Consultation with a neurologist – 1,750 rubles.
- What is encephalopathy?
- Types of acquired encephalopathy
- Symptoms of the disease
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of encephalopathy
- Popular questions
Encephalopathy
is a general term used to describe non-inflammatory diseases of the brain.
Characterized by a decrease in the volume of nervous tissue and impaired brain function. Encephalopathy of the brain can be congenital
or
acquired
. Congenital encephalopathy occurs due to genetic disorders or abnormal development of the brain during fetal development, or damage to the brain during childbirth.
Acquired encephalopathy is divided into several types.
Types of acquired encephalopathy
Depending on the cause of the disease, the following types of acquired encephalopathy are distinguished:
- Post-traumatic encephalopathy
- develops as a result of traumatic brain injury. It is often detected in athletes. It happens that signs of the disease appear long after the head injury. - Toxic encephalopathy
is caused by long-term negative effects on the brain of toxic substances, for example, alcohol, certain medications, heavy metals, and poisons. - Discirculatory encephalopathy
- occurs due to insufficient blood supply to the brain. - Residual encephalopathy
occurs due to the death of cells of the central nervous system. - Hepatic and uremic encephalopathy
- caused by severe diseases of the liver and kidneys. - Pancreatic encephalopathy
- occurs with diseases of the pancreas. - Hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic encephalopathy
- occurs in diabetes mellitus. - Radiation encephalopathy
– occurs due to radiation damage. - Vascular encephalopathies
- occur with chronic disruption of the blood supply to the brain. They develop as a result of atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, hypertension, etc.
Causes
All causes of this pathological condition in pediatric and adult practice are divided into congenital and acquired. Congenital encephalopathy develops during pregnancy or childbirth; the condition is detected by neurologists at an early age.
Acquired encephalopathic syndrome is more often identified in adults or adolescents. Among the reasons for the appearance are:
- head injuries;
- intoxication;
- infections;
- irradiation;
- metabolic disorders;
- somatic diseases;
- vascular lesions of the brain.
When questioning the patient or his relatives, the psychiatrist will clarify what factors influenced the occurrence of encephalopathy, at what speed the symptoms occurred - acutely or whether the condition worsened gradually.
Diagnosis of encephalography
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using a number of methods:
- Rheoencephalography (REG)
is a non-invasive examination method that allows you to obtain information about the condition of the walls of blood vessels in the brain. - Doppler ultrasound (USD)
is a safe and highly informative method for diagnosing vascular disorders that lead to the development of encephalopathy. - MRI
- MRI of the vessels of the brain, head and neck, pituitary gland, and eyeball is performed.
For some types of encephalopathies (for example, dyscirculatory encephalopathy), the following are used as diagnostics: Source: Kadykov A.S. Dyscirculatory encephalopathy: algorithm for diagnosis and treatment in patients with arterial hypertension / A.S. Kadykov, N.V. Shakhparonova // Neurology, neuropsychiatry, psychosomatics. - 2010. - pp. 12-17.
- neuropsychological research with special attention to the state of memory, attention and intelligence;
- ECG and dynamic blood pressure measurement, if necessary, echocardiography, Holter monitoring, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring;
- study of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism.
Danilova Olga Andreevna
neurologist
Encephalopathy is a group of diseases, the main manifestation of which is the gradual degeneration of brain tissue. To treat the disease, it is important to eliminate the main factor that is gradually destroying the brain. This may be insufficiency of liver or kidney function, atherosclerosis, previous traumatic brain injury, diabetes mellitus and many other reasons. At SM-Clinic we carry out a full diagnosis to determine the cause of encephalopathy, and only after that we begin treatment.
Types of course, forms and degrees of encephalopathic syndrome
There are three types of encephalopathy: stationary, progressive, regredient. In the stationary variant, the severity of the main symptoms remains practically unchanged over time, and decompensation of the condition is possible in response to the action of unfavorable factors.
The progressive course is characterized by a gradual worsening of clinical manifestations as a result of the addition of additional factors or an increase in the severity of the underlying disease. The regressive course is the most favorable - with the treatment of encephalopathy, the patient's condition gradually improves.
Depending on the degree of predominance of certain symptoms, several forms of psychoorganic syndrome are distinguished. Four of them are the most common.
| Form | Symptoms |
| Asthenic form | Asthenic symptoms and emotional instability come to the fore. The patient gets tired quickly and cannot maintain attention on the task at hand. When tired, he becomes irritable and whiny. Has difficulty withstanding emotional overload. The ability to remember new information decreases. Additional symptoms may include senestopathy, paresthesia, and a feeling of derealization. |
| Explosive form | With persistent asthenia and hypersensitivity, gross affective disturbances become increasingly important: anger, irritability, grumpiness. They are combined with tearfulness, emotional instability, slow thinking, and memory impairment. Such patients are prone to developing hypochondria and litigiousness. |
| Euphoric form | Such patients are complacent, careless, and their judgments are facile. Memory impairment is evident. Thinking is slow, detailed. Patients cannot cope with ordinary activities, are passive, and their intelligence decreases. Short attacks of anger are possible, ending in tearfulness and touchiness. |
| Apathetic form | The range of interests narrows, patients become spontaneous, spend a lot of time doing nothing and are not burdened by it. The scope of interest is limited to physiological needs. A sharp decrease in memory and attention. Thinking is viscous, detailed. |
In a number of patients, the syndrome manifests itself in the form of an amnestic form, in which memory impairment comes to the fore.
Treatment of encephalopathy is most effective in the early stages. Psychiatrists note that with a progressive course, the forms of the disease can be considered as stages of development. Depending on the severity, there are 3 degrees of the disorder:
Mild degree. The patient retains self-care skills, and often the ability to work. He gets tired faster, so it takes longer to complete normal tasks. Learning new skills is difficult.
Moderate (moderate severity). The patient loses the ability to work, and partially to self-care. Requires regular assistance to maintain normal functioning. Personality changes are increasing: explosiveness, complacency and lightness of judgment or apathy with lack of spontaneity.
Severe encephalopathy. With this level of impairment, the patient completely loses the ability to self-care and requires constant outside help.
Treatment of encephalopathy
Treatment methods for encephalopathy directly depend on the disease that caused the brain damage.
The most common treatment methods are:
Drug treatment
— a wide range of different groups of drugs are used, which are selected depending on the cause of the disease, possible concomitant diseases, and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Drugs that optimize cerebral circulation, neuroprotectors, vasodilators, diuretics, nootropics, amino acids and other drugs are prescribed.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
— for non-drug treatment of encephalopathy
magnetic therapy
, electromagnetic stimulation,
electrophoresis
,
ultraviolet irradiation of blood , ozone therapy
,
acupuncture
, and plasmapheresis are used.
Surgery
— most often, operations are performed on blood vessels necessary to normalize blood flow in the brain. Surgical treatment is used for brain tumors, traumatic brain injury, congenital anomalies of cerebral vessels
Lifestyle correction
— in order to increase the effectiveness of treatment, it is recommended to lose excess weight, eliminate saturated fats, salt, alcohol from the diet, move more, stop smoking and taking drugs.
If symptoms of encephalopathy occur, you should seek medical help as soon as possible. If you delay the start of treatment, there is a risk of depression of brain function and even disability.
Timely treatment, in turn, can not only slow down the development of the pathology, but also completely get rid of the negative consequences of the disease.
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price, rub.) | In installments* |
| Electrophoresis (1 field) | from 700 | — |
| UHF therapy (1 field) | from 700 | — |
| Magnetotherapy category I difficulty | from 550 | — |
* You can read more about the conditions here - Treatment on credit or in installments.
Symptoms and manifestations
The manifestations of encephalopathy depend on what caused it. Common symptoms of pathology in adults include:
- impaired memory and attention - difficulty concentrating, concentrating on a particular activity, poor memory for recent events;
- headaches, dizziness;
- bad mood, lack of initiative, irritability, tearfulness;
- general deterioration of health, fatigue;
- sleep disorders - insomnia at night and daytime sleepiness.
Timely treatment of encephalopathy is a task that mostly falls on the patient’s relatives and friends, since the patient may simply not notice alarming symptoms. This especially applies to pathologies that manifest themselves poorly. Therefore, in cases where you notice a deterioration in the health of a loved one, you need to make an appointment with a doctor.
Drugs used
If for some reason direct transfusion is not possible, medications that affect the synthesis and transformation of bilirubin (“Protoporphyrin”) are prescribed.
Due to the fact that kernicterus is the result of the toxic effect of bilirubin on neurons, neuroprotectors are always used in its treatment.
If indicated, anticonvulsant treatment is prescribed.
In the case of hemolytic disease with a direct positive Coombs test, intravenous infusions of immunoglobulin are effective.
Treatment of the condition
The treatment of kernicterus in children (regardless of its stage) is carried out by a pediatric neurologist. As a rule, such children are hospitalized.
Treatment of the disease in an adult is also carried out in a hospital setting under the constant supervision of a doctor.
Treatment of the disease consists of eliminating the causes of hyperbilirubinemia and restoring the normal concentration of bilirubin in the blood. Phototherapy is used as treatment.
Under the influence of radiation, toxic indirect bilirubin is transformed into a special isomer, which is easily excreted by the kidneys and liver and does not bind to blood albumin. In cases where the concentration of bilirubin does not decrease under the influence of phototherapy, plasma transfusion is prescribed.
If previous methods are ineffective, or symptoms rapidly increase, the patient is prescribed direct blood transfusions.
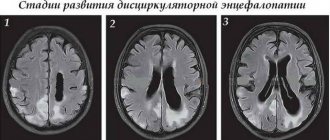
Complications of DEP grade 3
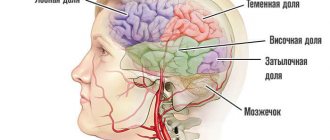
Since the patient is unable to perform certain actions and feels a decrease in performance, he experiences unreasonable mood swings. But the direct cause is damage to the subcortex of the brain, where the areas responsible for sleep, hearing and vision are located. The frontal lobes are affected. The result of all this is depression. These are not ordinary mood problems, but a mental disorder that is characterized by the “depressive triad.” This is the name of a complex of three symptoms:
- decreased mood and loss of the ability to feel joy;
- motor retardation;
- thinking disorders.
With this disease, you may notice a decrease in mood and loss of the ability to feel joy.
Attacks of aggression occur. Damage to the occipital zone is accompanied by visual disturbances. Difficulties with breathing appear, the normal voice turns into a nasal voice. Urinary incontinence is associated with a disruption in the transmission of information to organs from nerve cells. As a result, movement disorders appear.
There are more serious complications of stage 3 encephalopathy that can affect the patient’s life expectancy.
- A stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation, as a result of which some areas of the brain stop working. Often a stroke leads to loss of coordination, mobility, and sensitivity. In severe cases, the patient dies, especially if medical assistance is not provided on time.
- Cardiovascular collapse is a type of heart failure that develops due to a severe drop in vascular tone. At the same time, the mass of circulating fluid decreases, so blood flow to the heart suffers. There is a drop in arterial-venous pressure, as a result of which the most important functions of the body suffer.
- Myocardial infarction is a complication of coronary heart disease, which occurs with the appearance of necrosis of the myocardial zone. It is explained by a relative or absolute lack of blood supply.
Each of these consequences can result in death. Life expectancy depends on the occurrence of these consequences and their results.
Questions and answers
Mom has dyscirculatory encephalopathy. She hardly leaves the house. Is it possible to examine her in a hospital?
Yes. In a psychiatric clinic, experienced doctors will conduct all the necessary studies and select therapy. You can choose comfortable accommodation conditions and get more information about what kind of help is recommended for this condition by calling.
Why does a doctor recommend hospitalization of a patient with encephalopathy in a hospital?
A doctor may refer a patient to a 24-hour department in the following cases:
- the patient is aggressive, has delusions, hallucinations;
- the patient has acute toxic encephalopathy;
- it is necessary to examine a patient with limited mobility;
- selection of therapy with round-the-clock monitoring is required;
- the patient needs assistance, but will not be able to attend the clinic independently.
Is it possible to get information about how much treatment for encephalopathy will cost in Moscow: we are afraid of hidden fees.
When you contact the clinic, you will receive full information about the cost of consultations, examinations, and for inpatient treatment - the price of one day of stay. The institution does not practice “hidden payments” and sudden increases in the cost of treatment. Detailed information is available by calling the hospital or will be provided during a personal visit.
Is it possible to completely cure encephalopathy?
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely eliminate the symptoms of encephalopathy. But properly prescribed treatment can eliminate or reduce painful symptoms and slow down the progression of the disorder.