20 to 30 years. The causes can be external (infectious agents) and internal (chronic diseases, heredity).
Conventionally, according to the prevalence of muscle weakness, myasthenia gravis is divided into the following types:
- Generalized, when neuromuscular synapses throughout the body are affected.
- Ocular, bulbar, when predominantly the muscles localized in the head and neck are affected.
- With predominant damage to the muscles of the extremities.
This division is relative, since an in-depth study most often reveals damage to all muscles, but clinical manifestations of myasthenia gravis can occur only in certain muscle groups of a certain localization.
According to the nature of the flow, they are distinguished:
- The progressive course of myasthenia gravis is when the manifestations of the disease become more severe over time, more and more muscles are involved, and therapy becomes less and less effective.
- Remitting course – episodic myasthenic conditions. With this form of condition, improvements alternate with exacerbations.
- Myasthenic crisis is characteristic of a generalized form of the disease. Such conditions require urgent help. The patient experiences a sharp increase in weakness, difficulty swallowing and breathing, which may require resuscitation in the form of artificial ventilation.
Myasthenic crisis
Myasthenic crisis is considered a complication of the disorder in question. This condition is characterized by sudden weakness of the muscles responsible for breathing and swallowing. Myasthenic crisis manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- rapid and wheezing breathing;
- tachycardia;
- active salivation.
If a myasthenic crisis occurs, the patient requires emergency care. This condition causes paralysis of the respiratory muscles, which is life-threatening.
Myasthenia gravis tends to progress in most patients. The course of the disease is characterized by a sharp change in relapses and remissions. The development of myasthenic syndrome may stop for a while, but this is rare.
Exacerbation of pathology is episodic or long-term. In the first case, the symptoms of the syndrome subside quickly, after which the patient does not experience any problems with the functioning of the muscular system.
The long-term form of the disease (myasthenic state) is characterized by the appearance of all the symptoms characteristic of this type of disorder.
At the same time, there is no increase in the intensity of clinical manifestations. The duration of the myasthenic condition is often several years.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations of myasthenia gravis depend on the form of the disease.
Symptoms characteristic of the generalized form:
- Transient muscle weakness. This is the first sign that a sick person pays attention to. At first, muscle weakness worries you in the evening or after prolonged physical work. Then myasthenia gravis progresses, and the volume of feasible exercise decreases significantly.
- The work of all striated muscles is disrupted. The muscles of the arms and legs, neck, and torso cannot work at full strength.
- Facial muscles are affected.
- Against the background of general muscle flaccidity, tendon and periosteal reflexes are preserved.
- Difficulty breathing, shortness of breath due to weakness of the respiratory muscles.
- Inability to self-care, need for constant assistance due to severe muscle weakness.
Symptoms characteristic of the ocular form:
- Ptosis (or drooping eyelids), diplopia (“double vision”), strabismus. All these symptoms are caused by weakness of the extraocular muscles.
- Difficulty swallowing as the pharyngeal muscles are affected in a patient with myasthenia gravis.
- The voice changes, notes of nasality appear, speech becomes slow and unclear. These signs can be recognized through prolonged communication with the patient. Often, during a long conversation, due to increased muscle fatigue, speech disorders arise and increase.
The difficulty of diagnosing myasthenia gravis is due to the fact that the above symptoms may appear and disappear. They are most pronounced when a person plays sports, reads for a long time or works at the computer. That is, at those moments when the striated muscles are most involved. After all, even maintaining a certain posture or reading requires constant tension of certain muscle groups.
In the absence of adequate treatment, there is a risk of not only disability, but also death. At a time when the level of development of medicine did not allow long-term artificial ventilation, 8 out of 10 patients died from myasthenia gravis. If you notice alarming symptoms of myasthenia gravis, you must make an appointment with a neurologist. If necessary, a specialist will refer you for examination and select effective therapy.
Preventive actions
There is no prevention of myosthenia as such. You can only adhere to recommendations that exclude complicated variants of the course of the disease and include the following rules:
- avoid heavy physical effort at work and at home;
- do not play sports;
- do not be in direct sunlight (wear sunglasses);
- include dairy products, fruits, vegetables in the diet;
- stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- take vitamins regularly;
- firmly understand that taking medications containing magnesium, antipsychotics, antibiotics, diuretics, and sedatives is strictly prohibited;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- avoid stressful situations;
- treat various diseases in a timely manner.
Diagnostics
A neurologist diagnoses myasthenia gravis based on complaints, medical history, examination and research. The specialist compares the patient's complaints with symptoms characteristic of this disease. Diagnostic studies are performed to confirm the diagnosis.
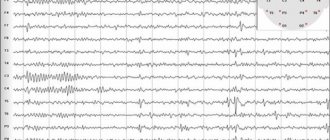
Electroneuromyography for myasthenia gravis is the “gold standard” and a mandatory study. A special ENMG mode is used - “decrement test”. During testing using electrical stimulation, the muscle being tested is forced to contract at a high frequency. As a result, with myasthenia gravis or myasthenic syndrome, a decrease in the intensity of muscle contraction is recorded.
Proserine test. Performed independently or after a decrement test. Prozerin is a substance that improves neuromuscular transmission. A small amount is injected subcutaneously, 30 minutes after this the patient is examined again by a doctor or a repeat ENMG is performed. The test is considered positive if there is clinical improvement or positive dynamics when performing the decrement test.
Laboratory diagnostics. Blood test for the content of specific antibodies to receptors and muscles. Antibodies are not detected in all cases of myasthenia gravis.
Computed tomography of the mediastinum. Used to rule out thymoma, a tumor of the thymus gland that can produce antibodies.
As a rule, these methods in combination with a consultation with a neurologist are sufficient to establish a diagnosis.
During the examination, the doctor may test for increased muscle fatigue. First, a load is given to a specific muscle group, then their condition is assessed. In the ocular form of myasthenia, the extraocular muscles are loaded; for this, the patient is asked to look at one point for 30 seconds. If there are complaints of pathological fatigue of the neck muscles, the patient is placed on his back and asked to keep his head raised for 1 minute. If there is weakness in the legs, the patient needs to do several squats or walk on his toes. To determine the degree of fatigue of the muscles of the hand and forearm, a person is asked to intensively bend and straighten the hand several times.
Read also
Intracranial hypertension
Intracranial hypertension is a condition (syndrome) associated with increased cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure inside the skull.
The main symptoms of increased intracranial pressure are... Read more
Encopresis
Encopresis is a condition in which a person does not control or feel the urge to defecate, and also cannot control the act of defecation itself; Fecal incontinence significantly impairs the patient’s quality of life,...
More details
Fainting
The term “fainting” (syncope, syncope) comes from the Greek word syncope, which means “to interrupt”, “to turn off”. Fainting is a spontaneous loss of consciousness with a rapid onset associated with a decrease in...
More details
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Clinical manifestation of carpal tunnel syndrome This disorder occurs in the median nerve. The causes are tenosynovitis of the flexor tendon in the hands, acute articular rheumatism, pregnancy...
More details
Pelvic pain
Pelvic pain is pain in the muscles that form the pelvic floor and organs located in the small pelvis, caused by microtrauma, chronic deformation of the sacrococcygeal region due to anatomical…
More details
Treatment
Surgical intervention
- Thymectomy is the complete or partial removal of the thymus in the presence of tumors in this area. Performed on patients no older than 60 years.
- It is possible to affect the thymus through radiation therapy.
Drug therapy
- Anticholinesterase drugs serve to improve the conduction of nerve impulses to muscle tissue. The number of drugs, frequency and duration of administration depends on the severity of symptoms and type of disease.
- Glucocorticosteroids are used to “inhibit” autoimmune reactions.
- Potassium-sparing diuretics (allow you to retain some potassium in the body) and drugs containing potassium. Potassium helps improve neuromuscular transmission.
- Immunosuppressants also serve to suppress autoimmune processes.
Plasmapheresis
Used to cleanse the blood of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors. The procedure is not effective for all forms of myasthenia gravis. Used in combination with drug treatment. The procedure for replacing plasma (plasmapheresis) with donor plasma or similar liquids requires a balanced approach and is carried out over several hours. Requires prior consultation with a transfusiologist, as there are a number of contraindications.
Thus, there are various algorithms for the conservative treatment of myasthenia gravis, which are used by the attending physician individually, depending on the clinical case. Self-medication, self-correction of therapy prescribed by a doctor can lead to deterioration and even death. Excessive use of drugs can lead to a life-threatening condition, a cholinergic crisis develops. Its symptoms are similar to myasthenic crisis, which occurs when treatment is insufficiently effective. Both conditions require monitoring in an intensive care setting.
Forecast
With timely contact with specialists, the patient receives effective treatment, allowing to achieve stable remission, without exacerbations and myasthenic crises. And in some cases, a complete cure is possible. Refusal of medical assistance can lead to disastrous consequences.
Make an appointment with CELT neurologists at a time convenient for you. The clinic has everything necessary to conduct high-quality diagnostics. Experienced specialists will conduct the necessary research and select adequate therapy.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions