Golden Neuron: 10 Reasons to Admire Your Brain
The human brain is the most productive in nature. It makes up up to 2.5% of body weight and is capable of developing throughout life. If you look at the brain from a scientific point of view, it becomes clear that every person is a real superman. Neurons faster than the Peregrine Falcon, the inability to tickle yourself and juggling instead of nootropics - T&P have collected 10 facts about the human brain that can change our understanding of ourselves.
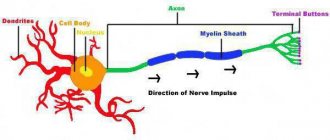
Your brain is made up of about 100 billion neurons.
If each of them were a star, a third of the Milky Way galaxy would fit into the skull. The brain has five sections: the medulla oblongata, the hindbrain, which includes the cerebellum and pons, the midbrain, the diencephalon, and the forebrain, which is represented by the cerebral hemispheres. Each of them performs dozens and even hundreds of different functions. The speed of information transfer in your brain can reach 432 km/h. For comparison, the speed of Sapsan trains running between Moscow and St. Petersburg is about 250 km/h. If the Sapsan moved as fast as your brain works, it would cover the distance between the two cities in 1 hour 36 minutes.
The average number of thoughts that come into your head every day is about 70,000. With such activity, the brain is forced to constantly forget unnecessary information in order not to overload itself and protect itself from unpleasant emotional experiences. This allows you to think faster and absorb new information more easily.
However, over the course of your life, your long-term memory can store up to 1 quadrillion (1 million billion) individual bits of information. This is equivalent to 25,000 DVDs.
When the brain is awake, it produces between 10 and 23 watts of energy. This is enough to power a light bulb. That is why this item fully justifies its status as a traditional symbol of insights and new ideas.
New physical connections between neurons are created every time you remember something. This can be done not only while awake, but also in the REM sleep phase. Scientists have found that in it a person is able to master new information and perform unfamiliar tasks (for example, memorizing pieces of music). During REM sleep, the large muscles of the body relax, brain activity increases, and the eyeballs begin to actively move under the eyelids. Every night you experience 9 to 12 “fast” phases. In total, they make up 20 to 25% of night sleep. This means that out of 80 years of life a person spends from 5 to 6.5 years in this state.
Your brain stops actively growing and becomes an “adult” at age 18. However, he does not stop developing. The skills of socialization and communication with other people, for which the prefrontal cortex is responsible, lend themselves especially well to training. It can grow up to 40 years or longer. The ability to grow throughout life is also preserved in other areas: for example, in the hippocampus, which is responsible for memory. Research conducted in the UK has shown that London taxi drivers who know the city well have, on average, a larger brain region than people in other professions. It was especially massive among drivers who had worked in the city for the greatest number of years.
The myth that you only use 10% of your brain is not true. Each part of the brain has a known function. For example, thanks to the work of two tiny areas called the amygdala, located inside the temporal lobes of the brain, you can silently recognize the feelings in other people's faces and their moods. But the desire to laugh at a joke requires using five different areas of the brain at once.
You not only have the five known senses: sight, hearing, touch, smell and taste. You also have a meta-sense called proprioception, which combines your brain's knowledge of what your muscles are doing with a sense of the size, shape, and position of your body in space. Thanks to proprioception, you know where your body parts are relative to each other and can touch the tip of your nose with your finger with your eyes closed. But tickling yourself is impossible: your brain is able to distinguish your own touches from outside touches, even if the latter are expected.
Daily juggling would change your brain in just seven days: you'd have more white matter in your parietal lobes, which is responsible for coordinating movements. This proves that the brain can develop and adapt very quickly.