A nervous tic is a condition in which the muscle structures of certain parts of the body involuntarily contract.
This is manifested by repeated movements, sounds or verbal expressions that are beyond control. The condition greatly worries the patient himself and annoys those around him. There are modern treatment methods to eliminate this pathology. Psychotherapeutic techniques are the most effective; medications are prescribed only for severe tics. The best results are achieved by therapy started in the early stages of the disease.
What it is
The term “tic” refers to sudden and rapid movements of individual muscles that do not serve a specific function. Usually this phenomenon repeats at different intervals.
An important sign of a tic is that movements occur involuntarily and without any provoking factor. Their intensity, frequency and content can be very different. The child (or adult) cannot control the motor paroxysms that arise; an attempt to suppress them increases anxiety and tension.
Recommendations for parents
To ensure the normal development of a child and maintain his health, constant monitoring of the child and proper upbringing are necessary. It is necessary to provide the child with proper nutrition, organize a daily routine, and ensure positive emotional contact.
Attention! If you notice any symptoms, consult a doctor rather than wait for self-healing.
Nervous tics are divided into several types and manifest themselves in different ways. They are primary and secondary. The former have a benign course and can go away on their own, while the latter require timely diagnosis and proper treatment, without which the child may develop severe complications. Therefore, parents should not ignore their children, but provide them with proper attention.
Causes
Depending on the cause, tics are distinguished as primary and secondary.
A tic is primary if it appears for no apparent reason. In this case, they talk about the idiopathic form of the pathology. Secondary occurs due to another disease.
Primary form
The causes of primary tics are still the subject of research. Scientists suggest that they are caused by a disturbance in the metabolism of certain transmitters, in particular dopamine, a substance involved in the transmission of impulses in the brain.
Before puberty, some functional areas of the brain are not yet fully developed. This explains the fact that tics are more common in children and disappear as they grow older.
Genetic predisposition also plays a role in the occurrence of the disorder. If the father or mother already has a similar disease, then the risk of its occurrence in the child is much higher.
A provoking factor may be taking certain medications or severe stress. In particular, some drugs used to treat psychosis (antipsychotics) sometimes cause involuntary muscle contractions.
Anticonvulsants, which are prescribed for childhood epilepsy, also sometimes provoke involuntary movements. Stressful conditions, such as grief or, conversely, great joy, often intensify the manifestations of tics.
Secondary form
Certain diseases of the central nervous system (CNS) can cause tic disorder:
- inflammation of the brain and its membranes (encephalitis, meningitis);
- traumatic brain injury;
- central nervous system tumors;
- poisoning, such as carbon monoxide.
In some children, the cause of tics is the so-called PANDAS syndrome (PANDAS: Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Streptococcal infections). After infection with certain bacteria (type A streptococci), tonsillitis and scarlet fever occur, and antibodies to these pathogens are formed. In some children, antibodies that are supposed to act against bacteria attack the body's own structures. If the nervous system is affected, this can lead to tics.
Sometimes pathology occurs against the background of various mental disorders. They have no direct connection with them, but nevertheless, doctors note a high frequency of tics in certain diseases. For example, violent movements are more common in children with ADHD, emotional disturbances, and autism (particularly Asperger's syndrome). Other background pathologies: depression, slow psychomotor and speech development.
Tiki after a fright
Most patients associate the occurrence of tics with severe stress or fear. For example, a child was scared of a dog, drowned in water, was scolded by the teacher, etc.
In some children, tic disorder occurs against the background of an existing neurosis. In this case, even small everyday problems can become a provoking factor. Combination therapy using sedatives, antidepressants, and psychotherapy is usually prescribed.
Other causes of nervous tics in adults
In adulthood, involuntary blinking and contractions of the muscles of the eyes and face are caused by:
- excessive strain on the eyes caused by prolonged work at the computer and reading books;
- injuries;
- pathologies of the central nervous system;
- depression, stress, neurosis;
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- somatic diseases;
- side effects of medications.
Some doctors associate the appearance of tics with liver disease. In fact, this phenomenon is still being studied. Nervous system disorders are quite complex diseases that require an integrated approach to study. Now let's look at the symptoms and treatment of nervous tics.
Onset and course of the disease
In 90% of cases, tics debut at the age of 6-8 years. Often the triggering factor for their appearance is the start of school. In this case, experts talk about “September 1st ticks.” In their opinion, this phenomenon is due to a stressful situation for the child: a change of team (kindergarten - school), new living and learning conditions, more independence.
About one in two children develop transient forms of tics during primary school. Motor violent movements occur more often. Boys are more predisposed to this pathology than girls.
As the child grows, tics may disappear or reappear. The maximum severity of symptoms usually occurs at the age of 10 years. After reaching the age of 14, the pathology often disappears - on average in 50% of cases.
Usually the disease occurs in waves with periods of exacerbation and improvement. A decrease in tics is observed during the holidays, after a long rest. But stress and emotional overstrain, on the contrary, intensify them.
Symptoms
There are motor (motor) and vocal (voice) tics. They can manifest themselves in both simple and complex forms.
Immediately before the onset of tics, most patients experience a strong urge to perform a stereotyped action. For example, a feeling of a lump in the throat and the need to cough, or pressure in the neck and shrugging of the shoulders. After performing any action, relief comes and internal tension goes away.
Motor tics (blinking, etc.)
Usually manifested by short-term movements of one or more muscles. Any muscle in the body can be involved in the process.
Often simple tics occur on the face, in which case the person performs the following actions:
- blinks, frowns, raises eyebrows;
- winces, turns his head.
Sometimes the pathology is manifested by shrugging the shoulders or moving the arm. Tics of the trunk and legs are relatively rare.
The most common tics are those located in the upper part of the face, such as blinking or raising the eyebrows. Then, in descending order of frequency of occurrence, there are tics of the lower part of the face, shoulder girdle, torso, and arms.
With complex motor tics, the following actions may occur:
- jumping, clapping;
- throwing movements;
- blows to the body or bites.
Some children are very good at integrating motor tics into their daily lives so as to attract as little attention as possible. With vocal symptoms this is much more difficult to do.
Vocal tics
They are characterized by the reproduction of any sounds. In the case of a simple form, this could be:
- screaming, barking, snorting;
- hissing, coughing, whistling;
- clicking, grunting.
Complex vocal tics occur in entire words or sentences. For example:
- repetition of foreign or own words and sentences (echolalia, palilalia);
- pronunciation of unusual words, sometimes they are obscene (coprolalia).
If the pathology is associated with the involuntary uttering of curses, then it creates significant social discomfort. This applies to both the patient himself and the people around him.
Complications
Tics do not pose a threat to health or life. However, they can create a number of problems, both physical and psychological.
Pain
It occurs with frequent and intense motor paroxysms due to excessive muscle tension. Relatively rarely, pain is associated with minor injuries, for example, with complex tics with a large range of motion.
Some children complain of increased headaches after a paroxysm of tics. For others, the pathology can trigger a migraine attack.
Social maladjustment
Complex and vocal tics are often the cause of ridicule from peers. This is especially true for children of high school age.
Vocal tics negatively affect the rate of speech, making communication difficult. In schoolchildren, they can interfere with learning: during times of excitement or when communicating with a teacher in the classroom, vocal or motor paroxysms intensify. As a result, the child avoids answering in class, which negatively affects academic performance.
Against the background of these problems, depressive and anxiety symptoms are formed. Most children with tics have low self-esteem and social withdrawal.
Classification
Depending on the symptoms and duration of existence of tics, the following types are distinguished:
- Temporary (transitory) - duration less than twelve months. This includes only motor paroxysms.
- Chronic - the disorder persists for more than a year. This group may include both motor and vocal tics.
The table shows the signs of different types of tics.
Table - Diagnostic criteria for tics
| Characteristics of ticks | Transient | Chronic | Tourette's syndrome |
| Type | Vocal or motor | A combination of several motor and one or more vocal | |
| Frequency | A couple of times during the day, sometimes daily, for at least two weeks and no more than a year | Several times a day, almost always daily, throughout the year | They occur repeatedly during the day, in paroxysms, and the duration of the pathology is at least a year. The frequency, location and severity of tics change |
| Anamnestic data | There is no history of hereditary diseases, drug intoxication, etc. | ||
Forecast
For most people, tics are temporary and disappear after a few weeks or months. But even if the pathology lasts more than a year, it does not necessarily become chronic. In some cases, after a period of remission, violent movements appear again.
Only in 6% of cases do tics persist permanently. With age, symptoms gradually become less severe. An exception is Tourette's syndrome. With this pathology, only 20% of patients experience improvement in symptoms.
Some people can suppress their tics for a short time. This, for example, occurs in situations of extreme concentration or concentration. However, it is quite difficult to do this all the time, which causes additional stress. An interesting fact is that violent movements do not occur during sleep.
Diagnostics
If tics appear in a child, you should definitely consult a doctor. This is necessary to identify a serious illness as the cause of tics. If treatment is started at an early stage, it will be possible to prevent the progression of symptoms and chronicity of the process.
The diagnosis and treatment of this pathology is usually carried out by a pediatric neurologist. At the appointment, you will need to inform the doctor about the duration of symptoms, their appearance, frequency, possible provoking factors and pre-existing diseases.
During the examination, the doctor conducts a differential diagnosis with the following pathologies:
- obsessive movements syndrome;
- epilepsy;
- hyperkinesis with damage to the extrapyramidal system.
The presence of tics is indicated by the following signs:
- stereotypical movements, that is, the same actions are repeated (the child blinks, nods his head, etc.);
- symptoms worsen during times of excitement or stress;
- lack of control over tics.
According to indications, the specialist will prescribe additional laboratory and instrumental examinations:
- general blood analysis;
- test for hemolytic streptococcus;
- determination of thyroid hormone levels;
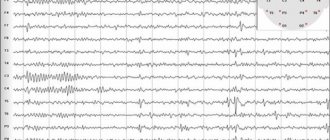
- electroencephalography (EEG);
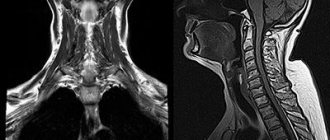
- MRI if an organic process of the brain is suspected.
Treatment of motor and vocal tics in Saratov
Treatment of tics should be comprehensive. It is necessary to take into account the types of tics, the stage of the disease, the individual characteristics of the patient’s nervous system, and the social situation in the family. Optimization of the daily routine, psychological correction and training, and drug therapy are mandatory. Doctor Sarklinik has been successfully using hardware and non-hardware methods of treating tics for many years. Treatment is being carried out for vocal tics in Saratov; — sound ticks in Saratov; - motor tics; - motor tics; - tic disorders; - clonic tics; - tonic tics; - dystonic, tonic-clonic tics; - turretism; - Tourette's syndrome. As a result of therapy, there is an improvement in the motor and emotional spheres, motor and sound tic-like movements disappear. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the individual characteristics of the child, adolescent or adult, the severity of symptoms at the time of treatment, the age of the patient, and the intensity of treatment. Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis, in courses. Under no circumstances should you scold children; if you notice any of the symptoms we mentioned above, it is better to consult a doctor. And remember that treating tics is a very complex process that requires persistence, persistence and time. Your child needs care, attention, understanding and help from you! Don't blame your child or yourself. Complex treatment will give positive results. On the sarclinics website you can ask a doctor a question about your problem online for free.
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Text: ® SARCLINIC | Sarclinic.com \ Sarсlinic.ru Photo 1: © zurijeta / Photobank Photogenica / photogenica.ru Photo 2: © altanaka / Photobank Photogenica / photogenica.ru The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all coincidences excluded. When using materials from the site sarclinic.ru, an active hyperlink is required!
Related posts:
Parasomnia, illnesses during sleep and upon awakening
Tourette, Tourette syndrome, Tourette's disease, treatment Gilles de la Tourette
Stuttering in children, stuttering treatment in Saratov, Russia
Depression in adolescents, children, treatment of depression in Saratov
Intracranial hypertension syndrome, liquorodynamic disorders
Comments ()
Treatment
With secondary tics, it is necessary, first of all, to treat the underlying disease. As you recover, nervous disorders also disappear. Primary forms of pathology require an integrated approach using both medication and psychotherapeutic methods.
Treatment is best carried out on an outpatient basis. According to doctors' observations, a child's stay in a hospital often intensifies tics. This is due to a change in environment, the absence of parents and, as a result, increased anxiety.
General recommendations
It is important for parents to understand that the child cannot control tics. Any requests to do this create additional stress, which ultimately makes the situation even worse.
Eliminate any irritants and stressful situations as much as possible. Experts recommend limiting TV viewing, especially with the lights off. Bright flickering glare on the screen affects the bioelectrical activity of the brain and can intensify the symptoms of tics.
Non-drug methods
First of all, explanatory work should be carried out with parents regarding the characteristics and benignity of the disease. Most children, especially teenagers, are very vulnerable and unsure of themselves. Parents should provide them with psychological support, instill self-confidence and increase their sense of self-worth.
The following techniques are effective in treating tics:
- Relaxation procedures and self-control (autogenic training). The patient is taught to purposefully relax and thus reduce the symptoms of tics.
- Forced exercises. A method used to provoke tics so that they can be better controlled.
- Biofeedback method (BFB). A set of procedures through which the patient learns to control physiological function. In the treatment of tics, electroencephalographic biofeedback with an increase in the power of the alpha rhythm has proven itself well.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapeutic techniques are most effective in the initial stages of development of a tic disorder. Therapy can be individual, family or play.
In most cases, family psychotherapy is used for tics. Experts view it as a way to restore the functional unity of the family. The process includes the following steps:
- examination of relatives;
- family condemnation;
- joint sessions with parents and child.
The main goal of treatment is to teach parents to treat their children more attentively and adequately. As a result, each family member learns to understand the other and is able to change their attitude towards him.
There is a theory that the cause of tics and various neurotic disorders is education on the principle of emotional rejection. It is based on the child’s unconscious identification with negative life moments. As a result, children feel unwanted and try to distance themselves from their father and mother. With the help of family psychotherapy, it is possible to correct these attitudes and achieve closer connections within the family.
Play is one of the important components of a child’s psychological development. Therefore, play-based therapy is often practiced in the presence of tics. It is especially indicated for children with hyperactivity syndrome and decreased attention. With the help of play, a child learns to manage his emotions and relieves internal tension.
Massage
The procedures effectively reduce psycho-emotional imbalance, muscle hypertonicity, and improve tissue trophism and lymphatic drainage. Sometimes massage is carried out in combination with color music or aeronization.
The effects are carried out on the collar and occipital region, and the shoulder girdle. A general massage involving the limbs and abdominal area is also indicated. Movements should be relaxing and exclude active influence (chopping, tapping, etc.). The duration of the session is not recommended to exceed more than 10-20 minutes. The course of treatment includes from 10 to 15 procedures.
Medicines for tics
The use of medications in children must be approached very reasonably. Each drug has its own side effects, especially when it comes to long-term therapy.
Usually they start with “soft” and safe medications. If necessary, they move on to more effective drugs, but at the same time not without side effects. Any pharmacological agent is first prescribed in a minimum dosage, gradually increasing it.
Pantogam
The active ingredient is gamma-aminobutyric acid. The mechanism of its action is due to its effect on the GABA receptor complex. This leads to the elimination of motor paroxysms.
Pantogam is prescribed to young children in the form of 10% syrup; older patients are given tablets of 0.25 mg 3-4 times a day. Syrup is taken 2.5-5 ml three times a day. The course of treatment is 1-2 months.
Phenibut
The drug has tranquilizing activity, and at the same time has a slight nootropic effect. In addition, it relieves internal stress and anxiety well.
Phenibut 0.25 mg is used. Prescribe 0.5-1 tablet 2-3 times a day. The dosage is adjusted depending on age.
Gelarium Hypericum
The active substances of this drug (hypericin, hyperforin) are obtained from St. John's wort. They have both antidepressant and anxiolytic effects.
Children over 12 years of age are prescribed 1 tablet three times a day. Usually its effect appears after 1-2 weeks. Sometimes skin photosensitivity occurs during use.
Dopamine receptor blockers
They are prescribed when previous medications are ineffective. There is no single regimen of drug therapy; in each specific case, medications are selected individually based on the characteristics of symptoms and concomitant diseases.
Dopamine receptor blockers have been used in the treatment of tics for more than 40 years. They act on the extrapyramidal system of the brain and thereby effectively eliminate motor and vocal paroxysms.
Haloperidol, Pimozide and Fluphenazine have been used in clinical practice for a long time. They reduce tics even in minimal dosages. However, they can cause a number of undesirable effects:
- drowsiness;
- extrapyramidal disorders (pseudoparkinsonism);
- akathisia (internal restlessness and the need to change position);
- increased appetite and weight gain.
Therefore, in recent years, doctors have preferred to prescribe selective dopamine receptor blockers (benzamides):
- Tiapride;
- Sulpiride;
- Amisulpride;
- Risperidone and others.
In pediatric practice, Sulpiride (Eglonil) is often used to treat tics. For children, the medicine is usually prescribed in the form of an oral solution of 5-10 mg/kg per day. One teaspoon of the medicine contains 25 mg of active ingredient. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. Unlike other antipsychotics, Eglonil is less likely to cause side effects (drowsiness, weight gain, extrapyramidal symptoms).
Another drug that is effective for tics is Risperidone. It has been well studied and a number of clinical studies have been conducted on it. Risperidone simultaneously eliminates tics and normalizes sleep. In addition, it is effective against aggressive tendencies.
Children are prescribed 0.25 mg per day with a body weight of less than 20 kg. 0.5 mg if the child’s weight exceeds 20 kg. Gradually, starting from the 4th day, the dosage is increased (on average twice) until a therapeutic effect is achieved.
According to surveys conducted among European doctors, Risperidone is the most commonly used drug in the treatment of tics.
Other medicines used in the treatment of tics:
- Clonidine;
- Aripiprazole;
- Quetiapine;
- Thioridazine, etc.
Tranquilizers
Of the benzodiazepine tranquilizers for tics, Clonazepam is the most effective. The average therapeutic dosage is 6 mg per day. Dose adjustment is carried out in accordance with the age of the child and the severity of tics. Like all tranquilizers, Clonazepam has a number of side effects such as drowsiness, memory impairment, and paradoxical disinhibition. It can also become addictive with prolonged use.
For Tourette's syndrome, the non-benzodiazepine tranquilizer Atarax, a histamine receptor antagonist, is indicated. In clinical studies, the drug helped reduce tics in 67% of patients. For children under six years of age, the drug is prescribed 1-2.5 mg/kg per day, at older ages - 1-2 mg/kg per day in several doses.
When do motor and vocal tics occur?
In recent years, according to Sarklinik, the frequency of occurrence of tics in the population has begun to constantly increase, and in childhood it ranges from 1.4 to 7.7% (in various age groups). Tics are more common in children and adolescents. Typically, the first signs and symptoms of tics appear between the ages of 3 and 9 years. In the absence of proper treatment, they remain at an older age, and then doctors classify them as tics in adults.
This is interesting! New directions in the treatment of tics
Scientific research has been conducted on nicotine as a method of combating tics. Quitting smoking has been found to worsen tic disorder. Scientists recommend special nicotine chewing gum as an additional treatment method (for example, in combination with haloperidol). In experiments, this leads to a decrease in the frequency and severity of tics and an increase in concentration.
However, the use of this method is limited by side effects: bitter taste and gastrointestinal disorders. Therefore, scientists have developed a special nicotine patch. Its use for 10 days resulted in a significant reduction in tics.
There are recommendations for the use of tetrahydrocannabinol (cannabis) in the treatment of motor paroxysms. Taking the drug 10 mg per day for 6 weeks gave a good therapeutic effect. There were no serious side effects. Some patients complained of mild drowsiness and dry mouth.
Another direction in the treatment of tics is injections of botulinum toxin. They are done for persistent uncomplicated motor tics, less often for vocal ones. There are reports of the effectiveness of the technique in children over 8 years of age.
Treatment of nervous tics
This disease is treated comprehensively using three methods: medications, special exercises and folk remedies. Medicines, traditional medicine and exercises help to completely get rid of tics or eliminate them quickly every time they appear. The most common medications prescribed for nervous tics are motherwort and valerian. They are sold in the form of tablets and infusions.
Such drugs are available without a prescription, but the instructions for use must be strictly followed, since these drugs in large quantities can cause fatigue and increased drowsiness.
Valerian and motherwort are taken in courses. They have a cumulative effect that is felt about a week after administration. This effect is the normalization of sleep and general calmness, and eye twitching occurs much less frequently when taking them.
Also, if there are problems in the functioning of the nervous system, it is recommended to take drugs containing magnesium and calcium, which are involved in the process of transmitting nerve impulses.
In rare cases, the doctor prescribes Botox injections, which gives elasticity to the eye muscles. Therefore, nervous twitching will be invisible to others.
This procedure is prescribed only to adults and helps eliminate only a cosmetic defect. Many people begin to have complexes about this, which does not contribute to treatment. In severe forms of the disease, when a nervous tic appears very often and greatly complicates a person’s life, courses of psychotherapy are prescribed.
Tips for parents
Tics are known to increase during times of stress. At home, you need to try to eliminate any traumatic situations and create a daily routine for the child. If possible, reduce school loads and spend more time walking in the fresh air.
When communicating with a sick child, it is recommended to be guided by the following important rule - tics must be invisible to parents: “they are not there, even if they are.” There is no need to discuss this problem at home or with friends and teachers. You can only talk about tics at a doctor's appointment. Fixing a problem and frequent reminders of it reduce self-esteem and cause increased motor paroxysms.
Another important point is that it is necessary to spend as much time as possible with the child and involve him in active games. This will breathe into him a stream of cheerfulness and optimism. You can go to the circus or children's theater, play active games together, and ride bicycles. During sports entertainment, the child will be able to get distracted, run, scream, and become more spontaneous, relaxed and cheerful. This has a positive effect on the general psychological state, eliminates anxiety and internal tension.
Prevention of nervous tics
You can reduce the likelihood of developing a nervous tic by maintaining a healthy lifestyle. You need to exercise, eat right, take a break from work more often and be in the fresh air. Giving up bad habits should be the first preventive measure. Proper organization of working time is another important step that every person should take. Also, nervous tics rarely occur in people who follow a sleep and rest schedule.
We examined the main issues related to such an ailment as nervous tics: causes, symptoms, treatment in adults and children. In conclusion, it is worth noting that a nervous tic in itself is not dangerous. It does not affect the functioning of the nervous system, much less other organs. However, a nervous tic can signal pathologies that require treatment. Do not ignore this symptom.