Where and when does pathology begin?
The disease begins to develop in the womb. When a baby is born with normally developed organs and body parts, which subsequently, due to various reasons, stop developing and growing, this cannot be called hypoplasia.
Hypoplasia in a child is not always detected immediately after birth. There are cases when pathology is revealed only after some time, for example, during puberty - this is hypoplasia of the genital organs or mammary glands. It appears only during their development and formation.
Signs of hypoplasia
The symptoms of this disease depend on which organ is affected by the pathological process and how severe its underdevelopment is.
For example:
- Hypoplasia of tooth enamel is manifested by the appearance of whitish spots, depressions, grooves on permanent teeth, up to the complete absence of a layer of enamel on the affected teeth.
- Kidney hypoplasia is practically asymptomatic and can go unnoticed for a long time. Often this pathology is diagnosed only during an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
- Symptoms of skin hypoplasia are sharply defined areas of hyperpigmented and thinned skin, which are often combined with abnormalities in the development of the larynx, eyes, skeleton and heart.
- Hypoplasia of the genital organs and especially the gonads - the ovaries in women and the testes in men - is characterized by a decrease in the level of sex hormones, which leads to disruption of the processes of sperm formation and egg maturation. Patients often note a decrease in sexual desire (libido) up to sexual coldness (frigidity) in women and a sharp weakening of potency in men.
Types of disease
Hypoplasia of the whole organism is called microsome or nanism. People affected by this disease hardly grow and become dwarfs. But such a manifestation of the disease is rare; doctors are often faced with underdevelopment of individual organs.
When hypoplasia occurs, any organ can be affected; the most common forms of hypoplasia are:
- Brain, which can be combined with anomalies and underdevelopment of the spinal cord.
- Teeth.
- Thyroid.
- Kidneys, lungs.
- Internal and external genitalia (infantilism).
- Cardiovascular hypoplasia.
- Vertebral arteries.
- Bones.
- Ears (microtia).
Often in medical practice a combined form of pathology occurs. An unhealthy organ is directly connected to other organs. The result is a defect in tissues and interconnected organs.
When one of the paired organs is affected by hypoplasia, the healthy organ takes responsibility and performs the main activities of the underdeveloped one, and the disease proceeds without serious complications.
Treatment of hypoplasia
Treatment of hypoplasia is symptomatic, i.e., it is aimed at eliminating the clinical signs of the existing pathology, since it is usually not possible to eliminate the pathology completely.
In case of enamel hypoplasia, damaged teeth are covered with crowns, this helps prevent their further destruction. If the area of underdeveloped enamel has a small surface, then it is bleached and then remineralized.
Hypoplasia of the left heart requires surgical correction, which is carried out in several stages. The first operation is performed in the first hours of the child’s life. During it, the hole in the interatrial septum is widened and, using a special biological prosthesis, the aorta and pulmonary artery are connected to each other, transforming them into a single vessel. This improves oxygenation of the body and reduces hypoxia. This operation is technically complex and is accompanied by high mortality (up to 40%). After the child reaches 6–10 months, the second stage of surgical treatment of hypoplasia of the left heart is performed. It consists in the partial separation of the systemic and pulmonary circulation. Complete separation of the pulmonary and systemic circulation occurs when the child reaches two years of age.
Kidney hypoplasia does not require treatment, provided that the second takes on the lost functions of the first. If pyelonephritis of the affected kidney develops or the patient develops arterial hypertension of renal origin, then indications for nephrectomy arise.
Treatment of cerebral hypoplasia is aimed at reducing the severity of neurological symptoms.
The most severe prognosis is observed with hypoplasia of the lungs and brain.
Main causes of hypoplasia
The disease begins to develop in the womb. This is due to the peculiarities of fetal formation and the influence of various factors on the mother’s body. Internal factors that provoke the emergence and development of pathology include “accidental damage” to the karyotype of the embryo, as well as all deviations that arose during the initial formation of embryonic tissue. Abnormal cell division of the fetus occurs, affecting the insufficient amount of amniotic fluid, which leads to fetal hypoplasia.
Internal negative factors are very numerous:
- radiation;
- trauma to the expectant mother;
- action of high temperature;
- smoking;
- alcohol;
- narcotic drugs;
- work in hazardous industries;
- poor environmental conditions;
- use of strong medications;
- infections (rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes, influenza, cancer, toxoplasmosis and much more).
It is better for expectant mothers to think more about themselves and about the baby, so that the birth of a child is a joy, and not anxiety or misfortune.
Signs of pathology, although congenital in nature, in some cases appear only after several years.
Possible consequences of hypoplasia
Enamel hypoplasia means that the enamel layer is underdeveloped and the tooth tissue remains unprotected from the influence of aggressive influences. Carious bacteria easily penetrate deep into the dentin, forming deep caries. Complications can manifest themselves in the form of damage to the inner part of the tooth (dentin, cement and pulp).
Important: Serious violations can provoke the formation of malocclusion in a child, and this, in turn, threatens with even more serious consequences.
Pulmonary artery hypoplasia
With pulmonary artery disease there is a combination with underdeveloped lung and cardiac ducts. Pathology can be localized either in a small area or cover a large area.
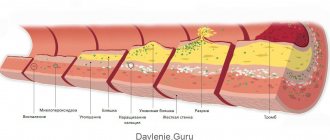
Hypoplasia of the pulmonary artery entails a narrowing of many vessels, at the ends of which aneurysms appear. In areas of narrowing of the arteries, the vascular walls noticeably thicken, which leads to structural deterioration of the lung.
The initial stage of the disease does not manifest itself in any way, but over time the following appear:
- rapid fatigue;
- shortness of breath;
- frequent respiratory diseases;
- inhibited physical development.
Various health measures will help, but the best way out of this situation is surgical intervention. The doctor will excise the abnormal area, and its passage will be enlarged by sewing a patch from the patient’s pericardium.
Symptoms of local and systemic hypoplasia
Diseases of underdevelopment of the enamel coating are divided into two types - local and systemic enamel hypoplasia. What is the difference?
Pathology of the systemic form of development
Systemic hypoplasia is divided into 3 forms of clinical manifestation: a weak degree, manifested by a change in the color of the enamel coating, pathology with underdevelopment of the enamel, and aplasia. Learn more about each form.
- Systemic hypoplasia is manifested by damage to tooth enamel along certain boundaries of several teeth formed in one period of time. In a mild form of pathology, white or yellowish spots are observed on the surface of the enamel, which have clear boundaries. They also have the same size and symmetrical location. Most often, lesions can be observed on the frontal surface of the dental crown. With this form of pathology, the child does not experience painful or unpleasant sensations. There are no changes in color or shape, as well as in the size and thickness of the resulting spots. They also do not spread to healthy areas of the teeth. With a weak form of hypoplasia, changes in the dental covering are not detected by x-rays.
- The average degree of the disease seems to be a more severe disorder in the formation of hard tissues of the tooth. It may appear in the form of pinpoint spots, grooves or waves of the enamel coating. Frequently encountered pathologies include the point form. Points are formed at arbitrary levels of dental units, regardless of their group and side of the surface (front or back). Over time, these manifestations change their color to a darker one, but the enamel structure remains dense and smooth. The wavy shape of the enamel coating is revealed after drying its surface. During visual inspection, small ridges are visible, combined with healthy areas of enamel. Most rarely, pathology manifests itself in the form of grooves, which can form over the entire surface area of the crown, alternating with healthy areas of enamel tissue. But the presence of a grooved type of hypoplasia does not entail a violation of the integrity of the dental covering.
- The most severe form of enamel underdevelopment is considered to be aplasia - there is no enamel layer on the dental crown. A visual examination of dental units reveals areas with a complete absence of enamel coating, which entails the occurrence of a painful reaction when the tooth is exposed to various irritants.
Types of systemic hypoplasia
Underdevelopment of enamel with a characteristic change in the shape of the incisors - Hutchinson's teeth . With this pathology, the shape of the incisors located in the center of the upper jaw changes. The cutting edge lags behind the neck of the tooth in its development and is smaller in diameter. You can see their unevenness in the shape of a moon with a depression in the middle. This depression may be covered with an enamel coating, but more often there is no enamel layer.
Incisors having the Hutchinson shape, but without a semilunar notch - Fournier's teeth . The first studies of hypoplasia revealed a relationship between the development of pathology and congenital syphilis. Modern research has shown that hypoplasia of this type can develop for other reasons.
Pflueger's teeth . This type of enamel underdevelopment is determined by the cone-shaped shape of the first molars. The affected teeth are characterized by underdevelopment of the cusps. Pathology is formed in the presence of syphilis infection in the child’s body.
Pathology of the local form of development
Local enamel hypoplasia is caused by disturbances during the formation of enamel of permanent teeth. The reason is the presence of an inflammatory process at the site of the tooth germ or when the developing follicle has been subjected to mechanical trauma.
Local enamel hypoplasia manifests itself as spots of different colors or pinpoint depressions scattered over the surface of the dental crown. Most often, premolars (the fourth teeth from the center) are affected by this type of disease.
The severe stage of local hypoplasia is manifested by aplasia. Without enamel areas of teeth are observed both in a single case and in the complete absence of the top layer. Turner's teeth – complete absence of the enamel layer in the formation of local hypoplasia.
Bone damage
What is bone hypoplasia? Congenital underdevelopment of bone tissue, that is, small bones. The anomaly can appear on any part of the human skeleton. The forms of the disease are different, it all depends on which bone is affected by the pathology:
- finger hypoplasia;
- hips;
- hypoplasia of the skull;
- bones of the base of the nose.
Like any organ underdevelopment that occurs inside the womb, bone tissue hypoplasia is no exception.
Reasons for appearance
Some genetic diseases, as well as the impact of negative factors on the body of a pregnant woman, can be the culprits for the appearance of the anomaly. These include:
- influence of nicotine;
- ionizing radiation;
- poisonous or narcotic drugs;
- industrial toxins;
- diseases.
The consequences of such an illness can be different: from deformity to disability. And the older a person becomes, the more clearly the signs of anomaly are expressed.
Treatment of the disease is very difficult and long, but the result is worth it.
Pathology of the thyroid gland
Underdevelopment of the endocrine organ affects the slow growth of its tissues and causes a failure in the production of necessary hormones. What is thyroid hypoplasia?
Medical reference books define several types:
- In the organ, one of the two lobes is underdeveloped. Hence the name of the disease – hypoplasia of the right/left lobe of the thyroid gland.
- Small size of the entire organ.
Both pathologies develop in the same way and the consequences of changes in the body are no different.
Treatment
Most patients with a hypoplastic vagina and no uterus can be treated with Frank's silicone or plastic vaginal dilators for 30 minutes a day. The success rate of this method is above 85% if it is combined with maintenance treatment two or three times a week. This is sufficient to have prospects for regular sex life in the future. No anesthesia or surgery is required, but the patient must be motivated.
The remaining 15% of women require surgical correction. It is also indicated if a woman already has scarring of the perineum, which makes the vagina stiff and unable to expand as needed. A simple but very effective surgical procedure is the Vecchietti procedure. It is performed laparoscopically using continuous abdominal traction on an acrylic olive placed in the vagina. The pull increases daily, stretching the vagina to its normal size within a week or 10 days. This can cause pain, so the patient is usually kept in the hospital for pain relief. Regular vaginal dilators are then used. The operation is contraindicated if previous scars are present.
Causes and consequences
Hypoplasia of the thyroid gland progresses for various reasons. In adults:
- Diseases of the pituitary gland caused by hemorrhage, strong radiation, infectious diseases, head injuries.
- Changes associated with age.
- Treatment with strong medications.
- Chronic inflammation of the thyroid gland.
In children, anomalies occur during the prenatal period for the following reasons:
- Negative influence of external sources (radioactive radiation, chemical intoxication).
- Iodine deficiency in the mother's body.
- Use of drugs containing hormones during pregnancy.
- Heredity.
Any disease has symptoms. With thyroid hypoplasia in a seven-year-old child or at an earlier age, the following signs are observed:
- weight loss;
- gastrointestinal problems (constipation);
- absent-minded attention;
- inhibited physical development;
- mental and neurological disorders;
- yellowish tint of the epidermis;
- decreased activity and apathy;
- hoarse voice;
- inhibited reaction to loud sounds or bright lights.
The main signs of hypoplasia in adults are not much different from those in children. When observing the patient, the following symptoms are revealed:
- weak short-term memory;
- decreased body temperature;
- constipation and flatulence;
- dysfunction of the genital organs;
- dry mouth;
- rapid fatigue, general weakness;
- bags in the eye area;
- deterioration of the condition of the epidermis and its derivatives;
- rapid weight gain.
Unfortunately, treatment not started on time or the lack thereof leads to cretinism and other unpleasant consequences.
Treatment of gland hypoplasia occurs with medication. The doctor prescribes medications containing hormones in the form of tablets or injections. They support the secretory functioning of the thyroid gland and are taken constantly.
Hypoplasia and pregnancy
One of the causes of female infertility or recurrent miscarriage (two or more spontaneous miscarriages) is uterine hypoplasia. However, the risk of infertility largely depends on the degree of underdevelopment of the uterus: if the uterus is slightly reduced in size, then the pregnancy will most likely proceed without any complications and will result in the birth of a healthy child.
Cervical hypoplasia poses a great danger to a favorable pregnancy outcome.
With this pathology there are no obstacles to pregnancy. However, later the pregnant woman develops isthmic-cervical insufficiency - weakness of the muscles in the area where the cervix connects with the body of the uterus.
As the fetus develops, it grows rapidly and becomes heavier every day. Weak muscles are unable to hold it in the correct position, and it begins to descend, putting pressure on the internal os of the cervix, leading to gradual dilatation of the cervix and spontaneous miscarriage.
The danger of isthmic-cervical insufficiency lies in the fact that it is practically asymptomatic and sometimes a woman turns to a doctor when it is no longer possible to help her. If treated in a timely manner, the doctor places special sutures on the cervix, which prevent it from opening until the birth process.
Hypoplasia of the vertebral arteries
The basis for a healthy blood supply to the entire body is the Circle of Willis. It is formed by large vertebral arteries (right and left branches). Under normal conditions, the arteries develop evenly.
Underdevelopment of arteries is the same as hypoplasia; this definition is given if the pathology is congenital and not acquired.
Doctors identify the following pathologies:
- right-sided;
- left-handed;
- bilateral.
The disease quickly wears out the body and leads to exhaustion. Surgeon intervention is often required.
Anomaly of the right vertebral artery
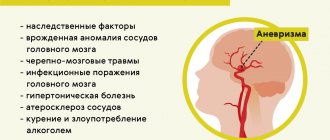
The roots of the disease usually go back to the distant prenatal period. The onset of the disease could be caused by radiation exposure of the expectant mother, bruises, prolonged exposure to high temperature (bath, sauna, beach), as well as alcohol, nicotine, or a viral infection.
With hypoplasia of the right vertebral artery, a person’s condition becomes worse with age. The following alarming symptoms occur:
- dizzy;
- weakness and drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- depression, mood swings;
- disorders of the vestibular apparatus;
- insensitivity.
The body does not need special treatment; it independently finds ways to compensate for the blood supply. Failures occur very rarely; in such emergency cases, a surgical scalpel comes to the rescue.
It is impossible to eliminate the pathology using a conservative method; sometimes drugs that dilate blood vessels are used.